Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access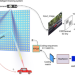 Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
The authors present an intelligent metasurface system that uses a target detection algorithm combined with a depth camera, to automatically detect the position of moving targets and achieve real-time wireless communications. The system can operate for multiple targets in limited ambient light, outdoor and other realistic environments.
- Weihan Li
- , Qian Ma
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access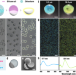 Nanostructure-free crescent-shaped microparticles as full-color reflective pigments
Nanostructure-free crescent-shaped microparticles as full-color reflective pigments
Structural colors arise from nanostructures or special microgeometries. Here, the authors report on crescent-shaped microparticles as full-color reflective pigments that show brilliant colors in directional light and are transparent in ambient light.
- Yi Yang
- , Jong Bin Kim
- & Shin-Hyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Giant polarization ripple in transverse pyroelectricity
Giant polarization ripple in transverse pyroelectricity
Pyroelectricity promises viable heat harvesting and sensing. Here, the authors identify transverse polarization ripple in pyroelectrics via heat localization and propagation decoupling and offer competitive power output to solar thermoelectrics.
- Yi Zhou
- , Tianpeng Ding
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access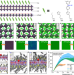 Suppressing phase disproportionation in quasi-2D perovskite light-emitting diodes
Suppressing phase disproportionation in quasi-2D perovskite light-emitting diodes
Quasi-2D halide perovskites are attracting increasing attention for light-emitting devices. Here, the authors demonstrated efficient and stable quasi-2D perovskite LEDs enabled by suppressed phase disproportionation with newly designed organic ligands.
- Kang Wang
- , Zih-Yu Lin
- & Letian Dou
-
Article
| Open Access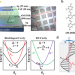 Circularly polarized electroluminescence from a single-crystal organic microcavity light-emitting diode based on photonic spin-orbit interactions
Circularly polarized electroluminescence from a single-crystal organic microcavity light-emitting diode based on photonic spin-orbit interactions
Nanoscale circularly polarized light sources are an important building block for future integrated photonics. Here the authors demonstrate circularly polarized light emission from a thin organic single crystal light-emitting diode.
- Jichao Jia
- , Xue Cao
- & Hongbing Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-growing photonic composites with programmable colors and mechanical properties
Self-growing photonic composites with programmable colors and mechanical properties
Structural coloration - i.e. colors arising from light interference in microstructures - is a good resource for several applications but usually involves elaborate fabrication techniques. Here, the authors achieve controllable coloration using silica particles embedded in a rearrangeable polymer network.
- Juan Xue
- , Xuewu Yin
- & Jiaxi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Constructing high-efficiency orange-red thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters by three-dimension molecular engineering
Constructing high-efficiency orange-red thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters by three-dimension molecular engineering
The design of high-efficiency solution-processable orange-red thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters remains to be a challenge. Here, the authors synthesize a series of emitters consisting of a trinaphtho[3,3,3]propellane core with highly efficient emission in the orange-red region of the spectrum.
- Lei Hua
- , Yuchao Liu
- & Zhongjie Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Circular polarized light-dependent anomalous photovoltaic effect from achiral hybrid perovskites
Circular polarized light-dependent anomalous photovoltaic effect from achiral hybrid perovskites
The manipulation of anomalous photovoltaic current by changing the light helicity has attracted an increasing interest in the field. Here, the authors realize circular polarized light-dependent anomalous bulk photovoltaic effect in achiral hybrid perovskites with a large asymmetry factor of 0.24.
- Tingting Zhu
- , Jie Bie
- & Junhua Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Radiative anti-parity-time plasmonics
Radiative anti-parity-time plasmonics
The parity-time symmetry has led to exotic phenomena and fruitful applications in optical systems. In this paper, the authors propose a leaky-wave-enabled anti-parity-time design and realize space-wave harnessing.
- Yumeng Yang
- , Xinrong Xie
- & Fei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of defect levels and rare earth emission centers in multimode luminescent phosphors
Interplay of defect levels and rare earth emission centers in multimode luminescent phosphors
Information encryption technology calls for versatile multi-mode luminescent materials. Here, the authors develop phosphors with five integrated luminescence modes by exploiting the interplay of defect levels and rare-earth emission centers.
- Xinquan Zhou
- , Lixin Ning
- & Zhiguo Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Arginine-modified black phosphorus quantum dots with dual excited states for enhanced electrochemiluminescence in bioanalysis
Arginine-modified black phosphorus quantum dots with dual excited states for enhanced electrochemiluminescence in bioanalysis
Electrochemiluminescence is emitted via the radiative transition of a singlet or triplet excited state. Here, the authors propose an arginine modification of black phosphorus quantum dots that exhibits enhanced emission based on dual excited states.
