Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting mortality from AI cardiac volumes mass and coronary calcium on chest computed tomography
Predicting mortality from AI cardiac volumes mass and coronary calcium on chest computed tomography
Chest computed tomography (CT) is one of the most common diagnostic tests. Here, the authors combine two AI models to measure from CT coronary artery calcium, left ventricular mass index, and left and right atrial and ventricular volumes, and show their association with cardiovascular mortality.
- Robert J. H. Miller
- , Aditya Killekar
- & Piotr J. Slomka
-
Comment
| Open Access Population imaging cerebellar growth for personalized neuroscience
Population imaging cerebellar growth for personalized neuroscience
Growth chart studies of the human cerebellum, which is increasingly recognized as pivotal for cognitive development, are rare. Gaiser and colleagues utilized population-level neuroimaging to unveil cerebellar growth charts from childhood to adolescence, offering insights into brain development.
- Zi-Xuan Zhou
- & Xi-Nian Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling large-scale screening of Barrett’s esophagus using weakly supervised deep learning in histopathology
Enabling large-scale screening of Barrett’s esophagus using weakly supervised deep learning in histopathology
Diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus depends on pathologist assessment of stained slides. Here, the authors utilise a deep learning approach to prioritize potential cases using diagnostic labels in two datasets, with the aim to improve Barrett’s screening capacity.
- Kenza Bouzid
- , Harshita Sharma
- & Javier Alvarez-Valle
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing the fairness of AI prediction models by Quasi-Pareto improvement among heterogeneous thyroid nodule population
Enhancing the fairness of AI prediction models by Quasi-Pareto improvement among heterogeneous thyroid nodule population
Artificial Intelligence (AI) models for medical diagnosis often face challenges of generalizability and fairness. Here, the authors show that the Quasi-Pareto Improvement approach is widely applicable to improving AI models among less-prevalent subgroups, promoting equitable healthcare outcomes.
- Siqiong Yao
- , Fang Dai
- & Hui Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Empirical data drift detection experiments on real-world medical imaging data
Empirical data drift detection experiments on real-world medical imaging data
Data drift is the systematic change in the underlying distribution of input features in prediction models, and can cause deterioration in model performance. Here, the authors highlight the importance of detecting data drift in clinical settings and evaluate methods for detecting drift in medical image data.
- Ali Kore
- , Elyar Abbasi Bavil
- & Mohamed Abdalla
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Manual processes to produce ocular prostheses are time-consuming and yield varying quality. Here, authors present an automatic digital end-to-end process for custom ocular prostheses. It creates shape and appearance from image data of an OCT device and produces them using a full-colour 3D printer.
- Johann Reinhard
- , Philipp Urban
- & Mandeep S. Sagoo
-
Article
| Open Access A deep-learning-based framework for identifying and localizing multiple abnormalities and assessing cardiomegaly in chest X-ray
A deep-learning-based framework for identifying and localizing multiple abnormalities and assessing cardiomegaly in chest X-ray
Accurate localization of abnormalities is crucial in the interpretation of chest X-rays. Here the authors present a deep learning framework for simultaneous localization of 14 thoracic abnormalities and calculation of cardiothoracic ratio, based on large X-ray dataset with bounding boxes created via a human-in-the-loop approach.
- Weijie Fan
- , Yi Yang
- & Dong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A multicenter clinical AI system study for detection and diagnosis of focal liver lesions
A multicenter clinical AI system study for detection and diagnosis of focal liver lesions
Early detection and accurate diagnosis of focal liver lesions are crucial for effective treatment and prognosis. Here, the authors present a fully automated diagnostic system that leverages multi-phase CT scans and clinical features, for diagnosing liver lesions.
- Hanning Ying
- , Xiaoqing Liu
- & Xiujun Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Segment anything in medical images
Segment anything in medical images
Segmentation is an important fundamental task in medical image analysis. Here the authors show a deep learning model for efficient and accurate segmentation across a wide range of medical image modalities and anatomies.
- Jun Ma
- , Yuting He
- & Bo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Many diseases can display distinct brain imaging phenotypes across individuals, potentially reflecting disease subtypes. However, biological interpretability is limited if the derived subtypes are not associated with genetic drivers or susceptibility factors. Here, the authors describe a deep-learning method that links imaging phenotypes with genetic factors, thereby conferring genetic correlations to the disease subtypes.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Junhao Wen
- & Christos Davatzikos
-
Article
| Open Access A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
Real-time MRI provides accurate navigation and targeting for neurological interventions. Here, the authors propose a deep unrolled neural network for MRI reconstruction that enables real-time monitoring of remote-controlled brain interventions and can be integrated into diagnostic scanners.
- Zhao He
- , Ya-Nan Zhu
- & Yuan Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of accelerometer-based sedentary time and physical activity on DEXA-measured fat mass in 6059 children
Effects of accelerometer-based sedentary time and physical activity on DEXA-measured fat mass in 6059 children
Childhood obesity remains a global epidemic. Here, using objective measurements, the authors show that sedentary time increased from 6 h/day in childhood to 9 h/day in young adulthood, and was cumulatively associated with increased total and trunk fat mass. Both light or moderate-to-vigorous physical activity similarly partly reversed risk.
- Andrew O. Agbaje
- , Wei Perng
- & Tomi-Pekka Tuomainen
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Changes of left ventricular structure are used to predict morbidity and mortality in cardiovascular diseases. Here the authors conducted a study using advanced deep learning technology to analyze left ventricular regional wall thickness (LVRWT) in a large population, identifying 72 significant genetic loci linked to LVRWT traits.
- Caibo Ning
- , Linyun Fan
- & Xiaoping Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Temporalis muscle thickness is a promising marker of lean muscle mass but has had limited utility due to its unknown normal growth trajectory and lack of standardized measurement. Here, the authors develop an automated deep learning pipeline to accurately measure temporalis muscle thickness from routine brain magnetic resonance imaging.
- Anna Zapaishchykova
- , Kevin X. Liu
- & Benjamin H. Kann
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent surgical workflow recognition for endoscopic submucosal dissection with real-time animal study
Intelligent surgical workflow recognition for endoscopic submucosal dissection with real-time animal study
AI-enabled cognitive assistance for therapeutic procedures has rarely been pre-clinically validated. Here, the authors propose an intelligent surgical workflow recognition suit AI-Endo for endoscopic submucosal dissection, extensively validated on external and animal trial datasets.
- Jianfeng Cao
- , Hon-Chi Yip
- & Qi Dou
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic correction of performance drift under acquisition shift in medical image classification
Automatic correction of performance drift under acquisition shift in medical image classification
Automatic correction of performance drift caused by changes in image acquisition is key for safe AI deployment. Here, the authors present a solution that restores the expected clinical performance of image classification systems in breast screening and histopathology.
- Mélanie Roschewitz
- , Galvin Khara
- & Ben Glocker
-
Article
| Open Access Improving model fairness in image-based computer-aided diagnosis
Improving model fairness in image-based computer-aided diagnosis
Deep learning models can reflect and amplify human bias, potentially resulting inaccurate missed diagnoses. Here, the authors show that by leveraging the marginal pairwise equal opportunity, their model reduces bias in medical image classification by over 35% compared to baseline models, with minimal impact on AUC values.
- Mingquan Lin
- , Tianhao Li
- & Yifan Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Assessment of different iron compounds in the living brain remains an open challenge. Here, the authors present a magnetic resonance imaging method which is sensitive to the iron homeostasis in the brain, and increases the detection of tumor tissue.
- Shir Filo
- , Rona Shaharabani
- & Aviv A. Mezer
-
Article
| Open Access Mining multi-center heterogeneous medical data with distributed synthetic learning
Mining multi-center heterogeneous medical data with distributed synthetic learning
Here the authors present Distributed Synthetic Learning, a system that addresses data privacy, isolated data islands, and heterogeneity concerns in healthcare analytics by learning to generate state-of-the-art synthetic data for downstream tasks.
- Qi Chang
- , Zhennan Yan
- & Dimitris N. Metaxas
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: The pitfalls of interpreting hyperintense FLAIR signal as lymph outside the human brain
Reply to: The pitfalls of interpreting hyperintense FLAIR signal as lymph outside the human brain
- Mehmet Sait Albayram
- , Garrett Smith
- & Onder Albayram
-
Article
| Open Access Bone marrow adiposity modulation after long duration spaceflight in astronauts
Bone marrow adiposity modulation after long duration spaceflight in astronauts
Bone marrow adiposity is linked to disease, and it is unknown how it is modulated during space travel. Here, the authors show that astronauts returning from ISS missions had decreased marrow fat and increased hematopoiesis and bone formation, suggesting that adipose reserves in the bone marrow might be used as an energy source to counteract anemia and bone loss associated with space flight.
- Tammy Liu
- , Gerd Melkus
- & Guy Trudel
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting shortcut learning for fair medical AI using shortcut testing
Detecting shortcut learning for fair medical AI using shortcut testing
Diagnosing shortcut learning in clinical models is difficult, as sensitive attributes may be causally linked with disease. Using multitask learning, the authors propose a method to directly test for the presence of shortcut learning in clinical ML systems.
- Alexander Brown
- , Nenad Tomasev
- & Jessica Schrouff
-
Review Article
| Open Access Radiochemistry for positron emission tomography
Radiochemistry for positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is widely used to diagnose and monitor different disease states and interest in the technique has led to the demand for the development of new method for radiolabelling. Here the authors review the recent progress in the development of new PET probes.
- Jian Rong
- , Ahmed Haider
- & Steven H. Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning to estimate lung disease mortality from chest radiographs
Deep learning to estimate lung disease mortality from chest radiographs
Risk assessment of lung disease mortality is currently limited. Here, authors show that deep learning can estimate lung disease mortality from a chest x-ray beyond risk factors, which may help to identify individuals at risk in screening and cancer populations.
- Jakob Weiss
- , Vineet K. Raghu
- & Hugo J.W.L. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access Interstitial lung disease diagnosis and prognosis using an AI system integrating longitudinal data
Interstitial lung disease diagnosis and prognosis using an AI system integrating longitudinal data
Accurate diagnosis of interstitial lung disease subtypes and prediction of patient survival rates remains challenging. Here, the authors develop AI algorithms to combine patient’s clinical history and longitudinal CT images to help clinicians diagnose and classify subtypes and dynamically predict disease progression and prognosis.
- Xueyan Mei
- , Zelong Liu
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Interoperable slide microscopy viewer and annotation tool for imaging data science and computational pathology
Interoperable slide microscopy viewer and annotation tool for imaging data science and computational pathology
There is a lack of standardisation in slide microscopy imaging data. Here the authors report Slim, an open-source, web-based slide microscopy viewer implementing the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard to achieve interoperability with a range of existing medical imaging systems.
- Chris Gorman
- , Davide Punzo
- & Markus D. Herrmann
-
Article
| Open Access A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature
A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature
The authors present a wearable photoacoustic patch, which integrates laser diodes and piezoelectric transducers for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and temperature in deep tissues.
- Xiaoxiang Gao
- , Xiangjun Chen
- & Sheng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Federated learning enables big data for rare cancer boundary detection
Federated learning enables big data for rare cancer boundary detection
Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here, the authors present the largest FL study to-date to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for glioblastoma.
- Sarthak Pati
- , Ujjwal Baid
- & Spyridon Bakas
-
Comment
| Open Access Developing medical imaging AI for emerging infectious diseases
Developing medical imaging AI for emerging infectious diseases
Very few of the COVID-19 ML models were fit for deployment in real-world settings. In this Comment, Huang et al. discuss the main steps required to develop clinically useful models in the context of an emerging infectious disease.
- Shih-Cheng Huang
- , Akshay S. Chaudhari
- & Matthew P. Lungren
-
Article
| Open Access Using domain knowledge for robust and generalizable deep learning-based CT-free PET attenuation and scatter correction
Using domain knowledge for robust and generalizable deep learning-based CT-free PET attenuation and scatter correction
Deep learning-based methods have been proposed to substitute CT-based PET attenuation and scatter correction to achieve CT-free PET imaging. Here, the authors present a simple way to integrate domain knowledge in deep learning for CT-free PET imaging.
- Rui Guo
- , Song Xue
- & Kuangyu Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Emergency triage of brain computed tomography via anomaly detection with a deep generative model
Emergency triage of brain computed tomography via anomaly detection with a deep generative model
Triage is essential for the early diagnosis and reporting of emergency patients in the emergency department. Here, the authors develop an anomaly detection algorithm with a deep generative model that reprioritizes radiology worklists and provides lesion attention maps for brain CT images with critical findings.
- Seungjun Lee
- , Boryeong Jeong
- & Namkug Kim
-
Article
| Open Access The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
International challenges have become the de facto standard for comparative assessment of image analysis algorithms. Here, the authors present the results of a biomedical image segmentation challenge, showing that a method capable of performing well on multiple tasks will generalize well to a previously unseen task.
- Michela Antonelli
- , Annika Reinke
- & M. Jorge Cardoso
-
Article
| Open Access Self-evolving vision transformer for chest X-ray diagnosis through knowledge distillation
Self-evolving vision transformer for chest X-ray diagnosis through knowledge distillation
Although deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis systems have recently achieved expert level performance, developing a robust model requires large, high-quality data with annotations. Here, the authors present a framework which can improve the performance of vision transformer simultaneously with self-supervision and self-training.
- Sangjoon Park
- , Gwanghyun Kim
- & Jong Chul Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Augmented ultrasonography with implanted CMOS electronic motes
Augmented ultrasonography with implanted CMOS electronic motes
Ultrasound has had tremendous success in medical imaging. Here, Zhang et al demonstrate a batteryless implantable CMOS mote, to further augment the potential of ultrasound, providing additional information via the backscattering of the acoustic waves used in ultrasound imaging.
- Yihan Zhang
- , Prashant Muthuraman
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely translating computed tomography diagnosis accuracy into therapeutic intervention by a carbon-iodine conjugated polymer
Precisely translating computed tomography diagnosis accuracy into therapeutic intervention by a carbon-iodine conjugated polymer
Poly(diiododiacetylene)—PIDA—contains iodine atoms, which are commonly found in computed tomography contrast agents. Here, the authors find that PIDA can function as a contrast agent and can also be used as a visual marker to delineate tumour margins.
- Mingming Yin
- , Xiaoming Liu
- & Liang Luo
-
Article
| Open Access A fully automatic AI system for tooth and alveolar bone segmentation from cone-beam CT images
A fully automatic AI system for tooth and alveolar bone segmentation from cone-beam CT images
Accurate delineation of individual teeth and alveolar bones from dental cone-beam CT images is an essential step in digital dentistry for precision dental healthcare. Here, the authors present a deep learning system for efficient, precise, and fully automatic segmentation of real-patient CBCT images presenting highly variable appearances.
- Zhiming Cui
- , Yu Fang
- & Dinggang Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Non-metallic T2-MRI agents based on conjugated polymers
Non-metallic T2-MRI agents based on conjugated polymers
The toxicity of heavy metals for MRI contrast agents is an issue. Here, the authors report on the development of conjugated polymers nanoparticles based on paramagnetic polypyrrole to generate T2 MRI contrast effects by changing the interactions between polarons and water protons.
- Qinrui Lin
- , Yuhong Yang
- & Zhengzhong Shao
-
Article
| Open Access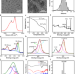 Carbonized paramagnetic complexes of Mn (II) as contrast agents for precise magnetic resonance imaging of sub-millimeter-sized orthotopic tumors
Carbonized paramagnetic complexes of Mn (II) as contrast agents for precise magnetic resonance imaging of sub-millimeter-sized orthotopic tumors
Improving the imaging of cancer may enhance the treatment of patients, Here, the authors develop a Mn(II) based nanoparticle contrast agent for MRI imaging and show that the nanoparticles can cross the brain barrier and image glioma cells.
- Ruixue Qin
- , Shi Li
- & Hongmin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Here the authors develop a method for accurate auto-labelling of CXR images from large public datasets based on quantitative probability-of similarity to an explainable AI model. The labels can be used to fine-tune the original model through iterative re-training.
- Doyun Kim
- , Joowon Chung
- & Synho Do
-
Article
| Open Access Active label cleaning for improved dataset quality under resource constraints
Active label cleaning for improved dataset quality under resource constraints
High quality labels are important for model performance, evaluation and selection in medical imaging. As manual labelling is time-consuming and costly, the authors explore and benchmark various resource-effective methods for improving dataset quality.
- Mélanie Bernhardt
- , Daniel C. Castro
- & Ozan Oktay
-
Article
| Open Access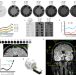 Non-invasive MR imaging of human brain lymphatic networks with connections to cervical lymph nodes
Non-invasive MR imaging of human brain lymphatic networks with connections to cervical lymph nodes
Studies in animal models have visualized drainage of interstitial or cerebrospinal fluid via lymphatic vessels, but there is limited data on in humans. Here, the authors non-invasively visualize lymphatic structures in the human brain, including evidence of lymphatic flow from cranial nerves to cervical lymph nodes, and differences by age and sex, without use of contrast agents.
- Mehmet Sait Albayram
- , Garrett Smith
- & Onder Albayram
-
Article
| Open Access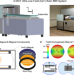 A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low cost MRI scanner may have the potential to meet clinical needs at point of care or in low and middle income countries. Here the authors describe a low cost 0.055 Tesla MRI scanner that operates using a standard AC power outlet, and demonstrate its preliminary feasibility in diagnosing brain tumor and stroke.
- Yilong Liu
- , Alex T. L. Leong
- & Ed X. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A machine and human reader study on AI diagnosis model safety under attacks of adversarial images
A machine and human reader study on AI diagnosis model safety under attacks of adversarial images
While active efforts are advancing medical AI model development and clinical translation, safety issues of medical AI models have emerged. Here, the authors investigate the effects on an AI model and on human experts of potential fake/adversarial images for breast cancer diagnosis.
- Qianwei Zhou
- , Margarita Zuley
- & Shandong Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
Alzheimer’s disease is heterogeneous in its neuroimaging and clinical phenotypes. Here the authors present a semi-supervised deep learning method, Smile-GAN, to show four neurodegenerative patterns and two progression pathways providing prognostic and clinical information.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Ilya M. Nasrallah
- & Balebail Ashok Raj
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial intelligence system reduces false-positive findings in the interpretation of breast ultrasound exams
Artificial intelligence system reduces false-positive findings in the interpretation of breast ultrasound exams
Ultrasound is an important imaging modality for the detection and characterization of breast cancer, but it has been noted to have high false-positive rates. Here, the authors present an artificial intelligence system that achieves radiologist-level accuracy in identifying breast cancer in ultrasound imaging.
- Yiqiu Shen
- , Farah E. Shamout
- & Krzysztof J. Geras
-
Article
| Open Access Automated bone mineral density prediction and fracture risk assessment using plain radiographs via deep learning
Automated bone mineral density prediction and fracture risk assessment using plain radiographs via deep learning
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool are recommended tools for osteoporotic fracture risk evaluation, but are underutilized. Here, the authors present an opportunistic tool to identify fractures, predict bone mineral density and evaluate fracture risk using plain pelvis and lumbar spine radiographs.
- Chen-I Hsieh
- , Kang Zheng
- & Chang-Fu Kuo
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based transformation of H&E stained tissues into special stains
Deep learning-based transformation of H&E stained tissues into special stains
Performing multiple histological stains on a biopsy can be costly and time consuming. Here the authors present a method for the digital transformation of H&E stained tissue into special stains (e.g., PAS, Masson’s Trichrome and Jones silver stain), and demonstrate that it improves diagnoses over the use of H&E only.
- Kevin de Haan
- , Yijie Zhang
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access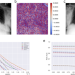 Advancing diagnostic performance and clinical usability of neural networks via adversarial training and dual batch normalization
Advancing diagnostic performance and clinical usability of neural networks via adversarial training and dual batch normalization
Unmasking the decision making process of machine learning models is essential for implementing diagnostic support systems in clinical practice. Here, the authors demonstrate that adversarially trained models can significantly enhance the usability of pathology detection as compared to their standard counterparts.
- Tianyu Han
- , Sven Nebelung
- & Daniel Truhn
-
Article
| Open Access Real-world stress resilience is associated with the responsivity of the locus coeruleus
Real-world stress resilience is associated with the responsivity of the locus coeruleus
Individuals vary considerably in how they are affected by stress. Here, the authors show that the severity of psychopathological symptoms triggered by prolonged real-life stress relate to fMRI-measured responsivity of the human brainstem arousal system and associated pupil responses.
- Marcus Grueschow
- , Nico Stenz
- & Birgit Kleim

 Flexible large-area ultrasound arrays for medical applications made using embossed polymer structures
Flexible large-area ultrasound arrays for medical applications made using embossed polymer structures