Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access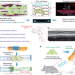 A biodegradable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold for advanced stem cell therapy
A biodegradable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold for advanced stem cell therapy
The promise of stem cell therapy for treating central nervous system disease is limited by low stem cell transplantation survival rates and poorly controlled cell fate. Here, the authors develop a biodegradable nanoscaffold for spinal cord injury that enhances transplantation and differentiation of neural stem cells and delivers drugs.
- Letao Yang
- , Sy-Tsong Dean Chueng
- & Ki-Bum Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-photosensitizer based on layered double hydroxide and isophthalic acid for singlet oxygenation and photodynamic therapy
Nano-photosensitizer based on layered double hydroxide and isophthalic acid for singlet oxygenation and photodynamic therapy
Usually, several components are needed for efficient 2-photon photodynamic therapy (PDT). Here, the authors sandwiched carboxylic acids between layered double hydroxide nanosheets to obtain a single-handed biocompatible photosensitizer that generates singlet oxygen in high quantum yield.
- Rui Gao
- , Xuan Mei
- & Min Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Red blood cell-hitchhiking boosts delivery of nanocarriers to chosen organs by orders of magnitude
Red blood cell-hitchhiking boosts delivery of nanocarriers to chosen organs by orders of magnitude
Unwanted uptake in the liver and limited accumulation in target organs is a major obstacle to targeted drug delivery. Here, the authors report on the hitchhiking of nanocarriers on red blood cells and the targeted upstream delivery to different target organs in mice, pigs and ex vivo human lungs.
- Jacob S. Brenner
- , Daniel C. Pan
- & Vladimir Muzykantov
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic and low adverse effect cancer immunotherapy by immunogenic chemotherapy and locally expressed PD-L1 trap
Synergistic and low adverse effect cancer immunotherapy by immunogenic chemotherapy and locally expressed PD-L1 trap
Microsatellite-stable (MSS) colorectal cancer (CRC) has shown poor response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Here, the authors show that the combination of oxaliplatin with anti-PDL1 mAb is specifically efficient in the treatment of MSS CRC.
- Wantong Song
- , Limei Shen
- & Leaf Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen and Pt(II) self-generating conjugate for synergistic photo-chemo therapy of hypoxic tumor
Oxygen and Pt(II) self-generating conjugate for synergistic photo-chemo therapy of hypoxic tumor
Photodynamic therapy has attracted interest in treating cancer but it is limited in hypoxic tumors due to a lack of oxygen. Here, the authors describe a nano-composite capable of generating oxygen under near-infrared light for improved photodynamic and chemotherapy for treating cancer.
- Shuting Xu
- , Xinyuan Zhu
- & Deyue Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Immunogene therapy with fusogenic nanoparticles modulates macrophage response to Staphylococcus aureus
Immunogene therapy with fusogenic nanoparticles modulates macrophage response to Staphylococcus aureus
In the context of increasing bacterial antibiotic-resistance, gene therapy that targets the immune system to clear infection is a major goal. Here the authors show a silicon based nanosystem that modulates the macrophage response in an in vivo model of Staphylococcal pneumonia.
- Byungji Kim
- , Hong-Bo Pang
- & Michael J. Sailor
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible glycosidic switch for secure delivery of molecular nanocargos
Reversible glycosidic switch for secure delivery of molecular nanocargos
Retention of drugs loaded into liposomes is a major challenge to effective targeted drug delivery. Here, the authors report on the modification of drugs with a glycosidic pH sensitive switch to improve encapsulation and retention of drugs and demonstrate application in an in vivo cancer model.
- Pierre-Alain Burnouf
- , Yu-Lin Leu
- & Steve R. Roffler
-
Article
| Open Access A self-destructive nanosweeper that captures and clears amyloid β-peptides
A self-destructive nanosweeper that captures and clears amyloid β-peptides
Cerebral amyloid β-peptide accumulation is a causative factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Here the authors design a 'nanosweeper' that binds amyloid β-peptide and induces autophagy to clear the accumulated plagues.
- Qiang Luo
- , Yao-Xin Lin
- & Hao Wang
-
Review Article
| Open Access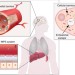 Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics
Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics
Targeted delivery strategies based on nanocarriers have immense potential to change cancer care but current strategies have been shown only limited translation in the clinic. Here, the authors survey the challenge, progress and opportunities towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics.
- Daniel Rosenblum
- , Nitin Joshi
- & Dan Peer
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy
In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy
If decorated with the right surface modifications, nanoparticles can function as Trojan horses, transporting cell death-facilitating compounds to tumor cells. Here, the authors prepare a particle with four enzyme-like activities and show that ferritin can direct nanoparticles to tumor cells.
- Kelong Fan
- , Juqun Xi
- & Lizeng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-photothermal therapy combination elicits anti-tumor immunity against advanced metastatic cancer
Chemo-photothermal therapy combination elicits anti-tumor immunity against advanced metastatic cancer
Photothermal therapy (PTT) for cancer treatment is currently limited to local, accessible, tumors. Here the authors show that PTT combination with chemotherapy, by stimulating an immune response, is effective against distant tumors and establishes immune memory, thus providing a strategy to target metastatic disease.
- Jutaek Nam
- , Sejin Son
- & James J. Moon
-
Article
| Open Access Polyrotaxane-based supramolecular theranostics
Polyrotaxane-based supramolecular theranostics
Multifunctional nanomedicine platforms are highly promising for anticancer therapy. Here, the authors design polyrotaxane-based theranostic nanoparticles that combine targeted drug delivery with photothermal behaviour to exhibit potent anti-tumour effects in vivo.
- Guocan Yu
- , Zhen Yang
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular aptamer nano-constructs for receptor-mediated targeting and light-triggered release of chemotherapeutics into cancer cells
Supramolecular aptamer nano-constructs for receptor-mediated targeting and light-triggered release of chemotherapeutics into cancer cells
Effective therapeutic platforms should combine serum stability, selective targeting, and controlled drug release. Here, the authors self-assemble an aptamer-based nanoscaffold that contains separate cell-targeting and photo-regulated drug-carrying domains, realizing multiple therapeutic functionalities in a single construct.
- Deepak K. Prusty
- , Volker Adam
- & Michael Famulok
-
Article
| Open Access Long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicines for malaria prophylaxis
Long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicines for malaria prophylaxis
Long-acting antimalarials could provide improved prophylaxis and treatment options in the field. Here, Bakshi et al. develop a long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicine that prevents malaria infection prophylactically for up to 4 weeks in mice with no evidence for generation of resistant parasites.
- Rahul P. Bakshi
- , Lee M. Tatham
- & Theresa A. Shapiro
-
Article
| Open Access Radionuclides transform chemotherapeutics into phototherapeutics for precise treatment of disseminated cancer
Radionuclides transform chemotherapeutics into phototherapeutics for precise treatment of disseminated cancer
Most of the systemic cancer therapies lack spatiotemporal control. Here, the authors show targeted activation of a light-sensitive drug by radiopharmaceuticals in disseminated cancer cells as potential in vivo treatment of metastatic diseases with reduced off-target toxicity.
- Nalinikanth Kotagiri
- , Matthew L. Cooper
- & Samuel Achilefu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle elasticity directs tumor uptake
Nanoparticle elasticity directs tumor uptake
Nanoparticle elasticity is thought to play an important role in drug delivery, but is little studied. Here, the authors use nanolipogels with tunable moduli to study the effect of particle elasticity on in vitro cellular uptake and in vivo tumor uptake, finding that stiffer particles are not as easily internalized.
- Peng Guo
- , Daxing Liu
- & Marsha A. Moses
-
Article
| Open Access Directed self-assembly of fluorescence responsive nanoparticles and their use for real-time surface and cellular imaging
Directed self-assembly of fluorescence responsive nanoparticles and their use for real-time surface and cellular imaging
Polymer nanoparticles that have an in-built capacity to elicit an output during drug delivery are highly desirable. Here the authors describe the self-assembly of an amphiphilic tri-block co-polymer that shows particle fluorescence in response to temperature, surface adsorption and cellular uptake.
- Shane Cheung
- & Donal F. O’Shea
-
Article
| Open Access Microneedle-array patches loaded with dual mineralized protein/peptide particles for type 2 diabetes therapy
Microneedle-array patches loaded with dual mineralized protein/peptide particles for type 2 diabetes therapy
Diabetes treatments often rely on frequent and scheduled drug administration, which reduces patient compliance and increases treatment cost. Here, the authors develop a microneedle-array patch that separately loads drug-releasing module and glucose-sensing element for on-demand, long-term diabetes therapy.
- Wei Chen
- , Rui Tian
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access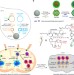 Intertwining DNA-RNA nanocapsules loaded with tumor neoantigens as synergistic nanovaccines for cancer immunotherapy
Intertwining DNA-RNA nanocapsules loaded with tumor neoantigens as synergistic nanovaccines for cancer immunotherapy
Nucleic acid nanomedicines are promising for cancer drug delivery. Here, the authors show using a mouse model the tumor immunotherapeutic efficacy of nanovaccines based on intertwining DNA-RNA nanocapsules loaded with DNA CpG, Stat3-silencing short hairpin RNA and tumor-specific peptide neoantigens.
- Guizhi Zhu
- , Lei Mei
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the bioactivity of a peptide hormone in vivo by reversible self-assembly
Controlling the bioactivity of a peptide hormone in vivo by reversible self-assembly
The clinical potential of peptide therapeutic agents can only be fully realised once their physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties are precisely controlled. Here the authors show a reversible peptide self-assembly strategy to control and prolong the bioactivity of a native peptide hormone in vivo.
- Myriam M. Ouberai
- , Ana L. Gomes Dos Santos
- & Mark E. Welland
-
Article
| Open Access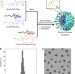 Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier crossing the BBB into the brain
Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier crossing the BBB into the brain
There are only a few examples of nanocarriers that can transport bioactive substances across the blood-brain barrier. Here the authors show that by rapid glycaemic increase the accumulation of a glucosylated nanocarrier in the brain can be controlled.
- Y. Anraku
- , H. Kuwahara
- & K. Kataoka
-
Article
| Open Access Hollow MnO2 as a tumor-microenvironment-responsive biodegradable nano-platform for combination therapy favoring antitumor immune responses
Hollow MnO2 as a tumor-microenvironment-responsive biodegradable nano-platform for combination therapy favoring antitumor immune responses
MnO2 nanostructures are promising TME-responsive theranostic agents in cancer. Here, the authors develop a nano-platform based on hollow H-MnO2 nanoshells able to modulate the tissue microenvironment, release a drug and inhibit tumor growth alone or in combination with check-point blockade therapy.
- Guangbao Yang
- , Ligeng Xu
- & Zhuang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic understanding of in vivo protein corona formation on polymeric nanoparticles and impact on pharmacokinetics
Mechanistic understanding of in vivo protein corona formation on polymeric nanoparticles and impact on pharmacokinetics
Understanding the interaction between nanoparticles and biomolecules is crucial for improving current drug-delivery systems. Here, the authors shed light on the essential role of the surface and other physicochemical properties of a library of nanoparticles on their in vivo pharmacokinetics.
- Nicolas Bertrand
- , Philippe Grenier
- & Omid C. Farokhzad
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-degradable highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles for bio-medical imaging applications
Bio-degradable highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles for bio-medical imaging applications
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals, but cannot readily be excreted through the renal system. Here the authors show fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units that can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages.
- Tatjana Repenko
- , Anne Rix
- & Alexander J. C. Kuehne
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-palladium is a cellular catalyst for in vivo chemistry
Nano-palladium is a cellular catalyst for in vivo chemistry
Palladium (Pd) is a well-known catalyst in organic chemistry but its use in nanomedicine is limited. Here, the authors design a Pd nanoparticle that triggers the activation of an antitumour prodrugin vivo, which shows efficacy and improves toxicity compared to traditional solvent- and nanoparticle-drug formulations.
- Miles A. Miller
- , Bjorn Askevold
- & Ralph Weissleder
-
Article
| Open Access In situ targeted MRI detection of Helicobacter pylori with stable magnetic graphitic nanocapsules
In situ targeted MRI detection of Helicobacter pylori with stable magnetic graphitic nanocapsules
The effective detection ofHelicobacter pylori has been a challenge clinically. Here, the authors demonstrate the potential of magnetic nanoparticles for non-invasive diagnosis of H. pylori using magnetic resonance imaging in vivo.
- Yunjie Li
- , Xiaoxiao Hu
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven liquid metal nanotransformers for biomedical theranostics
Light-driven liquid metal nanotransformers for biomedical theranostics
Liquid metals are excellent candidate materials for biomedicine, owing to their intriguing optical properties and chemical stability. Here, the authors design multifunctional theranostic liquid metal nanocapsules that, upon irradiation, generate heat and reactive oxygen species and change shape to release drugs.
- Svetlana A. Chechetka
- , Yue Yu
- & Eijiro Miyako
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial local magnetic field inhomogeneity enhances T2 relaxivity
Artificial local magnetic field inhomogeneity enhances T2 relaxivity
The signal detected in magnetic resonance imaging comes from the relaxation of proton nuclear magnetization. Here, Zhouet al. introduce magnetic field inhomogeneity as a parameter to design iron oxide nanoparticle clusters to enhance the relaxation rate of nearby protons, thereby increasing image contrast.
- Zijian Zhou
- , Rui Tian
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Water can function as a sustainable reactor for the synthesis of size-controlled, functional nanoparticles. Here, the authors introduce an underwater Leidenfrost synthesis that reproduces the dynamic chemistry of the deep ocean, in which anticancer therapeutic ZnO2nanoclusters form in an overheated zone and migrate to colder water to continue growth.
