Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access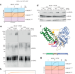 A common human MLKL polymorphism confers resistance to negative regulation by phosphorylation
A common human MLKL polymorphism confers resistance to negative regulation by phosphorylation
MLKL is regarded as an executor of the necroptotic inflammatory cell death pathway. Here authors show, by introducing a mutation into mouse MLKL representing a frequently occurring human single nucleotide polymorphism, that MLKL mutations could critically alter the inflammatory response and the clearance of Salmonella from organs upon infection.
- Sarah E. Garnish
- , Katherine R. Martin
- & Joanne M. Hildebrand
-
Article
| Open Access Inherited ARPC5 mutations cause an actinopathy impairing cell motility and disrupting cytokine signaling
Inherited ARPC5 mutations cause an actinopathy impairing cell motility and disrupting cytokine signaling
Mutations that impact the function of the Arp2/3 complex are known to cause inborn errors of immunity. Here the authors describe biallelic null mutations in the ARPC5 subunit of Arp2/3 that disrupt actin function and cytokine signaling, causing infections, autoimmunity, inflammation and dysmorphisms.
- Cristiane J. Nunes-Santos
- , HyeSun Kuehn
- & Sergio D. Rosenzweig
-
Article
| Open Access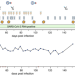 Accumulation of mutations in antibody and CD8 T cell epitopes in a B cell depleted lymphoma patient with chronic SARS-CoV-2 infection
Accumulation of mutations in antibody and CD8 T cell epitopes in a B cell depleted lymphoma patient with chronic SARS-CoV-2 infection
SARS-CoV-2 mutations associated with the escape from antibody-mediated neutralization have been widely reported. Here, in a patient with defective antibody responses, the authors find a potential association between SARS-CoV-2 mutations and CD8 T alterations to implicate possible contributions of CD8 T cells in evasion of SARS-CoV-2 from host immunity.
- Elham Khatamzas
- , Markus H. Antwerpen
- & Andreas Moosmann
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative SARS-CoV-2 mutations and corresponding changes in immunity in an immunocompromised patient indicate viral evolution within the host
Cumulative SARS-CoV-2 mutations and corresponding changes in immunity in an immunocompromised patient indicate viral evolution within the host
Variants of concerns arise from SARS-CoV-2 mutations poise as severe public health threats. Here the authors chronicle SARS-CoV-2 mutations onset and immune parameters in an immunocompromised patient with continuous virus-shedding, thereby hinting potential intra-host viral evolution and escape facilitated by ineffective T cell immunity.
- Sissy Therese Sonnleitner
- , Martina Prelog
- & Gernot Walder
-
Article
| Open Access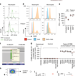 Somatic mosaicism and common genetic variation contribute to the risk of very-early-onset inflammatory bowel disease
Somatic mosaicism and common genetic variation contribute to the risk of very-early-onset inflammatory bowel disease
Adult forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are of a polygenic nature, but paediatric and very early onset (VEO) IBD also occur as monogenic forms. Here, using whole exome sequencing, the authors explore both the monogenic and polygenic contribution to VEO-IBD and characterize a rare somatic mosaic VEO-IBD patient.
- Eva Gonçalves Serra
- , Tobias Schwerd
- & Carl A. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in topoisomerase IIβ result in a B cell immunodeficiency
Mutations in topoisomerase IIβ result in a B cell immunodeficiency
Topoisomerases are required to release topological stress on DNA during replication and transcription. Here, Broderick et al. report genetic variants in TOP2B that cause a syndromic B cell immunodeficiency associated with reduced TOP2B function, defects in B cell development and B cell activation.
- Lori Broderick
- , Shawn Yost
- & Hal M. Hoffman
-
Article
| Open Access The histone methyltransferase Setd2 is indispensable for V(D)J recombination
The histone methyltransferase Setd2 is indispensable for V(D)J recombination
The repertoire of adaptive immune receptor is generated by V(D)J recombination, somatic rearrangements of V, D and J gene segments, in the respective loci. Here the authors show that the deficiency of Setd2, a histone methyl transfer, impairs V(D)J recombination and induces severe developmental blocks in both T and B lineages.
- Zhongzhong Ji
- , Yaru Sheng
- & Helen He Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) are multi-allelic and polymorphic genes that present antigens to immune cells for inducing protective immunity. Here, using systems biology and structural approaches, the authors show that micropolymorphism of three HLA has effects beyond the modulation of antigen diversity.
