Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access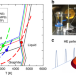 Detonation synthesis of carbon nano-onions via liquid carbon condensation
Detonation synthesis of carbon nano-onions via liquid carbon condensation
Detonation of high explosives can produce many nanocarbon allotropes and morphologies, but the mechanism of formation is challenging to explore. Here the authors observe, by time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering, a transient liquid phase that precedes the formation of carbon onions.
- M. Bagge-Hansen
- , S. Bastea
- & T. M. Willey
-
Article
| Open Access Nanosecond electron pulses in the analytical electron microscopy of a fast irreversible chemical reaction
Nanosecond electron pulses in the analytical electron microscopy of a fast irreversible chemical reaction
Detailed knowledge of the transition states and kinetics of fast reactions in nanoparticles is desirable for many applications, but challenging to access. Here the authors obtain insight in nickel oxide reduction, using single-shot electron pulses in an electron microscope with nanosecond resolution.
- Shyam K. Sinha
- , Amir Khammari
- & Florian Banhart
-
Article
| Open Access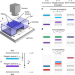 Band-collision gel electrophoresis
Band-collision gel electrophoresis
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays are widely used in gel electrophoresis to study binding interactions between different molecular species, but these assays access only a subset of reaction possibilities. Here, the authors develop a band-collision gel electrophoresis (BCGE) approach that demonstrates a much wider variety of reaction types.
- Dimitri A. Bikos
- & Thomas G. Mason
-
Article
| Open Access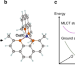 Tracking multiple components of a nuclear wavepacket in photoexcited Cu(I)-phenanthroline complex using ultrafast X-ray spectroscopy
Tracking multiple components of a nuclear wavepacket in photoexcited Cu(I)-phenanthroline complex using ultrafast X-ray spectroscopy
Nonadiabatic excited state processes involve mixing of electronic and nuclear wavefunctions, which are difficult to disentangle. Here the authors explore by time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure the wavepacket dynamics of a copper(I)-phenanthroline complex, resolving different vibrational modes.
- Tetsuo Katayama
- , Thomas Northey
- & Thomas J. Penfold
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling conical intersection and coherent molecular dynamics in methyl bromide with attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy
Disentangling conical intersection and coherent molecular dynamics in methyl bromide with attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy
Excited-state molecular dynamics may be too complex to be resolved by femtosecond spectroscopic studies. Here the authors resolve the competing pathways in the excited state dynamics of methyl bromide by attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy, from excitation to fragmentation.
- Henry Timmers
- , Xiaolei Zhu
- & Stephen R. Leone
-
Article
| Open Access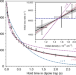 Sticky collisions of ultracold RbCs molecules
Sticky collisions of ultracold RbCs molecules
Ultracold polar molecules are an excellent platform for quantum science but experiments so far see fast trap losses that are poorly understood. Here the authors investigate collisional losses of nonreactive RbCs, and show they are consistent with the sticky collision hypothesis, but are slower than the universal rate.
- Philip D. Gregory
- , Matthew D. Frye
- & Simon L. Cornish
-
Article
| Open Access Zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance of chemically exchanging systems
Zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance of chemically exchanging systems
Zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance can identify species and collective behaviors in mixtures without applied magnetic fields. Here the authors demonstrate its use for resolving proton exchange in ammonium and for the detection of hyperpolarized pyruvic acid, an important imaging biomarker.
- Danila A. Barskiy
- , Michael C. D. Tayler
- & Alexander Pines
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast structural rearrangement dynamics induced by the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution
Ultrafast structural rearrangement dynamics induced by the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution
The interaction of biomolecules with ionizing radiation induces structural changes which are still largely unknown. The authors use femtosecond wave packet spectroscopy to observe ultrafast structural dynamics that follow the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution.
- Tushar Debnath
- , Muhammad Shafiq Bin Mohd Yusof
- & Zhi-Heng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Low-energy electrons transform the nimorazole molecule into a radiosensitiser
Low-energy electrons transform the nimorazole molecule into a radiosensitiser
Radiosensitisers are believed to interfere with cancer cells by dissociating upon interaction with electrons. Here the authors observe instead that the dominant path for nitroimidazolic radiosensitisers involves formation of a non-dissociated radical anion, prerequisite for their accumulation in tumour cells.
- Rebecca Meißner
- , Jaroslav Kočišek
- & Stephan Denifl
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule kinetics of pore assembly by the membrane attack complex
Single-molecule kinetics of pore assembly by the membrane attack complex
The membrane attack complex (MAC) is a hetero-oligomeric protein assembly that kills pathogens by perforating their cell envelopes. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to show that MAC proteins oligomerize within the membrane, allowing them to identify the kinetic bottleneck of MAC formation.
- Edward S. Parsons
- , George J. Stanley
- & Bart W. Hoogenboom
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid unimolecular reaction of stabilized Criegee intermediates and implications for atmospheric chemistry
Rapid unimolecular reaction of stabilized Criegee intermediates and implications for atmospheric chemistry
Criegee intermediates have received much attention in atmospheric chemistry because of their importance in ozonolysis mechanisms. Here, using quantum mechanical kinetics, the authors reveal an unexpectedly fast mechanistic pathway for unimolecular reactions of large stabilized Criegee intermediates.
- Bo Long
- , Junwei Lucas Bao
- & Donald G. Truhlar
-
Article
| Open Access Acceleration of dolomitization by zinc in saline waters
Acceleration of dolomitization by zinc in saline waters
The reason for dolomite being widespread in ancient rocks remains an unsolved conundrum and artificial attempts to form well-ordered dolomite at ambient conditions have proven very challenging. Here, the authors provide laboratory experiments that show the acceleration of dolomite formation via dissolved zinc.
- Veerle Vandeginste
- , Oliver Snell
- & Arne Vandeginste
-
Article
| Open Access Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer and its correlation with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer
Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer and its correlation with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer
Intramolecular electron-induced proton transfer (iEIPT) describes proton motion coupled with the attachment of an electron within a molecule. Here, the authors build a “search engine” for iEIPT-capable molecules that also have the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer property.
- Wei Wang
- , Mary Marshall
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Both electronic and vibrational coherences are involved in primary electron transfer in bacterial reaction center
Both electronic and vibrational coherences are involved in primary electron transfer in bacterial reaction center
Distinguishing electronic and vibrational coherences helps to clarify the near-unity efficiency of primary electron transfer in reaction centres. Here, the authors report their respective correlation with the electron transfer rate by comparing the 2D electronic spectra of three mutant reaction centres.
- Fei Ma
- , Elisabet Romero
- & Rienk van Grondelle
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-nuclear correlated multiphoton-route to Rydberg fragments of molecules
Electron-nuclear correlated multiphoton-route to Rydberg fragments of molecules
Rydberg atoms can be created from photoexcitation of molecules using intense ultrafast laser pulses. Here the authors use a coincidence detection of electrons, ion and excited Rydberg atoms and their energy sharing to reveal the general mechanism of Rydberg state excitation in a dissociating H2 molecule.
- Wenbin Zhang
- , Xiaochun Gong
- & Jian Wu
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: “The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails”
- Xinxin Cheng
- , Elvar Jónsson
- & Peter M. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Here, the authors explore the ultrafast photodynamics of methyl anthranilate. From the quantum beat behavior, the authors find evidence for ultrafast energy redistribution processes which hinder excited state relaxation, making methyl anthranilate a poor choice for a sunscreen chemical filter.
- Natércia d. N. Rodrigues
- , Neil C. Cole-Filipiak
- & Vasilios G. Stavros
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving orbital pathways for intermolecular electron transfer
Resolving orbital pathways for intermolecular electron transfer
It is known that intermolecular interactions impact electron transfer rates, but the mechanisms involved are challenging to define experimentally. Here, the authors have developed a platform that enables atomic orbital resolution of electron transfer through an explicit intermolecular interaction.
- Cameron W. Kellett
- , Wesley B. Swords
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion-limited reactions in dynamic heterogeneous media
Diffusion-limited reactions in dynamic heterogeneous media
“Diffusing diffusivity” concept has been recently put forward to account for rapid structural rearrangements in soft matter and biological systems. Here the authors propose a general mathematical framework to compute the distribution of first-passage times in a dynamically heterogeneous medium.
- Yann Lanoiselée
- , Nicolas Moutal
- & Denis S. Grebenkov
-
Article
| Open Access The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals is not a major source of atmospheric methanol
The reaction of hydroxyl and methylperoxy radicals has recently been suggested as the source of missing methanol in the remote troposphere. Here, the authors present direct experimental measurements demonstrating the reaction leads to further underprediction of modelled methanol.
- Rebecca L. Caravan
- , M. Anwar H. Khan
- & Craig A. Taatjes
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrational control of selective bond cleavage in dissociative chemisorption of methanol on Cu(111)
Vibrational control of selective bond cleavage in dissociative chemisorption of methanol on Cu(111)
Dissociative chemisorption of methanol on metal surfaces is a key step for hydrogen production. Here the authors use quasi-quantized molecular dynamics simulations to alter the branching ratios for methanol dissociative chemisorption on Cu(111) via selectively exciting specific vibrational modes.
- Jialu Chen
- , Xueyao Zhou
- & Bin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
The existence of a crystalline precursor is key to perovskite film formation, but the precise chemistry of the precursor and its transformation into perovskite are poorly understood. Here, the authors identify the crystal structure and conversion chemistry of the precursor for PbCl2-derived methylammonium lead iodide perovskites.
- Kevin H. Stone
- , Aryeh Gold-Parker
- & Christopher J. Tassone
-
Article
| Open Access A proline switch explains kinetic heterogeneity in a coupled folding and binding reaction
A proline switch explains kinetic heterogeneity in a coupled folding and binding reaction
How intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) undergo a coupled folding and binding reaction with their molecular targets remains to be understood. Here authors use single-molecule FRET to assess the contribution of cis/trans isomerization of peptidyl-prolyl bonds in regulating IDP interactions.
- Franziska Zosel
- , Davide Mercadante
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Article
| Open Access Higher activation barriers can lift exothermic rate restrictions in electron transfer and enable faster reactions
Higher activation barriers can lift exothermic rate restrictions in electron transfer and enable faster reactions
A widely-assumed principle of chemical reactivity is that, for elementary reactions, higher activation barriers lead to slower reactions. Here, the authors show that some intramolecular electron transfer processes become faster as their apparent activation energies increase, contradicting chemical intuition.
- Kamila K. Mentel
- , Arménio Serra
- & Luis G. Arnaut
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry
Coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry
Multidimensional spectroscopy is a powerful tool in exploring photo-induced dynamics and electron coupling processes in molecules. Here the authors demonstrate coherent two-dimensional electronic mass spectrometry on molecular beams and its application to photoionization studies of the NO2 molecule.
- Sebastian Roeding
- & Tobias Brixner
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of different reactivities of para and ortho-water towards trapped diazenylium ions
Observation of different reactivities of para and ortho-water towards trapped diazenylium ions
Water molecules exist as two distinct nuclear-spin isomers denoted ortho and para. Here, the authors separate these two isomers in the gas phase to show that they exhibit different reactivities in a prototypical proton-transfer reaction.
- Ardita Kilaj
- , Hong Gao
- & Stefan Willitsch
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular solar thermal energy storage in photoswitch oligomers increases energy densities and storage times
Molecular solar thermal energy storage in photoswitch oligomers increases energy densities and storage times
Molecular solar thermal systems are promising for storing solar energy but achieving high energy storage densities and absorption characteristics matching the solar spectrum is challenging. Here the authors present a design strategy for electronically coupled photoswitches which allow for high energy density storage for solar energy storage applications.
- Mads Mansø
- , Anne Ugleholdt Petersen
- & Kasper Moth-Poulsen
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-controlled atom–ion chemistry
Spin-controlled atom–ion chemistry
Chemical reactions with ultracold atoms and ions are explored so far with the atom–ion interactions. Here the authors discuss spin-exchange process and show that the spin state of an ensemble of neutral Rb atoms can be used to control the final spin of an imbedded Sr+ ion in the collisions.
- Tomas Sikorsky
- , Ziv Meir
- & Roee Ozeri
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of single-molecule hydrogen-bond dynamics with single-bond resolution
Direct observation of single-molecule hydrogen-bond dynamics with single-bond resolution
Hydrogen-bonds are widely found in many systems, such as DNAs and supramolecular assemblies, but it remains challenging to detect their dynamics at a molecular level. Here, Zhou et al. study the stochastic arrangement of hydrogen bonds using single-molecule junctions connected to graphene electrodes.
- Ce Zhou
- , Xingxing Li
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Directed gas phase formation of silicon dioxide and implications for the formation of interstellar silicates
Directed gas phase formation of silicon dioxide and implications for the formation of interstellar silicates
Interstellar silicates play a key role in star formation, however their synthetic routes are not fully understood. Here, the authors provide evidence for the formation of SiO2 along with SiO via low-temperature gas phase chemistry.
- Tao Yang
- , Aaron M. Thomas
- & Tom J. Millar
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution and stabilization of subnanometric metal species in confined space by in situ TEM
Evolution and stabilization of subnanometric metal species in confined space by in situ TEM
Understanding the behavior and structural transformation of metal species under reaction conditions is instrumental for developing more efficient and stable catalysts. Here, the authors reveal the evolution and stabilization of subnanometric Pt species confined in MCM-22 zeolite using in situ transmission electron microscopy.
- Lichen Liu
- , Dmitri N. Zakharov
- & Avelino Corma
-
Article
| Open Access Microkinetics of alcohol reforming for H2 production from a FAIR density functional theory database
Microkinetics of alcohol reforming for H2 production from a FAIR density functional theory database
The production of hydrogen from biomass is of fundamental importance for a sustainable future. Here, the authors present a multiscale method that allows the formulation of scaling relationships and microkinetics of C1-C2 alcohol decomposition based on a density functional theory open database.
- Qiang Li
- , Rodrigo García-Muelas
- & Núria López
-
Article
| Open Access Proton gradients and pH oscillations emerge from heat flow at the microscale
Proton gradients and pH oscillations emerge from heat flow at the microscale
Proton motive forces are central for life but it is not well understood how these pH gradients emerged at the beginning of life. Here the authors show that heat flow across a water-filled chamber forms and sustains stable pH gradients and support their experimental findings with simulations.
- Lorenz M. R. Keil
- , Friederike M. Möller
- & Christof B. Mast
-
Article
| Open Access Strong laser field control of fragment spatial distributions from a photodissociation reaction
Strong laser field control of fragment spatial distributions from a photodissociation reaction
Strong laser light can intervene and modify the dynamical processes of matter. Here, the authors show how an intense laser field affects the spatial distribution of fragments in a molecular bond-breaking process, and how the intensity of this laser field can be used as an external knob to control it.
- María E. Corrales
- , Rebeca de Nalda
- & Luis Bañares
-
Article
| Open Access Protein-peptide association kinetics beyond the seconds timescale from atomistic simulations
Protein-peptide association kinetics beyond the seconds timescale from atomistic simulations
Binding and unbinding kinetics are important determinants of protein-protein or small molecule protein functional interactions that can guide drug development. Here the authors exploit the multi-ensemble Markov model framework to develop a computational approach that allows the estimation of binding kinetics reaching into the seconds timescale.
- Fabian Paul
- , Christoph Wehmeyer
- & Frank Noé
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging dynamic fingerprints of competing E2 and SN2 reactions
Imaging dynamic fingerprints of competing E2 and SN2 reactions
The competition between chemical reactions critically affects our natural environment and the synthesis of new materials. Here, the authors present an approach to directly image distinct fingerprints of essential organic reactions and monitor their competition as a function of steric substitution.
- Eduardo Carrascosa
- , Jennifer Meyer
- & Roland Wester
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time observation of cation exchange kinetics and dynamics at the muscovite-water interface
Real-time observation of cation exchange kinetics and dynamics at the muscovite-water interface
Ion exchange at charged mineral-water interfaces is an important geochemical process, but a molecular-level understanding is still required. Here, the authors probe real-time variations of the interfacial ion exchange dynamics at the muscovite-water interface, providing a general picture of adsorbed ion coverage and speciation.
- Sang Soo Lee
- , Paul Fenter
- & Neil C. Sturchio
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring nanoscopic confines to maximize catalytic activity of hydronium ions
Tailoring nanoscopic confines to maximize catalytic activity of hydronium ions
The rates of acid-catalysed reactions vary in constrained environments. Here the authors show that molecularly sized pores greatly promote aqueous phase alcohol dehydration by enhancing the association between substrate and hydronium ions, and even by lowering the free energy barrier.
- Hui Shi
- , Sebastian Eckstein
- & Johannes A. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic molecular oxygen production in cometary comae
Dynamic molecular oxygen production in cometary comae
Abundant molecular oxygen was discovered recently in the coma of comet 67P, thought to be of primordial origin. Here, the authors propose a dynamic reaction mechanism for cometary comae, which produces O2directly in single collisions of energetic water ions with oxidized cometary surface analogues.
- Yunxi Yao
- & Konstantinos P. Giapis
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical barrier and isotope effects in the simplest substitution reaction via Walden inversion mechanism
Dynamical barrier and isotope effects in the simplest substitution reaction via Walden inversion mechanism
The H+CH4substitution reaction is the simplest reaction occurring via the Walden inversion mechanism. Here, the authors perform a theoretical study of the reaction and uncover the important effect of the umbrella motion of the non-reacting methyl group on the reaction dynamics.
- Zhiqiang Zhao
- , Zhaojun Zhang
- & Dong H Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
The atomic mechanisms of reversible phase transitions are challenging to probe experimentally. Here, the authors induce melting and freezing processes in bismuth nanoparticles inside a high-resolution electron microscope, observing the atom-level stages of this phase transition pathway in real time.
- Yingxuan Li
- , Ling Zang
- & Chuanyi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Surface single-molecule dynamics controlled by entropy at low temperatures
Surface single-molecule dynamics controlled by entropy at low temperatures
STM is capable of imaging the configurations of molecules on surfaces and measuring the rate of transitions between them. Here the authors demonstrate that, controlled by the STM tip position, the entropic and conservative forces on the molecule can modify the rate by orders of magnitude.
- J. C. Gehrig
- , M. Penedo
- & H. J. Hug
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical importance of van der Waals saddle and excited potential surface in C(1D)+D2 complex-forming reaction
Dynamical importance of van der Waals saddle and excited potential surface in C(1D)+D2 complex-forming reaction
It is commonly held that van der Waals wells are inevitable in chemical reactions. Here, the authors show that weak van der Waals forces in the entrance channel of a prototypical complex-forming reaction cause a van der Waals saddle instead, with different dynamical effects from a well at low collision energies.
- Zhitao Shen
- , Haitao Ma
- & Jianwei Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Bond selectivity in electron-induced reaction due to directed recoil on an anisotropic substrate
Bond selectivity in electron-induced reaction due to directed recoil on an anisotropic substrate
The ability to selectively break a chemical bond in a molecule is indispensable to chemical synthesis. Here, the authors show that a hundred-fold bond selectivity can be obtained in electron-induced surface reaction due simply to different bond alignments at the surface.
- Kelvin Anggara
- , Kai Huang
- & John C. Polanyi
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Understanding bimetallic alloy oxidation is key to design of hollow-structured binary oxides and their optimization for applications, e.g., as catalysts. Here the authors combine real-time imaging and chemically-sensitive electron tomography to uncover unexpected complexity in possible morphological outcomes of bimetallic oxidation.
- Lili Han
- , Qingping Meng
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical gating of a mechanochemical reaction cascade
Mechanical gating of a mechanochemical reaction cascade
Polymer mechanochemistry offers opportunities to control and engineer desired chemical transformations. Here, Craig and co-workers present a mechanical gating system whereby one mechanophore modulates the reactivity of another, resulting in a mechanochemical cascade reaction.
- Junpeng Wang
- , Tatiana B. Kouznetsova
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article
| Open Access Product lambda-doublet ratios as an imprint of chemical reaction mechanism
Product lambda-doublet ratios as an imprint of chemical reaction mechanism
Propensity for a given Λ-doublet level is a common feature in many chemical reactions, but has so far remained unexplained. Here, the authors show how to predict computationally those propensities and relate them to the reaction mechanism on concurrent potential energy surfaces.
- P. G. Jambrina
- , A. Zanchet
- & F. J. Aoiz
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared
Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared
Indium arsenide quantum dots are promising materials for short-wavelength infrared emissive applications. Here, the authors investigate the kinetics of indium arsenide nanocrystal growth and design large quantum dots with narrow emission wavelengths which can be used for through-skull fluorescence imaging.
- Daniel Franke
- , Daniel K. Harris
- & Moungi G. Bawendi
-
Article
| Open Access Competitive solvent-molecule interactions govern primary processes of diphenylcarbene in solvent mixtures
Competitive solvent-molecule interactions govern primary processes of diphenylcarbene in solvent mixtures
Photochemistry in solution often involves coexisting reaction channels that may comprise intermediates capturing a solvent molecule. Here, the authors show for one of the most reactive species, diphenylcarbene, that the decision-maker is not the nearest solvent molecule but its neighbour.
- Johannes Knorr
- , Pandian Sokkar
- & Patrick Nuernberger

 Reaction selectivity of homochiral versus heterochiral intermolecular reactions of prochiral terminal alkynes on surfaces
Reaction selectivity of homochiral versus heterochiral intermolecular reactions of prochiral terminal alkynes on surfaces