Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Non-coding variability at the APOE locus contributes to the Alzheimer’s risk
Non-coding variability at the APOE locus contributes to the Alzheimer’s risk
Several studies show that APOE-ε4 coding variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk. Here, Zhou et al. perform fine-mapping of the APOE region and find AD risk haplotypes with non-coding variants in the PVRL2 and APOC1 regions that are associated with relevant endophenotypes.
- Xiaopu Zhou
- , Yu Chen
- & Nancy Y. Ip
-
Article
| Open Access AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit defects are a cause of neurodevelopmental disorders
AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit defects are a cause of neurodevelopmental disorders
Genetic variants in ionotropic glutamate receptors have been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, the authors report heterozygous de novo mutations in the GRIA2 gene in 28 individuals with intellectual disability and neurodevelopmental abnormalities associated with reduced Ca2+ transport and AMPAR currents.”
- Vincenzo Salpietro
- , Christine L. Dixon
- & Henry Houlden
-
Article
| Open Access Paternal-age-related de novo mutations and risk for five disorders
Paternal-age-related de novo mutations and risk for five disorders
Advanced paternal age associates with increased risk for psychiatric and developmental disorders in offspring. Here, Taylor et al. utilize parent-child trio exome sequencing data sets to estimate the contribution of paternal age-related de novo mutations to multiple disorders, including heart disease and schizophrenia.
- Jacob L. Taylor
- , Jean-Christophe P. G. Debost
- & Elise B. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Locus coeruleus-CA1 projections are involved in chronic depressive stress-induced hippocampal vulnerability to transient global ischaemia
Locus coeruleus-CA1 projections are involved in chronic depressive stress-induced hippocampal vulnerability to transient global ischaemia
Depression and transient ischaemic attacks are tightly regulated but the neural circuits underlying depression-modulated ischaemic injury are not known. Here, the authors show that the locus coeruleus-CA1 pathway is involved in depression-associated ischaemia susceptibility.
- Qian Zhang
- , Dian Xing Hu
- & Bo Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Activating an anterior nucleus gigantocellularis subpopulation triggers emergence from pharmacologically-induced coma in rodents
Activating an anterior nucleus gigantocellularis subpopulation triggers emergence from pharmacologically-induced coma in rodents
The reticular activating system (RAS) of the brainstem regulates wakefulness, and stimulation of RAS areas can reverse effects of anaesthesia. Here, the authors show that stimulation of a particular RAS area, the anterior portion of nucleus gigantocellularis, can produce arousal from deep coma.
- S. Gao
- , A. Proekt
- & D. W. Pfaff
-
Article
| Open Access Aβ-induced vulnerability propagates via the brain’s default mode network
Aβ-induced vulnerability propagates via the brain’s default mode network
Amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition occurs in Alzheimer's disease but its relation to disease features such as local brain hypometabolism or cognitive decline is unclear. Here, the authors show that Aβ aggregation in the brain’s default mode network leads to hypometabolism in distant but functionally connected areas.
- Tharick A. Pascoal
- , Sulantha Mathotaarachchi
- & Pedro Rosa-Neto
-
Article
| Open Access A systems biology approach uncovers cell-specific gene regulatory effects of genetic associations in multiple sclerosis
A systems biology approach uncovers cell-specific gene regulatory effects of genetic associations in multiple sclerosis
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have so far uncovered more than 200 loci for multiple sclerosis (MS). Here, the authors integrate data from various sources for a cell type-specific pathway analysis of MS GWAS results that specifically highlights the involvement of the immune system in disease pathogenesis.
- Lohith Madireddy
- , Nikolaos A. Patsopoulos
- & Sergio E. Baranzini
-
Article
| Open Access Interpretable classification of Alzheimer’s disease pathologies with a convolutional neural network pipeline
Interpretable classification of Alzheimer’s disease pathologies with a convolutional neural network pipeline
Convolutional neural networks have been applied to various areas of medical imaging and histology. Here the authors develop an automated approach using interpretable neural networks to determine Alzheimer’s disease plaque and cerebral amyloid angiopathy burden in post-mortem human brain tissue.
