Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Nerve growth factor (NGF) contributes to the sustained growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Here, the authors develop a gold nanocluster-coupled siRNA against NGF that efficiently silences theNGFgene and inhibits tumour growth of pancreatic cancer in mice.
- Yifeng Lei
- , Lixue Tang
- & Xingyu Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Semiconducting materials are potential SERS substrates as alternatives to noble metals, but often suffer from poor stabilities and sensitivities. Here, the authors use molybdenum dioxide as a SERS material, showing high enhancement factors and stability to oxidation even at high temperatures.
- Qiqi Zhang
- , Xinshi Li
- & Guangcheng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
While crystal phase modification may endow materials with altered functionality, the fabrication of allomorphic noble metal nanomaterials is challenging. Here, the authors synthesize an unusual hexagonal close-packed platinum-nickel alloy and demonstrate its enhanced hydrogen evolution catalytic activity.
- Zhenming Cao
- , Qiaoli Chen
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Band structure engineered layered metals for low-loss plasmonics
Band structure engineered layered metals for low-loss plasmonics
Here the authors show that Ohmic losses are reduced in certain layered metals, such as the transition metal dichalcogenide, due to a small density of states for scattering in the near-IR originating from the electronic band structure, thus leading to improved performance for low-loss plasmonic applications.
- Morten N. Gjerding
- , Mohnish Pandey
- & Kristian S. Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Role of chiral quantum Hall edge states in nuclear spin polarization
Role of chiral quantum Hall edge states in nuclear spin polarization
Quantum Hall phases in two-dimensional systems have chiral edges, along which electrons propagate in one direction without backscattering. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance to demonstrate how chiral modes establish dynamical nuclear polarization in a quantum Hall ferromagnet.
- Kaifeng Yang
- , Katsumi Nagase
- & Hongwu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient electrical control of thin-film black phosphorus bandgap
Efficient electrical control of thin-film black phosphorus bandgap
Layered black phosphorous has gained significant attention in the 2D materials community, and dynamical control of its bandgap is key to enable novel applications. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous electrical bandgap tuning using moderate displacement fields.
- Bingchen Deng
- , Vy Tran
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable transmission of quantum Hall edge channels with full degeneracy lifting in split-gated graphene devices
Tunable transmission of quantum Hall edge channels with full degeneracy lifting in split-gated graphene devices
Quantum point contacts are gate-tunable constrictions allowing for control of charge carrier transmission in 2D electron gases. Here, the authors fabricate a hBN/graphene/hBN van der Waals heterojunction to enable quantum point contact devices in the integer and fractional quantum Hall regimes.
- Katrin Zimmermann
- , Anna Jordan
- & Benjamin Sacépé
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule electrical contacts on silicon electrodes under ambient conditions
Single-molecule electrical contacts on silicon electrodes under ambient conditions
The next level of miniaturization of electronic circuits calls for a connection between current single-molecule and traditional semiconductor processing technologies. Here, the authors show a method to prepare metal/molecule/silicon diodes that present high current rectification ratios exceeding 4,000.
- Albert C. Aragonès
- , Nadim Darwish
- & Ismael Díez-Pérez
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven cation exchange for in situ fabrication of individual nanostructures
Electrically driven cation exchange for in situ fabrication of individual nanostructures
Cation exchange, traditionally driven by ion solvation or thermal activation, is a robust approach for preparing heterogeneous nanostructures but lacks selectivity for preparation of individual nanocrystals. Here, the authors report an electrically driven cation exchange reaction that enables them to fabricate individual nanocrystals with high selectivity.
- Qiubo Zhang
- , Kuibo Yin
- & Litao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanics of individual aerographite tetrapods
Nanomechanics of individual aerographite tetrapods
Aerographite is a highly porous and lightweight carbon material obtained from hollow tubular tetrapod building units. Here, the authors present a comprehensive investigation of tetrapod deformation mechanisms which are at the core of aerographite nanomechanical properties.