- Siqi Yu
- , Yu Du
- & Huangxian Ju
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic complex opto-magnetic holography
Dynamic complex opto-magnetic holography
Holography recreates both the amplitude and wave front of a three dimensional object, meaning that the observer perceives the image in the nearly same way as they would the true object. Creating such holographic images is challenging computationally, and requires extremely fast display update. Here, the authors combine a fast memoryless computation algorithm with the ultra-rapid writing based on all-optical switching of a ferrimagnetic film.
- M. Makowski
- , J. Bomba
- & A. Stupakiewicz
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically responsive photonic crystals with bistable states for low-power electrophoretic color displays
Electrically responsive photonic crystals with bistable states for low-power electrophoretic color displays
Conventional electrophoretic color displays require a permanent electric field, increasing power consumption. Here, the authors report an electrically responsive photonic crystal with switchable bistable states by particle rearrangement for low power consumption displays.
- Qianqian Fu
- , Wenyuan Yu
- & Jianping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Hot-carrier tunable abnormal nonlinear absorption conversion in quasi-2D perovskite
Hot-carrier tunable abnormal nonlinear absorption conversion in quasi-2D perovskite
Controlling the high-power laser transmittance is built on the diverse manipulation of multiple nonlinear absorption processes in the nonlinear optical materials. Here, the authors demonstrate the crucial role of hot-carrier effect to tune the nonlinear absorption response in quasi-2D perovskite films.
- Gang Wang
- , Tanghao Liu
- & Guichuan Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive probing of plasmonic hot electron occupancies
Ultrasensitive probing of plasmonic hot electron occupancies
Experimental evidence is given that upon the optical excitation of surface plasmon polaritons, a nonthermal electron population appears in the topmost domain of the plasmonic film directly coupled to the local fields.
- Judit Budai
- , Zsuzsanna Pápa
- & Péter Dombi
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-tunable quantum pathways of high harmonic generation in graphene
Gate-tunable quantum pathways of high harmonic generation in graphene
Under strong laser fields, materials exhibit extreme non-linear optical response, such as high harmonic generation. These higher harmonics provide insights into electron behaviour in materials in sub-laser cycle timescale. Here, Cha et al study higher harmonic generation resulting from the laser driven motion of massless Dirac fermions in graphene.
- Soonyoung Cha
- , Minjeong Kim
- & Jonghwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Towards highly efficient NIR II response up-conversion phosphor enabled by long lifetimes of Er3+
Towards highly efficient NIR II response up-conversion phosphor enabled by long lifetimes of Er3+
Development of efficient upconversion (UC) phosphors that emit under irradiation in the NIR II region is challenging - most UC materials rely on the presence of sensitizers absorbing at shorter wavelengths. Here, authors synthesize Er3+ doped ternary sulfides phosphors with visible UC efficiency up to 2.6% and long emission lifetimes under 1532 nm irradiation, via an excited state absorption mechanism.
- Xiumei Yin
- , Wen Xu
- & Bin Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Nanophotonic light sources with programmable emission spectrum are important building blocks for integrated photonics, sensing and optical computing. Here the authors tune the complex laser spectrum of a network laser achieving selective lasing of a single, two or more modes.
- Dhruv Saxena
- , Alexis Arnaudon
- & Riccardo Sapienza
-
Article
| Open Access A warm-white light-emitting diode based on single-component emitter aromatic carbon nitride
A warm-white light-emitting diode based on single-component emitter aromatic carbon nitride
Designing single-component materials with white-light electroluminescence is highly demanded for artificial lighting applications. Here, the authors fabricate a single-component white-light electroluminescence device based on an aromatic carbon nitride material with high maximum luminance and external quantum efficiency.
- Yunhu Wang
- , Kunpeng Wang
- & Jun Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically regulating nonlinear optical limiting of metal-organic framework film
Electrically regulating nonlinear optical limiting of metal-organic framework film
Nonlinear optical properties of metal-organic framework can be tuned for potential optical applications. Here the authors demonstrate an enhancement the nonlinear absorption coefficient of MOF film by applying external electric field.
- Zhi-Zhou Ma
- , Qiao-Hong Li
- & Jian Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic high-entropy carbides
Plasmonic high-entropy carbides
Tunable plasmonic materials capable of surviving harsh environments are critical for advanced applications. Here, the authors report that some high-entropy transition-metal carbides can satisfy the requirements.
- Arrigo Calzolari
- , Corey Oses
- & Stefano Curtarolo
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor ultralong phosphorescence from perovskite-like octahedral α-AlF3
Multicolor ultralong phosphorescence from perovskite-like octahedral α-AlF3
Unravelling the origin of emission in luminescent inorganic materials is challenging. Here, the authors report that AlF6 octahedrons exhibit excitation-dependent color-tunable phosphorescence; structurally related compounds are also luminescent.
- Peisheng Cao
- , Haoyue Zheng
- & Peng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Soft shape-programmable surfaces by fast electromagnetic actuation of liquid metal networks
Soft shape-programmable surfaces by fast electromagnetic actuation of liquid metal networks
Low modulus materials that can change shape in response to external stimuli are promising for a wide range of applications. The authors here introduce a shape-reprogrammable construct, based on liquid metal microfluidic networks and electromagnetic actuation, that supports a unique collection of capabilities.
- Xinchen Ni
- , Haiwen Luan
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving molecular diffusion and aggregation of antibody proteins with megahertz X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Resolving molecular diffusion and aggregation of antibody proteins with megahertz X-ray free-electron laser pulses
The European X-ray FreeElectron Laser Facility generates ultrashort hard X-ray pulses with megahertz repetition rate. Here, the authors probe the dynamics of dense antibody protein (Ig-PEG) solutions using megahertz X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy at the European XFEL.
- Mario Reiser
- , Anita Girelli
- & Christian Gutt
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling Weyl-related optical responses in semiconducting tellurium by mid-infrared circular photogalvanic effect
Unveiling Weyl-related optical responses in semiconducting tellurium by mid-infrared circular photogalvanic effect
Materials with Weyl cones and band gaps coexisting are desired due to their combination of Weyl cones and the tunable and controllable nature of semiconductor. Here, the authors find Weyl-related band structures and semiconducting gap of tellurium.
- Junchao Ma
- , Bin Cheng
- & Dong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access A platform for blue-luminescent carbon-centered radicals
A platform for blue-luminescent carbon-centered radicals
Organic radicals, which have unique doublet spin-configuration, provide an alternative method to overcome the efficiency limitation of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) but extending their fluorescence into a short-wavelength region remains challenging. Here, the authors significantly expand the scope of luminescent radicals by showing a new platform of carbon-centered radicals that produce blue to green emission.
- Xin Li
- , Yi-Lin Wang
- & Ying-Feng Han
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorescence-based monitoring of the pressure-induced aggregation microenvironment evolution for an AIEgen under multiple excitation channels
Fluorescence-based monitoring of the pressure-induced aggregation microenvironment evolution for an AIEgen under multiple excitation channels
The develop of organic functional materials requires the exploration of the pressure dependent emissive mechanisms of molecular structures, conformations and stacking modes. Here, Tong et al propose a strategy for monitoring the pressure-induced fluorescence under multiple excitation channels.
- Shuang Tong
- , Jianhong Dai
- & Xinggui Gu
-
Article
| Open Access All-fluorescence white organic light-emitting diodes with record-beating power efficiencies over 130 lm W‒1 and small roll-offs
All-fluorescence white organic light-emitting diodes with record-beating power efficiencies over 130 lm W‒1 and small roll-offs
High power efficiency and low roll-off values are essential to the commercialization of white organic light-emitting diodes. Here, the authors construct all-fluorescence devices with an orange emitting layer sandwiched between two sky-blue emitting layers, achieving figure-of-merit of 130.7 lm/W.
- Hao Liu
- , Yan Fu
- & Zujin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Circularly polarized light-sensitive, hot electron transistor with chiral plasmonic nanoparticles
Circularly polarized light-sensitive, hot electron transistor with chiral plasmonic nanoparticles
One challenge with using circularly polarized light is an increased device complexity typically required to provide sufficient sensitivity to the polarization. Here, by integrating chiral plasmonic nanoparticles with a InGaZnO hot electron transistor, the authors present a polarization sensitive, optically active transistor.
- Seok Daniel Namgung
- , Ryeong Myeong Kim
- & Ki Tae Nam
-
Article
| Open Access A polymer electrolyte design enables ultralow-work-function electrode for high-performance optoelectronics
A polymer electrolyte design enables ultralow-work-function electrode for high-performance optoelectronics
Ambient-stable solution-processed conductive materials with a low work function are essential to facilitate electron injection. Here, the authors design and synthesise polymer electrolyte with work function down to 2.2 eV for applications in high-performance light-emitting diodes and solar cells.
- Bo Tong
- , Jinhong Du
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Strong and Localized Luminescence from Interface Bubbles Between Stacked hBN Multilayers
Strong and Localized Luminescence from Interface Bubbles Between Stacked hBN Multilayers
Optoelectronic properties of van der Waals heterostructures can be tuned via strain. Here, authors demonstrate strong and localized luminescence in the ultraviolet region from interface bubbles between stacked multilayers of hexagonal boron nitride.
- Hae Yeon Lee
- , Soumya Sarkar
- & Silvija Gradečak
-
Article
| Open Access Toward a BT.2020 green emitter through a combined multiple resonance effect and multi-lock strategy
Toward a BT.2020 green emitter through a combined multiple resonance effect and multi-lock strategy
The authors combine multiple resonance effect and multi-lock strategy to dope green-emitting thermally activated delayed fluorescent molecules into green-emitting phosphorescence OLEDs by endowing the device with a Broadcast Service Television 2020 color-gamut, 50% improved EQE, and a high luminescence of half a million nits.
- Junyuan Liu
- , Yunhui Zhu
- & Qisheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Excitation energy mediated cross-relaxation for tunable upconversion luminescence from a single lanthanide ion
Excitation energy mediated cross-relaxation for tunable upconversion luminescence from a single lanthanide ion
Here, the authors report tunable luminescence from a single lanthanide ion upon changing excitation conditions through co-doping an energy-modulator ion, thus adjusting the photon transition process of the lanthanide activator ion. Optical encryption has also been demonstrated as an application of this universal strategy.
- Xiao Fu
- , Shuai Fu
- & Qingsong Mei
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of ideal electromagnetic fluids
Direct observation of ideal electromagnetic fluids
This paper reports an experimental observation of irrotational, inviscid, and incompressible electromagnetic power flow within an epsilon-near-zero medium, exhibiting an analogy to an ideal fluid.
- Hao Li
- , Ziheng Zhou
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing colloidal crystal microstructures via sacrificial-scaffold-mediated two-photon lithography
3D printing colloidal crystal microstructures via sacrificial-scaffold-mediated two-photon lithography
Colloidal crystals are widely applied in the fabrication of optoelectronic devices, but realizing freedom of design, such as in 3D printing, in colloidal crystal fabrication remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a sacrificial-scaffold-mediated two-photon lithography strategy that enables the fabrication of complex 3D colloidal crystal microstructures with orderly arranged nanoparticles in the bulk.
- Keliang Liu
- , Haibo Ding
- & Zhongze Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Germanium silicon oxide achieves multi-coloured ultra-long phosphorescence and delayed fluorescence at high temperature
Germanium silicon oxide achieves multi-coloured ultra-long phosphorescence and delayed fluorescence at high temperature
Advanced security applications require materials responsive to different stimuli with remarkable stability. Here, Sargent et al. introduce Ge homogenously into a silica scaffold and obtain a colourtuned germanium silicon oxide with ultra-long phosphorescence and delayed fluorescence across a broad temperature range.
- Huai Chen
- , Mingyang Wei
- & Zhenyu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the fundamental scattering limit with gain metasurfaces
Breaking the fundamental scattering limit with gain metasurfaces
Wave-matter interaction suffers from fundamental limit to scattering cross section, referred to as the single-channel scattering limit. Here, the authors break this limit by exploiting gain metasurfaces and reveal the transient formation and relaxation of this phenomenon.
- Chao Qian
- , Yi Yang
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Decapod-inspired pigment modulation for active building facades
Decapod-inspired pigment modulation for active building facades
Typical buildings are static structures, unable to adjust to dynamic temperature and daylight fluctuations. Here, authors present an adaptive alternative, using shape-tuneable pigment injections to control solar ingress and reduce estimated building energy use by 30%.
- Raphael Kay
- , Charlie Katrycz
- & Benjamin D. Hatton
-
Article
| Open Access Electric-field control of nonlinear THz spintronic emitters
Electric-field control of nonlinear THz spintronic emitters
Spintronic terahertz (THz) emitters are a class of magnetic heterostructure where femtosecond laser excitations generate THz radiation emission. While they have great potential, electric field control of spintronic emitter remains a challenge. Here, by combining a spintronic emitter with a piezoelectric substrate, Agarwal et al. demonstrate electric field control of THz emission through induced piezostrain.
- Piyush Agarwal
- , Lisen Huang
- & Ranjan Singh
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic-circuited resonance fluorescence of single molecules with an ultrastable lifetime-limited transition
Photonic-circuited resonance fluorescence of single molecules with an ultrastable lifetime-limited transition
Single molecules can generate high-quality single photons for quantum technologies, but coupling to waveguides is difficult. Here, the authors show on-chip background-free resonance fluorescence generation and routing from single molecules with lifetime-limited transition and waveguide-aligned dipoles.
- Penglong Ren
- , Shangming Wei
- & Xue-Wen Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Organic phosphorescent scintillation from copolymers by X-ray irradiation
Organic phosphorescent scintillation from copolymers by X-ray irradiation
The authors achieved the X-ray-excited organic phosphorescent scintillation from copolymers through copolymerization of bromine-substituted chromophores and acrylic acid and demonstrated their potential application in X-ray radiography.
- Nan Gan
- , Xin Zou
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Geometry-independent antenna based on Epsilon-near-zero medium
Geometry-independent antenna based on Epsilon-near-zero medium
This paper proposes an unconventional type of antennas that are composed by epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) media. The operating frequencies of such antennas are independent of their geometries, and are determined by material dispersion.
- Hao Li
- , Ziheng Zhou
- & Nader Engheta
-
Article
| Open Access Active electrochemical high-contrast gratings as on/off switchable and color tunable pixels
Active electrochemical high-contrast gratings as on/off switchable and color tunable pixels
Two key display operations, color tuning and on/off switching, are achieved with reflective structural colors by changing the modal interference conditions and absorption via electrochemical control of Cu occupancy inside dielectric grating slits.
- Cheon Woo Moon
- , Youngji Kim
- & Jerome Kartham Hyun
-
Article
| Open Access Probing material absorption and optical nonlinearity of integrated photonic materials
Probing material absorption and optical nonlinearity of integrated photonic materials
Optical absorption and nonlinear index are important performance drivers in devices like microcombs. Here the authors use resonance-enhanced nonlinear spectroscopy to characterize absorption limits and nonlinear index for some integrated photonic materials.
- Maodong Gao
- , Qi-Fan Yang
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films
Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films
Setting any polarization value in ferroelectric thin films is a key step for their implementation in neuromorphic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous modulation of the remanent polarization at the nanoscale in PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 films.
- Martin F. Sarott
- , Marta D. Rossell
- & Morgan Trassin
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the origin of chiroptical activity in chiral 2D perovskites through nano-confined growth
Elucidating the origin of chiroptical activity in chiral 2D perovskites through nano-confined growth
In this study, Ma et al. demonstrated that asymmetric hydrogen-bonding interaction between chiral organic spacer and inorganic frameworks plays a key role in promoting the chiroptical activity of chiral perovskites.
- Sunihl Ma
- , Young-Kwang Jung
- & Jooho Moon
-
Article
| Open Access Lattice-mismatch-free growth of organic heterostructure nanowires from cocrystals to alloys
Lattice-mismatch-free growth of organic heterostructure nanowires from cocrystals to alloys
The large-scale synthesis of organic heterostructure nanowires is challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of organic triblock nanowires via a lattice mismatch-free strategy.
- Qiang Lv
- , Xue-Dong Wang
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Towards n-type conductivity in hexagonal boron nitride
Towards n-type conductivity in hexagonal boron nitride
Asymmetric n/p conductivity is a fundamental difficulty in wide bandgap semiconductors. Here the authors demonstrate a concept of orbital level engineering through sacrificial impurity coupling to achieve n-type conductivity (ne ~1016 cm-3) in hexagonal BN.
- Shiqiang Lu
- , Peng Shen
- & Junyong Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
The authors introduce stimulated-emission induced excitation depletion (STExD) nanoscopy using a single pair of low-power, near-infrared, continue-wave lasers. Emission of multichromatic probes is inhibited by cascade amplified depletion in lanthanide upconversion systems induced by manipulating their common sensitizer.
- Xin Guo
- , Rui Pu
- & Qiuqiang Zhan

 Orthogonal luminescence lifetime encoding by intermetallic energy transfer in heterometallic rare-earth MOFs
Orthogonal luminescence lifetime encoding by intermetallic energy transfer in heterometallic rare-earth MOFs