Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access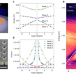 Exciton polariton condensation from bound states in the continuum at room temperature
Exciton polariton condensation from bound states in the continuum at room temperature
Bound states in continuum have attracted attention in various platforms, and recently condensation of bound states in continuum polariton modes was demonstrated at low temperatures. Here the authors report the observation of such a state in a periodic air-hole perovskite-based photonic crystal at room temperature.
- Xianxin Wu
- , Shuai Zhang
- & Xinfeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access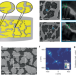 Ultrastrong exciton-plasmon couplings in WS2 multilayers synthesized with a random multi-singular metasurface at room temperature
Ultrastrong exciton-plasmon couplings in WS2 multilayers synthesized with a random multi-singular metasurface at room temperature
Here, the authors fabricate a metasurface with nanometre-sized plasmonic hotspots that interact coherently with WS2 excitons, achieving ultrastrong exciton-plasmon coupling.
- Tingting Wu
- , Chongwu Wang
- & Yu Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast photoluminescence and multiscale light amplification in nanoplasmonic cavity glass
Ultrafast photoluminescence and multiscale light amplification in nanoplasmonic cavity glass
This article presents a unique nanocomposite plasmonic-excitonic glass with extraordinary amplified optical properties: ultra-narrow photoluminescence (FWHM = 13 nm) and ultrashort photoluminescence lifetime (90 ps) at room temperature
- Piotr Piotrowski
- , Marta Buza
- & Dorota A. Pawlak
-
Article
| Open Access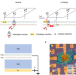 Correlation-driven nonequilibrium exciton site transition in a WSe2/WS2 moiré supercell
Correlation-driven nonequilibrium exciton site transition in a WSe2/WS2 moiré supercell
Correlated insulator states of moire excitons in transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures have attracted significant attention recently. Here the authors use time-resolved pump-probe spectroscopy to demonstrate the effects of non-equilibrium correlations of moire excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterobilayers.
- Jinjae Kim
- , Jiwon Park
- & Hyunyong Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable optoelectronic transistors for multimodal recognition
Reconfigurable optoelectronic transistors for multimodal recognition
Reconfigurable neuromorphic transistors are important for creating compact and efficient neuromorphic computing networks. Here, Li et al. introduce an optoelectronic electrolyte-gated transistor to perform multimodal recognition.
- Pengzhan Li
- , Mingzhen Zhang
- & Chen Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping
Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping
Research into the control of conformational arrangements is of great importance for achieving bespoke nanoarchitectures. Here, the authors achieve topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor by Se doping.
- Liangliang Cai
- , Tianhao Gao
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article
| Open Access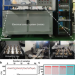 Continuous and low-carbon production of biomass flash graphene
Continuous and low-carbon production of biomass flash graphene
It is challenging to produce biomass FG continuously due to the lack of an integrated device. Here, we create an integrated automatic system with energy requirement-oriented allocation to achieve continuous biomass FG production with a much lower carbon footprint.
- Xiangdong Zhu
- , Litao Lin
- & Yong-Guan Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access All-silicon multidimensionally-encoded optical physical unclonable functions for integrated circuit anti-counterfeiting
All-silicon multidimensionally-encoded optical physical unclonable functions for integrated circuit anti-counterfeiting
The researchers introduce an all-silicon optical PUF that enhances IoT device security through CMOS-compatible fabrication, showcasing five unique optical responses per pixel for advanced authentication and high information entropy.
- Kun Wang
- , Jianwei Shi
- & Deren Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Double-walled Al-based MOF with large microporous specific surface area for trace benzene adsorption
Double-walled Al-based MOF with large microporous specific surface area for trace benzene adsorption
Trace benzene poses a risk to the health and safety of humans, resulting in a challenging task. Here authors synthesise double-walled Al-based MOF ZJU-520(Al) with trace benzene adsorption (5.98 mmol g–1) and excellent benzene/cyclohexane separation ability.
- Laigang Hu
- , Wenhao Wu
- & Kun Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-induced ordering evolution of 1D segmented heteronanostructures and their chemical post-transformations
Stress-induced ordering evolution of 1D segmented heteronanostructures and their chemical post-transformations
The formation mechanisms for periodic heterostructures are still poorly understood. Here, the authors propose a versatile approach to synthesize one-dimensional segmented heterostructures and reveal a stress-induced ordering mechanism through phase-field simulations.
- Qing-Xia Chen
- , Yu-Yang Lu
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Growth of millimeter-sized 2D metal iodide crystals induced by ion-specific preference at water-air interfaces
Growth of millimeter-sized 2D metal iodide crystals induced by ion-specific preference at water-air interfaces
Here, the authors report the growth of millimetre-scale 2D PbI2 single crystals via the spontaneous accumulation and in-plane arrangement of iodide ions at the water-air interface. The metal iodide crystals could be thinned down to a single monolayer via water etching, and subsequently converted into perovskite optoelectronic devices.
- Jingxian Zhong
- , Dawei Zhou
- & Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-free selective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics to azoxy compounds over Co single atoms decorated on Nb2O5 nanomeshes
Solvent-free selective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics to azoxy compounds over Co single atoms decorated on Nb2O5 nanomeshes
Single atom catalysts can endow exceptional activity and selectively. Here, the authors report a single atom Co catalyst and reveal the importance of geometric and electronic properties for synthesizing azoxy compounds under solvent-free conditions.
- Zhijun Li
- , Xiaowen Lu
- & Yu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional lead halide perovskite lateral homojunctions enabled by phase pinning
Two-dimensional lead halide perovskite lateral homojunctions enabled by phase pinning
Hong et al. report 2D perovskite lateral homojunction consists of ordered and disordered phases, achieved by organic cation doping induced phase pinning, built upon which they develop tuneable optical properties under external stimuli and directional exciton diffusion in the homojunctions.
- Huilong Hong
- , Songhao Guo
- & Yongping Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature quantum emission from interface excitons in mixed-dimensional heterostructures
Room-temperature quantum emission from interface excitons in mixed-dimensional heterostructures
Interlayer excitons in 2D homo- and heterostructures have been intensively investigated due to their emerging optical properties. Here, the authors report the observation of interface excitons in 1D/2D carbon nanotube/WSe2 heterostructures, showing evidence of photon antibunching at room temperature.
- N. Fang
- , Y. R. Chang
- & Y. K. Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Multilevel design and construction in nanomembrane rolling for three-dimensional angle-sensitive photodetection
Multilevel design and construction in nanomembrane rolling for three-dimensional angle-sensitive photodetection
Zhang et al. report a quasistatic multilevel finite element model to predict the 3D structures assembled by 2D nanomembranes, validated by large-scale, high-yield, and configurable fabrication. 3D Si/Cr photodetectors assisted by neural network are employed to resolve the incident light angle.
- Ziyu Zhang
- , Binmin Wu
- & Yongfeng Mei
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetically controlled metal-elastomer nanophases for environmentally resilient stretchable electronics
Kinetically controlled metal-elastomer nanophases for environmentally resilient stretchable electronics
Metal-elastomer nanophases are critical for stretchable electronics but face mixing challenges. This study introduces a kinetic method for precise mixing, yielding gyrified nanophases with improved durability and strain-invariant conductivity, which holds promise for resilient stretchable devices.
- Soosang Chae
- , Won Jin Choi
- & Tae Il Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of DNA origami folding elucidated by mesoscopic simulations
Mechanism of DNA origami folding elucidated by mesoscopic simulations
The self-assembly process of DNA nanostructures is still not well understood, especially for DNA origami. Here, the authors present a mesoscopic model that uses a switchable force field to capture the mechanical behavior of single- and double-stranded DNA motifs and transition between them, allowing access to the long assembly timescales of DNA origami up to several kilobases in size.
- Marcello DeLuca
- , Daniel Duke
- & Gaurav Arya
-
Article
| Open Access Water-assisted oxidative redispersion of Cu particles through formation of Cu hydroxide at room temperature
Water-assisted oxidative redispersion of Cu particles through formation of Cu hydroxide at room temperature
Redispersion of sintered metal species requires high temperatures in reactive atmospheres. Here, the authors report room temperature redispersion of supported Cu particles via formation of mobile hydroxylated Cu species induced by gaseous H2O and anchoring of the Cu species by surface OH groups.
- Yamei Fan
- , Rongtan Li
- & Qiang Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Essential role of lattice oxygen in hydrogen sensing reaction
Essential role of lattice oxygen in hydrogen sensing reaction
Understanding the sensing mechanism of metal oxide semiconductors is imperative for developing high-performance sensors. Here, the participation of lattice oxygen, caused by additional Ge, boosts the hydrogen sensing ability of SnO2.
- Jiayu Li
- , Wenzhe Si
- & Guo-Dong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport at KTaO3-based interfaces
Light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport at KTaO3-based interfaces
Optical control is an alternative pathway to boost nonlinear transport in noncentrosymmetric systems. Here, the authors observe a light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport coefficient as high as 105 A−1 T−1 at KTaO3-based Rashba interfaces.
- Xu Zhang
- , Tongshuai Zhu
- & Xuefeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access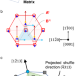 In situ observation of the atomic shuffles during the {\({{11}}\bar{{{2}}}{{1}}\)} twinning in hexagonal close-packed rhenium
In situ observation of the atomic shuffles during the {\({{11}}\bar{{{2}}}{{1}}\)} twinning in hexagonal close-packed rhenium
Atomic shuffles are important phenomena accompanying the twinning in hexagonal close-packed crystals, but the direct experimental observation on it is lacking. Here, the authors show the shuffling mechanism of {112 ̅1} twinning in rhenium nanocrystals by in situ transmission electron microscopy.
- Yang He
- , Zhengwu Fang
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Kekulé vortices in hexagonal lattices can host fractionalized charges at zero magnetic field, but have remained out of experimental reach. Here, the authors report a Kekulé vortex in the local density states of graphene around a chemisorbed hydrogen adatom.
- Yifei Guan
- , Clement Dutreix
- & Vincent T. Renard
-
Article
| Open Access Low thermal contact resistance boron nitride nanosheets composites enabled by interfacial arc-like phonon bridge
Low thermal contact resistance boron nitride nanosheets composites enabled by interfacial arc-like phonon bridge
Boron nitride nanosheets possess high in-plane thermal conductivity and high thermal contact resistance. Here the authors discover obliquely aligned nanosheets at the interface can act as a phonon bridge to lower the contact resistance.
- Ke Zhan
- , Yucong Chen
- & Ling Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
Carbaporphyrin dimers, known for their interesting photophysical properties and application in metal-organic chemistry, generally contain two identical subunits. Here, the authors highlight the benefits that can accrue from breaking the inherent symmetry of carbaporphyrin dimers and details a new approach to creating heterobimetallic complexes.
- Haodan He
- , Jiyeon Lee
- & Xian-Sheng Ke
-
Article
| Open Access Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Precise and scalable patterning is essential for the use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in solid-state electronics and photonics. Here, the authors report on resistance-free, direct photo- and electron-beam lithography of MOF films using crosslinking chemistry.
- Xiaoli Tian
- , Fu Li
- & Jinghong Li
-
Article
| Open Access The formation of unsaturated IrOx in SrIrO3 by cobalt-doping for acidic oxygen evolution reaction
The formation of unsaturated IrOx in SrIrO3 by cobalt-doping for acidic oxygen evolution reaction
SrIrO3-based catalyst is a promising candidate for acidic oxygen evolution reaction (OER), but the active sites and factors responsible for its effectiveness remain ambiguous. Here, the authors reveal that dynamic dissolution of Co in Co-SrIrO3 leads to the formation of unsaturated IrOx, enabling high-efficiency OER.
- Jia-Wei Zhao
- , Kaihang Yue
- & Gao-Ren Li
-
Article
| Open Access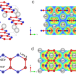 Extending carbon chemistry at high-pressure by synthesis of CaC2 and Ca3C7 with deprotonated polyacene- and para-poly(indenoindene)-like nanoribbons
Extending carbon chemistry at high-pressure by synthesis of CaC2 and Ca3C7 with deprotonated polyacene- and para-poly(indenoindene)-like nanoribbons
The authors demonstrate that carbides with infinite chains of fused [C6] and [C5] rings are synthesized at deep planetary pressures and temperatures. Hydrolysis of these carbides may lead to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Universe.
- Saiana Khandarkhaeva
- , Timofey Fedotenko
- & Leonid Dubrovinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Large area single crystal gold of single nanometer thickness for nanophotonics
Large area single crystal gold of single nanometer thickness for nanophotonics
2D metallic single crystals are sought after for nanophotonic applications, but their synthesis remains challenging. Here, the authors report an atomic level precision etching method to fabricate large-area crystalline gold flakes with nanometre thickness, showing enhanced plasmonic and nonlinear optical properties.
- Chenxinyu Pan
- , Yuanbiao Tong
- & Pan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access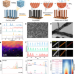 Defect-induced triple synergistic modulation in copper for superior electrochemical ammonia production across broad nitrate concentrations
Defect-induced triple synergistic modulation in copper for superior electrochemical ammonia production across broad nitrate concentrations
Converting nitrate to ammonia in wastewater with a wide range of nitrate concentrations remains a challenging task. Here the authors report defect-rich Cu nanowire electrocatalyst which can achieve 50 to 1100 mA cm−2 and over 90% Faradaic efficiency using 1–100 mM nitrate wastewater.