- Ziqi Tang
- , Kangway V. Chuang
- & Brittany N. Dugger
-
Article
| Open Access Felodipine induces autophagy in mouse brains with pharmacokinetics amenable to repurposing
Felodipine induces autophagy in mouse brains with pharmacokinetics amenable to repurposing
A key challenge is to find/re-purpose approved drugs that could be used in humans to induce autophagy-associated clearance of neurodegenerative proteins. Here, authors demonstrate that felodipine, an anti-hypertensive drug, can induce autophagy and clear a variety of aggregated neurodegenerative disease-associated proteins in mouse brains at plasma concentrations similar to those that would be seen in humans taking the drug.
- Farah H. Siddiqi
- , Fiona M. Menzies
- & David C. Rubinsztein
-
Article
| Open Access A PRPH splice-donor variant associates with reduced sural nerve amplitude and risk of peripheral neuropathy
A PRPH splice-donor variant associates with reduced sural nerve amplitude and risk of peripheral neuropathy
Diagnosis and classification of peripheral neuropathy (PN) is facilitated by nerve conduction (NC) studies. Here, Bjornsdottir et al. find a low-frequency PRPH splice-donor variant that associates with NC amplitude and neurological assessment of recalled PRPH variant carriers reveals increased risk of a mild sensory-negative PN.
- Gyda Bjornsdottir
- , Erna V. Ivarsdottir
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access NRG1 type I dependent autoparacrine stimulation of Schwann cells in onion bulbs of peripheral neuropathies
NRG1 type I dependent autoparacrine stimulation of Schwann cells in onion bulbs of peripheral neuropathies
Onion bulbs are a hallmark of demyelinating peripheral neuropathies. Here the authors identify Neuregulin-1 type I expression in Schwann cells as an essential mechanism involved in the formation of these characteristic structures.
- Robert Fledrich
- , Dagmar Akkermann
- & Ruth M. Stassart
-
Article
| Open Access Social networks and risk of delayed hospital arrival after acute stroke
Social networks and risk of delayed hospital arrival after acute stroke
Rapid arrival to hospital after stroke is critical for patients to receive effective treatment. Here, the authors examine how stroke patients’ social network structure relates to stroke arrival time, and show that small and close-knit personal networks predict delayed arrival.
- Amar Dhand
- , Douglas Luke
- & Jin-Moo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide association analysis identifies 16 novel susceptibility loci for carpal tunnel syndrome
A genome-wide association analysis identifies 16 novel susceptibility loci for carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is caused by entrapment of the median nerve at the wrist. Here, Wiberg et al. perform a GWAS for CTS in the UK Biobank cohort and identify 16 genetic loci, and find a causal relationship between short stature and CTS risk using Mendelian randomisation.
- Akira Wiberg
- , Michael Ng
- & Dominic Furniss
-
Article
| Open Access Prioritizing Parkinson’s disease genes using population-scale transcriptomic data
Prioritizing Parkinson’s disease genes using population-scale transcriptomic data
GWAS have identified over 41 susceptibility loci for Parkinson’s disease (PD). Here, the authors integrate PD GWAS summary statistics with transcriptome data from monocytes and DLFPC tissue in a TWAS approach and find 66 significant associations with PD risk highlighting lysosomal and innate immune functions.
- Yang I. Li
- , Garrett Wong
- & Towfique Raj
-
Article
| Open Access Biallelic mutations in valyl-tRNA synthetase gene VARS are associated with a progressive neurodevelopmental epileptic encephalopathy
Biallelic mutations in valyl-tRNA synthetase gene VARS are associated with a progressive neurodevelopmental epileptic encephalopathy
Valyl-tRNA synthetase (VARS) charges valyl-tRNA with the amino acid valine, required for translation. Here, the authors describe a progressive epileptic encephalopathy in individuals from five families carrying biallelic mutations in the VARS gene that leave the enzyme activity partially intact.
