Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning enhanced Rydberg multifrequency microwave recognition
Deep learning enhanced Rydberg multifrequency microwave recognition
Rydberg atoms are sensitive to microwave signals and hence can be used to detect them. Here the authors demonstrate a Rydberg receiver enhanced by deep learning, Rydberg atoms acting as antennae, to receive, extract, and decode the multi-frequency microwave signal effectively.
- Zong-Kai Liu
- , Li-Hua Zhang
- & Bao-Sen Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Using high-resolution contact networks to evaluate SARS-CoV-2 transmission and control in large-scale multi-day events
Using high-resolution contact networks to evaluate SARS-CoV-2 transmission and control in large-scale multi-day events
Here, the authors simulate COVID-19 outbreaks on an empirical contact network derived from digital contact data collected on cruise ships. They model impacts of different control measures and find that combinations of measures, particularly vaccination and rapid antigen testing, are important for mitigating outbreaks.
- Rachael Pung
- , Josh A. Firth
- & Adam J. Kucharski
-
Article
| Open Access Introducing principles of synaptic integration in the optimization of deep neural networks
Introducing principles of synaptic integration in the optimization of deep neural networks
Tasks involving continual learning and adaptation to real-time scenarios remain challenging for artificial neural networks in contrast to real brain. The authors propose here a brain-inspired optimizer based on mechanisms of synaptic integration and strength regulation for improved performance of both artificial and spiking neural networks.
- Giorgia Dellaferrera
- , Stanisław Woźniak
- & Evangelos Eleftheriou
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Here the authors develop a method for accurate auto-labelling of CXR images from large public datasets based on quantitative probability-of similarity to an explainable AI model. The labels can be used to fine-tune the original model through iterative re-training.
- Doyun Kim
- , Joowon Chung
- & Synho Do
-
Article
| Open Access Group testing via hypergraph factorization applied to COVID-19
Group testing via hypergraph factorization applied to COVID-19
This paper proposes HYPER, a method for screening more people using fewer tests by testing pools formed via hypergraph factorization. HYPER is not only efficient but is also simple to implement, flexible, and has maximally balanced pools.
- David Hong
- , Rounak Dey
- & Edgar Dobriban
-
Article
| Open Access Immunosuppressive niche engineering at the onset of human colorectal cancer
Immunosuppressive niche engineering at the onset of human colorectal cancer
Integration of mathematical modeling, ecological analyses of patient biopsies, and neoantigen heterogeneity suggests recruitment of immunosuppressive cells is key to initializing transformation from adenoma to carcinoma in human colorectal cancer.
- Chandler D. Gatenbee
- , Ann-Marie Baker
- & Alexander R. A. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access The world-wide waste web
The world-wide waste web
The 2001–2019 web of international waste trade is investigated, allowing the identification of countries at threat of improper handling and disposal of waste. Chemical tracers are used to identify the environmental impact of waste in these countries.
- Johann H. Martínez
- , Sergi Romero
- & Ernesto Estrada
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of ranking
Dynamics of ranking
Ranking lists are relevant to various areas of nature and society, however their evolution with the elements changing rank in time remained unexplored. The authors uncover a mechanism of ranking dynamics induced by the flux governing the arrival of new elements in the list, for improved predictability of ranking models.
- Gerardo Iñiguez
- , Carlos Pineda
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access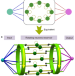 Rotating neurons for all-analog implementation of cyclic reservoir computing
Rotating neurons for all-analog implementation of cyclic reservoir computing
Reservoir computing has demonstrated high-level performance, however efficient hardware implementations demand an architecture with minimum system complexity. The authors propose a rotating neuron-based architecture for physically implementing all-analog resource efficient reservoir computing system.
- Xiangpeng Liang
- , Yanan Zhong
- & Huaqiang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access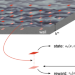 Scientific multi-agent reinforcement learning for wall-models of turbulent flows
Scientific multi-agent reinforcement learning for wall-models of turbulent flows
Simulations of turbulent flows are relevant for aerodynamic and weather modeling, however challenging to capture flow dynamics in the near wall region. To solve this problem, the authors propose a multi-agent reinforcement learning approach to discover wall models for large-eddy simulations.
- H. Jane Bae
- & Petros Koumoutsakos
-
Article
| Open Access Agent-based modelling of reactive vaccination of workplaces and schools against COVID-19
Agent-based modelling of reactive vaccination of workplaces and schools against COVID-19
The authors use an agent-based model to investigate the potential of reactive vaccination strategies for COVID-19 outbreak mitigation. They find that distributing vaccines in schools and workplaces where cases are detected is more impactful than non-reactive strategies in a wide range of epidemic scenarios.
- Benjamin Faucher
- , Rania Assab
- & Chiara Poletto
-
Article
| Open Access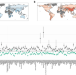 Population-scale dietary interests during the COVID-19 pandemic
Population-scale dietary interests during the COVID-19 pandemic
The SARS-CoV-2 virus has altered people’s lives around the world, not only through the disease it causes, but also through unprecedented restrictions. Here the authors document population-wide shifts in dietary interests in 18 countries in 2020, as revealed through time series of Google search volumes.
- Kristina Gligorić
- , Arnaud Chiolero
- & Robert West
-
Perspective
| Open Access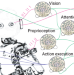 Embodied neuromorphic intelligence
Embodied neuromorphic intelligence
A grand challenge in robotics is realising intelligent agents capable of autonomous interaction with the environment. In this Perspective, the authors discuss the potential, challenges and future direction of research aimed at demonstrating embodied intelligent robotics via neuromorphic technology.
- Chiara Bartolozzi
- , Giacomo Indiveri
- & Elisa Donati
-
Article
| Open Access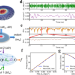 Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Deep learning has an increasing impact to assist research. Here, authors show that a dynamical neural network, trained on a minimal amount of data, can predict the behaviour of spintronic devices with high accuracy and an extremely efficient simulation time.
- Xing Chen
- , Flavio Abreu Araujo
- & Damien Querlioz
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
The targeted discovery of molecules with specific structural and chemical properties is an open challenge in computational chemistry. Here, the authors propose a conditional generative neural network for the inverse design of 3d molecular structures.
- Niklas W. A. Gebauer
- , Michael Gastegger
- & Kristof T. Schütt
-
Article
| Open Access Density of states prediction for materials discovery via contrastive learning from probabilistic embeddings
Density of states prediction for materials discovery via contrastive learning from probabilistic embeddings
Electrons and phonons give rise to important properties of materials. The machine learning framework Mat2Spec vastly accelerates their computational characterization, enabling discovery of materials for thermoelectrics and solar energy technologies.
- Shufeng Kong
- , Francesco Ricci
- & John M. Gregoire
-
Article
| Open Access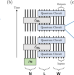 Quantum algorithmic measurement
Quantum algorithmic measurement
Applying the language of computational complexity to study real-world experiments requires a rigorous framework. Here, the authors provide such a framework and establish that there can be an exponential savings in resources if an experimentalist can entangle apparatuses with experimental samples.
- Dorit Aharonov
- , Jordan Cotler
- & Xiao-Liang Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven modeling and prediction of non-linearizable dynamics via spectral submanifolds
Data-driven modeling and prediction of non-linearizable dynamics via spectral submanifolds
Current data-driven modelling techniques perform reliably on linear systems or on those that can be linearized. Cenedese et al. develop a data-based reduced modeling method for non-linear, high-dimensional physical systems. Their models reconstruct and predict the dynamics of the full physical system.
- Mattia Cenedese
- , Joar Axås
- & George Haller
-
Article
| Open Access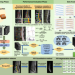 Deep learning-based high-accuracy quantitation for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration from MRI
Deep learning-based high-accuracy quantitation for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration from MRI
Globally, as a major public health problem, low back pain has been the leading cause of disability worldwide for the past 30 years. Here, the authors propose a segmentation network and a quantitative method lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration assessment.
- Hua-Dong Zheng
- , Yue-Li Sun
- & Yong-Jun Wang
-
Perspective
| Open Access Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
Animal ecologists are increasingly limited by constraints in data processing. Here, Tuia and colleagues discuss how collaboration between ecologists and data scientists can harness machine learning to capitalize on the data generated from technological advances and lead to novel modeling approaches.
- Devis Tuia
- , Benjamin Kellenberger
- & Tanya Berger-Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Representing individual electronic states for machine learning GW band structures of 2D materials
Representing individual electronic states for machine learning GW band structures of 2D materials
The study introduces novel methods for representing electronic states as input to machine learning models, which is used to learn high-fidelity band structures of two-dimensional materials from low- fidelity input.
- Nikolaj Rørbæk Knøsgaard
- & Kristian Sommer Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access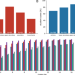 Assessing the impact of SARS-CoV-2 prevention measures in Austrian schools using agent-based simulations and cluster tracing data
Assessing the impact of SARS-CoV-2 prevention measures in Austrian schools using agent-based simulations and cluster tracing data
How to safely maintain open schools during a pandemic is still controversial. Here, the authors aim to identify those measures that effectively control the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in Austrian schools, with an agent-based mathematical model.
- Jana Lasser
- , Johannes Sorger
- & Peter Klimek
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction data are identifiable even across long periods of time
Interaction data are identifiable even across long periods of time
Large amounts of interaction data are collected by messaging apps, mobile phone carriers, and social media. Creţu et al. propose a behavioral profiling attack model and show that the stability of people’s interaction networks over time can allow individuals to be re-identified in interaction datasets.
- Ana-Maria Creţu
- , Federico Monti
- & Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye
-
Article
| Open Access The shape of memory in temporal networks
The shape of memory in temporal networks
The evolution of networks with structure changing in time is dependent on their past states and relevant to diffusion and spreading processes. The authors show that temporal network’s memory is described by multidimensional patterns at a microscopic scale, and cannot be reduced to a scalar quantity.
- Oliver E. Williams
- , Lucas Lacasa
- & Vito Latora
-
Article
| Open Access Self-directed online machine learning for topology optimization
Self-directed online machine learning for topology optimization
Topology optimization, relevant for materials design and engineering, requires solving of challenging high-dimensional problems. The authors introduce a self-directed online learning approach, as embedding of deep learning in optimization methods, that accelerates the training and optimization processes.
- Changyu Deng
- , Yizhou Wang
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open AccessEmergent Sasaki-Einstein geometry and AdS/CFT
It is an outstanding question in quantum gravity how to describe the emergence of classical spacetime geometry from a quantum state. Here, the authors propose a construction in the context of the gauge/gravity correspondence, producing the classical geometry from a quantum state at the boundary of spacetime.
- Robert J. Berman
- , Tristan C. Collins
- & Daniel Persson
-
Review Article
| Open Access Synthetic DNA applications in information technology
Synthetic DNA applications in information technology
Synthetic DNA is the basis for promising technologies in data storage, barcoding, computing 62 and sercurity. In this review, the authors provide an overview of the field and its future.
- Linda C. Meiser
- , Bichlien H. Nguyen
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access AI Pontryagin or how artificial neural networks learn to control dynamical systems
AI Pontryagin or how artificial neural networks learn to control dynamical systems
Optimal control of complex dynamical systems can be challenging due to cost constraints and analytical intractability. The authors propose a machine-learning-based control framework able to learn control signals and force complex high-dimensional dynamical systems towards a desired target state.
- Lucas Böttcher
- , Nino Antulov-Fantulin
- & Thomas Asikis
-
Comment
| Open Access Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Among the existing machine learning frameworks, reservoir computing demonstrates fast and low-cost training, and its suitability for implementation in various physical systems. This Comment reports on how aspects of reservoir computing can be applied to classical forecasting methods to accelerate the learning process, and highlights a new approach that makes the hardware implementation of traditional machine learning algorithms practicable in electronic and photonic systems.
- Lina Jaurigue
- & Kathy Lüdge
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access On the difficulty of achieving Differential Privacy in practice: user-level guarantees in aggregate location data
On the difficulty of achieving Differential Privacy in practice: user-level guarantees in aggregate location data
- Florimond Houssiau
- , Luc Rocher
- & Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-inspired global-local learning incorporated with neuromorphic computing
Brain-inspired global-local learning incorporated with neuromorphic computing
Global and local learning represent two distinct approaches to artificial intelligence. In this manuscript, Wu et al present a hybrid learning strategy, drawing from elements of both approaches, and implement it on a co-designed neuromorphic platform.
- Yujie Wu
- , Rong Zhao
- & Luping Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Emulator-based Bayesian optimization for efficient multi-objective calibration of an individual-based model of malaria
Emulator-based Bayesian optimization for efficient multi-objective calibration of an individual-based model of malaria
Individual-based models have become important tools in the global battle against infectious diseases, yet model complexity can make calibration challenging. Here, the authors propose a Bayesian optimization framework to calibrate a complex malaria transmission simulator.
- Theresa Reiker
- , Monica Golumbeanu
- & Melissa A. Penny
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of the London Millennium Bridge instability without synchronisation
Emergence of the London Millennium Bridge instability without synchronisation
The pedestrian-induced oscillation of the London Millennium Bridge is considered as an example of emerging synchronisation. Belykh et al. provide an alternative mechanism for emergence of coherent oscillatory bridge dynamics where synchrony is a consequence, not the cause, of the instability.
- Igor Belykh
- , Mateusz Bocian
- & Allan McRobie
-
Article
| Open Access Learning efficient navigation in vortical flow fields
Learning efficient navigation in vortical flow fields
Navigation and trajectory planning in environments with background flow, relevant for robotics, are challenging provided information only on local surrounding. The authors propose a reinforcement learning approach for time-efficient navigation of a swimmer through unsteady two-dimensional flows.
- Peter Gunnarson
- , Ioannis Mandralis
- & John O. Dabiri
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
Alzheimer’s disease is heterogeneous in its neuroimaging and clinical phenotypes. Here the authors present a semi-supervised deep learning method, Smile-GAN, to show four neurodegenerative patterns and two progression pathways providing prognostic and clinical information.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Ilya M. Nasrallah
- & Balebail Ashok Raj
-
Article
| Open Access Learning neural network potentials from experimental data via Differentiable Trajectory Reweighting
Learning neural network potentials from experimental data via Differentiable Trajectory Reweighting
In machine learning approaches relevant for chemical physics and material science, neural network potentials can be trained on the experimental data. The authors propose a training method applying trajectory reweighting instead of direct backpropagation for improved robustness and reduced computational cost.
- Stephan Thaler
- & Julija Zavadlav
-
Article
| Open Access Direct evidence that twisted flux tube emergence creates solar active regions
Direct evidence that twisted flux tube emergence creates solar active regions
Twisted flux tubes are prominent candidates for the progenitors of solar active regions. Here, the authors show a clear signature of the emergence of pre-twisted magnetic flux tubes using magnetic winding, which detects the emerging magnetic topology despite the deformation experienced by the emerging magnetic field.
- D. MacTaggart
- , C. Prior
- & S. L. Guglielmino
-
Article
| Open Access A Deep Gravity model for mobility flows generation
A Deep Gravity model for mobility flows generation
The movements of individuals within and among cities influence critical aspects of our society, such as well-being, the spreading of epidemics, and the quality of the environment. Here, the authors use deep neural networks to discover non-linear relationships between geographical variables and mobility flows.
- Filippo Simini
- , Gianni Barlacchi
- & Luca Pappalardo
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral analysis of climate dynamics with operator-theoretic approaches
Spectral analysis of climate dynamics with operator-theoretic approaches
The Earth’s climate system is highly complex, however it exhibits certain persistent cyclic patterns like the El Niño Southern Oscillation. The authors apply the spectral theory of dynamical systems and data science techniques to extract such coherent modes of climate variability from high-dimensional observational data.
- Gary Froyland
- , Dimitrios Giannakis
- & Joanna Slawinska
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous extraction of millimeter-scale deformation in InSAR time series using deep learning
Autonomous extraction of millimeter-scale deformation in InSAR time series using deep learning
A deep neural network is developed to automatically extract ground deformation from Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar time series. Applied to data over the North Anatolian Fault, the method can detect 2 mm deformation transients and reveals a slow earthquake twice as extensive as previously recognized.
- Bertrand Rouet-Leduc
- , Romain Jolivet
- & Claudia Hulbert
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal prediction of COVID-19 cases using inter- and intra-county proxies of human interactions
Spatiotemporal prediction of COVID-19 cases using inter- and intra-county proxies of human interactions
Measurements of human interaction through proxies such as social connectedness or movement patterns have proved useful for predictive modeling of COVID-19. In this study, the authors develop a spatiotemporal machine learning model to predict county level new cases in the US using a variety of predictive features.
- Behzad Vahedi
- , Morteza Karimzadeh
- & Hamidreza Zoraghein
-
Article
| Open Access Computational design and optimization of electro-physiological sensors
Computational design and optimization of electro-physiological sensors
Though skin-conformable electro-physiological sensors are attractive for epidermal electronics, their optimal design remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a computational design approach for realizing multi-modal electro-physiological sensors that optimizes electrode layout design.
- Aditya Shekhar Nittala
- , Andreas Karrenbauer
- & Jürgen Steimle
-
Article
| Open Access The Tharsis mantle source of depleted shergottites revealed by 90 million impact craters
The Tharsis mantle source of depleted shergottites revealed by 90 million impact craters
The ejection sites of the martian meteorites are still unknown. Here, the authors build a database of 90 million craters and show that Tharsis region is the most likely source of depleted shergottites ejected 1.1 Ma ago, thus confirming that some portions of the mantle were recently anomalously hot.
- A. Lagain
- , G. K. Benedix
- & K. Miljković
-
Article
| Open Access Correspondence between neuroevolution and gradient descent
Correspondence between neuroevolution and gradient descent
Gradient-based and non-gradient-based methods for training neural networks are usually considered to be fundamentally different. The authors derive, and illustrate numerically, an analytic equivalence between the dynamics of neural network training under conditioned stochastic mutations, and under gradient descent.
- Stephen Whitelam
- , Viktor Selin
- & Isaac Tamblyn
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding how Victoria, Australia gained control of its second COVID-19 wave
Understanding how Victoria, Australia gained control of its second COVID-19 wave
The state of Victoria, Australia experienced a substantial second wave of COVID-19 but brought it under control with strict non-pharmaceutical interventions. Here, the authors model the second wave in Victoria to estimate the impacts of the different interventions.
- James M. Trauer
- , Michael J. Lydeamore
- & Romain Ragonnet
-
Article
| Open Access Objective comparison of methods to decode anomalous diffusion
Objective comparison of methods to decode anomalous diffusion
Deviations from Brownian motion leading to anomalous diffusion are ubiquitously found in transport dynamics but often difficult to characterize. Here the authors compare approaches for single trajectory analysis through an open competition, showing that machine learning methods outperform classical approaches.
- Gorka Muñoz-Gil
- , Giovanni Volpe
- & Carlo Manzo
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-informed learning of governing equations from scarce data
Physics-informed learning of governing equations from scarce data
Recovery of underlying governing laws or equations describing the evolution of complex systems from data can be challenging if dataset is damaged or incomplete. The authors propose a learning approach which allows to discover governing partial differential equations from scarce and noisy data.
- Zhao Chen
- , Yang Liu
- & Hao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Individualised and non-contact post-mortem interval determination of human bodies using visible and thermal 3D imaging
Individualised and non-contact post-mortem interval determination of human bodies using visible and thermal 3D imaging
Establishing the time since death (TSD) is vital in many forensic investigations. By combining thermometry, photogrammetry and numerical thermodynamic modelling, the TSD can be determined non-invasively for bodies of arbitrary shape and posture with an unprecedented accuracy of 0.26 h ± 1.38 h.
- Leah S. Wilk
- , Gerda J. Edelman
- & Maurice C. G. Aalders
-
Article
| Open Access Nationwide rollout reveals efficacy of epidemic control through digital contact tracing
Nationwide rollout reveals efficacy of epidemic control through digital contact tracing
The effectiveness of digital contact tracing for COVID-19 control remains uncertain. Here, the authors use data from the Smittestopp app, used in Norway in spring 2020, and estimate that 80% of nearby devices were detected by the app, and at least 11% of close contacts were not visible to manual contact tracing.
- Ahmed Elmokashfi
- , Joakim Sundnes
- & Olav Lysne

 Local structure-function relationships in human brain networks across the lifespan
Local structure-function relationships in human brain networks across the lifespan