Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Losses of bandwidth are inevitable when interfacing between optical and electronic components. Here the authors present a switching device consisting of a two-dimensional disordered array of nanoholes that can potentially transfer information about 40 times faster than conventional switching devices.
- Wonjun Choi
- , Yonghyeon Jo
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Single electrons of solid-state defects can be used to detect nearby nuclear spins, but so far only a few at a time have been resolved. Here the authors propose an approach based on delayed entanglement echo that demonstrates improved detection and manipulation capabilities of nuclear spins by an NV centre.
- Zhen-Yu Wang
- , Jorge Casanova
- & Martin B. Plenio
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Optomechanical systems could form logic gates, but key requirements are two stable static states and the ability to switch between them. Here, the authors observe radiation-pressure induced buckling transitions in an optomechanical system, and control this transition by varying laser power and detuning.
- H. Xu
- , U. Kemiktarak
- & J. M. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Superconducting parity effect across the Anderson limit
Superconducting parity effect across the Anderson limit
How quantum size effects affect superconductivity has been predicted, but it has never been verified. Here, Vlaicet al. report superconducting parity effect as a function of lead nanocrystal volume, unambiguously validating the Anderson criterion.
- Sergio Vlaic
- , Stéphane Pons
- & Hervé Aubin
-
Article
| Open Access Transcending the slow bimolecular recombination in lead-halide perovskites for electroluminescence
Transcending the slow bimolecular recombination in lead-halide perovskites for electroluminescence
Slow bimolecular recombination in three-dimensional halide perovskites represents a fundamental limitation for electroluminescence efficiency. Using time-resolved spectroscopy Xinget al. demonstrate that this limitation can be overcome by employing van-der-Waals-coupled multiple quantum well structures.
- Guichuan Xing
- , Bo Wu
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Precise tuning in platinum-nickel/nickel sulfide interface nanowires for synergistic hydrogen evolution catalysis
Precise tuning in platinum-nickel/nickel sulfide interface nanowires for synergistic hydrogen evolution catalysis
Multicomponent, nanoscale heterostructures may exhibit notable catalytic properties imparted by the various building blocks. Here, the authors fabricate metal/sulfide heterostructures via direct sulfurization of segregated platinum-nickel nanowires, and assess their hydrogen evolution performance.
- Pengtang Wang
- , Xu Zhang
- & Xiaoqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Rosin-enabled ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene for large-area flexible organic light-emitting diodes
Rosin-enabled ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene for large-area flexible organic light-emitting diodes
Ultraclean and damage-free transfer of graphene over large areas is crucial for the future development of flexible electronics and optoelectronics. Using a rosin-assisted method, the authors transfer graphene with an ultraclean surface and uniform small sheet resistance—a 4-inch monolithic organic light-emitting diode is demonstrated.
- Zhikun Zhang
- , Jinhong Du
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Here Duanet al. demonstrate dynamic plasmonic colour displays using catalytic magnesium metasurfaces. Controlled hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of the constituent nanoparticles, which serve as dynamic pixels, allow plasmonic colour printing, tuning, erasing, restoration of colour and encoding of information.
- Xiaoyang Duan
- , Simon Kamin
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access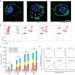 PEGylated graphene oxide elicits strong immunological responses despite surface passivation
PEGylated graphene oxide elicits strong immunological responses despite surface passivation
Polyethylene glycol has been widely utilized to functionalize nanomaterials in order to improve their biocompatibility. Here, the authors demonstrate that PEGylated nano-graphene oxide can elicit an inflammatory response, contradicting current literature.
- Nana Luo
- , Jeffrey K. Weber
- & Guanghui Ma
-
Article
| Open Access An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene
An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene
The functional integration of sound generation and detection on a single device is required to assist mute people. Here, the authors demonstrate a graphene-based artificial throat capable of detecting and converting diverse throat vibrations into meaningful sound within a single device.
- Lu-Qi Tao
- , He Tian
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Compiler-aided systematic construction of large-scale DNA strand displacement circuits using unpurified components
Compiler-aided systematic construction of large-scale DNA strand displacement circuits using unpurified components
DNA circuits hold promise for advancing information-based molecular technologies, yet it is challenging to design and construct them in practice. Thubagereet al. build DNA strand displacement circuits using unpurified strands whose sequences are automatically generated from a user-friendly compiler.
- Anupama J. Thubagere
- , Chris Thachuk
- & Lulu Qian
-
Article
| Open Access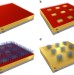 Magnetization switching in ferromagnets by adsorbed chiral molecules without current or external magnetic field
Magnetization switching in ferromagnets by adsorbed chiral molecules without current or external magnetic field
Spin manipulation in memory devices typically requires large electrical currents, limiting performance. Here the authors demonstrate magnetization switching in ferromagnetic films by depositing chiral molecules, making use of a proximity effect without needing magnetic or electric fields.
- Oren Ben Dor
- , Shira Yochelis
- & Yossi Paltiel
-
Article
| Open Access Product selectivity in plasmonic photocatalysis for carbon dioxide hydrogenation
Product selectivity in plasmonic photocatalysis for carbon dioxide hydrogenation
Atmospheric CO2 can be transformed into valuable hydrocarbons by reaction with H2, but CO is the favoured kinetic product. Here, Liu and co-workers show that plasmonic rhodium nanoparticles not only reduce the activation energy for CO2hydrogenation, but also photo-selectively produce methane.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Xueqian Li
- & Jie Liu
-
Article
| Open Access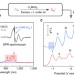 Interface confined hydrogen evolution reaction in zero valent metal nanoparticles-intercalated molybdenum disulfide
Interface confined hydrogen evolution reaction in zero valent metal nanoparticles-intercalated molybdenum disulfide
Interface confined reactions are a viable strategy for achieving stable and selective catalysts. Here, the authors demonstrate that 1T'-enriched lithiated MoS2 can reduce metal ions in situ, forming zero valent platinum nanoparticle-intercalated MoS2, with enhanced hydrogen evolution activity.
- Zhongxin Chen
- , Kai Leng
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast radiative heat transfer
Ultrafast radiative heat transfer
Electron relaxation, which is the dominant release channel of electronic heat in nanostructures, occurs with characteristic times of several picoseconds. Here, the authors predict that an ultrafast (femtosecond) radiative cooling regime takes place in plasmonically active neighboring graphene nanodisks prior to electron relaxation.
- Renwen Yu
- , Alejandro Manjavacas
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Few-layered graphene offers a powerful platform to investigate electronic interactions beyond the non-interacting electron picture approximation. Here, the authors report the signature of strong electronic interactions and quantum Hall ferromagnetism in trilayer graphene with ABA stacking.
- Biswajit Datta
- , Santanu Dey
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Materials that show twinning-induced plasticity can offer unusual combinations of strength and ductility. Here, authors study deformation twinning and dislocation behaviour in a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi and find a three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical twin network that forms from the activation of three twinning systems.
- Zijiao Zhang
- , Hongwei Sheng
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-controlled conductance switching in DNA
Gate-controlled conductance switching in DNA
Thanks to its base stacking structure, DNA can behave as an electric wire, but external control of its electronic properties has not been achieved yet. Here, the authors show that DNA conductance can be switched electrochemically when a DNA base is replaced by the redox molecule anthraquinone.
- Limin Xiang
- , Julio L. Palma
- & Nongjian Tao
-
Article
| Open Access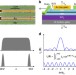 Edge currents shunt the insulating bulk in gapped graphene
Edge currents shunt the insulating bulk in gapped graphene
The absence of a bandgap in the electronic spectrum of graphene can be overcome by breaking its lattice symmetry. The authors show that the insulating state of gapped graphene is electrically shorted by narrow edge channels exhibiting high conductivity.
- M. J. Zhu
- , A. V. Kretinin
- & M. Ben Shalom
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody-controlled actuation of DNA-based molecular circuits
Antibody-controlled actuation of DNA-based molecular circuits
Existing DNA based circuits, designed to perform logic operations and signal processing, are generally responsive to DNA or RNA inputs. Here, the authors show that antibodies can actuate DNA logic gates, opening the way to applications of DNA computing in diagnostics and biomedicine.
- Wouter Engelen
- , Lenny H. H. Meijer
- & Maarten Merkx
-
Article
| Open Access Tailored protein encapsulation into a DNA host using geometrically organized supramolecular interactions
Tailored protein encapsulation into a DNA host using geometrically organized supramolecular interactions
Current strategies for protein encapsulation in DNA vessels for controlled enzymatic catalysis or therapeutic delivery rely on formation of covalent complexes. Here, the authors design a system that mimics natural reversible non-covalent host–guest interactions between a DNA host and the protein DegP.