- Raimonds Meija
- , Stefano Signetti
- & Nicola M. Pugno
-
Article
| Open Access Inverting polar domains via electrical pulsing in metallic germanium telluride
Inverting polar domains via electrical pulsing in metallic germanium telluride
Polar metals such as GeTe could store information using electric domains but the high conductivity screens electric fields, preventing the use of usual domain control techniques. Here, the authors demonstrate that polar domains in GeTe can be manipulated using electrically generated heat shocks.
- Pavan Nukala
- , Mingliang Ren
- & Ritesh Agarwal
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically-driven colossal supercurrent enhancement in InAs nanowire Josephson junctions
Magnetically-driven colossal supercurrent enhancement in InAs nanowire Josephson junctions
Physical details of a Josephson junction may drastically modify the properties of supercurrent. Here, the authors observe a colossal enhancement of the critical supercurrent in a Josephson junction subject to a perpendicular magnetic field, indicating topological phase transitions.
- J. Tiira
- , E. Strambini
- & F. Giazotto
-
Article
| Open Access A microprocessor based on a two-dimensional semiconductor
A microprocessor based on a two-dimensional semiconductor
Two-dimensional materials are receiving increasing interest as they could pave the way to a paradigm shift in nano-electronics. Here, the authors demonstrate a 1-bit implementation of a microprocessor consisting of 115 transistors, using atomically thin MoS2.
- Stefan Wachter
- , Dmitry K. Polyushkin
- & Thomas Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access DNA origami-based shape IDs for single-molecule nanomechanical genotyping
DNA origami-based shape IDs for single-molecule nanomechanical genotyping
Atomic force microscopy allows for the imaging of molecules at a nanometre resolution. Here the authors combine AFM with self-assembling DNA origami structures to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms and determine haplotypes.
- Honglu Zhang
- , Jie Chao
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling valley selective exciton scattering in monolayer WSe2 through upconversion
Enabling valley selective exciton scattering in monolayer WSe2 through upconversion
Monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides host excitons, bound electron-hole pairs that play a pivotal role in optoelectronic applications relying on strong light-matter interaction. Here, the authors unveil the spectroscopic signature of boson scattering of two-dimensional excitons in monolayer WSe2.
- M. Manca
- , M. M. Glazov
- & B. Urbaszek
-
Article
| Open Access Learning through ferroelectric domain dynamics in solid-state synapses
Learning through ferroelectric domain dynamics in solid-state synapses
Accurate modelling of memristor dynamics is essential for the development of autonomous learning in artificial neural networks. Through a combined theoretical and experimental study of the polarization switching process in ferroelectric memristors, Boynet al. establish a model that enables learning and retrieving patterns in a neural system.
- Sören Boyn
- , Julie Grollier
- & Vincent Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access A bright triggered twin-photon source in the solid state
A bright triggered twin-photon source in the solid state
Photon twins are important for interdisciplinary research fields using non-classical light, such as quantum biology. Here, Heindelet al. demonstrate that a single semiconductor quantum dot integrated into a microlens operates as an efficient photon-pair source.
- T. Heindel
- , A. Thoma
- & S. Reitzenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Improved ethanol electrooxidation performance by shortening Pd–Ni active site distance in Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts
Improved ethanol electrooxidation performance by shortening Pd–Ni active site distance in Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts
Incorporating oxophilic metals into noble metal catalysts can improve electrocatalytic performance; however, the influence of the distance between noble metal and oxophilic metal active site is not well understood. Here the authors make Pd–Ni–P nanocatalysts for ethanol oxidation, with improved performance achieved by shortening the Pd–Ni distance.
- Lin Chen
- , Lilin Lu
- & Leyu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene-like nanoribbons periodically embedded with four- and eight-membered rings
Graphene nanoribbons consist of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Despite non-hexagonal rings generally being more unstable, the authors demonstrate the successful synthesis of graphene-like nanoribbons with periodically embedded four- and eight-membered carbon rings, with tailored electronic properties.
- Meizhuang Liu
- , Mengxi Liu
- & Dingyong Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges
Electronic skins and health monitoring devices rely on integrated tactile sensors, which often require tailored degrees of sensitivity in specific pressure ranges. Here, the authors fabricate a versatile matrix array of pressure-sensitive graphene transistors operating in the wide 250 Pa to 3 MPa pressure range.
