Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Pinging the brain to reveal the hidden attentional priority map using encephalography
Pinging the brain to reveal the hidden attentional priority map using encephalography
Past experience with environmental regularities can influence attentional priority. Here the authors show that when observers have learned to expect information in certain locations during a visual search task, such otherwise hidden attentional biases can be visualized through neural responses evoked by the presentation of sudden task-irrelevant visual input (‘pings’).
- Dock H. Duncan
- , Dirk van Moorselaar
- & Jan Theeuwes
-
Article
| Open Access Single-neuron mechanisms of neural adaptation in the human temporal lobe
Single-neuron mechanisms of neural adaptation in the human temporal lobe
Behavioural adaptation from semantic priming is accompanied by reduced neural activity in bulk-tissue measurements, but the underlying single neuron mechanisms remain unclear. Here, the authors leverage simultaneous intracranial EEG and single neuron spiking recordings in the human medial temporal lobe to unveil differential sharpening and fatiguing mechanisms across different temporal lobe areas.
- Thomas P. Reber
- , Sina Mackay
- & Florian Mormann
-
Article
| Open Access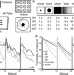 Brain-wide visual habituation networks in wild type and fmr1 zebrafish
Brain-wide visual habituation networks in wild type and fmr1 zebrafish
Habituation is a process in which animals stop responding to repetitive stimuli, and habituation is altered in autism and other conditions. Here, the authors describe visual habituation networks across the zebrafish brain, and find that fmr1 mutants show slower brain-wide and behavioural habituation.
- Emmanuel Marquez-Legorreta
- , Lena Constantin
- & Ethan K. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Light and pheromone-sensing neurons regulates cold habituation through insulin signalling in Caenorhabditis elegans
Light and pheromone-sensing neurons regulates cold habituation through insulin signalling in Caenorhabditis elegans
Cold tolerance in Caenorhabditis elegansis regulated by signalling pathways and neuronal circuits, but the exact mechanisms are unclear. Here the authors show that cold tolerance requires activity from specific light and pheromone-sensing neurons that release insulin to regulate gene expression in the intestine.
- Akane Ohta
- , Tomoyo Ujisawa
- & Atsushi Kuhara

 Hypothalamic CRH neurons represent physiological memory of positive and negative experience
Hypothalamic CRH neurons represent physiological memory of positive and negative experience