Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Ambient chemical transformations between nanoparticles are poorly explored in materials science. Here, the authors find that two atomically precise, isomorphic clusters of gold and silver can convert between each other in solution through a series of alloy clusters, preserving structure, topology, and metal-ligand stoichiometry.
- K. R. Krishnadas
- , Ananya Baksi
- & Thalappil Pradeep
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogenated monolayer graphene with reversible and tunable wide band gap and its field-effect transistor
Hydrogenated monolayer graphene with reversible and tunable wide band gap and its field-effect transistor
The absence of a band gap in graphene hinders its use in electronics. Here, the authors open a band gap as large as 3.9 electronvolts in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition by treating it in hydrogen plasma, and then use this material to create a room temperature field- effect transistor.
- Jangyup Son
- , Soogil Lee
- & Jongill Hong
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron sources are powerful tools for investigating dynamics at atomic and subatomic scales. Here, Li and Jones demonstrate the terahertz-driven emission of electrons with energies exceeding five kiloelectronvolts from nano-tips and study its dependence on the tip radius.
- Sha Li
- & R. R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Unusually efficient photocurrent extraction in monolayer van der Waals heterostructure by tunnelling through discretized barriers
Unusually efficient photocurrent extraction in monolayer van der Waals heterostructure by tunnelling through discretized barriers
Vertical integration of two-dimensional materials can open unprecedented possibilities towards design of efficient optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors investigate the photoresponse properties of a graphene/MoS2/graphene heterostructure, revealing promising quantum efficiency performances.
- Woo Jong Yu
- , Quoc An Vu
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Excitonic linewidth and coherence lifetime in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Excitonic linewidth and coherence lifetime in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
The interplay between dark and bright excitons has a significant impact on the optical properties of semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides. Here, the authors perform computational and experimental studies which unveil the microscopic origin of the excitonic coherence lifetime in WS2 and MoSe2.
- Malte Selig
- , Gunnar Berghäuser
- & Andreas Knorr
-
Article
| Open Access Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Most microelectronic devices today exploit the electronic properties of semiconductors. Here, the authors demonstrate a microelectronic device for free-space electrons by using the enhanced fields in a microstructured metal surface to induce effective photoemission.
- Ebrahim Forati
- , Tyler J. Dill
- & Dan Sievenpiper
-
Article
| Open Access The flux qubit revisited to enhance coherence and reproducibility
The flux qubit revisited to enhance coherence and reproducibility
Scalable quantum information processing requires controllable high-coherence qubits. Here, the authors present superconducting flux qubits with broad frequency tunability, strong anharmonicity and high reproducibility, identifying photon shot noise as the main source of dephasing for further improvements.
- Fei Yan
- , Simon Gustavsson
- & William D. Oliver
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Analysis of the mechanical properties of two-dimensional materials is important for device development. Here, the authors report a microscopic method for measuring the adhesion of graphene on top of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite, which exploits atomic-scale blisters formed upon neon atom intercalation.
- Jun Wang
- , Dan C. Sorescu
- & Petro Maksymovych
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
The wettability properties of graphene hold promise for the realisation of flow control devices. Here, the authors demonstrate that the degree of water penetration through a nickel mesh coated with graphene can be controlled electrically, enabling dynamic locomotion of water droplets.
- Rassoul Tabassian
- , Jung-Hwan Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access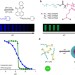 Molecular basis of cooperativity in pH-triggered supramolecular self-assembly
Molecular basis of cooperativity in pH-triggered supramolecular self-assembly
Understanding stimuli responsiveness on a molecular level can help with the rational design of nanomaterials with sharp responses. Here, Gao and co-workers have shown the molecular pathway of the supramolecular self-assembly of a series of ultra-pH sensitive block copolymers.
- Yang Li
- , Tian Zhao
- & Jinming Gao
-
Article
| Open Access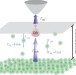 Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Probing individual impurities will become increasingly important as devices shrink towards the nanoscale. Here Rashidi et al., introduce a method based on time-resolved scanning tunnelling spectroscopy of surface dangling bonds to investigate the dynamics of individual dopants in silicon.