- Jennifer Friedman
- , Desiree E. Smith
- & Joseph G. Gleeson
-
Article
| Open Access Biallelic VARS variants cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly that is recapitulated in vars knockout zebrafish
Biallelic VARS variants cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly that is recapitulated in vars knockout zebrafish
tRNAs are linked with their cognate amino acid by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (ARS). Here, the authors report a developmental encephalopathy associated with biallelic VARS variants (valyl-tRNA synthetase) that lead to loss of function, as determined by several in vitro assays and a vars knockout zebrafish model.
- Aleksandra Siekierska
- , Hannah Stamberger
- & Peter De Jonghe
-
Article
| Open Access Correspondence between cerebral glucose metabolism and BOLD reveals relative power and cost in human brain
Correspondence between cerebral glucose metabolism and BOLD reveals relative power and cost in human brain
The brain primarily uses glucose to generate energy, but the relationship of neuronal activity to glucose utilization is not necessarily a simple linear one. Here, the authors introduce relative power (rPWR) and relative cost (rCST) as new metrics to quantify how brain activity relates to glucose consumption.
- Ehsan Shokri-Kojori
- , Dardo Tomasi
- & Nora D. Volkow
-
Article
| Open Access Combining lifestyle risks to disentangle brain structure and functional connectivity differences in older adults
Combining lifestyle risks to disentangle brain structure and functional connectivity differences in older adults
Lifestyle factors such as smoking and exercise contribute to the health of the brain during aging, but previous studies have focused on the effects of single lifestyle variables. Here, the authors examine the combined and individual effects of four lifestyle variables on brain structure and function.
- Nora Bittner
- , Christiane Jockwitz
- & Svenja Caspers
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals midbrain dopamine neuron diversity emerging during mouse brain development
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals midbrain dopamine neuron diversity emerging during mouse brain development
Midbrain dopamine (mDA) neurons are significantly associated with Parkinson’s disease and yet there is no systematic molecular classification of these heterogenous group of cells. Here authors use single cell RNA sequencing of isolated mouse neurons expressing the transcription factor Pitx3 (broad mDA neuronal marker) to identify and characterize seven neuron subgroups divided in two major branches of developing Pitx3-expressing neurons.
- Katarína Tiklová
- , Åsa K. Björklund
- & Thomas Perlmann
-
Article
| Open Access Reductions in prefrontal activation predict off-topic utterances during speech production
Reductions in prefrontal activation predict off-topic utterances during speech production
The ability to speak coherently is essential for effective communication, but little is known about the neural systems that support coherence. Here, the authors show that activity in two prefrontal cortex regions, BA10 and BA45, predicts the level of coherence in the speech of healthy older adults.
- Paul Hoffman
-
Article
| Open Access Early preclinical detection of prions in the skin of prion-infected animals
Early preclinical detection of prions in the skin of prion-infected animals
There are currently no validated methods for the diagnosis of prion disease at the preclinical stage. Here the authors show that serial protein misfolding cyclic amplification and real-time quaking-induced conversion can be used to detect prions in the skin of prion-inoculated hamsters and humanized transgenic mice at early preclinical stages.
- Zerui Wang
- , Matteo Manca
- & Wen-Quan Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Model-based lesion mapping of cognitive control using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
Model-based lesion mapping of cognitive control using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
The frontal cortex is involved in cognitive control, e.g. cognitive flexibility and behavioral inhibition, but the roles of frontal subdivisions are unclear. Here, the authors used computational modelling of cognitive control task performance to map lesions responsible for impairments in specific cognitive operations.
- Jan Gläscher
- , Ralph Adolphs
- & Daniel Tranel
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial fine-mapping for gene-by-environment effects identifies risk hot spots for schizophrenia
Spatial fine-mapping for gene-by-environment effects identifies risk hot spots for schizophrenia
Schizophrenia (SCZ) risk is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Here, the authors develop a statistical method for analyzing gene-by-environment effects in SCZ risk across Denmark with fine spatial resolution.
- Chun Chieh Fan
- , John J. McGrath
- & Carsten Bøcker Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Closed-loop functional optogenetic stimulation
Closed-loop functional optogenetic stimulation
Optogenetics is a promising alternative approach for restoration of neuromuscular function. Here the authors establish a closed-loop functional optogenetic stimulation for the control of limb joint angle in murine models, which demonstrates improved control and less fatigue than electrical stimulation systems.