- Sung-Ho Shin
- , Sangyoon Ji
- & Jang-Ung Park
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
One-step fabrication of crystalline metal nanostructures by direct nanoimprinting below melting temperatures
Rapid fabrication of well-controlled metallic nanostructures remains a challenge. Here, the authors directly nanoimprint several different crystalline metals by superplastic forming well below their melting temperatures, obtaining uniform nanostructures with small features and high aspect ratios in one step.
- Ze Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic hot electron transport drives nano-localized chemistry
Plasmonic hot electron transport drives nano-localized chemistry
Quantitative understanding of the spatial localization of hot carriers has been elusive. Here Corteset al. spatially map hot-electron-driven reduction chemistry with 15 nm resolution as a function of time and electromagnetic field polarization for different plasmonic nanostructures.
- Emiliano Cortés
- , Wei Xie
- & Stefan A. Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Field-emission from quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Field-emission from quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Efficient implementation of quantum dot and well architectures are restricted to costly vacuum-epitaxially-grown semiconductors. The authors use quantum dots in perovskite to build field-emission photodiodes that are sensitive across the visible and into the short-wavelength infrared.
- F. Pelayo García de Arquer
- , Xiwen Gong
- & Edward Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access The fourth crystallographic closest packing unveiled in the gold nanocluster crystal
The fourth crystallographic closest packing unveiled in the gold nanocluster crystal
Metal nanoclusters are explored for their precise structures and compelling properties. Here, the authors synthesize a gold cluster with unique structural features, including giant staple motifs, tetrahedral-coordinateμ4-S atoms, and a helical closest-packed crystallographic pattern that influences the cluster’s photoluminescence.
- Zibao Gan
- , Jishi Chen
- & Zhikun Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Constructive quantum interference in a bis-copper six-porphyrin nanoring
Constructive quantum interference in a bis-copper six-porphyrin nanoring
Quantum interference in charge transport is attracting interest with applications in nanoelectronics and quantum computing. Here, the authors present a method for quantifying electronic transmission through molecules, and demonstrate constructive quantum interference in a molecule with two identical, parallel coupling paths.
- Sabine Richert
- , Jonathan Cremers
- & Christiane R. Timmel
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical on-surface synthesis and electronic structure of carbonyl-functionalized one- and two-dimensional covalent nanoarchitectures
Hierarchical on-surface synthesis and electronic structure of carbonyl-functionalized one- and two-dimensional covalent nanoarchitectures
On-surface synthesis is an excellent tool for the controlled synthesis of tailored nanomaterials. Here, the authors hierarchically synthesize covalent structures on Au(111) through Ullmann-type coupling of triphenylamines, forming macrocycles, 1D chains, and 2D networks, allowing them to study the effect of dimensionality on electronic band gap.
- Christian Steiner
- , Julian Gebhardt
- & Sabine Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Periodic potentials in hybrid van der Waals heterostructures formed by supramolecular lattices on graphene
Two-dimensional material heterostructures enable unique electronic features by introducing periodic potentials. Here, Gobbiet al. use a monolayer supramolecular lattice with a tunable one-dimensional periodic potential to modify the electronic structure of graphene.
- Marco Gobbi
- , Sara Bonacchi
- & Emanuele Orgiu
-
Article
| Open Access Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Although DNA nanopores are widely explored as synthetic membrane proteins, it is still unclear how the anionic DNA assemblies stably reside within the hydrophobic core of a lipid bilayer. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal the key dynamic interactions and energetics stabilizing the nanopore-membrane interaction.
- Vishal Maingi
- , Jonathan R. Burns
- & Mark S. P. Sansom
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of acoustic Dirac-like cone and double zero refractive index
Observation of acoustic Dirac-like cone and double zero refractive index
Impedance mismatch between acoustic metamaterials and a surrounding medium hinders efficient applications, especially for zero-index materials. Here, Duboiset al. utilize the Dirac-like dispersion in a double-zero-index material to overcome this problem and to collimate sound.
