Featured
-
-
Article |
 Ultrafast collinear scattering and carrier multiplication in graphene
Ultrafast collinear scattering and carrier multiplication in graphene
Investigation of the initial stages of the interaction of light with carriers in graphene is challenging. Here the authors probe the process with ultrafast pump-probe spectroscopy and microscopic theory, and observe the role of collinear scattering, which gives rise to Auger processes, including carrier multiplication.
- D. Brida
- , A. Tomadin
- & M. Polini
-
Article |
 Suppression of electron–vibron coupling in graphene nanoribbons contacted via a single atom
Suppression of electron–vibron coupling in graphene nanoribbons contacted via a single atom
Graphene nanostructures have a tremendous potential for electronic applications, although contacting them with atomic precision remains a challenge. Here, van der Lit and colleagues achieve contacting graphene nanoribbons via only a single atom, without affecting its electronic structure.
- Joost van der Lit
- , Mark P. Boneschanscher
- & Ingmar Swart
-
Article |
 Dual origin of defect magnetism in graphene and its reversible switching by molecular doping
Dual origin of defect magnetism in graphene and its reversible switching by molecular doping
Local magnetic properties that can be controlled by an applied electric field are desirable for spintronics applications. Nair et al.show that tuning carrier concentration by molecular doping or electric field can be used to control adatoms magnetism on graphene, enabling magnetic moments to be switched on and off.
- R.R. Nair
- , I.-L. Tsai
- & I.V. Grigorieva
-
Article |
 Photocurrent in graphene harnessed by tunable intrinsic plasmons
Photocurrent in graphene harnessed by tunable intrinsic plasmons
By patterning graphene with sub-wavelength features to introduce plasmonic modes, its optical properties can be tailored. Freitag et al. show how tunable plasmons in graphene nanoribbons can be exploited to form polarization-sensitive graphene photodetectors in the mid-infrared spectral region.
- Marcus Freitag
- , Tony Low
- & Phaedon Avouris
-
Article |
 Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Vertically assembled graphene devices have received less attention than the typical two dimensional arrangements. Chen et al. show that an Au/graphene/Au assembly exhibits a large magnetoresistance ratio of up to 400%, while a Co/graphene/Co device displays a spin valve effect at room temperature.
- Jing-Jing Chen
- , Jie Meng
- & Da-Peng Yu
-
Article |
 Photo-switchable molecular monolayer anchored between highly transparent and flexible graphene electrodes
Photo-switchable molecular monolayer anchored between highly transparent and flexible graphene electrodes
The realization of molecular monolayers with graphene electrodes may allow for superior flexible, transparent and stable electronics. Here, a photo-switchable molecular monolayer device is demonstrated, which has one side physically attached, and the other chemically bonded, to graphene.
- Sohyeon Seo
- , Misook Min
- & Hyoyoung Lee
-
Article |
 Quantum Faraday and Kerr rotations in graphene
Quantum Faraday and Kerr rotations in graphene
Graphene exhibits interesting optical and electronic properties, resulting from a Dirac dispersion of electrons. Shimano et al.observe quantum magneto-optical Faraday and Kerr effects in the terahertz regime, where plateaus are observed at the quantum-Hall steps.
- R. Shimano
- , G. Yumoto
- & H. Aoki
-
Article |
 Broadband high photoresponse from pure monolayer graphene photodetector
Broadband high photoresponse from pure monolayer graphene photodetector
Graphene holds great potential for use in photodetectors, owing to its ability to absorb light over a wide range of wavelengths. Here Zhang et al. report a large photoresponsivity of 8.6 AW-1 over a broad wavelength range in pure monolayer graphene.
- By Yongzhe Zhang
- , Tao Liu
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant tunnelling and negative differential conductance in graphene transistors
Resonant tunnelling and negative differential conductance in graphene transistors
Multilayer stacks of graphene and related two-dimensional crystals can be tailored to create new classes of functional materials. Britnell et al. report resonant tunnelling of Dirac fermions and tunable negative differential conductance in a graphene-boron nitride-graphene transistor.
- L. Britnell
- , R. V. Gorbachev
- & L. Eaves
-
Article |
 Evolution of Landau levels into edge states in graphene
Evolution of Landau levels into edge states in graphene
It is difficult to observe the edge-bulk correspondence in two-dimensional electron systems, which display the quantum Hall effect. Here Li et al. follow the spatial evolution of Landau levels towards an edge of graphene by scanning tunnelling studies, revealing that the edge-bulk correspondence can be preserved.
