News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
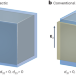 Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
By forming a heterostructure interface, and by judicious choice of crystallographic orientation, piezoelectrics are developed that show expansion or contraction along all axes on application of an electric field.
- Eugene A. Eliseev
- & Anna N. Morozovska
-
Article |
 Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Depositing textured functional materials on transparent conducting oxides remains a challenge. We demonstrate the formation of a coherent interface between a set of functional oxides and fluorine-doped-tin-oxide-based transparent conducting oxide substrate despite the lattice mismatch, owing to dimensional and chemical matching of oxygen sublattices at the interface.
- Huiting Huang
- , Jun Wang
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Research Briefing |
 Nano-oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes lead to superelastic properties
Nano-oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes lead to superelastic properties
Oxidation can degrade the properties and functionality of three-dimensional bulk metallic glasses. However, the formation of percolating oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes or nanosheets can induce interesting properties, such as a recoverable strain of 10–20% and elastic modulus of 20–30 GPa, which are rarely observed in their bulk counterparts.
-
Letter |
 Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation normally deteriorates the mechanical properties of metals. But it is now shown that the formation of a percolating oxide network in metallic glass nanotubes can result in an unprecedented superelasticity of 14% at room temperature.
- Fucheng Li
- , Zhibo Zhang
- & Yong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing emergent magnetic charge in an antiferromagnet with diamond quantum magnetometry
Revealing emergent magnetic charge in an antiferromagnet with diamond quantum magnetometry
Diamond quantum magnetometry is utilized to directly read the vorticity of antiferromagnetic spin textures through coupled multi-polar emergent magnetic charge distributions.
- Anthony K. C. Tan
- , Hariom Jani
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Article
| Open Access Auxetic piezoelectric effect in heterostructures
Auxetic piezoelectric effect in heterostructures
Piezoelectrics have longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients that are opposite in sign. Here, by tuning the interface inversion asymmetry in heterostructures, auxetic systems with positive longitudinal and transverse coefficients are realized, with expansion or contraction along all directions in an electric field.
- Ming-Min Yang
- , Tian-Yuan Zhu
- & Marin Alexe
-
Article
| Open Access Multistep magnetization switching in orthogonally twisted ferromagnetic monolayers
Multistep magnetization switching in orthogonally twisted ferromagnetic monolayers
The authors present magnetotransport measurements to demonstrate multistep magnetization switching in orthogonally twisted CrSBr ferromagnetic monolayers.
- Carla Boix-Constant
- , Sarah Jenkins
- & Eugenio Coronado
-
News & Views |
 Bowing to ferroelectric artificial flux closure
Bowing to ferroelectric artificial flux closure
By inserting an epitaxial in-plane buffer layer of Bi5FeTi3O15, an artificial flux closure architecture enables ferroelectric polarization from a single unit cell of BaTiO3 or BiFeO3.
- Neus Domingo
-
Research Briefing |
 Machine-learning-accelerated selection of perovskite passivants
Machine-learning-accelerated selection of perovskite passivants
The discovery of passivating agents for perovskite photovoltaics can be an arduous and time-consuming process. Now, a machine-learning model is reported that accelerates the selection of bifunctional pseudo-halide passivators. The identified pseudo-halide passivators were experimentally shown to enhance the performance of perovskite solar cells.
-
News & Views |
 Genetically encoded protein crystals by hierarchical design
Genetically encoded protein crystals by hierarchical design
Three protein interaction surfaces are computationally designed into one protein subunit to enable their accurate assembly into three-dimensional crystals with user-specified lattice architectures.
- Eduardo Anaya-Plaza
- & Mauri A. Kostiainen
-
Research Briefing |
 Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Polymers made by click chemistry with spirocyclic building blocks form membranes that separate the components of crude oil based on molecular size and type, potentially using far less energy than distillation. Key enablers of this separation are moderate levels of polymer dynamic motion and frustrated chain packing.
-
News & Views |
 Quadrupolar excitons take the stage
Quadrupolar excitons take the stage
Hybridized electron or hole states across semiconducting van der Waals monolayers in heterotrilayer systems enable the emergence of quadrupolar excitons. Quadrupolar excitons, unlike their dipolar counterparts, have a tunable static dipole moment that responds nonlinearly under an applied electric field.
- Elyse Barré
- , Medha Dandu
- & Archana Raja
-
News & Views |
 Transforming into fully commensurate bilayers
Transforming into fully commensurate bilayers
Heat treatment can transform some moiré superlattices into fully commensurate bilayers, where atoms in opposite layers align perfectly with each other. This structural transformation gives rise to markedly brighter interlayer excitons.
- Chun Hung Lui
-
Article |
 Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of electronics based on fully 2D materials is demonstrated in the performance of artificial intelligence tasks.
- Ji-Hoon Kang
- , Heechang Shin
- & Sang-Hoon Bae
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Optically stimulated vibrational control for materials has the potential to improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. The vibrational control of FAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells has been demonstrated, where the fast dynamics of coupling between cations and inorganic sublattice may suppress non-radiative recombinations in perovskites, leading to reduced voltage losses.
- Nathaniel. P. Gallop
- , Dmitry R. Maslennikov
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article |
 Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Early detection of electrical degradation in dielectric polymers is crucial but remains challenging. A general strategy of blending the polymer with chromogenic molecules is reported, which generates a visually discernible colour change as chemically activated by oxygen radicals generated in situ, indicating the early stage of electrical degradation in polymers.
- Xiaoyan Huang
- , Shuai Zhang
- & Jinliang He
-
Research Briefing |
 Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
A traditional physical-reservoir device has limited flexibility and cannot perform well across a range of computing tasks, owing to the fixed reservoir properties of the physical system. However, by exploiting the rich magnetic phase spaces of a single chiral magnet, reservoir properties can be reconfigured. This control enables on-demand optimization of computational performance across diverse machine-learning tasks.
-
Article
| Open Access Task-adaptive physical reservoir computing
Task-adaptive physical reservoir computing
Current physical neuromorphic computing faces critical challenges of how to reconfigure key physical dynamics of a system to adapt computational performance to match a diverse range of tasks. Here the authors present a task-adaptive approach to physical neuromorphic computing based on on-demand control of computing performance using various magnetic phases of chiral magnets.
- Oscar Lee
- , Tianyi Wei
- & Hidekazu Kurebayashi
-
Article |
 Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Chemical adsorption of CO on open metal sites enables separation from other gases but leads to selectivity and stability issues. Quasi-open metal sites in metal–organic frameworks are proposed here, which are accessible only by CO-induced structural transformation, enabling CO separation to 9N purity.
- Xue-Wen Zhang
- , Chao Wang
- & Jie-Peng Zhang
-
Article |
 Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines
Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines
Gold nanoclusters show promise as photothermal materials, but are often thermally unstable. Here ligand engineering is used to integrate molecular rotors with gold nanoclusters to dissipate thermal energy and improve photothermal therapy performance.
- Jing Chen
- , Peilin Gu
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article |
 Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Liquid electrolytes in batteries are considered to be macroscopically homogeneous ionic transport media despite having a complex chemical composition and atomistic solvation structures. A micelle-like structure in a localized high-concentration electrolyte for which the solvent acts as a surfactant is reported.
- Corey M. Efaw
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Bin Li
-
Article |
 Active learning guides discovery of a champion four-metal perovskite oxide for oxygen evolution electrocatalysis
Active learning guides discovery of a champion four-metal perovskite oxide for oxygen evolution electrocatalysis
Multi-metal and perovskite oxides are attractive as oxygen evolution electrocatalysts, and thus far the most promising candidates have emerged from experimental methodologies. Active-learning models supplemented by structural-characterization data and closed-loop experimentation can now identify a perovskite oxide with outstanding performance.
- Junseok Moon
- , Wiktor Beker
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article |
 Colloidal quasicrystals engineered with DNA
Colloidal quasicrystals engineered with DNA
The rational design and assembly of colloidal quasicrystals is achieved by exploring the hybridization of nanoscale decahedra nanoparticles functionalized with DNA linkers.
- Wenjie Zhou
- , Yein Lim
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Editorial |
 Electronics can be more sustainable
Electronics can be more sustainable
Integrated design assisted by materials and technology innovations can help a transition from traditional to sustainable electronics.
-
Article |
 Anion optimization for bifunctional surface passivation in perovskite solar cells
Anion optimization for bifunctional surface passivation in perovskite solar cells
Pseudo-halide anion engineering is an effective surface passivation strategy for perovskite-based optoelectronics but the large chemical space of molecules limits its potential. Here, the authors create a machine learning workflow to find optimized pseudo-halide anions, which are verified in devices with improved performances.
- Jian Xu
- , Hao Chen
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation in a dilute polymer network
Percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation in a dilute polymer network
A dilute water–polymer mixture exhibits a percolation-induced gel–gel phase separation, resulting in a two gel co-continuous substrate, which is used for adipose tissue development.
- Shohei Ishikawa
- , Yasuhide Iwanaga
- & Takamasa Sakai
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic proximity boosts chiral quantum emission
Magnetic proximity boosts chiral quantum emission
Chiral single-photon emitters are desirable, versatile tools for quantum information processing. Exploiting proximity to a strain-induced local magnetic field in the van der Waals antiferromagnet NiPS3 enables the emission of high-purity chiral single photons from monolayer WSe2 at zero external magnetic field.
- Jing Tang
- & Xi Ling
-
News & Views |
 Deciphering polymer networks
Deciphering polymer networks
An approach to analyse the deformation behaviour of polymer networks provides an enhanced set of structural information, improving our understanding of the elasticity of soft materials.
- Michael Lang
-
News & Views |
 Faster holes by delocalization
Faster holes by delocalization
Terahertz photoconductivity measurements coupled with theoretical modelling reveals that thermal transient excitations to more delocalized states enhances hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors.
- Zhigang Shuai
-
News & Views |
 Revived superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene
Revived superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene
By stacking few-layer WSe2 in proximity to twisted double bilayer graphene, researchers report solid evidence of superconductivity.
- Wei Yang
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article |
 Elastic microphase separation produces robust bicontinuous materials
Elastic microphase separation produces robust bicontinuous materials
Production of bulk bicontinuous materials is limited by the ability to make uniform microarchitectures across large volumes. Here elastic microphase separation is used to fabricate bicontinuous materials with a homogeneous microstructure, with feature sizes tuned by the matrix stiffness.
- Carla Fernández-Rico
- , Sanjay Schreiber
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article |
 Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Simultaneously highly elastic and deformable gels that maintain their mechanical properties have remained elusive. Here, using in situ polymerization confined within nanochannels, the authors prepare hysteresis-free gels insensitive to crack propagation.
- Weizheng Li
- , Xiaoliang Wang
- & Feng Yan
-
Comment |
 The organic electrochemical transistor conundrum when reporting a mixed ionic–electronic transport figure of merit
The organic electrochemical transistor conundrum when reporting a mixed ionic–electronic transport figure of merit
An essential part of developing organic mixed ionic–electronic conducting materials and organic electrochemical transistors is consistent and standardized reporting of the product of charge carrier mobility and volumetric capacitance, the μC* product. This Comment argues that unexpected changes in transistor channel resistance can overestimate this figure of merit, leading to a confusion of comparisons in the literature.
- Maryam Shahi
- , Vianna N. Le
- & Alexandra F. Paterson
-
Article |
 Accurate computational design of three-dimensional protein crystals
Accurate computational design of three-dimensional protein crystals
The process of protein crystallization is poorly understood and difficult to program through the primary sequence. Here the authors develop a computational approach to designing three-dimensional protein crystals with prespecified lattice architectures with high accuracy.
- Zhe Li
- , Shunzhi Wang
- & David Baker
-
Article |
 Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Solid polymer electrolytes are crucial for the development of lithium batteries, but their lower ionic conductivity compared with liquid/ceramics at room temperature limits their practical use. Precise positioning of designed repeating units in alternating polymer sequences now allows the Li+ conductivity to be tuned by up to three orders of magnitude.
- Shantao Han
- , Peng Wen
- & Mao Chen
-
Article |
 Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Thermal fractionation of petroleum consumes large amounts of energy. Here stable microporous polymers are synthesized using click chemistry, which have similar performance to commercial polyimides for the fractionation of light crude oils and successful application to heavy feeds under realistic conditions.
- Nicholas C. Bruno
- , Ronita Mathias
- & M. G. Finn
-
Article |
 Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing
Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing
Membrane/catalyst systems in the oxidative coupling of methane are promising for their high product selectivity but suffer from low volumetric chemical conversion rates, high capital cost and optimizing performance. A dual-layer additive manufacturing process, based on phase inversion, is now proposed to optimize a hollow-fibre membrane/catalyst system.
- James Wortman
- , Valentina Omoze Igenegbai
- & Suljo Linic
-
Article |
 Thermally induced atomic reconstruction into fully commensurate structures of transition metal dichalcogenide layers
Thermally induced atomic reconstruction into fully commensurate structures of transition metal dichalcogenide layers
Encapsulation annealing leads to atomic reconstruction of transition metal dichalcogenide layers into fully commensurate structures with zero twist angle, enabling control over interfacial properties.
- Ji-Hwan Baek
- , Hyoung Gyun Kim
- & Gwan-Hyoung Lee
-
Article |
 Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials for remote neural stimulation and motor function restoration
Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials for remote neural stimulation and motor function restoration
Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials with nonlinear responses generate electrical pulse sequences that enable precisely timed remote neural stimulation and restoration of sensory motor responses in vivo.
- Joshua C. Chen
- , Gauri Bhave
- & Jacob T. Robinson
-
Article |
 Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Lithium-rich nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathodes are widely explored due to their high capacities related to their anionic redox chemistry. A compositional optimization pathway for these materials investigating the variation of using cobalt and nickel now provides valuable guidelines for future high-capacity cathode design.
- Biao Li
- , Zengqing Zhuo
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article
| Open Access Defeating depolarizing fields with artificial flux closure in ultrathin ferroelectrics
Defeating depolarizing fields with artificial flux closure in ultrathin ferroelectrics
Ferroelectric dead layers can form at perovskite interfaces—a major challenge in integrating oxide thin films into devices. Here, by depositing an in-plane-polarized epitaxial buffer layer of Bi5FeTi3O15, out-of-plane polarization is demonstrated in ultrathin films down to the single-unit-cell level.
- Elzbieta Gradauskaite
- , Quintin N. Meier
- & Morgan Trassin
-
Article |
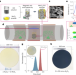 12-inch growth of uniform MoS2 monolayer for integrated circuit manufacture
12-inch growth of uniform MoS2 monolayer for integrated circuit manufacture
A route to the rapid and batch production of 12 inch MoS2 monolayers is reported, which shows a synergistic optimization of scale–cost–performance metrics for a transition from lab to fab.
- Yin Xia
- , Xinyu Chen
- & Peng Zhou
-
News & Views |
 Painting on programmable reconfigurable metastructures
Painting on programmable reconfigurable metastructures
Lattices of micrometre-sized metamaterials embedded in thermoresponsive hydrogels deform upon heating to reveal encrypted images from a blank gel canvas.
- Zixiao Liu
- & Ximin He
-
News & Views |
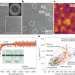 Toughening through faint crystallization
Toughening through faint crystallization
Oxide glasses can be intrinsically toughened by forming crystal-like, medium-range order clusters, which transform inversely to the amorphous state under stress, exciting multiple shear bands for plastic deformation.
- Hewei Zhao
- & Lin Guo
-
News & Views |
 Resistance to fatigue
Resistance to fatigue
An additively manufactured AlSi10Mg alloy shows high fatigue strength, even close to its tensile strength, for micro-sized samples. The fine cells in its inherent three-dimensional network are considered as cages to limit damage accumulation.
- Christopher Hutchinson
-
News & Views |
 Bioelectronics goes vertical
Bioelectronics goes vertical
Remotely powered vertical electrochemical transistors are demonstrated to track subtle nerve-cell activity even when the transistor core is fully shielded from the biological environment.
- C. Eckel
- & R. T. Weitz
-
Article |
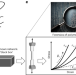 Forensics of polymer networks
Forensics of polymer networks
Extracting information about polymer network topology from mechanical properties alone remains challenging. Here the authors develop a forensic approach to quantify network structural information by analysing their nonlinear mechanics.
- Andrey V. Dobrynin
- , Yuan Tian
- & Sergei S. Sheiko
-
Research Briefing |
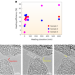 Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Self-healing behaviour in a nanotwinned diamond composite, at room temperature, has been quantitatively evaluated through tensile testing. The phenomenon is shown to arise from a transition of atomic interactions from repulsion to attraction and the formation of nanoscale diamond ‘osteoblasts’, in analogy to the process of bone healing in living organisms.
-
Article |
 Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) tape is widely used for lithium-ion batteries but its chemical stability has been largely overlooked. Reversible self-discharge is now shown to be virtually eliminated in LiFePO4–graphite cells by replacing PET with polypropylene jellyroll tape.
- Anu Adamson
- , Kenneth Tuul
- & Michael Metzger

 All-electric writing of a chiral quantum memory
All-electric writing of a chiral quantum memory