Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Researchers showcase an integrated photonic device with monocrystalline CsPbBr3 perovskite. Employing top-down etching approach, it introduces for micro lasers, beam splitters, X-couplers, Mach-Zehnder interferometers on perovskite films. This opens avenues for integrating perovskite semiconductors into optical chips, promising advancements in information and computing science.
- Qi Han
- , Jun Wang
- & Li Ji
-
Article
| Open Access VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
Frequency converters for wireless internet of things applications typically require separate circuits for different functions, causing energy and performance inefficiencies. Using an epitaxially grown VO2 memristor array, Liu et al. present a frequency converter with in-situ frequency synthesis and mix functionality.
- Chang Liu
- , Pek Jun Tiw
- & Yuchao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Stenus-inspired, swift, and agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsors
Stenus-inspired, swift, and agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsors
Inspired by the swift swingable abdomen, conducting canals, and body setae of Stenus comma, the authors present a swift, agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsor, offering new insights into systematically bio-inspired artificial soft robots.
- Xingxing Ke
- , Haochen Yong
- & Zhigang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Functional features in the spatiotemporal regulation of blood chemistry are not much explored. Here authors show vascular network-inspired fluidics, functionalizable for different region-specific trans-wall transport to regulate fluids over space and time.
- Yafeng Yu
- , Yi Pan
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-engineered synthesis of atomically thin te single crystals with high on-state currents
Phase-engineered synthesis of atomically thin te single crystals with high on-state currents
Phase engineering of 2D tellurium could enable potential applications for (opto-)electronic devices. Here, the authors report the phase- and thickness-controlled synthesis of α-Te nanosheets and β-Te nanoribbons, showing their application for the realization of short-channel transistors.
- Jun Zhou
- , Guitao Zhang
- & Junpeng Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Neuromorphic electro-stimulation based on atomically thin semiconductor for damage-free inflammation inhibition
Neuromorphic electro-stimulation based on atomically thin semiconductor for damage-free inflammation inhibition
Bao et al. report a neuromorphic bionic electro-stimulation solution based on atomic-scale semiconductor floating-gate memory circuit, which enables efficient inhibition of acute inflammation with low stimulation currents that are damage-free to neurons.
- Rong Bao
- , Shuiyuan Wang
- & Shen Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time monitoring polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials toward no batch-to-batch variations in device performance
Real-time monitoring polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials toward no batch-to-batch variations in device performance
Polymerization degree plays a vital role in controlling material properties and batch-to-batch variations in device performance of polymer solar cells. Here, authors develop in-situ photoluminescence system in tandem to track and estimate the polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials.
- Lin-Yong Xu
- , Wei Wang
- & Jie Min
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of giant room-temperature anisotropic magnetoresistance in the topological insulator β-Ag2Te
Observation of giant room-temperature anisotropic magnetoresistance in the topological insulator β-Ag2Te
Achieving room-temperature high anisotropic magnetoresistance ratios is highly desirable for magnetic sensors. Here, the authors observe a high anisotropic magnetoresistance ratio of −39% and a giant planar Hall effect (520 μΩ·cm) at room temperature under 9 T in β-Ag2Te crystals grown by CVD.
- Wei Ai
- , Fuyang Chen
- & Jinxiong Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Heavy-to-light electron transition enabling real-time spectra detection of charged particles by a biocompatible semiconductor
Heavy-to-light electron transition enabling real-time spectra detection of charged particles by a biocompatible semiconductor
New detector materials are crucial for radiation beam monitoring in dosimeters and X-ray imaging. The authors report a solution-grown biocompatible organic single crystalline semiconductor for real-time spectral detection of charged particles with single-particle sensitivity, X-ray detection and imaging.
- Dou Zhao
- , Ruiling Gao
- & Yadong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-friction gold-based stretchable electronics enabled by interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion
Anti-friction gold-based stretchable electronics enabled by interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion
Stretchable electronics require high interfacial strength between the inert metal and elastomer components for durable interconnection applications. Cao et al. show a chemical modification-free interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion strategy, using hydrophilic polyurethane to induce hydrogen bonding of gold grains.