- Guohong Li
- , Adina Luican-Mayer
- & Eva Y. Andrei
-
Article
| Open Access Probing relaxation times in graphene quantum dots
Probing relaxation times in graphene quantum dots
The experimental investigation of relaxation times in graphene quantum dots has long been hindered by the limited tunability of these devices. Here Volk et. al.employ a device design to study this problem and report charge relaxation times of around 60–100 ns.
- Christian Volk
- , Christoph Neumann
- & Christoph Stampfer
-
Article |
 Ballistic to diffusive crossover of heat flow in graphene ribbons
Ballistic to diffusive crossover of heat flow in graphene ribbons
Understanding heat flow in two-dimensional nanomaterials has wide-ranging implications. Here, the authors show that the thermal conductance of quarter-micron graphene samples is quasi-ballistic, but patterning the graphene into nanoribbons leads to diffusive heat flow strongly limited by edge scattering.
- Myung-Ho Bae
- , Zuanyi Li
- & Eric Pop
-
Article |
 Graphene-modified LiFePO4 cathode for lithium ion battery beyond theoretical capacity
Graphene-modified LiFePO4 cathode for lithium ion battery beyond theoretical capacity
The specific capacity of an important commercial cathode material, lithium iron phosphate, is much lower than its theoretical value. Hu et al. report that incorporation of electrochemically exfoliated graphene layers in a carbon coating improves capacity beyond that predicted by theory.
- By Lung-Hao Hu
- , Feng-Yu Wu
- & Lain-Jong Li
-
Article |
 Metallized DNA nanolithography for encoding and transferring spatial information for graphene patterning
Metallized DNA nanolithography for encoding and transferring spatial information for graphene patterning
The structuring of graphene is important towards its use in electronic applications. Here Strano et al. develop a fast and efficient lithography process enabling the transfer of shape information from self-assembled DNA templates to custom graphene patterns at a resolution of about 10 nm.
- Zhong Jin
- , Wei Sun
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Controlled charge trapping by molybdenum disulphide and graphene in ultrathin heterostructured memory devices
Controlled charge trapping by molybdenum disulphide and graphene in ultrathin heterostructured memory devices
Two-dimensional materials such as graphene and molybdenum disulphide are promising for ultrathin electronic devices. Here Choi et al. realize a non-volatile memory device from stacked graphene, boron nitride and molybdenum disulphide films.
- Min Sup Choi
- , Gwan-Hyoung Lee
- & Won Jong Yoo
-
Article |
 A low-temperature method to produce highly reduced graphene oxide
A low-temperature method to produce highly reduced graphene oxide
The chemical reduction of graphene oxide can provide large quantities of reduced graphene oxide for potential application in electronics and composite materials. Feng et al. report a highly efficient low-temperature one-pot reduction of graphene oxide that uses sodium-ammonia solution as the reducing agent.
- Hongbin Feng
- , Rui Cheng
- & Jinghong Li
-
Article |
 Scalable fabrication of high-power graphene micro-supercapacitors for flexible and on-chip energy storage
Scalable fabrication of high-power graphene micro-supercapacitors for flexible and on-chip energy storage
Microscale supercapacitors are promising alternative energy-storage devices; however, their use has been limited by the need for complicated fabrication techniques. This work reports the scalable fabrication of graphene supercapacitors with planar geometry that achieve power densities of up to 200 W cm−3.
- Maher F. El-Kady
- & Richard B. Kaner
-
Article
| Open Access Janus graphene from asymmetric two-dimensional chemistry
Janus graphene from asymmetric two-dimensional chemistry
Janus materials have distinct chemical functionalities on opposite faces. Zhang et al.report that a two-step covalent functionalisation and poly(methyl methacrylate)-mediated transfer process facilitates the synthesis of nonsymmetrically modified single-layer graphene.
- Liming Zhang
- , Jingwen Yu
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article |
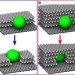 Catalytic subsurface etching of nanoscale channels in graphite
Catalytic subsurface etching of nanoscale channels in graphite
Metallic particles are known to etch the surface layers of graphite by catalytic hydrogenation. Here, the authors report the sub-surface etching of graphite by Ni nanoparticles, revealing the formation of networks of tunnels, which are observed microscopically and could be modified for various applications.