- Andreas Sprengel
- , Pascal Lill
- & Barbara Saccà
-
Article
| Open Access Giant heat transfer in the crossover regime between conduction and radiation
Giant heat transfer in the crossover regime between conduction and radiation
Kloppstechet al. report experimental observations of the heat transfer between a gold tip and an atomically flat gold sample in the 0.2–7 nm regime. The observed flux rates are four orders of magnitude larger than expected from theory, suggesting the possibility of additional heat transfer mechanisms.
- Konstantin Kloppstech
- , Nils Könne
- & Achim Kittel
-
Article
| Open Access Large positive in-plane magnetoresistance induced by localized states at nanodomain boundaries in graphene
Large positive in-plane magnetoresistance induced by localized states at nanodomain boundaries in graphene
Owing to long spin lifetime and diffusion length, graphene holds promise for spintronics, yet it does not possess intrinsic magnetic properties. Here, the authors observe experimentally a large, positive magnetoresistance at graphene nanodomain boundaries.
- Han-Chun Wu
- , Alexander N. Chaika
- & Ching-Ray Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Study of radiative heat transfer in Ångström- and nanometre-sized gaps
Study of radiative heat transfer in Ångström- and nanometre-sized gaps
Here, Cuiet al. report radiative heat transfer in few Ångström to 5 nm gap sizes, between a gold-coated probe and a heated planar gold substrate subjected to various surface cleaning procedures. They found that insufficiently cleaned probes and substrates led to unexpectedly large radiative thermal conductances.
- Longji Cui
- , Wonho Jeong
- & Pramod Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Superlubricity can be unstable in graphene systems, especially under high applied loads. Here the authors use microspheres uniformly coated by graphene to measure friction between 2D materials and show that superlow friction is preserved for long periods of time under high loads and various atmospheres.
- Shu-Wei Liu
- , Hua-Ping Wang
- & Jianbin Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Indications of chemical bond contrast in AFM images of a hydrogen-terminated silicon surface
Indications of chemical bond contrast in AFM images of a hydrogen-terminated silicon surface
Whether and under what circumstances chemical bonds could be imaged via force microscopy is a controversial topic. Here authors develop a particular combination of model surface, imaging procedures and simulation approach and discuss possible indications of chemical contrast in imaging data they obtain.
- Hatem Labidi
- , Mohammad Koleini
- & Robert A. Wolkow
-
Article
| Open Access In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
The atomic mechanisms of reversible phase transitions are challenging to probe experimentally. Here, the authors induce melting and freezing processes in bismuth nanoparticles inside a high-resolution electron microscope, observing the atom-level stages of this phase transition pathway in real time.
- Yingxuan Li
- , Ling Zang
- & Chuanyi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Franckeite as a naturally occurring van der Waals heterostructure
Franckeite as a naturally occurring van der Waals heterostructure
Van der Waals heterostructures have been so far mostly assembled by artificial stacking of individual 2D layers with diverse functionalities. Here, the authors shift the focus demonstrating the exfoliation of a naturally occurring franckeite heterostructure, a p-type narrow band-gap semiconductor.
- Aday J. Molina-Mendoza
- , Emerson Giovanelli
- & Andres Castellanos-Gomez
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-centred azaphosphatriptycene gear with a photo- and thermally driven mechanical switching function based on coordination isomerism
Metal-centred azaphosphatriptycene gear with a photo- and thermally driven mechanical switching function based on coordination isomerism
In metal-based molecular motors, the motion is generally triggered by changes in the ligand coordination around the metal centre. Here, the authors synthesize a molecular gear that switches between states through photo- and thermally driven geometrical isomerization around a platinum ion.
- Hitoshi Ube
- , Yoshihiro Yasuda
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access Slow cooling and highly efficient extraction of hot carriers in colloidal perovskite nanocrystals
Slow cooling and highly efficient extraction of hot carriers in colloidal perovskite nanocrystals
Harvesting excess energy from above-band gap photons could lead to solar cells which exceed conventional efficiency limits. Liet al., study hot carrier cooling in hybrid perovskite materials with reduced dimensionality using transient absorption spectroscopy and demonstrate efficient hot-electron extraction in such systems.
- Mingjie Li
- , Saikat Bhaumik
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale π–π stacked molecules are bound by collective charge fluctuations
Nanoscale π–π stacked molecules are bound by collective charge fluctuations
Attractive, non-covalent interactions between aromatic rings—termedπ−πstacking—is common in chemistry but difficult to model. Here the authors report a quantum-mechanical model to show the importance of collective charge fluctuations for understanding pi-stacked supramolecular systems.
- Jan Hermann
- , Dario Alfè
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-driven redox-neutral decarboxylative carbon-hydrogen trifluoromethylation of (hetero)arenes with trifluoroacetic acid
Photo-driven redox-neutral decarboxylative carbon-hydrogen trifluoromethylation of (hetero)arenes with trifluoroacetic acid
C–H bond functionalization has become an important tool for many organic transformations, however such reactions typically require stoichiometric amounts of external oxidants. Here the authors report the photo-driven decarboxylative C–H trifluoromethylation of arenes using only low amounts of oxidant.
- Jin Lin
- , Zhi Li
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy reveals spin charge separation in metallic MoSe2 grain boundary
Angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy reveals spin charge separation in metallic MoSe2 grain boundary
Line defects are 1D structures often embedded within 2D materials. Here, the authors use angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy to unveil the 1D nature of electron behaviour in such defects in atomically thin MoS2, providing evidence for spin- and charge-separation.
- Yujing Ma
- , Horacio Coy Diaz
- & Matthias Batzill
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide-coupled nanopillar metal-cavity light-emitting diodes on silicon
Waveguide-coupled nanopillar metal-cavity light-emitting diodes on silicon
Despite much progress, nanoscale light sources suitable for photonic integration are lacking. Here, the authors present a metal-cavity nanopillar LED on a silicon substrate working at telecommunications wavelengths, which demonstrates compatibility with membrane-on-Si photonic integration platforms.
- V. Dolores-Calzadilla
- , B. Romeira
- & D. Heiss
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative expression of atomic chirality in inorganic nanostructures
Cooperative expression of atomic chirality in inorganic nanostructures
Cooperative chirality is common in organic and biomolecular systems but is rarely explored in inorganic materials. Here, the authors combine synthesis and theory to uncover cooperative chirality in inorganic nanocrystals, arising from the interplay of independently-controlled crystallographic and morphological chirality.
- Peng-peng Wang
- , Shang-Jie Yu
- & Min Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
There is emerging interest in photodetectors in the mid-infrared driven by increasing need to monitor the environment for security and healthcare purposes. Sassiet al. show a thermal photodetector, based on the coupling between graphene and a pyroelectric crystal, which shows high temperature sensitivity.
- U. Sassi
- , R. Parret
- & A. Colli
-
Article
| Open Access Preserving π-conjugation in covalently functionalized carbon nanotubes for optoelectronic applications
Preserving π-conjugation in covalently functionalized carbon nanotubes for optoelectronic applications
While covalent modification of carbon nanotubes allows their use in a wide range of applications, it often results in disruption of their optoelectronic properties. Here, the authors design a cycloaddition reaction that preserves the nanotubes electronic structure.
- Antonio Setaro
- , Mohsen Adeli
- & Stephanie Reich
-
Article
| Open Access Single-step ambient-air synthesis of graphene from renewable precursors as electrochemical genosensor
Single-step ambient-air synthesis of graphene from renewable precursors as electrochemical genosensor
Graphene films are commonly produced by thermal chemical vapour deposition, which is capable of producing high-quality films but still limited by factors such as high cost. Here, the authors report the growth of single-to-few-layer continuous graphene films under ambient-air conditions.
- Dong Han Seo
- , Shafique Pineda
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov
-
Article
| Open Access A general patterning approach by manipulating the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams
A general patterning approach by manipulating the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams
Ostwald ripening is thermodynamically favoured in many liquid and gas systems, where small particles tend to dissolve into large ones. Against this effect, Huanget al. use patterned microstructures to guide the evolution of two-dimensional liquid foams as a platform for the assembly of nanoparticles.
- Zhandong Huang
- , Meng Su
- & Yanlin Song
-
Article
| Open Access Highly tensile-strained Ge/InAlAs nanocomposites
Highly tensile-strained Ge/InAlAs nanocomposites
Self-ordered heterogeneous nanostructures are of broad interest for both fundamental studies and technological applications. Here authors show that segregation in a multicomponent system during growth can yield highly strained germanium nanowire arrays embedded within a ternary semiconductor matrix.
