Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres
The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres
A comparison of two complete sets of human centromeres reveals that the centromeres show at least a 4.1-fold increase in single-nucleotide variation compared with their unique flanks, and up to 3-fold variation in size, resulting from an accelerated mutation rate.
- Glennis A. Logsdon
- , Allison N. Rozanski
- & Evan E. Eichler
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Integrator-dependent RNA polymerase II termination
Structural basis of Integrator-dependent RNA polymerase II termination
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human Integrator complex in three different functional states shed light on how Integrator terminates RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription by disengaging Pol II from the DNA template.
- Isaac Fianu
- , Moritz Ochmann
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access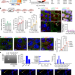 Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway
Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway
Learning results in persistent double-stranded DNA breaks, nuclear rupture and release of DNA fragments and histones within hippocampal CA1 neurons that, following TLR9-mediated DNA damage repair, results in their recruitment to memory circuits.
- Vladimir Jovasevic
- , Elizabeth M. Wood
- & Jelena Radulovic
-
Article |
 Structural basis of exoribonuclease-mediated mRNA transcription termination
Structural basis of exoribonuclease-mediated mRNA transcription termination
A study presents two cryo-EM structures of yeast Pol II pre-termination transcription complexes bound to Rat1–Rai1, and provides the mechanisms for termination of mRNA transcription in yeast and other eukaryotes.
- Yuan Zeng
- , Hong-Wei Zhang
- & Yu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription–replication conflicts underlie sensitivity to PARP inhibitors
Transcription–replication conflicts underlie sensitivity to PARP inhibitors
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) functions together with TIMELESS and TIPIN to protect the replisome in early S phase from transcription–replication conflicts, and inhibiting PARP1 enzymatic activity may suffice for treatment efficacy in homologous recombination-deficient settings.
- Michalis Petropoulos
- , Angeliki Karamichali
- & Thanos D. Halazonetis
-
Article |
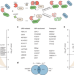 Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
A synthetic proteome-scale strategy enables the identification of a diverse range of human proteins that can induce the degradation or stabilization of a target protein in a proximity-dependent way.
- Juline Poirson
- , Hanna Cho
- & Mikko Taipale
-
News & Views |
 Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
In experiments dubbed the Random Genome Project, researchers have integrated DNA strands with random sequences into yeast and mouse cells to find the default transcriptional state of their genomes.
- Sean R. Eddy
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers
A multidimensional proteomics analysis of the interactions between around 2,000 nuclear proteins and over 80 modified dinucleosomes representing promoter, enhancer and heterochromatin states provides insights into how chromatin states are decoded by chromatin readers.
- Saulius Lukauskas
- , Andrey Tvardovskiy
- & Till Bartke
-
Article
| Open Access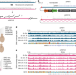 Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Introduction of a long synthetic DNA into yeast genomic loci results in high default transcriptional activity in yeast but low activity in mouse, suggesting distinct default levels of genomic activity in these organisms.
- Brendan R. Camellato
- , Ran Brosh
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Article |
 Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Structures of the yeast replisome associated with the FACT complex and an evicted histone hexamer offer insights into the mechanism of replication-coupled histone recycling for maintaining epigenetic inheritance.
- Ningning Li
- , Yuan Gao
- & Yuanliang Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
In Caenorhabditis tropicalis, selective expression of genetic alleles from one parent but not the other can arise from maternally inherited small transcripts acting via the PIWI-interacting RNA host defence pathway.
- Pinelopi Pliota
- , Hana Marvanova
- & Alejandro Burga
-
Article
| Open Access A concerted neuron–astrocyte program declines in ageing and schizophrenia
A concerted neuron–astrocyte program declines in ageing and schizophrenia
A synaptic neuron and astrocyte program (SNAP) varies among healthy humans, may shape interindividual differences in synapses and plasticity, and is undermined in schizophrenia and with advancing age.
- Emi Ling
- , James Nemesh
- & Steven A. McCarroll
-
Article
| Open Access Incomplete transcripts dominate the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcriptome
Incomplete transcripts dominate the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcriptome
A study reveals that most transcripts in Mycobacterium tuberculosis are incomplete, likely because of the tendency of the transcription machinery in this species to pause on genomic DNA.
- Xiangwu Ju
- , Shuqi Li
- & Shixin Liu
-
Article |
 CST–polymerase α-primase solves a second telomere end-replication problem
CST–polymerase α-primase solves a second telomere end-replication problem
Incomplete duplication of the C-rich telomeric repeat strand by lagging-strand DNA synthesis is counteracted by DNA synthesis mediated by CST–polymerase α-primase.
- Hiroyuki Takai
- , Valentina Aria
- & Titia de Lange
-
Comment |
 To unravel the origin of life, treat findings as pieces of a bigger puzzle
To unravel the origin of life, treat findings as pieces of a bigger puzzle
Explaining isolated steps on the road from simple chemicals to complex living organisms is not enough. Looking at the big picture could help to bridge rifts in this fractured research field.
- Nick Lane
- & Joana C. Xavier
-
Article
| Open Access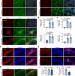 WNT signalling control by KDM5C during development affects cognition
WNT signalling control by KDM5C during development affects cognition
The demethylase KDM5C, mutations in which often lead to intellectual disability, is identified as a crucial player in regulating the precise timing of neurodevelopment together with the WNT signalling pathway.
- Violetta Karwacki-Neisius
- , Ahram Jang
- & Yang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms of action and resistance in histone methylation-targeted therapy
Mechanisms of action and resistance in histone methylation-targeted therapy
The mechanisms of action and resistance of valemetostat, an EZH1–EZH2 dual inhibitor, in patients with adult T cell leukaemia/lymphoma who initially responded but later showed disease progression are explored.
- Makoto Yamagishi
- , Yuta Kuze
- & Kaoru Uchimaru
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous transposons tune their sequences to ensure somatic suppression
Autonomous transposons tune their sequences to ensure somatic suppression
SAFB proteins protect genome integrity by preventing retrotransposition of L1 elements yet maintaining splicing integrity, via prevention of the exonization of previously integrated transposable elements, a major constituent of human genes.
- İbrahim Avşar Ilık
- , Petar Glažar
- & Tuğçe Aktaş
-
Article |
 Nuclear morphology is shaped by loop-extrusion programs
Nuclear morphology is shaped by loop-extrusion programs
In neutrophil progenitor cells, stopping the process of loop extrusion by depleting nipped-B-like protein (NIPBL) results in the assembly of polymorphonuclear structures and the activation of a neutrophil-specific gene program.
- Indumathi Patta
- , Maryam Zand
- & Cornelis Murre
-
Article
| Open Access A new family of bacterial ribosome hibernation factors
A new family of bacterial ribosome hibernation factors
A study identifies a new bacterial ribosome hibernation factor, Balon, and describes its association with EF-Tu and its initiation of mRNA-independent hibernation during protein synthesis.
- Karla Helena-Bueno
- , Mariia Yu. Rybak
- & Sergey V. Melnikov
-
Article |
 Nuclear export of circular RNA
Nuclear export of circular RNA
Circular RNAs are exported from the nucleus by Ran-GTP, exportin-2 and IGF2BP1 in a mechanism analogous to protein export rather than mRNA export.
- Linh H. Ngo
- , Andrew G. Bert
- & Vihandha O. Wickramasinghe
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic determinants of micronucleus formation in vivo
Genetic determinants of micronucleus formation in vivo
Genetic screening identifies a rich catalogue of regulators of micronucleus formation.
- D. J. Adams
- , B. Barlas
- & G. Balmus
-
Article
| Open Access Translation selectively destroys non-functional transcription complexes
Translation selectively destroys non-functional transcription complexes
Translation actively dislodges stalled transcription elongation complexes (ECs) from damaged DNA, which enables lesion repair and restoration of transcription activity, and coupled ribosomes discriminate between active ECs and stalled ECs, ensuring destruction of only the latter.
- Jason Woodgate
- , Hamed Mosaei
- & Nikolay Zenkin
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of ribosomal 30S subunit degradation by RNase R
Structural basis of ribosomal 30S subunit degradation by RNase R
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of intermediates formed during the degradation of the 30S ribosomal unit shed light on how the 3′ to 5′ exonuclease ribonuclease R controls the ribosomal degradation process.
- Lyudmila Dimitrova-Paternoga
- , Sergo Kasvandik
- & Helge Paternoga
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial transcriptomics reveal neuron–astrocyte synergy in long-term memory
Spatial transcriptomics reveal neuron–astrocyte synergy in long-term memory
Spatial and single-cell transcriptomic analyses of the mouse basolateral amygdala reveal transcriptomic signatures, spatial resolution and interactions of cells that constitute the memory engram, including crucial neuron–astrocyte interactions.
- Wenfei Sun
- , Zhihui Liu
- & Stephen R. Quake
-
Article |
 Coordination of cohesin and DNA replication observed with purified proteins
Coordination of cohesin and DNA replication observed with purified proteins
We study the interplay between cohesin and replication by reconstituting a functional replisome using purified proteins, showing how cohesin initially responds to replication and providing a molecular model for the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion.
- Yasuto Murayama
- , Shizuko Endo
- & Hiroyuki Araki
-
Article
| Open Access The HIV capsid mimics karyopherin engagement of FG-nucleoporins
The HIV capsid mimics karyopherin engagement of FG-nucleoporins
Dissection of the nuclear pore complex provides a model in which the HIV capsid enters the nucleus through karyopherin mimicry, a mechanism likely to be conserved across other viruses.
- C. F. Dickson
- , S. Hertel
- & D. A. Jacques
-
Article
| Open Access Affinity-optimizing enhancer variants disrupt development
Affinity-optimizing enhancer variants disrupt development
Low-affinity transcription factor binding sites are prevalent across the genome, and single nucleotide changes that increase binding affinity even slightly can cause gain-of-function gene expression and phenotypes (such as polydactyly).
- Fabian Lim
- , Joe J. Solvason
- & Emma K. Farley
-
News & Views |
 Snapshots of genetic copy-and-paste machinery in action
Snapshots of genetic copy-and-paste machinery in action
LINE-1 DNA elements self-duplicate, inserting the copy into new regions of the genome — a key process in chromosome evolution. Structures of the machinery that performs this process in humans are now reported.
- Gael Cristofari
-
News |
 ‘Set it and forget it’: automated lab uses AI and robotics to improve proteins
‘Set it and forget it’: automated lab uses AI and robotics to improve proteins
A self-driving lab system spent half a year engineering enzymes to work at higher temperatures.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article
| Open Access Adding α,α-disubstituted and β-linked monomers to the genetic code of an organism
Adding α,α-disubstituted and β-linked monomers to the genetic code of an organism
tRNA display enables the direct selection of orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that acylate orthogonal tRNAs with non-canonical monomers, enabling in vivo synthesis of proteins that include these monomers and expanding the repertoire of the genetic code.
- Daniel L. Dunkelmann
- , Carlos Piedrafita
- & Jason W. Chin
-
News Feature |
 How CRISPR could yield the next blockbuster crop
How CRISPR could yield the next blockbuster crop
Scientists are attempting to rapidly domesticate wild plant species by editing specific genes, but they face major technical challenges — and concerns about exploitation of Indigenous knowledge.
- Michael Marshall
-
Article
| Open Access RNA-mediated symmetry breaking enables singular olfactory receptor choice
RNA-mediated symmetry breaking enables singular olfactory receptor choice
Messenger RNAs transcribed from olfactory-receptor genes may have non-coding functions that include recruitment of transcriptional enhancers and inhibition of potentially thousands of competing alleles to ensure stable transcription of a single allele.
- Ariel D. Pourmorady
- , Elizaveta V. Bashkirova
- & Stavros Lomvardas
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of replication timing during early mammalian development
Emergence of replication timing during early mammalian development
Genome-wide replication timing maps of mouse embryos from the zygote to the blastocyst stage were generated using single-cell Repli-seq, shedding light on the establishment of the epigenome at the beginning of mammalian development.
- Tsunetoshi Nakatani
- , Tamas Schauer
- & Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla
-
Article
| Open Access Structures, functions and adaptations of the human LINE-1 ORF2 protein
Structures, functions and adaptations of the human LINE-1 ORF2 protein
X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, structural modelling, biochemistry, cell biology, and evolutionary analysis enable characterization of ORF2p, the reverse transcriptase of the ancient ‘parasitic’ LINE-1 retrotransposon that has written around one-third of the human genome.
- Eric T. Baldwin
- , Trevor van Eeuwen
- & Martin S. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Human LINE-1 ORF2p relies on upstream single-stranded target DNA to position the adjacent duplex in the endonuclease active site for nicking of the longer DNA strand, with a single nick generating a staggered DNA break.
- Akanksha Thawani
- , Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza
- & Kathleen Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain
Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain
Methylome-based clustering and cross-modality integration with companion datasets from the BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network enabled the construction of a 3D multi-omic genome atlas of the adult mouse brain featuring thousands of cell-type-specific profiles.
- Hanqing Liu
- , Qiurui Zeng
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
A single-cell multiomics analysis of over 200,000 cells of the primary motor cortex of human, macaque, marmoset and mouse shows that divergence of transcription factor expression corresponds to species-specific epigenome landscapes, and conserved and divergent gene regulatory features are reflected in the evolution of the three-dimensional genome.
- Nathan R. Zemke
- , Ethan J. Armand
- & Bing Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis of chromatin accessibility in the adult mouse brain
Single-cell analysis of chromatin accessibility in the adult mouse brain
An atlas of candidate cis-regulatory DNA elements (cCREs) in the adult mouse brain unravels the transcriptional regulatory programs that drive the heterogeneity and complexity of brain structure and function.
- Songpeng Zu
- , Yang Eric Li
- & Bing Ren
-
Article
| Open Access N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting
N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting
A study demonstrates that nucleotide modifications in mRNA-based therapeutics can lead to +1 ribosomal frameshifting during translation, yielding products that can trigger immune responses.
- Thomas E. Mulroney
- , Tuija Pöyry
- & Anne E. Willis
-
Article
| Open Access TAF15 amyloid filaments in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
TAF15 amyloid filaments in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
Cryogenic electron microscopy structures of amyloid filaments extracted from patient brains reveal that the protein TAF15 forms filaments that characterize certain cases of frontotemporal lobar degeneration.
- Stephan Tetter
- , Diana Arseni
- & Benjamin Ryskeldi-Falcon
-
News & Views |
 An immune-cell transcription factor tethers DNA together
An immune-cell transcription factor tethers DNA together
A transcription factor in immune cells forms an unexpectedly ladder-like complex with two DNA molecules, allowing the expression of genes that these cells need to suppress harmful immune responses.
- Zhi Liu
- & Ye Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Whole-genome alignment of 239 primate species reveals noncoding regulatory elements that are under selective constraint in primates but not in other placental mammals, that are enriched for variants that affect human gene expression and complex traits in diseases.
- Lukas F. K. Kuderna
- , Jacob C. Ulirsch
- & Kyle Kai-How Farh
-
Article |
 mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation
mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation
The accuracy of eukaryotic ribosome translocation relies on eukaryote-specific elements of the 80S ribosome, elongation factor 2 and transfer RNAs, all of which contribute to the maintenance of the messenger RNA reading frame.
- Nemanja Milicevic
- , Lasse Jenner
- & Gulnara Yusupova
-
Article |
 Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Polymerase delta is required for multiple steps in polymerase theta-dependent repair of chromosome breaks, a pathway targeted in cancer therapy.
- Susanna Stroik
- , Juan Carvajal-Garcia
- & Dale A. Ramsden
-
Article |
 Asymmetric distribution of parental H3K9me3 in S phase silences L1 elements
Asymmetric distribution of parental H3K9me3 in S phase silences L1 elements
The epigenetic modification H3K9me3 is asymmetrically partitioned at long interspersed nuclear element retrotransposons for their silencing in S phase, a newly discovered mechanism that is mediated by the HUSH complex and the DNA polymerase Pol ε.
- Zhiming Li
- , Shoufu Duan
- & Zhiguo Zhang
-
Article |
 TNRC18 engages H3K9me3 to mediate silencing of endogenous retrotransposons
TNRC18 engages H3K9me3 to mediate silencing of endogenous retrotransposons
Trinucleotide-repeat-containing 18 (TNRC18), which has poorly understood functions, is now identified as an H3K9me3-specific reader that silences endogenous retroviruses.
- Shuai Zhao
- , Jiuwei Lu
- & Gang Greg Wang
-
News & Views |
 Viruses use RNA decoys to thwart CRISPR defences
Viruses use RNA decoys to thwart CRISPR defences
Bacteria and archaea are microorganisms that often use RNA-guided defences called CRISPR to destroy the genomes of viruses that infect them. It now emerges that viruses make RNAs that act as mimics to divert such defences.
- Carolyn Kraus
- & Erik J. Sontheimer
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin compartmentalization regulates the response to DNA damage
Chromatin compartmentalization regulates the response to DNA damage
After the production of double-stranded breaks in mammalian cells, ATM drives the formation of the D compartment, which regulates DNA damage-responsive genes, through the clustering of damaged topologically associating domains, with a mechanism that is consistent with polymer–polymer phase separation.
- Coline Arnould
- , Vincent Rocher
- & Gaëlle Legube
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cell division
- Chromatin
- Chromosomes
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- DNA damage and repair
- DNA metabolism
- DNA recombination
- DNA replication
- Epigenetics
- Non-coding RNAs
- Nuclear organization
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- Riboswitches
- Ribozymes
- RNA metabolism
- RNAi
- Single-molecule biophysics
- Transcription
- Transcriptomics
- Translation
- Transposition

 Ligand efficacy modulates conformational dynamics of the µ-opioid receptor
Ligand efficacy modulates conformational dynamics of the µ-opioid receptor