- Mady Elbahri
- , Ramzy Abdelaziz
- & Moheb Abdelaziz
-
Article
| Open Access Lipoprotein-biomimetic nanostructure enables efficient targeting delivery of siRNA to Ras-activated glioblastoma cells via macropinocytosis
Lipoprotein-biomimetic nanostructure enables efficient targeting delivery of siRNA to Ras-activated glioblastoma cells via macropinocytosis
Drug delivery in brain tumours is still a significant clinical concern. In this study, the authors develop a biomimetic lipoprotein nanoparticle for the efficient delivery of ATF5 siRNA inRas-activated brain cancer cells, where the nanoparticle is internalized by macropinocytosis in a Ras-dependent manner.
- Jia-Lin Huang
- , Gan Jiang
- & Xiao-Ling Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Nerve growth factor (NGF) contributes to the sustained growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Here, the authors develop a gold nanocluster-coupled siRNA against NGF that efficiently silences theNGFgene and inhibits tumour growth of pancreatic cancer in mice.
- Yifeng Lei
- , Lixue Tang
- & Xingyu Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Polymeric mechanical amplifiers of immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis
Polymeric mechanical amplifiers of immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis
Fluid shear stress plays a critical role in receptor-mediated signalling and has been shown to sensitize cancer cells to apoptosis. Here, Mitchellet al. introduce polymer micro- and nanoparticles tethered to tumour cells to amplify fluid shear stress effects, and find that they can enhance immune cytokine-mediated apoptosis of tumour cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Michael J. Mitchell
- , Jamie Webster
- & Robert Langer
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Nanomedicine efficacy in a clinical setting depends on the pharmacological properties of the therapeutic nanoparticles. Here, the authors exemplify an accelerated translational strategy from small-scale screening to clinical scale-up for an orally-dosed aqueous paediatric HIV nanomedicine.
- Marco Giardiello
- , Neill J. Liptrott
- & Andrew Owen
-
Article
| Open Access A centrifugation-based physicochemical characterization method for the interaction between proteins and nanoparticles
A centrifugation-based physicochemical characterization method for the interaction between proteins and nanoparticles
Thein vivobehaviour of nanoparticles is influenced by the presence of the protein corona. Here, the authors use analytical ultracentrifugation to study the interaction of gold nanoparticles with bovine serum albumin, to gain insight into the corona formation process.
- Ahmet Bekdemir
- & Francesco Stellacci
-
Article
| Open Access Core-shell nanoscale coordination polymers combine chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy to potentiate checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy
Core-shell nanoscale coordination polymers combine chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy to potentiate checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy
Blockade of PD-L1 is usually not very effective in colon cancer patients. Here, the authors show the efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in combination with coordination polymer nanoparticles carrying oxaliplatin and a photosensitizer to induce anti-tumor immunity in metastatic models of colon cancer.
- Chunbai He
- , Xiaopin Duan
- & Wenbin Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Transformable liquid-metal nanomedicine
Transformable liquid-metal nanomedicine
The use of inorganic carriers for drug delivery is often limited by toxicity and persistence of inorganic species in the body. Here, the authors report the use of nanocarriers with a liquid-phase eutectic gallium-indium core capable of delivering doxorubicin and subsequently fusing and degrading under mildly acidic conditions.
- Yue Lu
- , Quanyin Hu
- & Zhen Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Single-band upconversion nanoprobes for multiplexed simultaneous in situ molecular mapping of cancer biomarkers
Single-band upconversion nanoprobes for multiplexed simultaneous in situ molecular mapping of cancer biomarkers
The excitation–emission profiles of upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) make them attractive biological probes. Here the authors present a lanthanide UCNP for the in situmultiplexed detection of cancer biomarkers, with different single-colour upconversion emissions.
- Lei Zhou
- , Rui Wang
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural reorganization of cylindrical nanoparticles triggered by polylactide stereocomplexation
Structural reorganization of cylindrical nanoparticles triggered by polylactide stereocomplexation
A polymer stereocomplex can possess quite different properties to its constituent homopolymers. Here, the authors prepare stereocomplex micelles of amphiphilic block-copolymers via crystallization-driven self-assembly, and observe a change from cylindrical to mixed spherical micelle morphology.
- Liang Sun
- , Anaïs Pitto-Barry
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
Article |
 Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
An integrated electronic platform with site-specific sensitivity is highly needed for medical applications. Here, Kim et al.report a stretchable prosthetic skin composed of ultrathin single crystalline silicon nanoribbon array, which can sense strain, pressure and temperature spontaneously.
- Jaemin Kim
- , Mincheol Lee
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Cell therapy requires sufficient amounts of therapeutic cells to be delivered to the injured tissue. Here the authors use magnetic iron nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies that bind therapeutic cells and cardiomyocytes to treat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and show that targeting to the heart is enhanced upon local application of a magnetic field.
- Ke Cheng
- , Deliang Shen
- & Eduardo Marbán
-
Article |
 A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
Nanoparticles can be used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Here, the authors report that nanoparticles made of a single chemical building block, called nanoporphyrins, incorporate eight different functionalities, including various types of imaging, drug delivery and cancer therapy.
- Yuanpei Li
- , Tzu-yin Lin
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation
A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation
Photosensitisers are used in cancer therapy to promote the formation of reactive oxygen species on irradiation with light. Here, the authors present a graphene quantum dot photosensitiser with a singlet oxygen quantum yield of approximately 1.3, and investigate its in vitro and in vivoapplications
- Jiechao Ge
- , Minhuan Lan
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article |
 Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy
Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy
Nanoscale coordination polymers are promising materials for use as drug delivery nanoparticles, as their structural properties can be easily and precisely controlled to influence drug loading and release. Here, the authors present such a structure for effective in vivoanticancer therapy.
- Demin Liu
- , Christopher Poon
- & Wenbin Lin
-
Article |
 Poly-cyclodextrin and poly-paclitaxel nano-assembly for anticancer therapy
Poly-cyclodextrin and poly-paclitaxel nano-assembly for anticancer therapy
Polymer-based drug-delivery strategies can sometimes be hampered by the poor stability of polymer–drug conjugates and their ineffectual drug-release profiles. Here, the authors fabricate a cyclodextrin-based polymer–drug nano-assembly and demonstrate effective in vivotumour reduction activity.
- Ran Namgung
- , Yeong Mi Lee
- & Won Jong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing photochemical internalization with dual degradable nanoparticles for combinatorial photo–chemotherapy
Harnessing photochemical internalization with dual degradable nanoparticles for combinatorial photo–chemotherapy
Photochemical internalisation is the process by which a laser source activates light sensitive compounds for cellular uptake. Here, the authors combine this technique with photo–chemo degradable polymers for the controlled uptake of chemotherapeutics into cancer cells showing increased cell death.
- George Pasparakis
- , Theodore Manouras
- & Panagiotis Argitis
-
Article
| Open Access Porphyrin–phospholipid liposomes permeabilized by near-infrared light
Porphyrin–phospholipid liposomes permeabilized by near-infrared light
The delivery of therapeutics using an external trigger is an attractive route for the improvement of targeted disease treatment. Here, the authors have discovered a porphyrin–phospholipid liposome for light-controlled membrane permeabilization and use the system to deliver an anticancer drug in vivo.
- Kevin A. Carter
- , Shuai Shao
- & Jonathan F. Lovell
-
Article |
 ATP-triggered anticancer drug delivery
ATP-triggered anticancer drug delivery
Nanoparticles can deliver drugs to tumours but improvements in selectively targeting tumour cells are required. Here, Mo et al. develop nanocarriers that take advantage of high ATP levels in tumour cells and show that these nanoparticles encapsulating the chemotherapeutic doxorubicin can inhibit tumour growth in mice.
- Ran Mo
- , Tianyue Jiang
- & Zhen Gu
-
Article |
 Environment-responsive nanophores for therapy and treatment monitoring via molecular MRI quenching
Environment-responsive nanophores for therapy and treatment monitoring via molecular MRI quenching
Iron oxide nanoparticles are used for iron supplementation and as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Here, Kaittanis et al. show that these nanoparticles can also be used as pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicles, and that drug loading and release can be monitored in vivoby magnetic resonance imaging.
- Charalambos Kaittanis
- , Travis M. Shaffer
- & Jan Grimm
-
Article |
 A statin-loaded reconstituted high-density lipoprotein nanoparticle inhibits atherosclerotic plaque inflammation
A statin-loaded reconstituted high-density lipoprotein nanoparticle inhibits atherosclerotic plaque inflammation
Inflammatory processes in atherosclerotic lesions promote disease progression and plaque rupture. Here the authors load the drug statin into nanoparticles made of recombinant high-density lipoprotein and show that these accumulate in atherosclerotic plaques and reduce plaque inflammation in mice.
- Raphaël Duivenvoorden
- , Jun Tang
- & Willem J. M. Mulder

 Trojan Horse nanotheranostics with dual transformability and multifunctionality for highly effective cancer treatment
Trojan Horse nanotheranostics with dual transformability and multifunctionality for highly effective cancer treatment