- Maya Lukas
- , Velimir Meded
- & Ralph Krupke
-
Article |
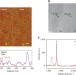 Controllable unzipping for intramolecular junctions of graphene nanoribbons and single-walled carbon nanotubes
Controllable unzipping for intramolecular junctions of graphene nanoribbons and single-walled carbon nanotubes
The formation of junctions between graphene and other materials could aid the development of nanoelectronics. We et al. partially unzip single-walled carbon nanotubes to produce graphene/nanotube junctions that show gate-dependent rectifying behaviour.
- Dacheng Wei
- , Lanfei Xie
- & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon transport in graphene investigated by time-resolved electrical measurements
Plasmon transport in graphene investigated by time-resolved electrical measurements
In metals, plasmon properties are fixed once the structure is built, but in graphene they can be altered by electric or magnetic fields. Using electrical time-of-flight measurements, Kumada et al. show wide plasmon velocity tunability in graphene with a varying magnetic field.
- N. Kumada
- , S. Tanabe
- & T. Fujisawa
-
Article |
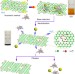 Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Graphene oxide has been proposed as an alternative to precious metals for the catalysis of aerobic oxidative reactions; however, high catalyst loadings are needed. Here a simple base and acid treatment is shown to enhance its catalytic activity for the oxidative coupling of amines under ambient conditions.
- Chenliang Su
- , Muge Acik
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access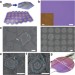 Modulation-doped growth of mosaic graphene with single-crystalline p–n junctions for efficient photocurrent generation
Modulation-doped growth of mosaic graphene with single-crystalline p–n junctions for efficient photocurrent generation
Combination of p- and n-doped graphene is important in optoelectronic applications, but spatially selective doping of graphene is challenging. This work reports large-scale growth of graphene monolayers with spatially modulation doping and built-in single-crystalline p–n junctions.
- Kai Yan
- , Di Wu
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article |
 Quantum and classical confinement of resonant states in a trilayer graphene Fabry-Pérot interferometer
Quantum and classical confinement of resonant states in a trilayer graphene Fabry-Pérot interferometer
Multilayer graphene is a promising electronic material because of its tunable band structure and pseudospin properties. Campos et al.show giant conductance oscillations in a ballistic trilayer graphene Fabry-Pérot interferometer that can be suppressed both classically and quantum mechanically.
- L.C. Campos
- , A.F. Young
- & P. Jarillo-Herrero
-
Article |
 Water tribology on graphene
Water tribology on graphene
The frictional force required to move a liquid drop on a surface is known to depend upon the drop resting time. N'guessan et al. demonstrate that water drops on graphene surfaces are an exception, which is attributable to the chemical homogeneity and stability of graphene surfaces.
- Hartmann E. N’guessan
- , Aisha Leh
- & Priyanka Wasnik
-
Article |
 Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
The exploitation of the properties of graphene, such as mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, in deformable macroscopic materials is desirable. Here, a combination of graphene chemistry and ice physics is used to fabricate biomimetic, ultralight and superelastic graphene cellular monoliths.
- Ling Qiu
- , Jeffery Z. Liu
- & Dan Li
-
Article |
 Giant Rashba splitting in graphene due to hybridization with gold
Giant Rashba splitting in graphene due to hybridization with gold
The potential use of graphene in spintronic devices is limited by its weak spin–orbit coupling. Marchenko et al. report an enhancement of the spin splitting in graphene due to hybridization with gold 5dorbitals, showing a very large Rashba spin–orbit splitting of about 100 meV.
- D. Marchenko
- , A. Varykhalov
- & O. Rader
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme sensitivity of graphene photoconductivity to environmental gases
Extreme sensitivity of graphene photoconductivity to environmental gases
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms whose high electron mobility offers potential for cheap, high-speed opto-electronic devices. Docherty et al.show that the terahertz frequency photoconductivity in graphene depends crucially on the type and density of environmental gas adsorbed.
- Callum J. Docherty
- , Cheng-Te Lin
- & Michael B. Johnston
-
Article |
 A seamless three-dimensional carbon nanotube graphene hybrid material
A seamless three-dimensional carbon nanotube graphene hybrid material
Graphene and single-walled carbon nanotubes have high electrical conductivities and large specific surface areas. Here, these properties are extended into three dimensions by producing a seamless carbon nanotube graphene hybrid material.
- Yu Zhu
- , Lei Li
- & James M. Tour
-
Article
| Open Access Direct writing of electronic devices on graphene oxide by catalytic scanning probe lithography
Direct writing of electronic devices on graphene oxide by catalytic scanning probe lithography
Controlled nanoscale reduction of graphene oxide could aid the development of graphene-based electronics. Here, a relatively mild technique is reported that uses a platinum-coated atomic force microscope tip to catalyse the reduction of graphene oxide to graphene.
- Kun Zhang
- , Qiang Fu
- & Jianguo Hou
-
Article |
 Spatial control of defect creation in graphene at the nanoscale
Spatial control of defect creation in graphene at the nanoscale
Intentional defect creation in graphene is key to engineering its electrical, chemical, magnetic and mechanical properties. Robertsonet al. create defects by electron beam irradiation with sub-knock-on damage threshold, and show control over the defect position at the nanoscale and over the defect complexity.
- Alex W. Robertson
- , Christopher S. Allen
- & Jamie H. Warner
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-contact electrically driven microdisk lasers
Graphene-contact electrically driven microdisk lasers
Microdisk lasers are useful for compact wavelength-scale photonic devices and circuits, but their operation by electrical injection can hamper their optical properties. Kimet al. show that a graphene-contact electrode provides efficient electrical injection while minimising optical losses.
- Yoon-Ho Kim
- , Soon-Hong Kwon
- & Hong-Gyu Park
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Landau levels in potassium-intercalated graphite under a zero magnetic field
Observation of Landau levels in potassium-intercalated graphite under a zero magnetic field
A signature of the Dirac-like physics of charge carriers in graphene is the occurrence of an anomalous Hall effect, resulting in a quantization of the Landau levels. Guoet al. observe Landau levels of Dirac fermions in potassium-intercalated graphite arising in the absence of an applied magnetic field.
- Donghui Guo
- , Takahiro Kondo
- & Junji Nakamura
-
Article |
 Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
The spectral position of Raman peaks is a useful diagnostic for determining the degree of strain and excess electronic charges present in graphene. This study demonstrates that these two contributions can be separated from each other and therefore be obtained at the same time.
- Ji Eun Lee
- , Gwanghyun Ahn
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article |
 Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Signal modulation is a mechanism which embeds an information-carrying signal into a carrier wave to broadcast information and is essential for high-speed communication. Zhonget al. report a flexible, transparent all-graphene modulator circuit performing quaternary modulation schemes with only two transistors.
- Seunghyun Lee
- , Kyunghoon Lee
- & Zhaohui Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Along with its electronic characteristics, the spin properties of graphene have recently received increasing attention in the context of spintronic applications. Using microwave radiation, Maniet al. identify resistively detected spin resonance in monolayer and trilayer graphene sheets and extract the value for the Landé g-factor.
- Ramesh G. Mani
- , John Hankinson
- & Walter A. de Heer
-
Article |
 Gate-defined quantum confinement in suspended bilayer graphene
Gate-defined quantum confinement in suspended bilayer graphene
The ability to manipulate single charges is a key requisite for novel nanoelectronic devices. Allenet al. show how to electrostatically confine electrons in suspended bilayer graphene quantum dots by local control of the graphene band structure.
- M. T. Allen
- , J. Martin
- & A. Yacoby
-
Article
| Open Access Light–matter interaction in a microcavity-controlled graphene transistor
Light–matter interaction in a microcavity-controlled graphene transistor
Graphene's remarkable properties make it ideal for optoelectronic devices, and its two-dimensional nature enables its integration with photonic structures. By combining a graphene transistor with a planar microcavity, Engelet al. control the spectrum of the photocurrent and the light emitted by the device.
- Michael Engel
- , Mathias Steiner
- & Ralph Krupke
-
Article
| Open Access Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Current top-down and bottom-up syntheses of graphene nanostructures suffer from low yields or do not produce structures with different and controlled shapes. Here, monodisperse graphene shapes are produced by diamond-edge cutting of pyrolytic graphite followed by exfoliation.
- Nihar Mohanty
- , David Moore
- & Vikas Berry
-
Article |
 Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Strain engineering has been proposed as a promising strategy for manipulating the electronic properties of graphene. This scanning tunnelling microscopy study demonstrates the feasibility of controlling strain patterns in graphene down to the nanoscale.