- Marc Dubois
- , Chengzhi Shi
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Polymeric mechanical amplifiers of immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis
Polymeric mechanical amplifiers of immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis
Fluid shear stress plays a critical role in receptor-mediated signalling and has been shown to sensitize cancer cells to apoptosis. Here, Mitchellet al. introduce polymer micro- and nanoparticles tethered to tumour cells to amplify fluid shear stress effects, and find that they can enhance immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis of tumour cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Michael J. Mitchell
- , Jamie Webster
- & Robert Langer
-
Article
| Open Access Optical imaging of localized chemical events using programmable diamond quantum nanosensors
Optical imaging of localized chemical events using programmable diamond quantum nanosensors
The use of nanoscale sensors capable of detection of biological parameters is of great interest in diagnosis. Here, the authors use experimental and theoretical methods to develop a nanodiamond sensor with nitrogen vacancy defects for detection of pH and redox in a microfluidic device.
- Torsten Rendler
- , Jitka Neburkova
- & Jörg Wrachtrup
-
Article
| Open Access The best features of diamond nanothread for nanofibre applications
The best features of diamond nanothread for nanofibre applications
Carbon fibres are emerging as a promising material for multifunctional nanotextiles. Here, the authors show that diamond nanothread possesses excellent torsional deformation capability and interfacial load transfer efficiency, ideal for constructing next generation carbon fibres.
- Haifei Zhan
- , Gang Zhang
- & Yuantong Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Gold nanostructures have shape-dependent properties, making synthetic control over their morphology critical. Here, the authors use dynamic compression to obtain a variety of gold nanoarchitectures, which are formed at very fast timescales by the controlled coalescence of spherical particle arrays.
- Binsong Li
- , Kaifu Bian
- & Hongyou Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Proteins can template the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles, but the formation mechanisms remain vague. Here, the authors directly observe, through a sequence of X-ray crystal structures, the stages of gold sub-nanocluster growth within the confined environment of a ferritin cage.
- Basudev Maity
- , Satoshi Abe
- & Takafumi Ueno
-
Article
| Open Access Proposal for dark exciton based chemical sensors
Proposal for dark exciton based chemical sensors
Two-dimensional materials have shown great promise as efficient chemical sensors. Here, the authors present a sensing mechanism to allow the detection of molecules based on dark excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides.
- Maja Feierabend
- , Gunnar Berghäuser
- & Ermin Malic
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable conversion of quasi-freestanding polymer chains to graphene nanoribbons
Controllable conversion of quasi-freestanding polymer chains to graphene nanoribbons
A key step in the on-surface synthesis of graphene nanoribbons is thermal annealing of polymer precursors on a metal substrate. Here, Maet al. decouple the cyclodehydrogenation reaction from the catalytic metal substrate and grow graphene nanoribbons by injecting charges at molecular sites.
- Chuanxu Ma
- , Zhongcan Xiao
- & An-Ping Li
-
Article
| Open Access Barcode extension for analysis and reconstruction of structures
Barcode extension for analysis and reconstruction of structures
Techniques for structural characterization and quantification of DNA origami are still poorly developed, despite advances in other aspects of DNA nanotechnology. Here, the authors combine barcoding and next generation sequencing to simultaneously image and quantify self-assembled DNA nanostructures.
- Cameron Myhrvold
- , Michael Baym
- & Peng Yin
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo gastrointestinal drug-release monitoring through second near-infrared window fluorescent bioimaging with orally delivered microcarriers
In vivo gastrointestinal drug-release monitoring through second near-infrared window fluorescent bioimaging with orally delivered microcarriers
The sustained release of drugs within the gastrointestinal tract as well as their detection following administration is a challenge. Here, the authors develop a microcarrier that supported sustained drug release in the gastrointestinal tractin vivoand could be monitored with real-time imaging.
- Rui Wang
- , Lei Zhou
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and assembly of scalable porous protein cages
Structure and assembly of scalable porous protein cages
Self-assembling proteins that form capsid-like structures act as molecular containers for diverse cargoes. Here, the authors solve the cryo-EM structures of lumazine synthase shells, and show that supercharged mutants form expanded assemblies, indicating that electrostatics can be exploited to engineer cage architecture.
- Eita Sasaki
- , Daniel Böhringer
- & Donald Hilvert
-
Article
| Open Access A molecule-like PtAu24(SC6H13)18 nanocluster as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen production
A molecule-like PtAu24(SC6H13)18 nanocluster as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen production
Volcano plots for electrocatalytic hydrogen production show the best catalysts as those ensuring the hydrogen binding step is thermodynamically neutral. Here, the authors report fabrication of a highly active thermoneutral electrocatalyst via doping of a single platinum atom into a gold nanocluster.
- Kyuju Kwak
- , Woojun Choi
- & Dongil Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Graphene nanoribbons are promising candidates for 2D material electrical interconnects; however, the top-down fabrication of nanoribbons has remained a challenge. Here, Chenet al. have used a hexagonal boron nitride template to grow narrow, integrated graphene nanoribbons with small bandgaps.
- Lingxiu Chen
- , Li He
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2 revealed by double-resonance Raman spectroscopy
Intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2 revealed by double-resonance Raman spectroscopy
Double-resonance Raman scattering is a sensitive spectroscopic probe of the interplay between electrons and phonons in a crystal. Here, the authors unveil the signature of double-resonance intervalley scattering by acoustic phonons in two-dimensional MoS2, underpinning the physics of valley depolarization.
- Bruno R. Carvalho
- , Yuanxi Wang
- & Marcos A. Pimenta
-
Article
| Open Access An electrically actuated molecular toggle switch
An electrically actuated molecular toggle switch
Robust molecular junctions demand highly reproducible switching between two or more well-defined conductance states upon control. Here, Gerhardet al. show the utility of elastic deformation of tripodal spirobifluorene derivatives in the junction of a scanning tunnelling microscope to achieve this goal.
- Lukas Gerhard
- , Kevin Edelmann
- & Wulf Wulfhekel
-
Article
| Open Access A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells
A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells
Synthetic DNA nanomachines have been designed to perform a variety of tasksin vitro. Here, the authors build a nanomotor system that integrates a DNAzyme and DNA track on a gold nanoparticle, to facilitate cellular uptake, and apply it as a real-time miRNA imaging tool in living cells.
- Hanyong Peng
- , Xing-Fang Li
- & X. Chris Le
-
Article
| Open Access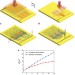 Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Losses of bandwidth are inevitable when interfacing between optical and electronic components. Here the authors present a switching device consisting of a two-dimensional disordered array of nanoholes that can potentially transfer information about 40 times faster than conventional switching devices.
- Wonjun Choi
- , Yonghyeon Jo
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access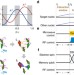 Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Single electrons of solid-state defects can be used to detect nearby nuclear spins, but so far only a few at a time have been resolved. Here the authors propose an approach based on delayed entanglement echo that demonstrates improved detection and manipulation capabilities of nuclear spins by an NV centre.
- Zhen-Yu Wang
- , Jorge Casanova
- & Martin B. Plenio
-
Article
| Open Access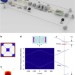 Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Optomechanical systems could form logic gates, but key requirements are two stable static states and the ability to switch between them. Here, the authors observe radiation-pressure induced buckling transitions in an optomechanical system, and control this transition by varying laser power and detuning.
- H. Xu
- , U. Kemiktarak
- & J. M. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Superconducting parity effect across the Anderson limit
Superconducting parity effect across the Anderson limit
How quantum size effects affect superconductivity has been predicted, but it has never been verified. Here, Vlaicet al. report superconducting parity effect as a function of lead nanocrystal volume, unambiguously validating the Anderson criterion.
- Sergio Vlaic
- , Stéphane Pons
- & Hervé Aubin
-
Article
| Open Access Transcending the slow bimolecular recombination in lead-halide perovskites for electroluminescence
Transcending the slow bimolecular recombination in lead-halide perovskites for electroluminescence
Slow bimolecular recombination in three-dimensional halide perovskites represents a fundamental limitation for electroluminescence efficiency. Using time-resolved spectroscopy Xinget al. demonstrate that this limitation can be overcome by employing van-der-Waals-coupled multiple quantum well structures.
- Guichuan Xing
- , Bo Wu
- & Wei Huang

 Holey two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets for efficient energy storage
Holey two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets for efficient energy storage