- Jie Cao
- , Xusheng Liu
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating solvent fluidic dynamics for large-area perovskite film-formation and white light-emitting diodes
Manipulating solvent fluidic dynamics for large-area perovskite film-formation and white light-emitting diodes
Achieving large-area uniform film is the primary challenge to commercialise perovskite LEDs. The authors here employ green binary solvents to regulate the fluidic dynamics in perovskite quantum dot inks during blade-coating to achieve efficient 28 cm2-sized red and white perovskite LEDs.
- Guangyi Shi
- , Zongming Huang
- & Zhengguo Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Printed smart devices for anti-counterfeiting allowing precise identification with household equipment
Printed smart devices for anti-counterfeiting allowing precise identification with household equipment
The authors introduce a flexible laser printing method for synthesizing integrated optical and electric Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs). The PUF devices can be read out by simple household equipment and show high uniqueness and stability.
- Junfang Zhang
- , Rong Tan
- & Felix F. Loeffler
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the amorphous structure and crystallization mechanism of GeTe phase change memory materials
Unravelling the amorphous structure and crystallization mechanism of GeTe phase change memory materials
The structure of an ideal glass, crystallisation mechanism, nanoscale effects, and even parallels to organic chemistry can be drawn by conceptualizing the amorphous GeTe structure as a superposition of Te and Ge lattices with atom-specific dynamics.
- Simon Wintersteller
- , Olesya Yarema
- & Maksym Yarema
-
Article
| Open Access Well-defined in-textile photolithography towards permeable textile electronics
Well-defined in-textile photolithography towards permeable textile electronics
It is challenging to achieve simultaneous robustness, permeability and high electrical performance when patterning textile electronics. Here, the authors report an in-textile photolithography method for precise metal patterns while maintaining the 3D porous structure for wearable textile electronics.
- Pengwei Wang
- , Xiaohao Ma
- & Zijian Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically induced cancellation and inversion of piezoelectricity in ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2
Electrically induced cancellation and inversion of piezoelectricity in ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2
Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 ferroelectric capacitors undergo a continuous transition from a positive effective to a fully inverted negative piezoelectric coefficient d33 upon electrical cycling. With proper ac training, both the net effective and the local piezoresponses can be nullified while the polarization is kept fully switchable.
- Haidong Lu
- , Dong-Jik Kim
- & Catherine Dubourdieu
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-restricted transfer of ferromagnetic electrodes for constructing reproducibly superior-quality spintronic devices
Strain-restricted transfer of ferromagnetic electrodes for constructing reproducibly superior-quality spintronic devices
To optimize the interfacial quality and electrode magnetism in spintronic devices, the authors develop an electrode transfer technique that can greatly improve device interfacial quality, performance and reproducibility, universal to various spacers.
- Lidan Guo
- , Xianrong Gu
- & Xiangnan Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Myocardial infarction can lead to malignant arrhythmia and myocardial remodeling. Here, the authors report a microchanneled hydrogel suture for two-way signal communication, pumping drugs on demand, and cardiac repair.
- Fangchao Xue
- , Shanlan Zhao
- & Wen Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Phase transitions associated with magnetic-field induced topological orbital momenta in a non-collinear antiferromagnet
Phase transitions associated with magnetic-field induced topological orbital momenta in a non-collinear antiferromagnet
Recent work has demonstrated the potential of polycrystalIine antiferromagnetic materials for spintronics. Here the authors report evidence of magnetic phase transitions in a polycrystalline non-collinear antiferromagnet, which are explained by a phenomenological model with topological orbital momenta.
- Sihao Deng
- , Olena Gomonay
- & Christoph Sürgers
-
Article
| Open Access Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Lightweight flexible piezoelectric polymers are demanded for various applications, but restricted by the low instinctively piezoelectric coefficient and complex poling process. Here, the authors develop a high performance lightweight, flexible self-poled piezoelectric polymer composite towards sustainable self-powered sensing and energy harvesting.
- Zhao-Xia Huang
- , Lan-Wei Li
- & Jin-Ping Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Designing transparent piezoelectric metasurfaces for adaptive optics
Designing transparent piezoelectric metasurfaces for adaptive optics
Most multi-degrees-of-freedom systems are composed of several piezoelectric stacks, leading to cumbersome and complicated structures. Here, the authors propose a piezo metasurface to achieve various types of high strains in a wide frequency range.
- Liao Qiao
- , Xiangyu Gao
- & Fei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Down-selection of biomolecules to assemble “reverse micelle” with perovskites
Down-selection of biomolecules to assemble “reverse micelle” with perovskites
Introducing biomaterials into semiconductors to manifest bio-mimetic functionality is impactful to trigger new enhancement mechanisms. Here, the authors utilize different types of biomolecules to regulate the perovskite crystal lattice and endow a mechanism for stabilizing the metastable lattice.
- Haodong Wu
- , Yuchen Hou
- & Kai Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting the electron beam transmittance of field emission cathode using a self-charging gate
Boosting the electron beam transmittance of field emission cathode using a self-charging gate
Gate-type field emission cathodes based on carbon nanotubes face challenges of achieving high E-beam transmittance to avoid the collision with the gate to form irreversible damages. Here, the authors present a self-charging gate to control the E-beam trajectory by inducing a local electric field.
- Dongyang Xiao
- , Huanhuan Du
- & Peiyi Song
-
Article
| Open Access Effective electrical manipulation of a topological antiferromagnet by orbital torques
Effective electrical manipulation of a topological antiferromagnet by orbital torques
Electrical control of topological magnets is of great interest for future spintronic applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the effective manipulation of antiferromagnetic order in a Weyl semimetal using orbital torques, with implications for neuromorphic device applications.
- Zhenyi Zheng
- , Tao Zeng
- & Jingsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetoresistive-coupled transistor using the Weyl semimetal NbP
Magnetoresistive-coupled transistor using the Weyl semimetal NbP
L. Rocchino et al. experimentally demonstrate a magnetic field effect transistor based on the Weyl semimetal NbP as the active channel material. A gate magnetic field is generated by current flowing in an integrated superconductor NbN. The device operation relies on the extreme magnetoresistance of the NbP.
- Lorenzo Rocchino
- , Federico Balduini
- & Cezar B. Zota
-
Article
| Open Access Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Fabrication methods for ionic conductive hydrogel fibers are challenged by complexity and poor stability. Using a stress-induced adaptive phase transition strategy, Liu et al. fabricate self-encapsulated hydrogel fibers for depth-of-field sensing applications in a sustainable, two-step process.
- Ying Liu
- , Chan Wang
- & Zhou Li
-
Article
| Open Access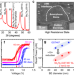 Novel nanocomposite-superlattices for low energy and high stability nanoscale phase-change memory
Novel nanocomposite-superlattices for low energy and high stability nanoscale phase-change memory
Data-centric applications benefit from dense, low-power memory. Here the authors use a combination of chalcogenide superlattices and nanocomposites to achieve low switching voltage (0.7 V) and fast speed (40 ns) in 40-nm-scale phase-change memory.
- Xiangjin Wu
- , Asir Intisar Khan
- & Eric Pop
-
Article
| Open Access Interindividual- and blood-correlated sweat phenylalanine multimodal analytical biochips for tracking exercise metabolism
Interindividual- and blood-correlated sweat phenylalanine multimodal analytical biochips for tracking exercise metabolism
The in-depth study on the sweat–blood partitioning mechanisms of amino acids is promising for noninvasive metabolic monitoring. Here, the authors develop a wearable biochip for sweat phenylalanine multimodal analysis aimed at tracking exercise metabolic risk and exploring the sweat–blood correlation.
- Bowen Zhong
- , Xiaokun Qin
- & Lili Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the crucial role of trace oxygen in organic semiconductors
Unraveling the crucial role of trace oxygen in organic semiconductors
Conventional deoxygenation methods typically result in inevitable trace oxygen residue in organic semiconductors. Here, Huang et al. reports a non-destructive soft-plasma treatment for deoxygenation and that removal of trace oxygen can be used to modulate p-type characteristics.