- Daehwan Jung
- , Joseph Faucher
- & Minjoo Larry Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-wavelength modulation of χ(2) optical nonlinearity in organic thin films
Sub-wavelength modulation of χ(2) optical nonlinearity in organic thin films
Materials with spatially modulated nonlinear optical properties are used for quasi-phase matching. Here, Yanet al. exploit the nonlinearity of intermolecular charge transfer states together with oblique-angle deposition to achieve nanoscale modulation of the second-order susceptibility.
- Yixin Yan
- , Yakun Yuan
- & Noel C. Giebink
-
Article
| Open Access Deep eutectic-solvothermal synthesis of nanostructured ceria
Deep eutectic-solvothermal synthesis of nanostructured ceria
Synthesis of nanostructured ceria on green deep eutectic solvent reline is one of the less energy-intensive routes to date. Here, the authors show that the reline solvent plays the role of a latent supramolecular catalyst driving the pre-organization of the reactants, allowing morphology and porosity control.
- Oliver S. Hammond
- , Karen J. Edler
- & Laura Torrente-Murciano
-
Article
| Open Access Optical gating and streaking of free electrons with sub-optical cycle precision
Optical gating and streaking of free electrons with sub-optical cycle precision
Pulsed electron beams with ultrafast duration are desirable to study atomic processes occurring over the natural time scales of electronic motion. Here the authors demonstrate the generation of electron pulses down to attosecond time scales by using optical gating and streaking method.
- M. Kozák
- , J. McNeur
- & P. Hommelhoff
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable high-precision tuning of photonic resonators by resonant cavity-enhanced photoelectrochemical etching
Scalable high-precision tuning of photonic resonators by resonant cavity-enhanced photoelectrochemical etching
Aligning the resonances of sets of optical cavities is necessary for advanced photonics and sensing applications. Here, the authors introduce resonant photoelectrochemical etching as a method to collectively and permanently tune the resonant wavelengths of ensembles of resonators on a photonic chip.
- Eduardo Gil-Santos
- , Christopher Baker
- & Ivan Favero
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale integration of sacrificial nanofluidic chips for detecting and manipulating single DNA molecules
Wafer-scale integration of sacrificial nanofluidic chips for detecting and manipulating single DNA molecules
The wide use of microfluidics for biological analysis demands scalable preparation methods, yet in practice it is very challenging. Here, Wanget al. show a wafer-scale fabrication of nanofluidic chips with single-digit nanometre dimension, which is compatible with standard semiconductor processing.
- Chao Wang
- , Sung-Wook Nam
- & Qinghuang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Imperfect two-dimensional topological insulator field-effect transistors
Imperfect two-dimensional topological insulator field-effect transistors
A challenge of using 2D materials for nanoelectronic devices is the need for defect-free lattice supporting efficient carrier transport. Here, the authors show theoretically that 2D topological insulators enable high-performance, low-power field-effect transistors without requiring defect-free materials.
- William G. Vandenberghe
- & Massimo V. Fischetti
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals
Nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals
A material with a deep melted zone (MZ) but small heat-affected zone (HAZ) is ideal for manufacturing, but improving one zone comes at the expense of the other. Here, the authors resolve this contradiction in metals by adding nanoparticles, which change the metals’ properties in such a way that both expands MZ and minimizes HAZ.
- Chao Ma
- , Lianyi Chen
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical observations on the crack tip zone and stress corrosion of two-dimensional MoS2
Dynamical observations on the crack tip zone and stress corrosion of two-dimensional MoS2
How well the linear elastic fracture picture holds at small length scales and systems with reduced dimensionality remains an active area of inquiry. Here authors usein situ electron microscopy to study fracture in MoS2monolayers and report dislocation emission rates greater than expected accompanying crack propagation.
- Thuc Hue Ly
- , Jiong Zhao
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically tunable organic–inorganic hybrid polaritons with monolayer WS2
Electrically tunable organic–inorganic hybrid polaritons with monolayer WS2
Hybrid polariton states originating from the strong coupling of photonic and excitonic states hold promise for control of nonlinear light behaviour. Here, the authors fabricate a microcavity containing organic dye and WS2, featuring hybrid polaritons arising from both Frenkel and Wannier-Mott excitons.
- Lucas C. Flatten
- , David M. Coles
- & Jason M. Smith

 A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells
A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells