Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Pro-ferroptotic signaling promotes arterial aging via vascular smooth muscle cell senescence
Pro-ferroptotic signaling promotes arterial aging via vascular smooth muscle cell senescence
Ferroptosis is a novel form of regulated cell death associated with lipid oxidation. Here, the authors demonstrate that the proferroptosis signal is activated and drives vascular aging by inducing senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells.
- Di-Yang Sun
- , Wen-Bin Wu
- & Pei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access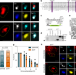 The vacuolar iron transporter mediates iron detoxification in Toxoplasma gondii
The vacuolar iron transporter mediates iron detoxification in Toxoplasma gondii
Iron is essential to cells, however without correct storage can lead to cell damage. Aghabi et al. show that the vacuolar iron transporter (VIT) is required for iron storage in the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. They find VIT protects against iron toxicity and has a role in parasite virulence.
- Dana Aghabi
- , Megan Sloan
- & Clare R. Harding
-
Article
| Open Access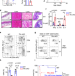 Microbiota-assisted iron uptake promotes immune tolerance in the intestine
Microbiota-assisted iron uptake promotes immune tolerance in the intestine
Iron deficiencies are a common non intestinal symptom seen in patients with irritable bowel disease. Here the authors show an associative link between microbiota assisted uptake of nutrients including iron and the promotion of immune tolerance in the intestine.
- Lizhen Zhu
- , Geng Li
- & Xing Chang
-
Article
| Open Access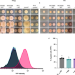 Pulcherriminic acid modulates iron availability and protects against oxidative stress during microbial interactions
Pulcherriminic acid modulates iron availability and protects against oxidative stress during microbial interactions
Microbes often produce molecules (termed siderophores) that bind iron and then are taken up using specific receptors for iron acquisition. Here, the authors show that a compound produced by Bacillus subtilis plays a more complex role, by modulating iron availability and conferring protection against oxidative stress during inter-species competition.
- Vincent Charron-Lamoureux
- , Lounès Haroune
- & Pascale B. Beauregard
-
Article
| Open Access LncRNA modulates Hippo-YAP signaling to reprogram iron metabolism
LncRNA modulates Hippo-YAP signaling to reprogram iron metabolism
Iron metabolism dysregulation is associated with various diseases including cancer. Here, the authors show that one iron-triggered lncRNA LncRIM regulates cellular iron metabolism effectively by wiring up the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway and promotes breast cancer development.
- Xin-yu He
- , Xiao Fan
- & Aifu Lin
-
Article
| Open Access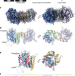 Uptake mechanism of iron-phytosiderophore from the soil based on the structure of yellow stripe transporter
Uptake mechanism of iron-phytosiderophore from the soil based on the structure of yellow stripe transporter
Iron is an essential mineral in plant physiology. YS1 transporter imports iron–phytosiderophore complex (Fe(III)–DMA) from the soil. Here, the authors describe the cryo-EM structures of barley YS1 in complex with substrate, and a synthetic substrate analog.
- Atsushi Yamagata
- , Yoshiko Murata
- & Mikako Shirouzu
-
Article
| Open Access Intramyocardial hemorrhage drives fatty degeneration of infarcted myocardium
Intramyocardial hemorrhage drives fatty degeneration of infarcted myocardium
It is unclear why hemorrhagic myocardial infarctions (hMI) are destined for adverse outcomes. Here, the authors show that hMI drives fatty degeneration of infarct territories and contributes to adverse remodeling of the heart, which can be mitigated via timely depletion of iron within the hMI zone.
- Ivan Cokic
- , Shing Fai Chan
- & Rohan Dharmakumar
-
Article
| Open Access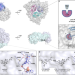 Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
SxtT and GxtA are Rieske oxygenases that are involved in paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis and catalyze monohydroxylation reactions at different positions on the toxin scaffold. Here, the authors present crystal structures of SxtT and GxtA with the native substrates β-saxitoxinol and saxitoxin as well as a Xenon-pressurized structure of GxtA, which reveal a substrate access tunnel to the active site. Through structure-based mutagenesis studies the authors identify six residues in three different protein regions that determine the substrate specificity and site selectivity of SxtT and GxtA. These findings will aid the rational engineering of other Rieske oxygenases.
- Jianxin Liu
- , Jiayi Tian
- & Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Iron is an essential plant nutrient that is poorly bioavailable in alkaline soils, resulting in reduced agricultural productivity. Here, the authors report the synthesis of stable and cheap iron-chelator, proline-2’-deoxymugineic acid (PDMA), and demonstrate its utility as potential fertilizer.
- Motofumi Suzuki
- , Atsumi Urabe
- & Kosuke Namba
-
Article
| Open Access Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biogenesis but the molecular connection between these pathways is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that the heme biosynthesis enzyme ALAD contains an Fe-S cluster, disruption of which reduces ALAD activity and heme production in human cells.
- Gang Liu
- , Debangsu Sil
- & Tracey Ann Rouault
-
Article
| Open Access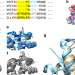 Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Glutaredoxins are a family of essential enzymes divided into two major classes with either a CGFS or a CxxC active site, of which only the latter exhibits oxidoreductase activity. Here the authors address the structural basis for the functional difference between the two classes of glutaredoxins.
- Daniel Trnka
- , Anna D. Engelke
- & Christopher Horst Lillig
-
Article
| Open Access Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
The mechanism of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors develop a physiologically relevant in vitro model of Fe-S cluster assembly, allowing them to elucidate the sequence of Fe-S cluster synthesis along with the respective roles of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin.
- Sylvain Gervason
- , Djabir Larkem
- & Benoit D’Autréaux
-
Article
| Open Access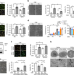 Involvement of cigarette smoke-induced epithelial cell ferroptosis in COPD pathogenesis
Involvement of cigarette smoke-induced epithelial cell ferroptosis in COPD pathogenesis
Altered iron homeostasis resulting in excessive oxidative stress has been implicated in smoke-induced lung diseases. Here the authors show that ferroptosis of lung epithelial cells, potentially resulting from excessive ferritinophagy, is involved in the pathogenesis of COPD.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Shunsuke Minagawa
- & Kazuyoshi Kuwano
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and functional dynamics of the mitochondrial Fe/S cluster synthesis complex
Structure and functional dynamics of the mitochondrial Fe/S cluster synthesis complex
Fe/S clusters are synthesized by the mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly (ISC) machinery. Here the authors combine crystallography and small angle X-ray scattering measurements to structurally characterize the core ISC complex and give functional insights into eukaryotic Fe/S cluster synthesis.
- Michal T. Boniecki
- , Sven A. Freibert
- & Miroslaw Cygler
-
Article
| Open Access Hepcidin is regulated by promoter-associated histone acetylation and HDAC3
Hepcidin is regulated by promoter-associated histone acetylation and HDAC3
Hepcidin controls systemic iron levels by inhibiting intestinal iron absorption and iron recycling. Here, Pasricha et al. demonstrate that the hepcidin-chromatin locus displays HDAC3-mediated reversible epigenetic modifications during both erythropoiesis and iron deficiency.
- Sant-Rayn Pasricha
- , Pei Jin Lim
- & Hal Drakesmith
-
Article
| Open Access Biological iron-sulfur storage in a thioferrate-protein nanoparticle
Biological iron-sulfur storage in a thioferrate-protein nanoparticle
The biosynthesis of iron-sulfur clusters in anaerobic organisms has not been extensively investigated. Here, the authors identify and characterize a multi-subunit protein that stores iron and sulfur in thioferrate for the assembly of the clusters inPyrococcus furiosus.
- Brian J. Vaccaro
- , Sonya M. Clarkson
- & Michael W. W. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access Essential role of FBXL5-mediated cellular iron homeostasis in maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
Essential role of FBXL5-mediated cellular iron homeostasis in maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
The iron-regulated F-box protein FBXL5 regulates iron homeostasis by mediating the degradation of iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP2). Here the authors show that FBXL5 and its regulation of IRP2 are required for HSC self-renewal and reconstitution capability.
- Yoshiharu Muto
- , Masaaki Nishiyama
- & Keiichi I. Nakayama
-
Article
| Open Access ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
The mitochondrial proteins ISCA1 and ISCA2 form a complex that is involved in the biogenesis of Fe–S clusters. Here the authors report that ISCA1 and ISCA2 interact differently with proteins of the Fe–S machinery and that under certain conditions, ISCA2 seems dispensable for Fe–S biogenesis.
- Lena Kristina Beilschmidt
- , Sandrine Ollagnier de Choudens
- & Alain Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access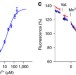 Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Cellular uptake of transition metal ions is mediated by members of the SLC11/NRAMP family. Here the authors determine the structural and functional properties of EcoDMT, a bacterial SLC11 transporter, gathering molecular insight into its transport mechanism and proton coupling process.
- Ines A. Ehrnstorfer
- , Cristina Manatschal
- & Raimund Dutzler
-
Article
| Open Access Disposal of iron by a mutant form of lipocalin 2
Disposal of iron by a mutant form of lipocalin 2
Iron overload can be either hereditary or acquired via transfusions, and current treatments include the use of iron chelators that have adverse effects in some patients. Here the authors modify siderocalin to enhance iron excretion in urine, and demonstrate therapeutic efficacy in iron overload mouse models.
- Jonathan Barasch
- , Maria Hollmen
- & Andong Qiu

 Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2
Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2