Featured
-
-
Perspective |
 Recompensation in cirrhosis: unravelling the evolving natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Recompensation in cirrhosis: unravelling the evolving natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Cirrhosis recompensation is gradually gaining traction, but a definition for recompensation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-related cirrhosis is currently lacking. This Perspective provides an overview of the natural history of NAFLD and discusses NAFLD-related cirrhosis recompensation.
- Gong Feng
- , Luca Valenti
- & Ming-Hua Zheng
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
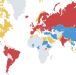 Global epidemiology of cirrhosis — aetiology, trends and predictions
Global epidemiology of cirrhosis — aetiology, trends and predictions
In this Review, Huang et al. highlight global trends in the epidemiology of cirrhosis, including contributions of various aetiologies of liver disease, and consider what needs to be done to address projected increases in the burden of cirrhosis.
- Daniel Q. Huang
- , Norah A. Terrault
- & Rohit Loomba
-
-
Year in Review |
 Advancing alcohol-related liver disease: from novel biomarkers to refining selection for liver transplantation
Advancing alcohol-related liver disease: from novel biomarkers to refining selection for liver transplantation
In 2022, we witnessed advances in the field of alcohol-related liver disease. Key developments included the discovery of novel proteomics-based biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets that regulate the recognition of molecules derived from gut microbiota to modulate liver injury. Additionally, there have been significant advances in refining selection for liver transplantation in severe alcohol-associated hepatitis.
- Juan Pablo Arab
- & Ramon Bataller
-
In Brief |
Investigating two versus three doses of mRNA vaccine in patients with cirrhosis
- Jordan Hindson
-
Review Article |
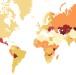 Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: trends, projections and risk factors
Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: trends, projections and risk factors
Global alcohol consumption has increased in the past two decades and is projected to increase further. In this Review, Loomba and colleagues discuss the global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, including risk factors, trends and projections.
- Daniel Q. Huang
- , Philippe Mathurin
- & Rohit Loomba
-
-
-
Perspective |
 Machine perfusion of the liver: applications in transplantation and beyond
Machine perfusion of the liver: applications in transplantation and beyond
Ceresa et al. discuss machine perfusion technologies for liver preservation and transplantation, including the potential of hypothermic and normothermic machine perfusion to improve preservation time and organ quality, as well as the future applications of perfusion technologies.
- Carlo D. L. Ceresa
- , David Nasralla
- & Peter J. Friend
-
-
Review Article |
 Management of alcohol use disorder in patients with cirrhosis in the setting of liver transplantation
Management of alcohol use disorder in patients with cirrhosis in the setting of liver transplantation
In this Review, Arab and colleagues discuss management of alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol-associated liver disease, particularly in the setting of liver transplantation. An integrative, multidisciplinary approach is proposed.
- Juan Pablo Arab
- , Manhal Izzy
- & Vijay H. Shah
-
Review Article |
 Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction
Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction
In this Review, Albillos and colleagues describe cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction (CAID) and its components — systemic inflammation and immune deficiency — as well as the role of CAID in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Therapies that aim to modulate CAID are discussed.
- Agustín Albillos
- , Rosa Martin-Mateos
- & Melchor Álvarez-Mon
-
Review Article |
 Regulation and functional roles of chemokines in liver diseases
Regulation and functional roles of chemokines in liver diseases
Chemokines have an important role in liver diseases such as alcohol-associated liver disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. This Review describes the regulation of chemokines in the liver, their roles in liver diseases and the potential therapeutic targets.
- Sheng Cao
- , Mengfei Liu
- & Vijay H. Shah
-
News & Views |
Novel insights into liver homeostasis and regeneration
Studies of liver regeneration after injury have provided knowledge of the role of external signals and internal metabolic and regenerative pathways. However, less is understood about homeostatic maintenance of normal liver size in the absence of external injury. Three important new studies explore liver regeneration and homeostasis using novel lineage tagging of hepatic cells and single-cell RNA transcriptomics.
- George K. Michalopoulos
-
-
Review Article |
 COVID-19 and liver disease: mechanistic and clinical perspectives
COVID-19 and liver disease: mechanistic and clinical perspectives
This Review provides mechanistic and clinical insights into COVID-19 in the context of liver disease, discussing the potential underlying biology and clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with pre-existing liver conditions. The management of these patients is also discussed, including SARS-CoV-2 vaccination strategies.
- Thomas Marjot
- , Gwilym J. Webb
- & Eleanor Barnes
-
Review Article |
 Utilizing the gut microbiome in decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure
Utilizing the gut microbiome in decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure
The common end stage of liver disease is decompensated cirrhosis and the further development towards acute-on-chronic liver failure. In this Review, the authors discuss the possible pathogenic, diagnostic and therapeutic role of the gut microbiota in decompensation of cirrhosis and progression to acute-on-chronic liver failure.
- Jonel Trebicka
- , Peer Bork
- & Manimozhiyan Arumugam
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
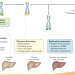 The role of telomeres and telomerase in cirrhosis and liver cancer
The role of telomeres and telomerase in cirrhosis and liver cancer
Telomerase is a key enzyme for cell survival that prevents telomere shortening. In this Review, the roles of telomeres and telomerase in cirrhosis and liver carcinogenesis are discussed, in addition to their potential in clinical practice as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
- Jean-Charles Nault
- , Massih Ningarhari
- & Jessica Zucman-Rossi
-
-
Review Article |
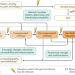 Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota
Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Here, Bajaj discusses clinical studies on the gut microbiota in individuals with ALD and explores the specific alterations in the gut–liver–brain axis that might alter patient outcomes.
- Jasmohan S. Bajaj
-
Review Article |
 Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of portal hypertension
Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of portal hypertension
Liver microcirculatory dysfunction is one of the key mechanisms that promotes the progression of chronic liver disease. In this Review, the authors explore the role of liver microcirculatory dysfunction in cirrhotic portal hypertension, the preclinical models used to study liver circulation and potential therapeutics.
- Jordi Gracia-Sancho
- , Giusi Marrone
- & Anabel Fernández-Iglesias
-
Review Article |
 Novel perspectives in the management of decompensated cirrhosis
Novel perspectives in the management of decompensated cirrhosis
Current approaches to manage decompensated cirrhosis are based on targeted strategies aimed at preventing or treating specific complications of the disease. Here, Bernardi and Caraceni discuss the shift in focus from individual treatments targeting individual complications to disease-modifying agents able to slow the progression of decompensation.
- Mauro Bernardi
- & Paolo Caraceni
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Liver — guardian, modifier and target of sepsis
Liver — guardian, modifier and target of sepsis
The liver regulates immune defence during sepsis, but is also a target for sepsis-related injury. Liver dysfunction can affect the prognosis of sepsis, particularly in patients with cirrhosis. In this Review, the importance of the liver in sepsis, the factors contributing to sepsis in patients with liver cirrhosis and new therapeutic strategies are discussed.
- Pavel Strnad
- , Frank Tacke
- & Christian Trautwein
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Critical comparison of elastography methods to assess chronic liver disease
Critical comparison of elastography methods to assess chronic liver disease
Elastography techniques for the noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis, disease severity and prognosis are increasingly included in guidelines and clinical practice. In this Review, the authors summarize the problems of noninvasive tests in general, and provide an overview on available techniques and developments in liver elastography.
- Mireen Friedrich-Rust
- , Thierry Poynard
- & Laurent Castera
-
News & Views |
 Osteopontin and HMGB1: novel regulators of HSC activation
Osteopontin and HMGB1: novel regulators of HSC activation
Liver fibrosis, the accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins caused by chronic liver damage, results from the activation of hepatic stellate cells. In a new study, Arriazu et al. explore in detail the mechanisms by which the multifunctional protein osteopontin drives hepatic fibrosis, and show that interaction with HMGB1 mediates the fibrogenic response.
- Lee A. Borthwick
- & Derek A. Mann
-
Review Article |
 Circadian rhythms of liver physiology and disease: experimental and clinical evidence
Circadian rhythms of liver physiology and disease: experimental and clinical evidence
The circadian clock plays a central part in the regulation of liver function. In this Review, Tahara and Shibata discuss the mechanisms by which the circadian clock controls hepatic metabolism and the processing of xenobiotics, and how clock dysfunction can influence liver disease.
- Yu Tahara
- & Shigenobu Shibata
-
Review Article |
 Acute-on-chronic liver failure: terminology, mechanisms and management
Acute-on-chronic liver failure: terminology, mechanisms and management
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a distinct clinical entity with a serious risk of death. However, much debate surrounds the pathogenesis and definitions of this disease. Sarin and Choudhury describe the differences and similarities between Eastern and Western definitions of ACLF and present a common approach to manage these patients for better clinical outcomes.
- Shiv K. Sarin
- & Ashok Choudhury
-
Research Highlight |
New genetic insights into the development of alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Christine Weber
-
Review Article |
 The evolving concept of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis
The evolving concept of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis
Traditionally, the diagnosis of hepatorenal syndrome has been based on stringent criteria that are not ideal for patients with cirrhosis and kidney injury, leading to underdiagnosis. Acute kidney injury is now proposed to characterize renal disease in patients with cirrhosis. Florence Wong describes the evolution of these criteria that have addressed this issue and improved care for these patients.
- Florence Wong
-
Review Article |
 Pathogenesis of biliary atresia: defining biology to understand clinical phenotypes
Pathogenesis of biliary atresia: defining biology to understand clinical phenotypes
Biliary atresia is a severe cholangiopathy with a poorly defined pathogenesis and treatment strategy that leads to end-stage cirrhosis in most children. The authors of this Review bring together the most up-to-date understanding of the pathogenesis of biliary atresia, how environmental and genetic factors create various clinical phenotypes and provide insights into future clinical trial design.
- Akihiro Asai
- , Alexander Miethke
- & Jorge A. Bezerra
-
-
-

 Screening for liver fibrosis: lessons from colorectal and lung cancer screening
Screening for liver fibrosis: lessons from colorectal and lung cancer screening New insights into aetiology of paediatric liver cirrhosis
New insights into aetiology of paediatric liver cirrhosis Tuft cells restrain PDAC progression
Tuft cells restrain PDAC progression Predicting development of ACLF
Predicting development of ACLF Clues to cirrhosis — a focus on fibrosis
Clues to cirrhosis — a focus on fibrosis Viral hepatitis: beginning of the end?
Viral hepatitis: beginning of the end?