Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rewritable two-dimensional DNA-based data storage with machine learning reconstruction
Rewritable two-dimensional DNA-based data storage with machine learning reconstruction
Current DNA-based data storage platforms encode information only in the nucleotide sequence. Here, the authors report a 2DDNA platform that can store data in both sequence context and backbone structure, and has improved image inpainting and enhancement via automatic discoloration detection and deep learning.
- Chao Pan
- , S. Kasra Tabatabaei
- & Olgica Milenkovic
-
Article
| Open Access A high-throughput multiparameter screen for accelerated development and optimization of soluble genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors
A high-throughput multiparameter screen for accelerated development and optimization of soluble genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors
Fluorescent biosensors are important tools for studying cellular metabolism, but development and optimization are challenging. Koveal et al. present a high-throughput multiparameter screen for sensor performance, and used it to generate LiLac, a high-performance, quantitative lactate sensor.
- Dorothy Koveal
- , Paul C. Rosen
- & Gary Yellen
-
Article
| Open Access A framework to efficiently describe and share reproducible DNA materials and construction protocols
A framework to efficiently describe and share reproducible DNA materials and construction protocols
DNA constructs and their annotated sequence maps have been rapidly accumulating with the advancement of DNA cloning, synthesis, and assembly methods. Here the authors introduce QUEEN, a framework to describe and share DNA materials and construction protocols.
- Hideto Mori
- & Nozomu Yachie
-
Article
| Open Access Broad-spectrum CRISPR-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 variants and endemic coronaviruses in vitro
Broad-spectrum CRISPR-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 variants and endemic coronaviruses in vitro
A major challenge in coronavirus vaccination and treatment is to counteract rapid viral evolution and mutations. Here the authors show that CRISPR-Cas13d can be used as a broad-spectrum antiviral to inhibit human coronaviruses, including new SARS-CoV-2 variants, combined with small molecule drugs for an enhanced antiviral effect in human primary cells.
- Leiping Zeng
- , Yanxia Liu
- & Lei S. Qi
-
Article
| Open Access PERSIST platform provides programmable RNA regulation using CRISPR endoRNases
PERSIST platform provides programmable RNA regulation using CRISPR endoRNases
Gene circuits must resist epigenetic silencing for reliable therapeutic applications. Here the authors develop an RNA-level regulation platform using CRISPR endoRNases that is modular, scalable, and more stable than traditional transcriptional versions.
- Breanna DiAndreth
- , Noreen Wauford
- & Ron Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolite trafficking enables membrane-impermeable-terpene secretion by yeast
Metabolite trafficking enables membrane-impermeable-terpene secretion by yeast
The engineering of metabolite secretion from microorganisms can lead to many applications in synthetic biology. In this article, the authors engineer a metabolite trafficking system for the secretion of medicinal terpenes.
- So-Hee Son
- , Jae-Eung Kim
- & Ju Young Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic cells with self-activating optogenetic proteins communicate with natural cells
Synthetic cells with self-activating optogenetic proteins communicate with natural cells
Synthetic biology and engineering approaches are harnessed to incorporate new capabilities in synthetic cells. Here, the authors designed bioluminescent signaling mechanisms for intracellular and intercellular synthetic-to-natural cell communication.
- Omer Adir
- , Mia R. Albalak
- & Avi Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access A reversibly gated protein-transporting membrane channel made of DNA
A reversibly gated protein-transporting membrane channel made of DNA
Artificial systems to control the transport of molecules across biomembranes can be useful for biosensing or drug delivery. Here, the authors assemble a DNA channel enabling the precisely timed, stimulus-controlled transport of functional proteins across bilayer membranes.
- Swarup Dey
- , Adam Dorey
- & Hao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis enables resource-efficient engineering of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editor activities
Machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis enables resource-efficient engineering of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editor activities
Screening combinatorial mutants is too massive for wet-lab experiment alone. Here the authors present a machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis approach to vastly reduce experimental burden for engineering Cas9 genome editing enzymes.
- Dawn G. L. Thean
- , Hoi Yee Chu
- & Alan S. L. Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Development of NanoLuc-targeting protein degraders and a universal reporter system to benchmark tag-targeted degradation platforms
Development of NanoLuc-targeting protein degraders and a universal reporter system to benchmark tag-targeted degradation platforms
t ag-T argetedP roteinD egrader (tTPD) systems are powerful tools for preclinical target validation. Here the authors extend the tTPD platform by developing NanoTACs that degrade NanoLuc tagged substrates and benchmark each tTPD system using an interchangeable tag reporter system.- Christoph Grohmann
- , Charlene M. Magtoto
- & Rebecca Feltham
-
Article
| Open Access A genetic toolkit and gene switches to limit Mycoplasma growth for biosafety applications
A genetic toolkit and gene switches to limit Mycoplasma growth for biosafety applications
Mycoplasmas are minimal cell model organisms but lack genetic tools. Here the authors provide a robust genetic toolkit for Mycoplasma demonstrating gene circuit engineering applications.
- Alicia Broto
- , Erika Gaspari
- & Mark Isalan
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-responsive regulation of enzyme catalysis using genetically encoded chemical switches
Metal-responsive regulation of enzyme catalysis using genetically encoded chemical switches
Dynamic control over protein function is a central challenge in synthetic biology. Here the authors present an integrated computational and experimental workflow for engineering reversible protein switches; metal-chelating unnatural amino acids genetically encoded into two conformationally dynamic enzymes to yield robust switches.
- Yasmine S. Zubi
- , Kosuke Seki
- & Jared C. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of a LptDE transporter in complex with Pro-macrobodies offer insight into lipopolysaccharide translocation
Cryo-EM structures of a LptDE transporter in complex with Pro-macrobodies offer insight into lipopolysaccharide translocation
Lateral opening of the LptDE transporter in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria is necessary for insertion of lipopolysaccharides. Here, Botte et al. report a cryo-EM structure of a partially opened LptDE transporter, in complex with rigid chaperones derived from nanobodies.
- Mathieu Botte
- , Dongchun Ni
- & Michael Hennig
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of stabilized recombinant influenza neuraminidase tetramers
Structure-based design of stabilized recombinant influenza neuraminidase tetramers
Influenza virus neuraminidase (NA) is a drug target and a potential vaccine antigen. Here, the authors provide a detailed analysis of the conformational stability of NA, and show how expression and stability of recombinant NA antigens can be strengthened through structure-based design.
- Daniel Ellis
- , Julia Lederhofer
- & Masaru Kanekiyo
-
Article
| Open Access Selective optogenetic control of Gq signaling using human Neuropsin
Selective optogenetic control of Gq signaling using human Neuropsin
Gq proteins are one of four major classes of G proteins; optogenetic receptors for selective and repetitive activation of Gq proteins with fast kinetics are lacking. Here the authors report UV light-dependent Gq signalling using human Neuropsin (hOPN5) and demonstrate its potential as an optogenetic tool.
- Ahmed Wagdi
- , Daniela Malan
- & Tobias Bruegmann
-
Article
| Open Access De novo design and directed folding of disulfide-bridged peptide heterodimers
De novo design and directed folding of disulfide-bridged peptide heterodimers
Peptide heterodimers are prevalent in nature, which are not only functional macromolecules but molecular tools for chemical and synthetic biology. Here the authors report de novo design and directed folding of peptide heterodimers crosslinked through multiple disulfide bonds, which can be explored as chemical tools for orthogonal labeling of proteins and preparing protein hybrids.
- Sicong Yao
- , Adam Moyer
- & Chuanliu Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Precise tumor immune rewiring via synthetic CRISPRa circuits gated by concurrent gain/loss of transcription factors
Precise tumor immune rewiring via synthetic CRISPRa circuits gated by concurrent gain/loss of transcription factors
“Reinvigoration of antitumor immunity has recently become the central theme for the development of cancer therapies. Here the authors present an adaptable gene circuit to harness the CRISPRa for tumorlocalized immune activation.”
- Yafeng Wang
- , Guiquan Zhang
- & Jianghuai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes
Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes
Biocontainment is a key to developing safe genetically-engineered microbes (GEMs). Here the authors demonstrate genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches that control GEMs’ viability in animal hosts, enabling their safe biomedical applications.
- Austin G. Rottinghaus
- , Aura Ferreiro
- & Tae Seok Moon
-
Article
| Open Access Improved gRNA secondary structures allow editing of target sites resistant to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage
Improved gRNA secondary structures allow editing of target sites resistant to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage
Some DNA sequences are refractory to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage, partially due to gRNA misfolding. Here the authors engineer gRNAs to prevent misfolding and further enhanced their stability by chemical modifications allowing robust genome editing regardless of target sequence.
- Stephan Riesenberg
- , Nelly Helmbrecht
- & Svante Pääbo
-
Comment
| Open AccessPandemic preparedness: synthetic biology and publicly funded biofoundries can rapidly accelerate response time
Synthetic biology has played a key role in responding to the current pandemic. Biofoundries are critical synthetic biology infrastructure which should be available to all nations as a part of their independent bioengineering, biosecurity, and countermeasure response systems.
- Claudia E. Vickers
- & Paul S. Freemont
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA editing in human cells with zinc finger deaminases
Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA editing in human cells with zinc finger deaminases
Base editing in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is broadly useful for biomedical research, medicine, and biotechnology. Here the authors present zinc finger deaminases which catalyze targeted C-to-T base conversions without inducing unwanted indels in human cells.
- Kayeong Lim
- , Sung-Ik Cho
- & Jin-Soo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a generic prototyping approach for therapeutically-relevant peptides and proteins in a cell-free translation system
Towards a generic prototyping approach for therapeutically-relevant peptides and proteins in a cell-free translation system
Generic approach for rapid prototyping is essential for the progress of synthetic biology. Here the authors modify the cell-free translation system to control protein aggregation and folding and validate the approach by using single conditions for prototyping of various disulfide-constrained polypeptides.
- Yue Wu
- , Zhenling Cui
- & Sergey Mureev
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by shark variable new antigen receptors elucidated through X-ray crystallography
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by shark variable new antigen receptors elucidated through X-ray crystallography
Shark antibodies (Variable New Antigen Receptors, VNARs) are the smallest naturally occurring antibody fragments. Here, the authors screen a VNAR phage display library against the SARS-CoV2 receptor binding domain (RBD) and identify VNARs that neutralize the SARSCoV-2 virus and discuss their mechanisms of viral neutralization.
- Obinna C. Ubah
- , Eric W. Lake
- & Caroline J. Barelle
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting a Y chromosome-linked Cas9 for sex selection and gene drive
Exploiting a Y chromosome-linked Cas9 for sex selection and gene drive
CRISPR-based engineering can be used to bias sex ratios. Here the authors develop a transgenic line of Drosophila melanogaster expressing Cas9 from the Y chromosome and functionally characterize the utility of this strain for both sex selection and gene drive.
- Stephanie Gamez
- , Duverney Chaverra-Rodriguez
- & Omar S. Akbari
-
Article
| Open Access Probing ion channel functional architecture and domain recombination compatibility by massively parallel domain insertion profiling
Probing ion channel functional architecture and domain recombination compatibility by massively parallel domain insertion profiling
Here, the authors perform a large-scale, high-throughput biochemical assay to determine the compatibility of over 300,000 domain recombination variants of the inward rectifier K+ channel Kir2.1. They derive rules for designing domain insertion variants that fold and traffic to the cell surface and conclude that the insertion of domains at protein termini is evolutionary favoured.
- Willow Coyote-Maestas
- , David Nedrud
- & Daniel Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
l-lactate is an important intercellular energy currency. Here the authors report a genetically encoded biosensor eLACCO1.1 to monitor extracellular l-lactate; they use eLACCO1.1 to image extracellular l-lactate in cultured mammalian cells and brain tissue.
- Yusuke Nasu
- , Ciaran Murphy-Royal
- & Robert E. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Directed evolution of and structural insights into antibody-mediated disruption of a stable receptor-ligand complex
Directed evolution of and structural insights into antibody-mediated disruption of a stable receptor-ligand complex
Facilitated dissociation is a mechanism where antibody-mediated disruption of high-affinity complexes can enhance the therapeutic effects of a drug. Here the authors present a yeast display approach to select and engineer omalizumab variants that dissociate receptor-bound IgE to accelerate its inhibition of the allergic response.
- Luke F. Pennington
- , Pascal Gasser
- & Theodore S. Jardetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile selective evolutionary pressure using synthetic defect in universal metabolism
Versatile selective evolutionary pressure using synthetic defect in universal metabolism
Rational design of enzymes with new or improved properties is rarely straightforward, and artificial selection pressure approaches that link an improvement in the target to cell growth are an alternative. Here, the authors show that diverse enzymes sharing the ubiquitous cofactor NAD(P)+ can substitute for defective NAD+ regeneration, representing a very broadly-applicable artificial selection.
- Lara Sellés Vidal
- , James W. Murray
- & John T. Heap
-
Article
| Open Access Gene editing enables rapid engineering of complex antibiotic assembly lines
Gene editing enables rapid engineering of complex antibiotic assembly lines
Engineering biosynthetic assembly lines is a powerful path to new natural products but is challenging with current methods. Here the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 to exchange subdomains within NRPS to alter substrate selectivity.
- Wei Li Thong
- , Yingxin Zhang
- & Jason Micklefield
-
Comment
| Open Access Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Developing more productive and sustainable crops will be essential to achieving food security in coming decades. A core process in plant evolution has been the transfer of chloroplast-encoded genes to the nuclear genome. We propose reverting this process as a new approach to improve plant disease resistance and photosynthesis in future crops.
- Briardo Llorente
- , María Eugenia Segretin
- & Nicolás E. Blanco
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic principles of an ultra-long bovine CDR reveal strategies for antibody design
Mechanistic principles of an ultra-long bovine CDR reveal strategies for antibody design
Certain bovine antibodies have ultra-long long complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) that contain a knob for antigen interaction, which is connected to the antibody through a stalk. Here, the authors combine biophysical experiments and MD simulations and show that the stalk length is critical for the folding and stability of these antibodies. The authors also demonstrate that ultra-long bovine CDRs can be grafted into human antibodies, and furthermore show that de novo designed mini-domains that bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with high affinity can be integrated as a knob in ultra-long CDRs in bovine and human antibodies, which neutralize SARS-CoV-2.
- Hristo L. Svilenov
- , Julia Sacherl
- & Johannes Buchner
-
Article
| Open Access Two-input protein logic gate for computation in living cells
Two-input protein logic gate for computation in living cells
Traditional synthetic biology tools operate by complex re-programming of DNA, requiring significant amount of ‘nucleotide-based code’ to implement instructions that are transcribed at the protein level. Here the authors demonstrate the direct regulation of cellular phenotype at the single-protein level by creating a two-input logic gate for biological computation using ‘allosteric wiring’.
- Yashavantha L. Vishweshwaraiah
- , Jiaxing Chen
- & Nikolay V. Dokholyan
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric requirement of Dpp/BMP morphogen dispersal in the Drosophila wing disc
Asymmetric requirement of Dpp/BMP morphogen dispersal in the Drosophila wing disc
Morphogens disperse to pattern tissues and control their growth during development, allowing for the specification of multiple fates across space. Here the authors block dispersal of a morphogen Dpp (BMP2/4) and show that the requirement for Dpp dispersal is much lower than previously thought.
- Shinya Matsuda
- , Jonas V. Schaefer
- & Markus Affolter
-
Article
| Open Access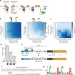 Selection for constrained peptides that bind to a single target protein
Selection for constrained peptides that bind to a single target protein
Peptide secondary metabolites have a diverse range of functions. Here the authors present a method to design and screen a large library of modified peptides in E. coli against a target of interest.
- Andrew M. King
- , Daniel A. Anderson
- & Christopher A. Voigt
-
Article
| Open Access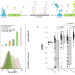 Improvement of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for phenylketonuria with biosensor-enabled enzyme engineering
Improvement of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for phenylketonuria with biosensor-enabled enzyme engineering
PKU patients have elevated phenylalanine levels which can result in neurological impairment. Here the authors utilize biosensor-based ultra-high-throughput screening to optimize PAL activity in a synthetic biotic platform for improved in vivo performance.
- Kristin J. Adolfsen
- , Isolde Callihan
- & Vincent M. Isabella
-
Article
| Open Access De novo biosynthesis of bioactive isoflavonoids by engineered yeast cell factories
De novo biosynthesis of bioactive isoflavonoids by engineered yeast cell factories
Isoflavonoids are a class of industrially important plant natural products, but their low abundance and structural complexity limits their availability. Here, the authors engineer Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism to become a platform for efficient production of daidzein which is core chemical scaffold for isoflavonoid biosynthesis, and show its application for production of bioactive glucosides from glucose.
- Quanli Liu
- , Yi Liu
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-reporter system for investigating and optimizing protein translation and folding in E. coli
A dual-reporter system for investigating and optimizing protein translation and folding in E. coli
Heterologous expression of recombinant proteins often results in misfolding, aggregation and degradation. Here, we show an in vivo dual-biosensor system that simultaneously assesses protein translation and protein folding, thereby enabling rapid screening of expression strains as well as mutant libraries.
- Ariane Zutz
- , Louise Hamborg
- & Alex Toftgaard Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access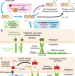 Disulfide-compatible phage-assisted continuous evolution in the periplasmic space
Disulfide-compatible phage-assisted continuous evolution in the periplasmic space
The directed evolution of antibodies yields important tools for research and therapy. Here the authors develop a periplasmic phage-assisted continuous evolution platform for improvement of protein-protein interactions in the disulfidecompatible E. coli periplasm.
- Mary S. Morrison
- , Tina Wang
- & David R. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A standardized genome architecture for bacterial synthetic biology (SEGA)
A standardized genome architecture for bacterial synthetic biology (SEGA)
Genome engineering is challenging compared to plasmid DNA manipulation. Here the authors create a simple methodology called SEGA that enables genome engineering by combining DNA and bacterial cells followed by identification of recombinant clones by a change in colour when grown on agar plates.
- Carolyn N. Bayer
- , Maja Rennig
- & Morten H. H. Nørholm
-
Article
| Open Access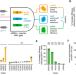 Multiplex suppression of four quadruplet codons via tRNA directed evolution
Multiplex suppression of four quadruplet codons via tRNA directed evolution
Genetic code expansion strategies are limited to specific codons that can be reassigned to new amino acids. Here the authors show that quadruplet-decoding tRNAs (qtRNAs) can be rapidly discovered and evolved to decode new quadruplet codons, enabling four independent decoding events in a single protein in living cells.
- Erika A. DeBenedictis
- , Gavriela D. Carver
- & Ahmed H. Badran
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive deletion landscape of CRISPR-Cas9 identifies minimal RNA-guided DNA-binding modules
Comprehensive deletion landscape of CRISPR-Cas9 identifies minimal RNA-guided DNA-binding modules
Proteins evolve through the modular rearrangement of domains. Here the authors introduce MISER, a minimization by iterative size-exclusion and recombination method to make all possible deletions of a protein, uncovering functions for Cas9 domains involved in DNA binding.
- Arik Shams
- , Sean A. Higgins
- & David F. Savage
-
Article
| Open Access Directed evolution of rRNA improves translation kinetics and recombinant protein yield
Directed evolution of rRNA improves translation kinetics and recombinant protein yield
Ribosome kinetics are rate-limiting for protein synthesis. Here the authors evolve diverse 16S rRNAs for enhanced protein synthesis rates and genetic code expansion efficiencies in vivo.
- Fan Liu
- , Siniša Bratulić
- & Ahmed H. Badran
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid prototyping and design of cybergenetic single-cell controllers
Rapid prototyping and design of cybergenetic single-cell controllers
Practical implementation of genetic circuits is difficult due to low predictability and time-intensive troubleshooting. Here the authors present Cyberloop, which interfaces a computer with single cells to enable cell-in-the-loop testing and optimization of circuit designs before they are built.
- Sant Kumar
- , Marc Rullan
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of a more efficient prime editor 2 by addition of the Rad51 DNA-binding domain
Generation of a more efficient prime editor 2 by addition of the Rad51 DNA-binding domain
While prime editing is a promising technology, PE2 systems often have low efficiency. Here the authors fuse a Rad51 DNA-binding domain to create hyPE2 with improved editing efficiency.
- Myungjae Song
- , Jung Min Lim
- & Hyongbum Henry Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Coevolutionary methods enable robust design of modular repressors by reestablishing intra-protein interactions
Coevolutionary methods enable robust design of modular repressors by reestablishing intra-protein interactions
Genetic sensors can be created by mix and matching DNA-binding modules with ligand-binding modules. Here the authors use a computational model to overcome module incompatibilities and restore function by rescuing key interactions.
- Xian-Li Jiang
- , Rey P. Dimas
- & Faruck Morcos
-
Article
| Open Access One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
Circularised nanodiscs (cNDs) are able to stabilise large lipid bilayer patches and are used for structural and functional studies. Current techniques to build cNDs have numerous steps and low yields; here the authors report a single step construction method using the SpyCatcher-SpyTag system.
- Shanwen Zhang
- , Qian Ren
- & Huan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access A versatile genetic engineering toolkit for E. coli based on CRISPR-prime editing
A versatile genetic engineering toolkit for E. coli based on CRISPR-prime editing
CRISPR prime editing enables double-strand break free engineering of the genome. Here the authors present a toolkit for prime editing in E. coli.
- Yaojun Tong
- , Tue S. Jørgensen
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable receptors enable bacterial biosensors to detect pathological biomarkers in clinical samples
Programmable receptors enable bacterial biosensors to detect pathological biomarkers in clinical samples
Bacterial biosensors have promising applications in medical and environmental diagnostics. Here the authors use EMeRALD synthetic receptors to design bile salt sensors for use in liver transplant patient serum.
- Hung-Ju Chang
- , Ana Zúñiga
- & Jerome Bonnet
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries
Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries
Existing Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) biosensors are often limited in their sensitivity. Here the authors report FRET-seq which they use to identify Fyn and ZAP70 kinase biosensors with enhanced performance, and use them to image T-cell activation and screen drugs.
- Longwei Liu
- , Praopim Limsakul
- & Yingxiao Wang

 Computationally designed hyperactive Cas9 enzymes
Computationally designed hyperactive Cas9 enzymes