- Shriya S. Srinivasan
- , Benjamin E. Maimon
- & Hugh M. Herr
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide mega-analysis identifies 16 loci and highlights diverse biological mechanisms in the common epilepsies
Genome-wide mega-analysis identifies 16 loci and highlights diverse biological mechanisms in the common epilepsies
Epilepsies are common brain disorders and are classified based on clinical phenotyping, imaging and genetics. Here, the authors perform genome-wide association studies for 3 broad and 7 subtypes of epilepsy and identify 16 loci - 11 novel - that are further annotated by eQTL and partitioned heritability analyses.
- Bassel Abou-Khalil
- , Pauls Auce
- & Fritz Zimprich
-
Article
| Open Access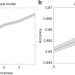 Neural network analysis of sleep stages enables efficient diagnosis of narcolepsy
Neural network analysis of sleep stages enables efficient diagnosis of narcolepsy
The diagnosis of sleep disorders such as narcolepsy and insomnia currently requires experts to interpret sleep recordings (polysomnography). Here, the authors introduce a neural network analysis method for polysomnography that could reduce time spent in sleep clinics and automate narcolepsy diagnosis.
- Jens B. Stephansen
- , Alexander N. Olesen
- & Emmanuel Mignot
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput brain activity mapping and machine learning as a foundation for systems neuropharmacology
High-throughput brain activity mapping and machine learning as a foundation for systems neuropharmacology
A major goal in neuropharmacology is to develop new tools to effectively test the therapeutic potential of pharmacological agents to treat neurological and psychiatric conditions. Here, authors present an in vivo drug screening system that generates large-scale brain activity maps to be used with machine learning to predict the therapeutic potential of clinically relevant drug leads.
- Xudong Lin
- , Xin Duan
- & Peng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Tamoxifen therapy in a murine model of myotubular myopathy
Tamoxifen therapy in a murine model of myotubular myopathy
Myotubular myopathy is a severe muscle disease for which no effective treatment exists. Here, the authors show that tamoxifen ameliorates pathology and extends survival in a mouse model of the disease, and that the effect is mediated via estrogen receptor signaling and involves modulation of DNM2 expression.
- Nika Maani
- , Nesrin Sabha
- & James J. Dowling
-
Article
| Open Access Slc7a5 regulates Kv1.2 channels and modifies functional outcomes of epilepsy-linked channel mutations
Slc7a5 regulates Kv1.2 channels and modifies functional outcomes of epilepsy-linked channel mutations
Kv1.2 is a voltage-gated potassium channel that influences action potential generation and propagation in the central nervous system. Here authors use electrophysiology and find that Slc7a5, a neutral amino acid transporter, has a profound impact on Kv1.2.
- Victoria A. Baronas
- , Runying Y. Yang
- & Harley T. Kurata
-
Article
| Open Access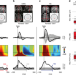 Sleep-like cortical OFF-periods disrupt causality and complexity in the brain of unresponsive wakefulness syndrome patients
Sleep-like cortical OFF-periods disrupt causality and complexity in the brain of unresponsive wakefulness syndrome patients
Many brain-injured patients retain large cortical islands that are intact, active and reactive but blocked in a state of low complexity, leading to unconsciousness. Here, the authors show that this loss of complexity is due to the pathological engagement of sleep-like neuronal mechanisms.
- M. Rosanova
- , M. Fecchio
- & M. Massimini
-
Article
| Open Access An intrinsic association between olfactory identification and spatial memory in humans
An intrinsic association between olfactory identification and spatial memory in humans
Olfaction, the sense of smell, may have originally evolved to aid navigation in space, but there is no direct evidence of a link between olfaction and navigation in humans. Here the authors show that olfaction and spatial memory abilities are correlated and rely on similar brain regions in humans.
- Louisa Dahmani
- , Raihaan M. Patel
- & Véronique D. Bohbot
-
Article
| Open Access A distal centriolar protein network controls organelle maturation and asymmetry
A distal centriolar protein network controls organelle maturation and asymmetry
Removal of daughter centriole-specific/enriched proteins (DCPs) and assembly of distal appendages (DA) are important for centrosome asymmetry. Here, the authors report that a centriolar distal end protein network regulates DCP removal, DA assembly, and ciliary vesicle docking.
- Lei Wang
- , Marion Failler
- & Brian D. Dynlacht
-
Article
| Open Access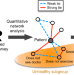 A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
An individual’s social network—their friends, family, and acquaintances—is important for their health, but existing tools for assessing social networks have limitations. Here, the authors introduce a quantitative social network assessment tool on a secure open-source web platform and show its utility in a nation-wide study.
- Amar Dhand
- , Charles C. White
- & Philip L. De Jager
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
Patients with myotonic dystrophy need to undergo invasive muscle biopsies to monitor disease progression and response to therapy. Here, the authors show that extracellular RNAs in human urine can be used as biomarkers to differentiate patients from unaffected controls, and to monitor exon skipping in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy taking the drug eteplirsen.
- Layal Antoury
- , Ningyan Hu
- & Thurman M. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell molecular alterations reveal target cells and pathways of concussive brain injury
Single cell molecular alterations reveal target cells and pathways of concussive brain injury
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) affects the hippocampus and can lead to neurological and psychiatric disorders. Here, the authors perform single-cell RNA sequencing to reveal molecular pathways across a range of cell types affected during TBI.
- Douglas Arneson
- , Guanglin Zhang
- & Xia Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into SorCS2–Nerve Growth Factor complex formation
Structural insights into SorCS2–Nerve Growth Factor complex formation
The Sortilin-related CNS-expressed receptor 2 (SorCS2)–proneurotrophin signaling system regulates neuronal plasticity and its dysfunction is linked to schizophrenia. Here the authors present the structures of the SorCS2 ectodomain alone and in complex with Nerve Growth Factor, which provides insights into SorCS2 ligand binding and signaling.
- Nadia Leloup
- , Lucas M. P. Chataigner
- & Bert J. C. Janssen
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenome-wide DNA methylation profiling in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy reveals major changes at DLX1
Epigenome-wide DNA methylation profiling in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy reveals major changes at DLX1
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by aggregation of Tau, encoded by MAPT. Here, the authors perform an EWAS for PSP in prefrontal lobe tissue and find hypermethylation of DLX1 and its antisense transcript DLX1AS to associate with MAPT expression.
- Axel Weber
- , Sigrid C. Schwarz
- & Ulrich Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Blood–brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound
Blood–brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound
Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound with injected microbubbles has been used to temporarily open the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in animal models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, the authors use this technology to non-invasively open the BBB in 5 patients with mild-to-moderate AD in a phase I trial, and show that the procedure is safe.
- Nir Lipsman
- , Ying Meng
- & Sandra E. Black
-
Article
| Open Access Intraamniotic Zika virus inoculation of pregnant rhesus macaques produces fetal neurologic disease
Intraamniotic Zika virus inoculation of pregnant rhesus macaques produces fetal neurologic disease
Zika virus infection of pregnant women can cause congenital brain defects. Here, Coffey et al. establish a pregnant rhesus macaque model, using intravenous and intraamniotic route of infection, that reliably reproduces fetal neurologic defects of congenital Zika syndrome in humans.
- Lark L. Coffey
- , Rebekah I. Keesler
- & Koen K. A. Van Rompay
-
Article
| Open Access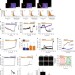 α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease
α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease
How toxic aggregated forms of α-synuclein lead to neurodegeneration is unclear. Here authors use biophysical and cellular imaging methods to show that specific oligomers of α-synuclein exert effects on mitochondria to induce opening of the permeability transition pore, leading to cell death in Parkinson’s disease.
- Marthe H. R. Ludtmann
- , Plamena R. Angelova
- & Sonia Gandhi
-
Article
| Open Access CREB controls cortical circuit plasticity and functional recovery after stroke
CREB controls cortical circuit plasticity and functional recovery after stroke
Increasing excitability in the peri-infarct area enhances motor recovery after stroke. Here the authors show that expressing CREB, a transcription factor known for its role in synaptic plasticity, or increasing activity of CREB-expressing cells near the stroke site improves recovery in an effect that is strong enough that it can be used to turn on and off motor recovery after stroke.