- Yinan Huang
- , Kunjie Wu
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential spectrometers recognise different wavelength via their differential photodetector responsivity. The authors combine an 8-pixel hemispherical perovskite photodetector with neural network algorithms to realise 3D trajectory tracking and 2D location tacking with colour classification.
- Xiaopeng Feng
- , Chenglong Li
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding of multi-modal emotional information via personalized skin-integrated wireless facial interface
Encoding of multi-modal emotional information via personalized skin-integrated wireless facial interface
Technologies in human emotion recognition are challenged by their capability to accurately extract and exploit the emotional information. Lee et al. report a personalized skin-integrated facial interface to sense and combine facial and vocal expression data, enabling enhanced communication in virtual reality.
- Jin Pyo Lee
- , Hanhyeok Jang
- & Jiyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access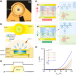 Flexible switch matrix addressable electrode arrays with organic electrochemical transistor and pn diode technology
Flexible switch matrix addressable electrode arrays with organic electrochemical transistor and pn diode technology
Organic neural implants hold considerable promise for biocompatible neural interfaces. Here, the authors employ polymer-based organic electrochemical diodes and transistors to develop neuron-sized complex circuits, enabling multiplexing without crosstalk and demonstrate that, when integrated onto ultra-thin plastic, these circuits achieve high performance while maintaining minimal invasiveness.
- Ilke Uguz
- , David Ohayon
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article
| Open Access A ferroelectric fin diode for robust non-volatile memory
A ferroelectric fin diode for robust non-volatile memory
Designing efficient high-density crossbar arrays are nowadays highly demanded for many artificial intelligence applications. Here, the authors propose a two-terminal ferroelectric fin diode non-volatile memory in which a ferroelectric capacitor and a fin-like semiconductor channel are combined to share both top and bottom electrodes with high performance and easy fabrication process
- Guangdi Feng
- , Qiuxiang Zhu
- & Chungang Duan
-
Article
| Open Access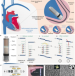 A self-powered intracardiac pacemaker in swine model
A self-powered intracardiac pacemaker in swine model
Harvesting biomechanical energy from cardiac motion is an attractive power source for implantable bioelectronic devices. Here, the authors report a battery-free, transcatheter, self-powered intracardiac pacemaker for the treatment of arrhythmia in large animal models.
- Zhuo Liu
- , Yiran Hu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access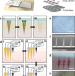 Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Microneedle patches that can actively address individual needles are challenging to realize. Here, the authors introduce a spatiotemporal on-demand patch for precise and personalized drug delivery, utilizing electrically triggered control with drug-loaded microneedles and biocompatible metallic membranes.
- Yihang Wang
- , Zeka Chen
- & Wubin Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Wide-range soft anisotropic thermistor with a direct wireless radio frequency interface
Wide-range soft anisotropic thermistor with a direct wireless radio frequency interface
Thermistors typically read at DC or low frequencies have limited temperature-sensing ranges. Here, authors show how a radio frequency readout can overcome the decades-old range limitation of thermistors, while creating a wireless interface for a soft thermistor composite through antennas and RFID.
- Mahmoud Wagih
- , Junjie Shi
- & Steve Beeby
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Electro-active ionic soft actuators generally present slow responses and poor durability when are applied as artificial muscles. Here, the authors describe a polyelectrolyte membrane based on the assembly of Nafion molecules into micelles with efficient ionic conducting pathways for electro-ionic soft actuators and soft robotics with fast responses and long durability.
- Van Hiep Nguyen
- , Saewoong Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
In this work, authors demonstrate highly stretchable conductive porous elastomers that can achieve up to 1200% strain with low or negative Poisson’s ratios by uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial hot-pressing strategies.
- Xiaoyu Zhang
- , Qi Sun
- & Guoqing Zu
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain
Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain
The sign of longitudinal piezoelectric coefficients is typically positive. Here, the authors tune the sign of the linear piezoelectric coefficient of HfO2 from positive to negative via epitaxial strain, finding nonlinear and parabolic piezoelectric behaviors at tensile epitaxial strain.