- Mohammad Rashidi
- , Jacob A. J. Burgess
- & Robert A. Wolkow
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic microfluidic control of supramolecular peptide self-assembly
Dynamic microfluidic control of supramolecular peptide self-assembly
The organization of supramolecular peptide polymers determines their properties; however, controlling their dimensions still remains a problem. Here, Gazitet al. show the spontaneous elongation and shortening of these polymers at an individual nano-assembly level by using a microfluidic platform.
- Zohar A. Arnon
- , Andreas Vitalis
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution from the plasmon to exciton state in ligand-protected atomically precise gold nanoparticles
Evolution from the plasmon to exciton state in ligand-protected atomically precise gold nanoparticles
Little is known about the transition of a metal nanoparticle from the plasmonic to excitonic state. Here, the authors map this evolution in atomically precise gold nanoparticles, a critical step for understanding the origins of surface plasmon resonance, metallic bonding, and catalytic behaviour.
- Meng Zhou
- , Chenjie Zeng
- & Rongchao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Nanomedicine efficacy in a clinical setting depends on the pharmacological properties of the therapeutic nanoparticles. Here, the authors exemplify an accelerated translational strategy from small-scale screening to clinical scale-up for an orally-dosed aqueous paediatric HIV nanomedicine.
- Marco Giardiello
- , Neill J. Liptrott
- & Andrew Owen
-
Article
| Open Access A centrifugation-based physicochemical characterization method for the interaction between proteins and nanoparticles
A centrifugation-based physicochemical characterization method for the interaction between proteins and nanoparticles
Thein vivobehaviour of nanoparticles is influenced by the presence of the protein corona. Here, the authors use analytical ultracentrifugation to study the interaction of gold nanoparticles with bovine serum albumin, to gain insight into the corona formation process.
- Ahmet Bekdemir
- & Francesco Stellacci
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing electric-field control of ferromagnetism through nanoscale engineering of high-Tc MnxGe1−x nanomesh
Enhancing electric-field control of ferromagnetism through nanoscale engineering of high-Tc MnxGe1−x nanomesh
Voltage control of magnetism in ferromagnetic semiconductor is appealing for spintronic applications, which is yet hindered by compound formation and low Curie temperature. Here, Nie et al. report electric-field control of ferromagnetism in MnxGe1−xnanomeshes with a Curie temperature above 400 K and controllable giant magnetoresistance.
- Tianxiao Nie
- , Jianshi Tang
- & Kang L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access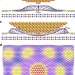 Pressure-induced commensurate stacking of graphene on boron nitride
Pressure-induced commensurate stacking of graphene on boron nitride
Van der Waals heterostructures enable fabrication of materials with engineered functionalities. Here, the authors demonstrate precise control over the interaction between layers by application of pressure with a scanning tunnelling microscopy tip.
- Matthew Yankowitz
- , K. Watanabe
- & Brian J. LeRoy
-
Article
| Open Access Approaching the standard quantum limit of mechanical torque sensing
Approaching the standard quantum limit of mechanical torque sensing
Cavity optomechanics enables measurement of torque at levels unattainable by previous techniques, but the main obstacle to improved sensitivity is thermal noise. Here the authors present cryogenic measurement of a cavity-optomechanical torsional resonator with unprecedented torque sensitivity of 2.9 yNm/√Hz.
- P. H. Kim
- , B. D. Hauer
- & J. P. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Robust ultra-low-friction state of graphene via moiré superlattice confinement
Robust ultra-low-friction state of graphene via moiré superlattice confinement
Two-dimensional materials show remarkable lubrication properties, yet chemical modifications may hinder such capabilities. Here, the authors show that when graphene is aligned on a Ge(111) substrate, ultra-low friction can be preserved even after graphene fluorination or oxidation.
- Xiaohu Zheng
- , Lei Gao
- & Xi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access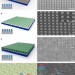 Ordered fragmentation of oxide thin films at submicron scale
Ordered fragmentation of oxide thin films at submicron scale
Fracture and related processes are typically considered detrimental, but have also attracted interest in more constructive roles. Here authors demonstrate ordered fragmentation at submicron scales of a metal oxide/hydroxide thin film by introducing preferential sites for fracture on the underlying substrate.
- L. Guo
- , Y. Ren
- & S. Y. Chiam
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Alternative ways to fabricate chiral media which give rise to interesting optical phenomena are sought. Here, Banzeret al. demonstrate a two-dimensional geometrically achiral nanoparticle assembly, which exhibits a chiral optical response due to its heterogeneous composition.
- Peter Banzer
- , Paweł Woźniak
- & Robert W. Boyd
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
The efficiency of a catalyst relies on the stability of intermediates on its surface. Here, the authors find that van der Waals interactions between acetate adsorbates on Au(110) provide a small but necessary energy contribution to stabilize the acetate and drive restructuring of the Au surface.
- Fanny Hiebel
- , Bonggeun Shong
- & Cynthia M. Friend
-
Article
| Open Access A quantum spin-probe molecular microscope
A quantum spin-probe molecular microscope
Single spin defects can allow high-resolution sensing of molecules under an applied magnetic field. Here, the authors propose a protocol for three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging with angstrom-level resolution exploiting the dipolar field of a spin qubit, such as a diamond nitrogen-vacancy.
- V. S. Perunicic
- , C. D. Hill
- & L.C.L. Hollenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Visualizing surface plasmon polaritons at buried interfaces has remained elusive. Here, the authors develop a methodology to study the spatiotemporal evolution of buried near-fields within complex heterostructures, enabling the characterization of the next generation of plasmonic devices.
- Tom T. A. Lummen
- , Raymond J. Lamb
- & F. Carbone
-
Article
| Open Access Thermoelectric signature of the chiral anomaly in Cd3As2
Thermoelectric signature of the chiral anomaly in Cd3As2
The thermoelectric effect can be used to explore electronic properties. Here, the authors show experimentally that Cd3As2exhibits a negative magnetic thermopower which reverses sign at high field, and relate it to the chiral anomaly, a signature of Weyl fermions.
- Zhenzhao Jia
- , Caizhen Li
- & Xiaosong Wu
-
Article
| Open Access High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
It has been suggested that strong field enhancement for high harmonic generation may be achievable with nano-antennas. Here, the authors show relevant field enhancement using a metal-sapphire nanostructure that provides a solid tip as the high harmonic emitter, replacing commonly used gaseous atoms.
- Seunghwoi Han
- , Hyunwoong Kim
- & Seung-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Isotope analysis in the transmission electron microscope
Isotope analysis in the transmission electron microscope
Electron microscopy can reveal a material’s chemical structure down to the atomic level, but has so far been blind to isotopic differences. Here the authors are able to map isotope concentrations in graphene by measuring the probability of ejecting atoms, demonstrating a ‘mass spectrometer in the microscope’.
- Toma Susi
- , Christoph Hofer
- & Jani Kotakoski
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the spinor nature of electronic states in nanosize non-collinear magnets
Probing the spinor nature of electronic states in nanosize non-collinear magnets
Non-collinear magnetization textures which are established by chiral exchange interactions have recently provided a route to novel phenomena and device concepts. Here, the authors demonstrate the effects of symmetry breaking on non-collinear magnetization by lateral confinement.
- Jeison A. Fischer
- , Leonid M. Sandratskii
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Silk protein fibres are exceptionally strong, owing to their high β-sheet nanocrystal content. Here, the authors use an electron beam to guide silk β-sheet crystals through structural transitions, and visualize the changes by infrared near-field optics, achieving close to molecular-level resolution.
- Nan Qin
- , Shaoqing Zhang
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental creation of quantum Zeno subspaces by repeated multi-spin projections in diamond
Experimental creation of quantum Zeno subspaces by repeated multi-spin projections in diamond
Repeated observations of quantum states inhibit coherent evolution through the Zeno effect, providing opportunities for controlling multi-qubit systems. Here the authors demonstrate that projecting joint observables of three spins in diamond creates quantum Zeno subspaces that suppress dephasing.
- N. Kalb
- , J. Cramer
- & T. H. Taminiau
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally-nucleated self-assembly of water and alcohol into stable structures at hydrophobic interfaces
Thermally-nucleated self-assembly of water and alcohol into stable structures at hydrophobic interfaces
Alcohol-water mixtures are characterized by the existence of segregated clusters, whose dynamics are too fast to be investigated in bulk solution. Here, Voïtchovsky et al. show the formation of stable two-dimensional water-alcohol wire-like structures via H-bonds on graphite surface at room temperature.
- Kislon Voïtchovsky
- , Daniele Giofrè
- & Michele Ceriotti
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic control of H+ current in a bioprotonic device with Gramicidin A and Alamethicin
Electronic control of H+ current in a bioprotonic device with Gramicidin A and Alamethicin
Conventional electronics use electrons as charge carriers whereas biological systems use ions, confounding integration of electronics with biology. Here the authors show voltage-regulated flow of protons across a supported lipid bilayer using the ion channel Gramicidin A and the voltage-gated ion channel Alamethicin.
- Zahra Hemmatian
- , Scott Keene
- & Marco Rolandi
-
Article
| Open Access A modular platform for one-step assembly of multi-component membrane systems by fusion of charged proteoliposomes
A modular platform for one-step assembly of multi-component membrane systems by fusion of charged proteoliposomes
Assembling multiple biological components into synthetic lipid vesicles is a limiting step in the manufacture of biomimetic cell-like structures. Here the authors use fusogenic proteoliposomes of opposite charge for fast assembly of a minimal electron transport chain consisting of F1F0 ATP-synthase and the proton pump bo3-oxidase.
- Robert R. Ishmukhametov
- , Aidan N. Russell
- & Richard M. Berry
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling the pentagonal nature of perfectly aligned single-and double-strand Si nano-ribbons on Ag(110)
Unveiling the pentagonal nature of perfectly aligned single-and double-strand Si nano-ribbons on Ag(110)
The atomic structure of Si nanoribbons on metallic surfaces has been disputed for years and yet remained elusive. Here, the authors unveil the nature of aligned Si nanoribbons on Ag(110), shifting the focus from a hexagonal silicene-like arrangement to a 1D phase solely comprising Si pentagons.
- Jorge I. Cerdá
- , Jagoda Sławińska
- & María E. Dávila
-
Article
| Open Access Thermopile detector of light ellipticity
Thermopile detector of light ellipticity
Differences in the intensity of the left- and right-circularly polarized components of light can provide useful information about the chirality of electromagnetic radiation. Here, the authors demonstrate a monolithic photodetector that translates this difference in incident radiation directly into a voltage
- Feng Lu
- , Jongwon Lee
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental determination of excitonic band structures of single-walled carbon nanotubes using circular dichroism spectra
Experimental determination of excitonic band structures of single-walled carbon nanotubes using circular dichroism spectra
The experimental determination of band structure of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) is a challenging task, and often must be theoretically predicted. Here, the authors separate SWCNTs in high purity and experimentally determine their excitonic band structures using circular dichroism spectra.
- Xiaojun Wei
- , Takeshi Tanaka
- & Hiromichi Kataura
-
Article
| Open Access Structure sensitivity of Cu and CuZn catalysts relevant to industrial methanol synthesis
Structure sensitivity of Cu and CuZn catalysts relevant to industrial methanol synthesis
The dependence of the Cu-catalysed methanol synthesis on the structure of the Cu surface is a matter of debate. Here the authors show that activity falls for Cu and Cu-Zn particles below 8 nm and propose this is due to the absence of certain atomic configurations on the smaller particle surfaces.
- Roy van den Berg
- , Gonzalo Prieto
- & Krijn P. de Jong
-
Article
| Open Access Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect
Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect
The energy harvesting potential of triboelectric nanogenerators is currently limited by their output power. Here, the authors design a triboelectric nanogenerator inspired by lightning generation, featuring an electric double layer that delivers impressive charge separation and electric potential.
- Jinsung Chun
- , Byeong Uk Ye
- & Jeong Min Baik
-
Article
| Open Access Novel near-infrared emission from crystal defects in MoS2 multilayer flakes
Novel near-infrared emission from crystal defects in MoS2 multilayer flakes
Impurities and vacancies are commonly found within the crystalline lattice of transition metal dichalcogenides, however they are usually seen as detrimental for their optical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate that sulfur vacancies in MoS2can give rise to a near-infrared emission peak.
