Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Conversion of graded phosphorylation into switch-like nuclear translocation via autoregulatory mechanisms in ERK signalling
Conversion of graded phosphorylation into switch-like nuclear translocation via autoregulatory mechanisms in ERK signalling
While ERK signalling can produce switch-like cell behaviour, phosphorylation of ERK increases linearly with extracellular signals. Here, the authors solve this seeming contradiction by showing that nuclear translocation of ERK behaves in a switch-like manner and is controlled by ERK activity.
- Yuki Shindo
- , Kazunari Iwamoto
- & Koichi Takahashi
-
Article
| Open Access Novel RNA- and FMRP-binding protein TRF2-S regulates axonal mRNA transport and presynaptic plasticity
Novel RNA- and FMRP-binding protein TRF2-S regulates axonal mRNA transport and presynaptic plasticity
The molecular mechanisms regulating axonal mRNA transport are only partially understood. Here, Zhang et al. show a nontelomeric TRF2 splice variant interacts with FMRP to regulate the transport of several axonal mRNAs involved in axonal elongation and neurotransmitter release.
- Peisu Zhang
- , Kotb Abdelmohsen
- & Mark P. Mattson
-
Article
| Open Access Combining Spinach-tagged RNA and gene localization to image gene expression in live yeast
Combining Spinach-tagged RNA and gene localization to image gene expression in live yeast
Measuring single-cell mRNA dynamics is critical to understand gene expression. Here, using RNA Spinach technique to detect very low abundant mRNAs, Guet et al. report an analysis of the osmotic shock response in live yeast by localizing induced transcription factors, target gene loci and corresponding transcripts.
- David Guet
- , Laura T. Burns
- & Catherine Dargemont
-
Article
| Open Access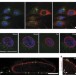 Nuclear envelope-associated endosomes deliver surface proteins to the nucleus
Nuclear envelope-associated endosomes deliver surface proteins to the nucleus
Endocytosis typically directs proteins on a recycling route back to the plasma membrane, transport to the Golgi apparatus or delivery to the lysosome. Here Chaumet et al.describe a population of vesicles that can fuse directly with the outer nuclear membrane and deliver cargo into the nuclear envelope, where it can be translocated into the nucleoplasm.
- Alexandre Chaumet
- , Graham D. Wright
- & Frederic Bard
-
Article |
 Perinuclear tethers license telomeric DSBs for a broad kinesin- and NPC-dependent DNA repair process
Perinuclear tethers license telomeric DSBs for a broad kinesin- and NPC-dependent DNA repair process
Damaged DNA is often targeted to nuclear pore complexes for repair. Here, the authors show that kinesin-14 mediates this process ensuring error-prone repair, while perinuclear telomere attachment licenses damaged telomeric loci for this repair and kinesin-14 blocks senescence in the absence of telomerase.
- Daniel K.C. Chung
- , Janet N.Y. Chan
- & Karim Mekhail
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and gating of the nuclear pore complex
Structure and gating of the nuclear pore complex
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are large macromolecular assemblies that mediate the exchange of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Here the authors present a ∼20 Å cryo-EM structure of the X. laevisNPC in different states of transport to propose a model for the architecture of the NPC’s molecular gate within its central channel.
- Matthias Eibauer
- , Mauro Pellanda
- & Ohad Medalia
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the origin of the nuclear localization signals in conserved ribosomal proteins
Insights into the origin of the nuclear localization signals in conserved ribosomal proteins
Eukaryotic ribosomal proteins contain nuclear localization signals (NLSs) that their bacterial counterparts lack. Here the authors compare homologous proteins from bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes to show how NLSs could emerge in the course of evolution, and use this knowledge to identify novel NLSs.
- Sergey Melnikov
- , Adam Ben-Shem
- & Marat Yusupov
-
Article
| Open Access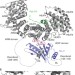 Symportin 1 chaperones 5S RNP assembly during ribosome biogenesis by occupying an essential rRNA-binding site
Symportin 1 chaperones 5S RNP assembly during ribosome biogenesis by occupying an essential rRNA-binding site
Biogenesis of the 80S ribosome involves more than 200 pre-ribosomal factors, which ensure the sequential assembly of ribosomal proteins and RNAs. Here the authors show that the nuclear transport adaptor Syo1 shields the 5S RNP-docking site on RpL11 before incorporation into the pre-60S through molecular mimicry.
- Fabiola R. Calviño
- , Satyavati Kharde
- & Irmgard Sinning
-
Article |
 The nuclear translocation of ERK1/2 as an anticancer target
The nuclear translocation of ERK1/2 as an anticancer target
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) cascade is involved in the induction and maintenance of cancers. Here the authors design an ERK-derived peptide that blocks ERK nuclear import, thus proposing a novel approach to treat tumours with mutational activation of the ERK pathway.
- Alexander Plotnikov
- , Karen Flores
- & Rony Seger
-
Article
| Open Access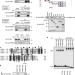 Mitochondrial SSBP1 protects cells from proteotoxic stresses by potentiating stress-induced HSF1 transcriptional activity
Mitochondrial SSBP1 protects cells from proteotoxic stresses by potentiating stress-induced HSF1 transcriptional activity
Heat shock induces proteotoxic stress, and the cellular response is mediated by heat-shock factor 1 (HSF1). Here, Tan et al.show that following heat shock, mitochondrial SSBP1 translocates to the nucleus and binds HSF1 to enhance the expression of chaperones and support the maintenance of mitochondrial function.
- Ke Tan
- , Mitsuaki Fujimoto
- & Akira Nakai
-
Article
| Open Access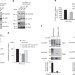 Chromatin organization at the nuclear pore favours HIV replication
Chromatin organization at the nuclear pore favours HIV replication
Retroviruses such as HIV integrate into the host genome as an essential step prior to their replication. Here Lelek et al. identify nuclear pore complex proteins that are essential for HIV nuclear import and productive integration, and show that the intranuclear protein Tpr influences integration into transcriptionally active chromatin.
- Mickaël Lelek
- , Nicoletta Casartelli
- & Francesca Di Nunzio
-
Article
| Open Access Cytoplasmic TAF2–TAF8–TAF10 complex provides evidence for nuclear holo–TFIID assembly from preformed submodules
Cytoplasmic TAF2–TAF8–TAF10 complex provides evidence for nuclear holo–TFIID assembly from preformed submodules
TFIID is an essential transcription factor complex that controls the expression of most protein-coding genes in eukaryotes. Here the authors identify and characterize a complex containing TAF2, TAF8 and TAF10, which assembles in the cytoplasm before integration into the nuclear holo–TFIID complex.
- Simon Trowitzsch
- , Cristina Viola
- & Imre Berger
-
Article
| Open Access RNA export factor Ddx19 is required for nuclear import of the SRF coactivator MKL1
RNA export factor Ddx19 is required for nuclear import of the SRF coactivator MKL1
Nuclear import of transcriptional regulators and export of mRNA are essential steps for the manufacture of proteins in the cytoplasm. Here, Rajakylä et al.link these two activities by showing that the mRNA export factor Ddx19 promotes the nuclear import of the transcriptional coactivator MKL1.
- Eeva Kaisa Rajakylä
- , Tiina Viita
- & Maria K. Vartiainen
-
Article
| Open Access OM14 is a mitochondrial receptor for cytosolic ribosomes that supports co-translational import into mitochondria
OM14 is a mitochondrial receptor for cytosolic ribosomes that supports co-translational import into mitochondria
Mitochondrial proteins can be imported post-translationally; however, a role for co-translational import has recently provoked renewed interest. Lesnik et al.identify OM14 as a mitochondrial ribosome receptor required for efficient co-translational import of mitochondrial proteins.
- Chen Lesnik
- , Yifat Cohen
- & Yoav Arava
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial control of the GEN1 Holliday junction resolvase ensures genome stability
Spatial control of the GEN1 Holliday junction resolvase ensures genome stability
The human Holliday junction resolvase GEN1 functions during anaphase to eliminate recombination intermediates that block proper chromosome segregation. Here, the authors demonstrate that GEN1 activity is regulated independently of its phosphorylation status and relies on its active exclusion from the nucleus.
- Ying Wai Chan
- & Stephen C. West
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering light-inducible nuclear localization signals for precise spatiotemporal control of protein dynamics in living cells
Engineering light-inducible nuclear localization signals for precise spatiotemporal control of protein dynamics in living cells
Designing inducible and reversible nuclear localization signals would enable researchers to dissect and engineer cellular networks. Here Niopek et al.create a light-inducible nuclear localization signal to regulate gene expression and mitosis in mammalian cells, using blue light.
- Dominik Niopek
- , Dirk Benzinger
- & Barbara Di Ventura
-
Article |
 Separation of a functional deubiquitylating module from the SAGA complex by the proteasome regulatory particle
Separation of a functional deubiquitylating module from the SAGA complex by the proteasome regulatory particle
The SAGA transcriptional coactivator is modulated by the 19S proteasome to increase the interaction of SAGA with transcription activators. Here, Limet al.show that the 19S proteasome mediates dissociation of a submodule of the SAGA complex in a non-proteolytic manner, which is implicated in mRNA export in yeast.
- Sungsu Lim
- , Jaechan Kwak
- & Daeyoup Lee
-
Article |
 High-resolution three-dimensional mapping of mRNA export through the nuclear pore
High-resolution three-dimensional mapping of mRNA export through the nuclear pore
Messenger RNAs and their associated proteins are transported from the nucleus through highly selective nuclear pore complexes. Using ultrahigh resolution single-molecule imaging, the authors visualise the path taken by each messenger RNA as it negotiates the pore’s selectivity filter.
- Jiong Ma
- , Zhen Liu
- & Weidong Yang
-
Article |
 CPEB-mediated ZO-1 mRNA localization is required for epithelial tight-junction assembly and cell polarity
CPEB-mediated ZO-1 mRNA localization is required for epithelial tight-junction assembly and cell polarity
Zonal occludens and claudin form tight junctions near the apical surface of cells and are important in polarized epithelia. In this study, the translational regulatory sequence-specific RNA binding protein CPEB is shown to be required for the correct localization of zona occluden 1 mRNA in mammary epithelial cells.
- Kentaro Nagaoka
- , Tsuyoshi Udagawa
- & Joel D. Richter
-
Article
| Open Access TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
TGFβ can function as both a tumour suppressor and tumour promoter under different cellular contexts. Here, the cleavage product of the TGFβ type I receptor is shown to be generated in a TGFβ-dependent manner, and can induce the expression of genes involved in tumour cell invasion.
- Yabing Mu
- , Reshma Sundar
- & Marene Landström
-
Article |
 Wwp2 is essential for palatogenesis mediated by the interaction between Sox9 and mediator subunit 25
Wwp2 is essential for palatogenesis mediated by the interaction between Sox9 and mediator subunit 25
Sox9 is an important transcription factor in the formation of cartilage chondrogenesis that occurs during skeletal development. Nakamuraet al.show that Sox9 interacts with Wwp2 and Med25 to form a complex and that loss of either protein in zebrafish results in altered palate chondrogenesis.
- Yukio Nakamura
- , Koji Yamamoto
- & Haruhiko Akiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Differential use of importin-α isoforms governs cell tropism and host adaptation of influenza virus
Differential use of importin-α isoforms governs cell tropism and host adaptation of influenza virus
Interspecies transmission of influenza A viruses requires adaptation of the viral polymerase to the host importin-α. Here, the polymerase subunit PB2 and the nucleoprotein of avian viruses are found to require importin-α3, whereas mammalian viruses are shown to require importin-α7.
- Gülsah Gabriel
- , Karin Klingel
- & Hans-Dieter Klenk
-
Article |
 A role for TREX components in the release of spliced mRNA from nuclear speckle domains
A role for TREX components in the release of spliced mRNA from nuclear speckle domains
The pre-mRNA splicing and TREX mRNA export machineries are found in nuclear speckle domains. Diaset al. microinject CMV-DNA constructs into cells and find that transcripts containing functional splice sites accumulate in nuclear speckles and that the TREX complex is required to release the mRNA once processed.
- Anusha P. Dias
- , Kobina Dufu
- & Robin Reed

 Optogenetic control of nuclear protein export
Optogenetic control of nuclear protein export