- Jiong Lu
- , A.H. Castro Neto
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene quilts for thermal management of high-power GaN transistors
Graphene quilts for thermal management of high-power GaN transistors
Electronic and optoelectronic devices based on gallium nitride suffer from self-heating arising as a result of their operation. This study presents and demonstrates a strategy for managing this problem that relies on graphene quilts which dissipate the heat away.
- Zhong Yan
- , Guanxiong Liu
- & Alexander A. Balandin
-
Article |
 Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions
Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions
The terahertz spectral region is desirable for applications such as imaging or spectroscopy, but progress is hampered by a lack of efficient terahertz devices. By exploiting intraband transitions in graphene, Sensale-Rodriguezet al. demonstrate a broadband intensity modulator working at terahertz frequencies.
- Berardi Sensale-Rodriguez
- , Rusen Yan
- & Huili Grace Xing
-
Article |
 Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel
Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel
Graphene is characterized by unique physical properties that offer substantial promise, most notably for electronic applications. Mannooret al. present a wireless graphene-based sensor for detecting bacteria on a range of biological tissues.
- Manu S. Mannoor
- , Hu Tao
- & Michael C. McAlpine
-
Article |
 Probing charge scattering mechanisms in suspended graphene by varying its dielectric environment
Probing charge scattering mechanisms in suspended graphene by varying its dielectric environment
A factor limiting the mobility of charge carriers in graphene, and therefore its use in electronic applications, is the Coulomb scattering due to charged impurities. By exposing graphene devices to a range of non-polar liquids, Newazet al. observe an enhancement of the mobility due to screening.
- A.K.M. Newaz
- , Yevgeniy S. Puzyrev
- & Kirill I. Bolotin
-
Article
| Open Access Repeated growth and bubbling transfer of graphene with millimetre-size single-crystal grains using platinum
Repeated growth and bubbling transfer of graphene with millimetre-size single-crystal grains using platinum
Grain boundaries in graphene degrade its properties, and large single-crystal graphene is desirable for electronic applications of graphene. Gaoet al. develop a method to produce millimetre-sized hexagonal single-crystal graphene grains, and films composed of the grains, on platinum by chemical vapour deposition.
- Libo Gao
- , Wencai Ren
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved ultrafast photocurrents and terahertz generation in freely suspended graphene
Time-resolved ultrafast photocurrents and terahertz generation in freely suspended graphene
Graphene's broad bandwidth makes it promising as a photodetector, but common electronics cannot analyse the currents at high frequencies. Here, using photocurrent measurements, laser-induced carrier generation effects in freely suspended graphene and at graphene–metal interfaces are clarified up to 1 THz.
- Leonhard Prechtel
- , Li Song
- & Alexander W. Holleitner
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Composite fibres made of polymers reinforced by carbon nanotubes are known for their exceptional toughness. Shinet al. make these composites even tougher, by self-aligning carbon nanotubes and reduced graphene oxide flakes within the polymer matrix.
- Min Kyoon Shin
- , Bommy Lee
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article |
 Near room-temperature synthesis of transfer-free graphene films
Near room-temperature synthesis of transfer-free graphene films
Current methods for fabricating graphene rely on its transfer from metal surfaces to substrates suitable for device applications. This study demonstrates a transfer-free approach for growing graphene on substrates such as thermally oxidized silicon and plastic that forms the material underneath a nickel film, at the nickel–substrate interface.
- Jinsung Kwak
- , Jae Hwan Chu
- & Soon-Yong Kwon
-
Article |
 Chemical structures of hydrazine-treated graphene oxide and generation of aromatic nitrogen doping
Chemical structures of hydrazine-treated graphene oxide and generation of aromatic nitrogen doping
Parket al. use 13C and 15N solid-state NMR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study the chemical structure of hydrazine-treated graphite oxide. Hydrazine treatment is shown to lead to the incorporation of aromatic N2moieties at the graphene edges and restore graphitic networks on the basal planes.
- Sungjin Park
- , Yichen Hu
- & Rodney S. Ruoff

 Molecular adsorption induces the transformation of rhombohedral- to Bernal-stacking order in trilayer graphene
Molecular adsorption induces the transformation of rhombohedral- to Bernal-stacking order in trilayer graphene