- Bocheng Zhang
- , Zechuan Dai
- & Genqiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access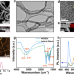 Tailoring coordination environments of single-atom electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution by topological heteroatom transfer
Tailoring coordination environments of single-atom electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution by topological heteroatom transfer
The rational design of carbon-supported transition metal single atom catalysts with precise coordination tailoring remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a topological heteroatom-transfer strategy to precisely control the P coordination in Co single atoms for hydrogen evolution.
- Sheng Qian
- , Feng Xu
- & Jingqi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Machine-learning-assisted and real-time-feedback-controlled growth of InAs/GaAs quantum dots
Machine-learning-assisted and real-time-feedback-controlled growth of InAs/GaAs quantum dots
Finding the process parameters in molecular beam epitaxy for a specific density of quantum dots is a multidimensional optimization challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time feedback controlled self-assembled InAs/GaAs QDs growth based on machine learning (ML) outputs.
- Chao Shen
- , Wenkang Zhan
- & Zhanguo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Charge state-dependent symmetry breaking of atomic defects in transition metal dichalcogenides
Charge state-dependent symmetry breaking of atomic defects in transition metal dichalcogenides
The microscopic structure of quantum defects in 2D materials is crucial to understand their optical properties and spin-photon interface. Here, the authors report the direct imaging of charge state-dependent symmetry breaking of sulfur vacancies and rhenium dopants in 2D MoS2, showing evidence of a Jahn-Teller effect.
- Feifei Xiang
- , Lysander Huberich
- & Bruno Schuler
-
Article
| Open Access Significant enhancement of proton conductivity in solid acid at the monolayer limit
Significant enhancement of proton conductivity in solid acid at the monolayer limit
High performance proton conductor is highly desired for energy application. Here authors report an increase in the number of active protons in solid acid at the monolayer limit, enabling membranes with proton conductivity 5 times higher than that of Nafion.
- Zhangcai Zhang
- , Lixin Liang
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous anti-Kasha excited-state luminescence from symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops
Anomalous anti-Kasha excited-state luminescence from symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops
It is a long-standing scientific controversy to achieve anti-Kasha emissions by tuning structures at a molecular level. Herein, the authors constructed two symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops with unusual anti-Kasha characteristics.
- Xinyu Zhang
- , Cheng Chen
- & Pingwu Du
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of naturally canalized phonon polaritons in LiV2O5 thin layers
Observation of naturally canalized phonon polaritons in LiV2O5 thin layers
Canalized polaritons are light-matter excitations characterized by intrinsic collimation of electromagnetic energy along a specific crystal axis. Here, the authors report the observation of intrinsically canalized phonon polaritons in a single thin layer of a van der Waals crystal, LiV2O5.
- Ana I. F. Tresguerres-Mata
- , Christian Lanza
- & Pablo Alonso-González
-
Article
| Open Access Electricity generation from carbon dioxide adsorption by spatially nanoconfined ion separation
Electricity generation from carbon dioxide adsorption by spatially nanoconfined ion separation
Nanogenerators have promising applications in energy and environment-related fields. Here, the authors developed Nanosheet-Agarose Hydrogel generators to enable near-perfect anion/cation separation, leading to simultaneously CO2 adsorption and energy generation.
- Zhuyuan Wang
- , Ting Hu
- & Xiwang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of sextuple polarization states and interstate switching in antiferroelectric CuInP2S6
Realization of sextuple polarization states and interstate switching in antiferroelectric CuInP2S6
Materials with higher-order multistates are desired for non-Boolean high-density storage. Here the authors realized sextuple intrinsic polarization states in vdW CuInP2S6, and reversible transformation among sextuple-, quadruple-, and double-polarization orders.
- Tao Li
- , Yongyi Wu
- & Tai Min
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Efficient heat dissipation is critical to optimize high-power devices. Here, the authors report high interfacial thermal conductance in GaN-BAs heterostructures and investigate the competition between grain size and boundary resistance by multiscale simulations.
- Jing Wu
- , E Zhou
- & Guangzhao Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Velocities of transmission eigenchannels and diffusion
Velocities of transmission eigenchannels and diffusion
Wave scattering can be described with a diffusion model in which the velocity is randomized by scattering. Here the authors find that the velocities of different transmission eigenchannels are distinct on all length scales.
- Azriel Z. Genack
- , Yiming Huang
- & Zhou Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Layer-polarized ferromagnetism in rhombohedral multilayer graphene
Layer-polarized ferromagnetism in rhombohedral multilayer graphene
Rhombohedral multilayer graphene has emerged as an exciting solid-state platform for studying correlated electron physics. Here, the authors demonstrate field-tunable layer-polarized ferromagnetism and isolated surface flat bands engineered with a moiré potential.
- Wenqiang Zhou
- , Jing Ding
- & Shuigang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Forward-predictive SERS-based chemical taxonomy for untargeted structural elucidation of epimeric cerebrosides
Forward-predictive SERS-based chemical taxonomy for untargeted structural elucidation of epimeric cerebrosides
SERS-based chemical taxonomy is attractive for practical SERS applications where the identity and concentration of analytes are unknown. Here, the authors demonstrate a machine learning framework for classifying “unknown” molecules that lie outside the boundaries of the models used.
- Emily Xi Tan
- , Shi Xuan Leong
- & Xing Yi Ling
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
The authors report an in situ investigation of interfacial hydrogen spillover in Pd/ZIF-8 structures with X-ray and Raman techniques. A mechanistic picture of how Pd/ZIF-8 catalyst mediate alkyne semihydrogenation to alkynes is described.
- Qiaoxi Liu
- , Wenjie Xu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
The controllability of deformation height in reconfigurable touch displays currently limits their deliverable information. Hwang et al. present a light-triggered morphable tactile display enabling generation of refreshable, height-adjustable, and latchable 3D topologies with varying textures on a thin film surface.
- Inwook Hwang
- , Seongcheol Mun
- & Sungryul Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visualization of stacking-selective self-intercalation in epitaxial Nb1+xSe2 films
Direct visualization of stacking-selective self-intercalation in epitaxial Nb1+xSe2 films
The interplay between stacking configurations and atom intercalation in van der Waals materials has been rarely characterized at the microscopic level. Here, the authors report an electron microscopy study of stacking-selective self-intercalation in Nb1+xSe2 films, showing potential for nanoscale engineering of electronic properties in van der Waals materials and devices.
- Hongguang Wang
- , Jiawei Zhang
- & Hidenori Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast all-optical second harmonic wavefront shaping
Ultrafast all-optical second harmonic wavefront shaping
Enhancing the data encoding into the orbital angular momentum of light beams could enable faster and more efficient optical communications. This work demonstrates complex control of the second harmonic wavefront with dynamics solely limited by the pulse duration.
- Artem Sinelnik
- , Shiu Hei Lam
- & Isabelle Staude
-
Article
| Open Access High performance artificial visual perception and recognition with a plasmon-enhanced 2D material neural network
High performance artificial visual perception and recognition with a plasmon-enhanced 2D material neural network
Here, the authors demonstrate a low-power neuromorphic visual architecture based on a plasmon-enhanced 2D semiconductor phototransistor array, showing high-speed sensing, preprocessing and image recognition functionalities.
- Tian Zhang
- , Xin Guo
- & Linjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
2D materials are being investigated for several applications in micro- and nanoelectronics, but their weak adhesion represents a critical challenge for device integration. Here, the authors propose a button shear testing method to evaluate the adhesion forces of various large-area 2D films on SiO2 and Si3N4 substrates.
- Josef Schätz
- , Navin Nayi
- & Max C. Lemme
-
Article
| Open Access Well-defined diatomic catalysis for photosynthesis of C2H4 from CO2
Well-defined diatomic catalysis for photosynthesis of C2H4 from CO2
Principal interest lies in diatomic catalysts (DACs) for efficient CO2 to C2H4 photoconversion yet optimizing catalytic performance and exploring reaction mechanisms are impeded by heteronuclear atom random distribution. Here, a novel up-bottom ion-cutting architecture is proposed for fabricating well-defined DACs.
- Zhongkai Xie
- , Shengjie Xu
- & Shuyan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Broadened quantum critical ground state in a disordered superconducting thin film
Broadened quantum critical ground state in a disordered superconducting thin film
The authors present Nernst measurements on a 2D film of amorphous MoxGe1−x, which shows a magnetic-field-induced superconductor-metal-insulator transition. The intermediate metal phase is known as the “anomalous metal” (AM) state. The authors conclude that the AM state originates from broadening of the superconductor-insulator transition.
- Koichiro Ienaga
- , Yutaka Tamoto
- & Satoshi Okuma
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Carbon nanotubes and fullerenes
- Electronic properties and materials
- Graphene
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Metamaterials
- Molecular machines and motors
- Molecular self-assembly
- Nanoparticles
- Nanowires
- Organic–inorganic nanostructures
- Quantum dots
- Structural properties
- Synthesis and processing
- Two-dimensional materials

 Mechanoelectronic stimulation of autologous extracellular vesicle biosynthesis implant for gut microbiota modulation
Mechanoelectronic stimulation of autologous extracellular vesicle biosynthesis implant for gut microbiota modulation