- L. Caracciolo
- , M. Marosi
- & S. T. Carmichael
-
Article
| Open Access Variability in the location of high frequency oscillations during prolonged intracranial EEG recordings
Variability in the location of high frequency oscillations during prolonged intracranial EEG recordings
High frequency oscillations (HFO) are a promising biomarker for identifying epileptogenic zones without the need to monitor spontaneous seizure episodes. Here the authors report that there is much variability in the location of HFOs offering a note of caution toward using HFO locations from short recordings as a guide for surgery.
- Stephen V. Gliske
- , Zachary T. Irwin
- & William C. Stacey
-
Article
| Open Access Intron retention and nuclear loss of SFPQ are molecular hallmarks of ALS
Intron retention and nuclear loss of SFPQ are molecular hallmarks of ALS
Intron retention (IR) can increase protein diversity and function, and yet unregulated IR may be detrimental to cellular health. This study shows that aberrant IR occurs in ALS and finds nuclear loss of an RNA-binding protein called SFPQ as a new molecular hallmark in this devastating condition.
- Raphaelle Luisier
- , Giulia E. Tyzack
- & Rickie Patani
-
Article
| Open Access Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment
Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment
Exosomes function as intercellular information transmitters and are candidates for delivery of therapeutic agents. Here the authors present EXOtic, a synthetic biology device for in-situ production of designer exosomes and demonstrate in vivo application in models of Parkinson's disease.
- Ryosuke Kojima
- , Daniel Bojar
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive map coupling histone modifications with gene regulation in adult dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons
A comprehensive map coupling histone modifications with gene regulation in adult dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons
The limited size of some neuronal types and their entangled environment renders it difficult to study their transcription regulation. Here the authors present a comparative analysis of histone modifications and transcription in dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons and embryonic neural progenitors.
- Erik Södersten
- , Konstantinos Toskas
- & Johan Holmberg
-
Article
| Open Access Next generation histology methods for three-dimensional imaging of fresh and archival human brain tissues
Next generation histology methods for three-dimensional imaging of fresh and archival human brain tissues
Current available tissue clearing techniques are mostly used for rodent tissues. Here, the authors develop OPTIClear solution for fresh and archival human brain tissue clearing and establish associated protocols for three-dimensional histological investigations.
- Hei Ming Lai
- , Alan King Lun Liu
- & Steve M. Gentleman
-
Article
| Open Access EGFL7 reduces CNS inflammation in mouse
EGFL7 reduces CNS inflammation in mouse
Endothelial cells release extracellular matrix components that regulate inflammation. Here the authors demonstrate that the extracellular matrix component epidermal growth factor-like protein 7 regulates inflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse.
- Catherine Larochelle
- , Timo Uphaus
- & Frauke Zipp
-
Article
| Open Access Impaired β-arrestin recruitment and reduced desensitization by non-catechol agonists of the D1 dopamine receptor
Impaired β-arrestin recruitment and reduced desensitization by non-catechol agonists of the D1 dopamine receptor
Dopamine receptor agonists are used for the treatment of various psychiatric diseases. Here, the authors screen approximately three million compounds and identify a novel class of D1R agonists that do not have a catechol scaffold and possess promising pharmacokinetic properties.
- David L. Gray
- , John A. Allen
- & Michael D. Ehlers
-
Article
| Open Access Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Microrchidia CW-type zinc finger protein 2 (MORC2) is an effector of epigenetic silencing by the human silencing hub (HUSH). Here the authors present the crystal structures of MORC2 and disease-causing MORC2 mutants and give mechanistic insights into how MORC2 mediates HUSH-dependent silencing.
- Christopher H. Douse
- , Stuart Bloor
- & Yorgo Modis

 A human memory circuit derived from brain lesions causing amnesia
A human memory circuit derived from brain lesions causing amnesia