- F. Fabbri
- , E. Rotunno
- & G. Salviati
-
Article
| Open Access Contextuality without nonlocality in a superconducting quantum system
Contextuality without nonlocality in a superconducting quantum system
Tests of the Bell-Kochen-Specker theorem aim at showing that the measurement statistics of a single qutrit are incompatible with noncontextual realism. Here, the authors use a superconducting qutrit with deterministic readouts to violate a noncontextuality inequality, ruling out several loopholes.
- Markus Jerger
- , Yarema Reshitnyk
- & Arkady Fedorov
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolour synthesis in lanthanide-doped nanocrystals through cation exchange in water
Multicolour synthesis in lanthanide-doped nanocrystals through cation exchange in water
De novosynthesis is the primary way to tune the emission colour of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanocrystals. Here, the authors introduce post-synthetic cation exchange as a strategy to access multiple colours of luminescent nanocrystals, preserving the size and morphology of the original template.
- Sanyang Han
- , Xian Qin
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Oscillating edge states in one-dimensional MoS2 nanowires
Oscillating edge states in one-dimensional MoS2 nanowires
Unusual properties arise in transition metal dichalcogenides as dimensionality decreases. Here, the authors introduce a templated growth approach to precisely control the width of MoS2nanowires on a substrate, allowing them to reveal a relationship between size and electronic properties.
- Hai Xu
- , Shuanglong Liu
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Sensing surface mechanical deformation using active probes driven by motor proteins
Sensing surface mechanical deformation using active probes driven by motor proteins
It is challenging to characterize the mechanical properties of soft surfaces owing to the coupling between surface deformation and elasticity of bulk materials. Here, Inoue et al. use motile cytoskeletal filaments as active probes, whose direction reflects the stress field experienced by the surface.
- Daisuke Inoue
- , Takahiro Nitta
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Article
| Open Access A 17 GHz molecular rectifier
A 17 GHz molecular rectifier
Molecular electronics holds promise to overcome scaling limits of conventional technologies, but is currently limited to low frequency operation. Here, Trasobares et al. show radio frequencies of up to 17.8 GHz in a molecular diode based on ferrocenyl undecanethiol self-assembled monolayers on gold nanodots.
- J. Trasobares
- , D. Vuillaume
- & N. Clément
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between hydrophilicity and surface barriers on water transport in zeolite membranes
Interplay between hydrophilicity and surface barriers on water transport in zeolite membranes
Zeolite crystal with porous structure is predicted to be a good membrane material for water purification, but experiments show water uptake orders of magnitude smaller than the theory. Here, Fasano et al. attribute this disagreement to the additional diffusion resistance induced by surface defects.
- Matteo Fasano
- , Thomas Humplik
- & Pietro Asinari
-
Article
| Open Access Unsupervised vector-based classification of single-molecule charge transport data
Unsupervised vector-based classification of single-molecule charge transport data
The stochastic nature of single-molecule charge transport measurements requires collection of large data sets to capture their full complexity. Here, the authors adopt strategies from machine learning for the unsupervised classification of single-molecule charge transport data without a prioriassumptions.
- Mario Lemmer
- , Michael S. Inkpen
- & Tim Albrecht
-
Article
| Open Access Incipient ferroelectricity of water molecules confined to nano-channels of beryl
Incipient ferroelectricity of water molecules confined to nano-channels of beryl
Ferroelectric orders hardly exist in liquid or ice state of water, despite its enormous molecular electrical polarizability. Here, Gorshunov et al. report incipient ferroelectricity in chains of interacting water molecules by placing them in the structural channels of a beryl crystal.
- B. P. Gorshunov
- , V. I. Torgashev
- & M. Dressel
-
Article
| Open Access Quantized conductance doubling and hard gap in a two-dimensional semiconductor–superconductor heterostructure
Quantized conductance doubling and hard gap in a two-dimensional semiconductor–superconductor heterostructure
Interface transparency between 2D semiconductors and superconductors is a longstanding problem, seriously hindering potential applications. Here, using a new hybrid system, Kjaergaard et al. report quantized conductance doubling and a hard superconducting gap measured via a quantum point contact, indicating a near pristine interface.
- M. Kjaergaard
- , F. Nichele
- & C. M. Marcus

 Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared
Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared