Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cancer lineage-specific regulation of YAP responsive elements revealed through large-scale functional epigenomic screens
Cancer lineage-specific regulation of YAP responsive elements revealed through large-scale functional epigenomic screens
YAP activation is a key driver in both malignant pleural mesothelioma and uveal melanoma through engagement of different regulatory elements. Here, the authors use functional epigenomic analyses to reveal lineage-specific YAP-dependent cistrome.
- Inês A. M. Barbosa
- , Rajaraman Gopalakrishnan
- & Giorgio G. Galli
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic BH3 profiling identifies pro-apoptotic drug combinations for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Dynamic BH3 profiling identifies pro-apoptotic drug combinations for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive malignancy with few effective treatment options available. Here, the authors use dynamic BH3 profiling to measure drug-induced mitochondrial priming and identify AZD8055 and navitoclax as a pro-apoptotic drug combination in ex vivo and preclinical MPM models.
- Danielle S. Potter
- , Ruochen Du
- & Anthony Letai
-
Article
| Open Access Hand2 delineates mesothelium progenitors and is reactivated in mesothelioma
Hand2 delineates mesothelium progenitors and is reactivated in mesothelioma
The mesothelium supports homeostasis and regeneration, yet its development origins remain unclear. Here, the authors uncovered the earliest mesothelium progenitor cells in zebrafish, linking Hand2 gene function to mesothelium formation and its re-activation to mesothelioma tumors.
- Karin D. Prummel
- , Helena L. Crowell
- & Christian Mosimann
-
Article
| Open Access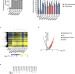 The pathogenesis of mesothelioma is driven by a dysregulated translatome
The pathogenesis of mesothelioma is driven by a dysregulated translatome
Treating malignant pleural mesothelioma (MpM) is challenging due to a lack of druggable genes, but other molecular features could be clinically useful. Here the authors profile mRNA translation dysregulation in MpM cell lines using polysome profiling, and identify mTORC1 and 2 as potential pharmacological targets.
- Stefano Grosso
- , Alberto Marini
- & Anne E. Willis
-
Comment
| Open Access The therapeutic implications of the genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma
The therapeutic implications of the genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Delineation of the genomic complexities of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) has lagged behind other malignancies. Zhang et al. meaningfully add to our understanding of MPM, and their findings emphasize the need to combine drug development efforts with appropriate predictive biomarkers.
- Marjorie G. Zauderer
-
Article
| Open Access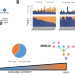 Clonal architecture in mesothelioma is prognostic and shapes the tumour microenvironment
Clonal architecture in mesothelioma is prognostic and shapes the tumour microenvironment
The impact of intratumour heterogeneity on immune surveillance and clinical outcomes has not been adequately explored in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). Here the authors analyse the influence of evolution on the survival and immune landscape of MPM patients using multi-region sequencing data.
- Min Zhang
- , Jin-Li Luo
- & Dean A. Fennell
-
Article
| Open Access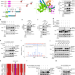 Monoubiquitination of ASXLs controls the deubiquitinase activity of the tumor suppressor BAP1
Monoubiquitination of ASXLs controls the deubiquitinase activity of the tumor suppressor BAP1
Additional sex combs-like (ASXLs) stimulate BAP1 deubiquitinase activity to induce tumor suppression, but how these complexes work in coordination in vivo is unclear. Here, the authors show the mutually reinforcing roles of BAP1 and ASXLs such that BAP1 promotes DEUBAD monoubiquitination of ASXL2, which in turn stimulates BAP1 DUB activity.
- Salima Daou
- , Haithem Barbour
- & El Bachir Affar
-
Article
| Open Access Human CD26high T cells elicit tumor immunity against multiple malignancies via enhanced migration and persistence
Human CD26high T cells elicit tumor immunity against multiple malignancies via enhanced migration and persistence
The role of human CD4+ T cell subsets in cancer immunotherapy is still unclear. Here, the authors show that CD26 identifies three CD4+ T cell subsets with distinct immunological properties in both healthy individuals and cancer patients.
- Stefanie R. Bailey
- , Michelle H. Nelson
- & Chrystal M. Paulos
-
Article
| Open Access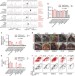 Mutant KRAS promotes malignant pleural effusion formation
Mutant KRAS promotes malignant pleural effusion formation
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a lethal condition associated with various cancers. Here, the authors show that cancer cells withKRASmutations promote MPE by recruiting myeloid cells via CCL2 signalling and that pharmaceutical targeting of KRAS results in reduced MPE incidence and volume in mouse models.
- Theodora Agalioti
- , Anastasios D. Giannou
- & Georgios T. Stathopoulos

 Development of mesothelioma-specific oncolytic immunotherapy enabled by immunopeptidomics of murine and human mesothelioma tumors
Development of mesothelioma-specific oncolytic immunotherapy enabled by immunopeptidomics of murine and human mesothelioma tumors