- Patricia T. Illing
- , Phillip Pymm
- & Anthony W. Purcell
-
Article
| Open Access A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
Mutations in genes encoding NAPDH oxidase subunits are known to be causative for the primary immunodeficiency chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Here, the authors identify CYBC1 mutations in patients with CGD and show that CYBC1 is important for formation of the NADPH complex and respiratory burst.
- Gudny A. Arnadottir
- , Gudmundur L. Norddahl
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access A human immunodeficiency syndrome caused by mutations in CARMIL2
A human immunodeficiency syndrome caused by mutations in CARMIL2
CARMIL2 (Rltpr) is involved in T-cell function. Here, the authors identify human CARMIL2-deficiency as an autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by EBV+smooth muscle tumours, CD28 co-signalling deficiency and impaired cytoskeletal dynamics.
- T. Schober
- , T. Magg
- & F. Hauck
-
Article
| Open Access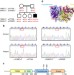 Biallelic JAK1 mutations in immunodeficient patient with mycobacterial infection
Biallelic JAK1 mutations in immunodeficient patient with mycobacterial infection
JAK1 mediates intracellular signalling from multiple cytokine receptors. Here, Elettoet al. identify JAK1 mutations that disrupt multiple signalling pathways and are associated with primary immunodeficiency, atypical mycobacterial infection susceptibility and early-onset metastatic bladder carcinoma.
- Davide Eletto
- , Siobhan O. Burns
- & Sergey Nejentsev
-
Article
| Open Access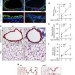 Airway bacteria drive a progressive COPD-like phenotype in mice with polymeric immunoglobulin receptor deficiency
Airway bacteria drive a progressive COPD-like phenotype in mice with polymeric immunoglobulin receptor deficiency
The mechanisms driving lung inflammation and remodelling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are incompletely understood. Here the authors show that lack of secretory IgA promotes bacterial invasion in small airways, resulting in leukocyte recruitment and a COPD-like phenotype.
- Bradley W. Richmond
- , Robert M. Brucker
- & Vasiliy V. Polosukhin
-
Article
| Open Access Elimination of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies
Elimination of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies
Broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) are promising as potential therapies targeting HIV-1 but their overall antiviral activity remains to be fully elucidated. Here the authors evaluate the ability of a panel of bNAbs to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and identify the most effective antibody combinations.
- Timothée Bruel
- , Florence Guivel-Benhassine
- & Olivier Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access Immunological biomarkers predict HIV-1 viral rebound after treatment interruption
Immunological biomarkers predict HIV-1 viral rebound after treatment interruption
In some HIV-1-infected individuals, viraemia remains undetectable after antiretroviral treatment, but which of these patients will experience viral rebound is difficult to predict. Here the authors show that T cell exhaustion markers before treatment are predictive of shorter time to viral rebound.
- Jacob Hurst
- , Matthias Hoffmann
- & John Frater
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in CDCA7 and HELLS cause immunodeficiency–centromeric instability–facial anomalies syndrome
Mutations in CDCA7 and HELLS cause immunodeficiency–centromeric instability–facial anomalies syndrome
Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome is a life threatening autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in DNMT3B and ZBTB24. Here Thijssen et al. identify mutations in CDCA7 and HELLSin previously unexplained cases.
- Peter E. Thijssen
- , Yuya Ito
- & Hiroyuki Sasaki
-
Article
| Open Access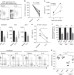 IL-21 induces antiviral microRNA-29 in CD4 T cells to limit HIV-1 infection
IL-21 induces antiviral microRNA-29 in CD4 T cells to limit HIV-1 infection
HIV-infected patients who maintain undetectable virus levels possess elevated plasma concentrations of IL-21. Here, Adoroet al. show that IL-21 inhibits early viral infection in humanized mice and suppresses HIV-1 replication in vitroby upregulating a microRNA via the regulatory protein STAT3.
- Stanley Adoro
- , Juan R. Cubillos-Ruiz
- & Laurie H. Glimcher
-
Article
| Open Access Monozygotic twins discordant for common variable immunodeficiency reveal impaired DNA demethylation during naïve-to-memory B-cell transition
Monozygotic twins discordant for common variable immunodeficiency reveal impaired DNA demethylation during naïve-to-memory B-cell transition
Epigenetic changes are thought to contribute to the aetiology of common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), a disease characterized by loss of B-cell function. Here, by comparing DNA methylation profile in B cells from monozygotic twins discordant for CVID, the authors show a gain of DNA methylation in CVID B cells.
- Virginia C. Rodríguez-Cortez
- , Lucia del Pino-Molina
- & Esteban Ballestar
-
Article |
 HIV-1 Rev downregulates Tat expression and viral replication via modulation of NAD(P)H:quinine oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1)
HIV-1 Rev downregulates Tat expression and viral replication via modulation of NAD(P)H:quinine oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1)
Tat and Rev are HIV-1 proteins involved in feedback mechanisms that regulate the expression of viral genes. Here, the authors show that Rev reduces the intracellular Tat levels by inhibiting the expression of the cellular protein NQO1, which prevents Tat degradation.
- Sneh Lata
- , Amjad Ali
- & Akhil C. Banerjea
-
Article
| Open Access ASK1 restores the antiviral activity of APOBEC3G by disrupting HIV-1 Vif-mediated counteraction
ASK1 restores the antiviral activity of APOBEC3G by disrupting HIV-1 Vif-mediated counteraction
The human protein APOBEC3G (A3G) inhibits HIV-1 replication, but the viral protein Vif counteracts by inducing A3G degradation. Here Miyakawa et al. show that the antiretroviral drug AZT restores A3G function in vitroby stimulating expression of a host protein, ASK1, which interferes with the action of Vif.
- Kei Miyakawa
- , Satoko Matsunaga
- & Akihide Ryo
-
Article |
 HIV-1 Tat inhibits phagocytosis by preventing the recruitment of Cdc42 to the phagocytic cup
HIV-1 Tat inhibits phagocytosis by preventing the recruitment of Cdc42 to the phagocytic cup
Phagocytic activity of macrophages is reduced in HIV-1-infected patients, but the reason for this is unknown. Here, the authors report that secreted Tat protein inhibits phagocytosis by binding to the phospholipid PI(4,5)P2and impairing the recruitment of small GTPase Cdc42 to the phagocytic cup.
- Solène Debaisieux
- , Simon Lachambre
- & Bruno Beaumelle
-
Article
| Open Access Maturation of the HIV-1 core by a non-diffusional phase transition
Maturation of the HIV-1 core by a non-diffusional phase transition
Current models of HIV maturation involve the diffusion of the cleaved capsid protein into the viral core. Here, Frank et al. use cryo-electron tomography to characterize HIV assembly intermediates, and propose a novel maturation mechanism involving a non-diffusional phase transition.
- Gabriel A. Frank
- , Kedar Narayan
- & Sriram Subramaniam
-
Article
| Open Access Biallelic loss-of-function mutation in NIK causes a primary immunodeficiency with multifaceted aberrant lymphoid immunity
Biallelic loss-of-function mutation in NIK causes a primary immunodeficiency with multifaceted aberrant lymphoid immunity
Primary immunodeficiency disorders can be used to identify key immune functions. Here, the authors identify a biallelic mutation in the gene encoding NF-κB-inducing kinase in a family suffering a range of infections, and show that it causes defects in NK and T-cell function and has broad effects on B-cell function.
- Katharina L. Willmann
- , Stefanie Klaver
- & Kaan Boztuğ
-
Article |
 PTPN2 attenuates T-cell lymphopenia-induced proliferation
PTPN2 attenuates T-cell lymphopenia-induced proliferation
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene encoding the protein phosphatase PTPN2 are associated with autoimmunity in humans. Here, Wiede et al. show that PTPN2 suppresses the proliferative capacity of T cells in lymphopenia and prevents the development of autoimmunity resulting from overt homoeostatic proliferation.
- Florian Wiede
- , Nicole L. La Gruta
- & Tony Tiganis
-
Article
| Open Access B-cell depletion reveals a role for antibodies in the control of chronic HIV-1 infection
B-cell depletion reveals a role for antibodies in the control of chronic HIV-1 infection
HIV infection can be partially regulated by the host immune system; however whether B cells contribute to this response is unclear. Huanget al. show that transient depletion of B cells can result in an increase in HIV viral load suggesting that these immune cells do participate in the control of HIV infection.
- Kuan-Hsiang G. Huang
- , David Bonsall
- & Paul Klenerman

 Centrosome amplification and aneuploidy driven by the HIV-1-induced Vpr•VprBP•Plk4 complex in CD4+ T cells
Centrosome amplification and aneuploidy driven by the HIV-1-induced Vpr•VprBP•Plk4 complex in CD4+ T cells