- Hao Cheng
- , Peijie Jiao
- & Yurong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Motion and teleportation of polar bubbles in low-dimensional ferroelectrics
Motion and teleportation of polar bubbles in low-dimensional ferroelectrics
Nanoscale ferroelectric domains called electric bubbles are shown to behave as dynamical particles. Using atomistic simulations and experiments, the authors reveal a bubble liquid phase and demonstrate teleportation-like displacements of single bubbles.
- S. Prokhorenko
- , Y. Nahas
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access Multistate structures in a hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework with diverse resistive switching behaviors
Multistate structures in a hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework with diverse resistive switching behaviors
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks as stimuli responsive multistate structures show potential in the field of resistive switching. Here, the authors report a 0D+1D hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework showing reversible transformation of multistate-structures triggered by electrical field and temperature, enabling reversibly switchable resistive random-access memory and write-once-read-many-times memory behavior.
- Shimin Chen
- , Yan Ju
- & Zhangjing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
This work addresses the fundamental challenge of the frequency up-scaling of microacoustic devices. The manuscript presents the first bank of on-chip multi-frequency, low-loss, wideband, and compact passband filters for mobile 5G and 6G applications.
- Gabriel Giribaldi
- , Luca Colombo
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
The water stability of perovskites remains challenging due to their intrinsic ionic nature. Here, the authors present water stable perovskite X-ray imager driven by strong cation-π interactions between organic cations and a complete release of microstrain during dimension transformation process.
- Wanting Pan
- , Yuhong He
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
The simultaneous scaling down of the channel length and gate length of 2D transistors remains challenging. Here, the authors report a self-alignment process to fabricate vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1 nm gate length and sub−50 nm channel length, exhibiting on-off ratios over 105 and on-state currents of 250 μA/μm at 4 V bias.
- Liting Liu
- , Yang Chen
- & Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Designing memristor-integrated passive crossbar arrays to accelerate artificial neural networks with high reliability remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a self-rectifying resistive switching device incorporated into a crossbar array with a density of 1 kb whose operational performance is assessed in terms of defected-cell proportion, reading margin, and selection functionality.
- Kanghyeok Jeon
- , Jin Joo Ryu
- & Gun Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
The design of multifunctional platforms with tunable spectroscopic and fluorescent properties that span the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectral regions remains challenging. Here, the authors report an actuator-type system that leverages a readily-prepared, easily-processable, and exceptionally-stable nonacene-like molecule to achieve multiple complementary dynamic operating modes.
- Preeta Pratakshya
- , Chengyi Xu
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
Gas sensors typically detect only few specific gases; the authors show a broad-spectrum sensor based on correlated 2-dimensional electron gas (C-2DEG), which detects various gases quantitatively and measures partial pressures, through a purely physical mechanism.
- Yuhao Hong
- , Long Wei
- & Zhaoliang Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
A differentiable design framework that integrates both geometrical and magnetomechanical analyses to inversely program the shape morphing in magnetically actuated kirigami is proposed, achieving intricate shapes and multistate transitions.
- Liwei Wang
- , Yilong Chang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Full hardware implementation of neuromorphic visual system based on multimodal optoelectronic resistive memory arrays for versatile image processing
Full hardware implementation of neuromorphic visual system based on multimodal optoelectronic resistive memory arrays for versatile image processing
In-sensor and near-sensor computing are emerging as the next-generation computing paradigm, for high-density and low-power sensory processing. Here, the authors report a fully hardware-implemented artificial visual system for versatile image processing based on multimodal-multifunctional optoelectronic resistive memory devices with optical and electrical resistive switching modes.
- Guangdong Zhou
- , Jie Li
- & Shukai Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Nonstoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenides break symmetry, enabling piezo/ferroelectric effects. Here, the authors propose an approach to integrate these properties with diverse 2D materials, advancing multifunctional materials and devices.
- Yi Hu
- , Lukas Rogée
- & Shu Ping Lau

 A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity