Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane potential drives the exit from pluripotency and cell fate commitment via calcium and mTOR
Membrane potential drives the exit from pluripotency and cell fate commitment via calcium and mTOR
The plasma membrane’s electrical potential is maintained by ion channels, though the impact of this potential on cell fate has not been clearly elucidated. Here they show that changes in membrane potential can affect calcium levels and mTOR in pluripotent stem cells, altering their transition from pluripotency to differentiation.
- Emily Sempou
- , Valentyna Kostiuk
- & Mustafa K. Khokha
-
Article
| Open Access Tmem65 is critical for the structure and function of the intercalated discs in mouse hearts
Tmem65 is critical for the structure and function of the intercalated discs in mouse hearts
The intercalated disc (ICD) is a membrane structure of the cardiac muscle involved in normal heart function. Here the authors report that knockdown of the ICD-bound transmembrane protein 65 results in impaired ICD structure, abnormal cardiac electrophysiology and cardiomyopathy in mice.
- Allen C. T. Teng
- , Liyang Gu
- & Anthony O. Gramolini
-
Article
| Open Access Segregated cation flux by TPC2 biases Ca2+ signaling through lysosomes
Segregated cation flux by TPC2 biases Ca2+ signaling through lysosomes
TPC2 is a lysosomal ion channel permeable to both calcium and sodium ions. Here, the authors show that TPC2 can selectively increase its calcium permeability when simultaneously challenged by both its natural activators- NAADP and PI(3,5)P2.
- Yu Yuan
- , Dawid Jaślan
- & Sandip Patel
-
Article
| Open Access Macrocycle-stabilization of its interaction with 14-3-3 increases plasma membrane localization and activity of CFTR
Macrocycle-stabilization of its interaction with 14-3-3 increases plasma membrane localization and activity of CFTR
Mutations in the chloride channel CFTR that impair plasma membrane insertion and ion transport are the cause of cystic fibrosis. Here, the authors identify a macrocycle that stabilizes the interaction of mutant CFTR with the chaperone-like protein 14-3-3 and rescues its biological function.
- Loes M. Stevers
- , Madita Wolter
- & Christian Ottmann
-
Article
| Open Access TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration
TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration
Supplementation of magnesium (Mg2+) or its inclusion in biomaterials has beneficial effects for bone formation, but it has also been reported that it can have detrimental effects. Here, the authors analyse dose- and time-dependent effects of Mg2+ on bone regeneration and show that it can stimulate monocyte-macrophage lineage cells to support bone formation in the early phases of repair, but inhibit bone repair and mineralization in later stages by promoting a pro-inflammatory environment.
- Wei Qiao
- , Karen H. M. Wong
- & Kelvin W. K. Yeung
-
Article
| Open Access AKAP5 complex facilitates purinergic modulation of vascular L-type Ca2+ channel CaV1.2
AKAP5 complex facilitates purinergic modulation of vascular L-type Ca2+ channel CaV1.2
Molecular mechanisms by which glucose modulates L-type Ca2+ channel activity and vascular reactivity are unclear. Here the authors report a nanocomplex orchestrated by AKAP5 that facilitates local purinergic stimulation of L-type Ca2+ channels and vasoconstriction during diabetic hyperglycemia.
- Maria Paz Prada
- , Arsalan U. Syed
- & Madeline Nieves-Cintrón
-
Article
| Open Access Cyst growth in ADPKD is prevented by pharmacological and genetic inhibition of TMEM16A in vivo
Cyst growth in ADPKD is prevented by pharmacological and genetic inhibition of TMEM16A in vivo
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is characterized by the formation of large renal cysts, which lead to a decline in renal function. Here the authors show that genetic and chemical inhibition of TMEM16A largely reduces cyst enlargement in an in vivo model of autosomal dominant PKD.
- Ines Cabrita
- , Andre Kraus
- & Björn Buchholz
-
Article
| Open Access Rieske iron-sulfur protein induces FKBP12.6/RyR2 complex remodeling and subsequent pulmonary hypertension through NF-κB/cyclin D1 pathway
Rieske iron-sulfur protein induces FKBP12.6/RyR2 complex remodeling and subsequent pulmonary hypertension through NF-κB/cyclin D1 pathway
Pulmonary hypertension is a devastating disease with elevation of pulmonary artery pressure and related to abnormal calcium signalling. Here, the authors show that suppression or stabilization of the calcium channel ryanodine receptor 2 may be a potential treatment approach for this disease.
- Lin Mei
- , Yun-Min Zheng
- & Yong-Xiao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Olfactory marker protein directly buffers cAMP to avoid depolarization-induced silencing of olfactory receptor neurons
Olfactory marker protein directly buffers cAMP to avoid depolarization-induced silencing of olfactory receptor neurons
The physiological role of the olfactory marker protein (OMP) has been elusive. Here, the authors demonstrate that OMP buffers cAMP and modulates cAMP-gated channel activity upon sensory stimulation, maintaining neuronal firing during odour-source searching.
- Noriyuki Nakashima
- , Kie Nakashima
- & Makoto Takano
-
Article
| Open Access TRPML1 links lysosomal calcium to autophagosome biogenesis through the activation of the CaMKKβ/VPS34 pathway
TRPML1 links lysosomal calcium to autophagosome biogenesis through the activation of the CaMKKβ/VPS34 pathway
It was known that prolonged TRMPL1 activation induces TFEB translocation and upregulates autophagic gene regulation. Here, the authors show that acute TRMPL1 activation also induces autophagy through VPS34 and by lysosomal calcium release independent of TFEB.
- A. Scotto Rosato
- , S. Montefusco
- & D. L. Medina
-
Article
| Open Access A calcium/cAMP signaling loop at the ORAI1 mouth drives channel inactivation to shape NFAT induction
A calcium/cAMP signaling loop at the ORAI1 mouth drives channel inactivation to shape NFAT induction
ORAI1 constitutes the store-operated Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channel, but how this channel is turned off through Ca2+-dependent inactivation (CDI) remained unclear. Here the authors identify a spatially-restricted Ca2+/cAMP signaling crosstalk critical for mediating CDI which in turn regulates cellular Ca2+ signals and NFAT activation.
- Xuexin Zhang
- , Trayambak Pathak
- & Mohamed Trebak
-
Article
| Open Access Remodeling of secretory lysosomes during education tunes functional potential in NK cells
Remodeling of secretory lysosomes during education tunes functional potential in NK cells
Natural killer (NK) cells are functionally calibrated against self MHC during a process termed education. Here the authors show that NK cell education is associated with the accumulation of dense-core secretory lysosomes for expedited release of granzyme B and Ca2+ flux upon target recognition and NK cell activation.
- Jodie P. Goodridge
- , Benedikt Jacobs
- & Karl-Johan Malmberg
-
Article
| Open Access The TRPV4 channel links calcium influx to DDX3X activity and viral infectivity
The TRPV4 channel links calcium influx to DDX3X activity and viral infectivity
The ion channel TRPV4 senses many environmental cues, but its role in virus infection is not known. Here, Doñate-Macián et al. show that Zika virus induces TRPV4-mediated Ca2+ influx into cells, resulting in the nuclear accumulation of the DDX3X RNA helicase, which increases virus replication.
- P. Doñate-Macián
- , J. Jungfleisch
- & M. A. Valverde
-
Article
| Open Access LRRC8/VRAC anion channels enhance β-cell glucose sensing and insulin secretion
LRRC8/VRAC anion channels enhance β-cell glucose sensing and insulin secretion
Insulin secretion by β-cells is stimulated by glucose and is dependent on the induction of β-cell membrane depolarization, mainly driven by the closure of KATP channels, which in turn promotes voltage-gated Ca2+ channel opening. Here the authors show that LRRC8 volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) modulate glucose-stimulated calcium increase and insulin secretion.
- Till Stuhlmann
- , Rosa Planells-Cases
- & Thomas J. Jentsch
-
Article
| Open Access Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP
Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP
The popular genetically-encoded Ca2+ indicator, GCaMP, has several side-effects. Here the authors show that GCaMP containing CaM interferes with gating and signaling of L-type calcium channels, which disrupts Ca2+ dynamics and gene expression, and develop GCaMP-X to overcome these limitations.
- Yaxiong Yang
- , Nan Liu
- & Xiaodong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access SWELL1 is a glucose sensor regulating β-cell excitability and systemic glycaemia
SWELL1 is a glucose sensor regulating β-cell excitability and systemic glycaemia
Insulin secretion by β-cells is stimulated by glucose and is dependent on the induction of β-cell membrane depolarization, mainly driven by the closure of KATP channels, which in turn promotes voltage-gated Ca2+ channel opening. Here Kang et al. show that the volume-regulated anion channel, SWELL1, is involved in glucose-stimulated calcium increase and insulin secretion.
- Chen Kang
- , Litao Xie
- & Rajan Sah
-
Article
| Open Access A protein interaction mechanism for suppressing the mechanosensitive Piezo channels
A protein interaction mechanism for suppressing the mechanosensitive Piezo channels
Mechanosensitive Piezo channels are important for a wide range of mechanotransduction processes. Here the authors show that Piezos interact with sarcoplasmic /endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+ ATPases (SERCA) and give mechanistic insights into mechanogating and SERCA2-mediated regulation of Piezo1.
- Tingxin Zhang
- , Shaopeng Chi
- & Bailong Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV4 activation triggers protective responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in airway epithelial cells
TRPV4 activation triggers protective responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in airway epithelial cells
LPS is a major component of gram-negative bacterial cell walls, and triggers immune responses in airway epithelium by activating TLR4. Here the authors show that LPS also activates TRPV4, thereby inducing fast defense responses such as nitric oxide production and increased ciliary beating in mice.
- Yeranddy A. Alpizar
- , Brett Boonen
- & Karel Talavera
-
Article
| Open Access CIB2 interacts with TMC1 and TMC2 and is essential for mechanotransduction in auditory hair cells
CIB2 interacts with TMC1 and TMC2 and is essential for mechanotransduction in auditory hair cells
Inner ear hair cells detect sound through deflection of stereocilia that harbor mechanically-gated channels. Here the authors show that protein responsible for Usher syndrome, CIB2, interacts with these channels and is essential for their function and hearing in mice.
- Arnaud P. J. Giese
- , Yi-Quan Tang
- & Zubair M. Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access ORAI2 modulates store-operated calcium entry and T cell-mediated immunity
ORAI2 modulates store-operated calcium entry and T cell-mediated immunity
Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+(CRAC) channels are essential for protective immunity, but the immunological functions of the three ORAI homologues that form CRAC channels are unclear. Here the authors show that ORAI1 and ORAI2 form heteromeric CRAC channels, which fine-tune T cell activation and immune responses.
- Martin Vaeth
- , Jun Yang
- & Stefan Feske
-
Article
| Open Access Potassium channels Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 cooperatively and compensatorily regulate antigen-specific memory T cell functions
Potassium channels Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 cooperatively and compensatorily regulate antigen-specific memory T cell functions
Potassium channels are essential for modulating T-cell functions. Here, by characterizing rat models and analysing human T cells, the authors identify differential requirements of two potassium channel proteins, Kv1.3 and KCa3.1, for the induction of conventional versus autoreactive T-cell responses.
- Eugene Y. Chiang
- , Tianbo Li
- & Jane L. Grogan
-
Article
| Open Access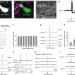 Ciliated neurons lining the central canal sense both fluid movement and pH through ASIC3
Ciliated neurons lining the central canal sense both fluid movement and pH through ASIC3
Cerebrospinal fluid-contacting (CSF-c) cells line the central canal of the vertebrate spinal cord yet their function remains unknown. Here, Javaland et al. show that CSF-c neurons in the lamprey respond to mechanical stimulation and lowered pH, effects likely mediated by ASIC3-channels.
- Elham Jalalvand
- , Brita Robertson
- & Sten Grillner
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenous opioids contribute to insensitivity to pain in humans and mice lacking sodium channel Nav1.7
Endogenous opioids contribute to insensitivity to pain in humans and mice lacking sodium channel Nav1.7
Nav1.7 channels are known to regulate pain perception in humans and mice. Here, the authors provide evidence that Nav1.7 deletion leads to transcriptional upregulation of opioid peptides in sensory neurons, and that treatment with the opioid blocker naloxone helps reverse analgesia in mice and human Nav1.7 nulls.
- Michael S. Minett
- , Vanessa Pereira
- & John N. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access STIM1 dimers undergo unimolecular coupling to activate Orai1 channels
STIM1 dimers undergo unimolecular coupling to activate Orai1 channels
STIM1, the endoplasmic reticulum calcium sensor, is activated in response to calcium store depletion and translocates to the ER–plasma membrane junctions to activate Orai1 channels. Here the authors present a new model of unimolecular coupling between STIM1 and Orai1 whereby STIM1 dimers may be involved in crosslinking Orai1 channels.
- Yandong Zhou
- , Xizhuo Wang
- & Donald L. Gill
-
Article
| Open Access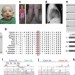 Impaired PIEZO1 function in patients with a novel autosomal recessive congenital lymphatic dysplasia
Impaired PIEZO1 function in patients with a novel autosomal recessive congenital lymphatic dysplasia
Lukacs et al. identify mutations in the PIEZO1gene in patients with congenital lymphatic dysplasia. The study also characterizes the functional consequence of the disease-associated Piezo1 mutant proteins and show attenuated ion channel function in cellular context.
- Viktor Lukacs
- , Jayanti Mathur
- & Bryan L. Krock
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational rearrangements in the transmembrane domain of CNGA1 channels revealed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Conformational rearrangements in the transmembrane domain of CNGA1 channels revealed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Cyclic nucleotide gated channels are activated after binding cyclic nucleotides. Here, using single molecule force spectroscopy, the authors reveal that cyclic nucleotide binding causes conformational changes and tighter coupling of the S4 helix to the pore forming domain.
- Sourav Maity
- , Monica Mazzolini
- & Vincent Torre
-
Article |
 Atomistic mechanism for the activation and desensitization of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor
Atomistic mechanism for the activation and desensitization of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor
Upon agonist binding, ionotropic glutamate receptors are activated and then become desensitized, but the detailed molecular events of this process are unclear. Here, molecular dynamics simulations are used to probe how conformational changes of the ligand-binding domain are transmitted to the transmembrane domain.
- Hao Dong
- & Huan-Xiang Zhou

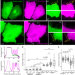 Membrane curvature governs the distribution of Piezo1 in live cells
Membrane curvature governs the distribution of Piezo1 in live cells