Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Kekulé vortices in hexagonal lattices can host fractionalized charges at zero magnetic field, but have remained out of experimental reach. Here, the authors report a Kekulé vortex in the local density states of graphene around a chemisorbed hydrogen adatom.
- Yifei Guan
- , Clement Dutreix
- & Vincent T. Renard
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals
Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals
One-dimensional photonic crystals provide a platform to modulate Weyl quasiparticles with properties of bound states in the continuum both dynamically (transition and rotation) and topologically (singularities in bilateral drumhead surface states).
- Shengyu Hu
- , Zhiwei Guo
- & Hong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring coordination environments of single-atom electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution by topological heteroatom transfer
Tailoring coordination environments of single-atom electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution by topological heteroatom transfer
The rational design of carbon-supported transition metal single atom catalysts with precise coordination tailoring remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a topological heteroatom-transfer strategy to precisely control the P coordination in Co single atoms for hydrogen evolution.
- Sheng Qian
- , Feng Xu
- & Jingqi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Layer-polarized ferromagnetism in rhombohedral multilayer graphene
Layer-polarized ferromagnetism in rhombohedral multilayer graphene
Rhombohedral multilayer graphene has emerged as an exciting solid-state platform for studying correlated electron physics. Here, the authors demonstrate field-tunable layer-polarized ferromagnetism and isolated surface flat bands engineered with a moiré potential.
- Wenqiang Zhou
- , Jing Ding
- & Shuigang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
The controllability of deformation height in reconfigurable touch displays currently limits their deliverable information. Hwang et al. present a light-triggered morphable tactile display enabling generation of refreshable, height-adjustable, and latchable 3D topologies with varying textures on a thin film surface.
- Inwook Hwang
- , Seongcheol Mun
- & Sungryul Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven amplification of terahertz acoustic waves in graphene
Electrically driven amplification of terahertz acoustic waves in graphene
Electron–phonon interactions are a crucial aspect of high-quality graphene devices. Here, the authors show that graphene resistivity grows strongly in the direction of the carrier flow when the drift velocity exceeds the speed of sound due to the electrical amplification of acoustic terahertz phonons.
- Aaron H. Barajas-Aguilar
- , Jasen Zion
- & Javier D. Sanchez-Yamagishi
-
Article
| Open Access Higher order gaps in the renormalized band structure of doubly aligned hBN/bilayer graphene moiré superlattice
Higher order gaps in the renormalized band structure of doubly aligned hBN/bilayer graphene moiré superlattice
In moiré superlattices, a multitude of higher order Bragg gaps and van Hove singularities emerges as the band structure renormalizes. Here, the authors map these gaps uniquely to the recently predicted topological Bragg indices of the underlying supermoiré lattice.
- Mohit Kumar Jat
- , Priya Tiwari
- & Aveek Bid
-
Article
| Open Access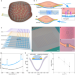 Graphene-integrated mesh electronics with converged multifunctionality for tracking multimodal excitation-contraction dynamics in cardiac microtissues
Graphene-integrated mesh electronics with converged multifunctionality for tracking multimodal excitation-contraction dynamics in cardiac microtissues
Tracking electrical and mechanical activity in in-vitro cardiac microtissues is challenging. Here, authors develop tissue-like electronics that can ‘grow’ with the cardiac microtissues and realize the simultaneous tracking of both signals.
- Hongyan Gao
- , Zhien Wang
- & Jun Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
To maximize composite reinforcing efficiency, a semi-infinite reinforcement should be aligned in the matrix. Here, the authors report a float-stacking strategy for graphene-PMMA laminate with precisely aligned monolayer graphene in a polymer matrix.
- Seung-Il Kim
- , Ji-Yun Moon
- & Jae-Hyun Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Electron/infrared-phonon coupling in ABC trilayer graphene
Electron/infrared-phonon coupling in ABC trilayer graphene
Via Raman and infrared spectroscopy measurements, X. Zan et al. find that rhombohedral ABC trilayer graphene has stronger electron/infrared-phonon coupling than Bernal ABA trilayer graphene.
- Xiaozhou Zan
- , Xiangdong Guo
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access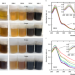 Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Graphene oxide is in demand for various applications - however, this is complicated by changing physicochemical properties over time. Here, the authors show the intrinsic, metastable, and transient states of graphene oxide colloids upon ripening.
- Hayato Otsuka
- , Koki Urita
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Here, the authors report the synthesis and characterization of doped nanoporous graphene superlattices, showing their improved properties for electromagnetic shielding, energy harvesting, optoelectronic and thermoelectric applications.
- Hualiang Lv
- , Yuxing Yao
- & Xiaoguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access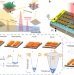 Synergistic-potential engineering enables high-efficiency graphene photodetectors for near- to mid-infrared light
Synergistic-potential engineering enables high-efficiency graphene photodetectors for near- to mid-infrared light
The integration of 2D materials with metasurfaces can enhance their quantum efficiency, but the approach is usually limited to a narrow spectral band. Here, the authors report the realization of gate-tunable graphene photodetectors combined with all-dielectric periodic slits, leading to enhanced photoresponse in the short-to-long-wave infrared.
- Hao Jiang
- , Jintao Fu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Experimentally validated design principles of heteroatom-doped-graphene-supported calcium single-atom materials for non-dissociative chemisorption solid-state hydrogen storage
Experimentally validated design principles of heteroatom-doped-graphene-supported calcium single-atom materials for non-dissociative chemisorption solid-state hydrogen storage
Via the first-principles calculations and experimental verifications, a guiding principle is established to design heteroatom-doped-graphene-supported Ca single-atom carbon nanomaterials for efficient non-dissociative solid-state hydrogen storage.
- Yong Gao
- , Zhenglong Li
- & Hongge Pan
-
Article
| Open Access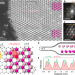 Alkali metal bilayer intercalation in graphene
Alkali metal bilayer intercalation in graphene
Here, the authors report a study of the structural properties of intercalated alkali metals in bilayer graphene and graphite via low-voltage scanning transmission electron microscopy, providing mechanistic insights for the development of energy storage applications.
- Yung-Chang Lin
- , Rika Matsumoto
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectionally promoting assembly order for ultrastiff and highly thermally conductive graphene fibres
Bidirectionally promoting assembly order for ultrastiff and highly thermally conductive graphene fibres
Aligned 2D assembled fibres have been developed by drawing like 1D polymers, yet with disorders in cross-section. Here, the authors bidirectionally promote assembly order of graphene fibres, achieving high modulus and highly thermal conductivity.
- Peng Li
- , Ziqiu Wang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable quantum interferometer for correlated moiré electrons
Tunable quantum interferometer for correlated moiré electrons
Gate-defined superconducting moiré devices offer high tunability for probing the nature of superconducting and correlated insulating states. Here, the authors report the Little–Parks and Aharonov–Bohm effects in a single gate-defined magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene device.
- Shuichi Iwakiri
- , Alexandra Mestre-Torà
- & Klaus Ensslin
-
Article
| Open Access Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Understanding the surface growth mechanism of carbon nanostructures would help designing better catalysts. Here, the authors combine active machine learning force fields with time-stamped Monte Carlo methods, to dynamically predict carbon growth on metal surfaces.
- Di Zhang
- , Peiyun Yi
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-tunable anomalous Hall effect in Bernal tetralayer graphene
Gate-tunable anomalous Hall effect in Bernal tetralayer graphene
Intrinsic anomalous Hall effect has been observed in twisted graphene multilayers, but these structures are typically not energetically favorable. This study extends these observations to Bernal-stacked tetralayer graphene, which is the most stable configuration of four-layer graphene.
- Hao Chen
- , Arpit Arora
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent charge oscillations in a bilayer graphene double quantum dot
Coherent charge oscillations in a bilayer graphene double quantum dot
Graphene quantum dots promise applications for spin and valley qubits; however a demonstration of phase coherent oscillations has been lacking. Here the authors report coherent charge oscillations and measurements of coherence times in highly tuneable double quantum dots in bilayer graphene.
- K. Hecker
- , L. Banszerus
- & C. Stampfer
-
Article
| Open Access Proton and molecular permeation through the basal plane of monolayer graphene oxide
Proton and molecular permeation through the basal plane of monolayer graphene oxide
GO monolayers are presumed to invariably contain a large density of nanoscale pinholes. Here the authors present gas and proton transport measurements which show that GO monolayers can be pinhole-free over micrometer-scale areas.
- Z. F. Wu
- , P. Z. Sun
- & M. Lozada-Hidalgo
-
Article
| Open Access Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
The authors provide an experimental demonstration of magnetic field generation in graphene disks via the inverse Faraday effect. When the disks are illuminated with circularly polarized radiation in resonance with the graphene plasmon frequency, the corresponding rotational motion of the charge carriers gives rise to a unipolar magnetic field.
- Jeong Woo Han
- , Pavlo Sai
- & Martin Mittendorff
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced copper anticorrosion from Janus-doped bilayer graphene
Enhanced copper anticorrosion from Janus-doped bilayer graphene
Atomically thick anticorrosion coatings on Cu are desired for future applications, but still at its infancy. Here, the authors report a Janus-doping mechanism in bilayer graphene on Cu substrate that results in an enhanced anticorrosion performance.
- Mengze Zhao
- , Zhibin Zhang
- & Kaihui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-controlled suppression of light-driven proton transport through graphene electrodes
Gate-controlled suppression of light-driven proton transport through graphene electrodes
Recent experiments have shown that proton transport through graphene electrodes can be promoted by light, but the understanding of this phenomenon remains unclear. Here, the authors report the electrical tunability of this photo-effect, showing a connection between graphene electronic and proton transport properties.
- S. Huang
- , E. Griffin
- & M. Lozada-Hidalgo
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Designing an efficient activation function for optical neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a modulator-detector-in-one graphene/silicon heterojunction ring resonators enabling on-chip reconfigurable activation function devices with phase activation capability for optical neural networks.
- Chuyu Zhong
- , Kun Liao
- & Hongtao Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting the spin-polarization of edge states in graphene nanoribbons
Detecting the spin-polarization of edge states in graphene nanoribbons
Zig-Zag graphene nanoribbons have edge states that are predicted to be spin-polarized, however, measurement of these spin-polarized states has proved elusive. Here, Brede et al overcome this challenge by growing graphene nanoribbons on ferromagnetic GdAu2, allowing for the direct observation of the spin-polarized edge states.
- Jens Brede
- , Nestor Merino-Díez
- & David Serrate
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Here, the authors report the realization of a sub-THz wireless data link based on a graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer with a >96 GHz bandwidth, −44 dB upconversion efficiency and <0.1 mm2 footprint, providing an alternative approach for the realization of millimeter-wave transmitters.
- Alberto Montanaro
- , Giulia Piccinini
- & Marco Romagnoli
-
Article
| Open Access Ballistic transport spectroscopy of spin-orbit-coupled bands in monolayer graphene on WSe2
Ballistic transport spectroscopy of spin-orbit-coupled bands in monolayer graphene on WSe2
By combining graphene with transition metal dichalcogenides, such as WSe2, it is possible to induce a large spin-orbit interaction in the graphene layer. Here, Rao et al study the spin-orbit coupling in graphene/WSe2 heterostructures using the ballistic transport based technique, known transverse magnetic focusing.
- Qing Rao
- , Wun-Hao Kang
- & Dong-Keun Ki
-
Article
| Open Access Stacking transfer of wafer-scale graphene-based van der Waals superlattices
Stacking transfer of wafer-scale graphene-based van der Waals superlattices
The large-scale fabrication of twisted van der Waals heterostructures remains challenging due to the formation of defects and contaminations during the transfer process. Here, the authors report a transfer method to fabricate graphene-based van der Waals superlattices at the wafer scale, showing controllable twist angles and robust quantum Hall effect.
- Guowen Yuan
- , Weilin Liu
- & Libo Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Mimicking reductive dehalogenases for efficient electrocatalytic water dechlorination
Mimicking reductive dehalogenases for efficient electrocatalytic water dechlorination
Designing electrocatalysts for water treatment with high activity/selectivity as elaborately as natural enzymes remains a challenge. This work presents the design of electrocatalysts by mimicking the binding pocket configuration and active center of dehalogenases, achieving efficient water dechlorination.
- Yuan Min
- , Shu-Chuan Mei
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Nanographenes, as their name suggests, are small sections of graphene. They offer a diverse array of magnetic behaviors; for example, sublattice imbalances in the nanographene lead to unpaired spins. Here, Du et al uncover a large variation in the exchange energy in nanographenes, due to changes in the frontier orbital symmetries.
- Qingyang Du
- , Xuelei Su
- & Ping Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of structure and photophysics of individualized rod-shaped graphene quantum dots with up to 132 sp² carbon atoms
Interplay of structure and photophysics of individualized rod-shaped graphene quantum dots with up to 132 sp² carbon atoms
The use and characterization of graphene quantum dots is limited by their pronounced tendency to form aggregates. Here, the authors synthesize rod-shaped motifs of nanographenes with up to 132 sp2 carbon atoms that are fully individualized, which allows the precise description of their intrinsic photophysical properties.
- Daniel Medina-Lopez
- , Thomas Liu
- & Stephane Campidelli
-
Article
| Open Access In-sensor computing using a MoS2 photodetector with programmable spectral responsivity
In-sensor computing using a MoS2 photodetector with programmable spectral responsivity
Here, the authors report the design and realization of an in-sensor computing optoelectronic device with programmable spectral responsivity based on an ensemble of cavity-enhanced MoS2 photodetectors. The device can perform direct analog processing during the light detection process, without the need to computationally reconstruct the entire optical spectra.
- Dohyun Kwak
- , Dmitry K. Polyushkin
- & Thomas Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
The bulk photovoltaic effect (BPVE) is a nonlinear optical effect offering a promising approach to overcome the limitations of conventional photovoltaics. Here, the authors report the observation of BPVE-induced photocurrents at the edges of 2D semiconductors embedded in various van der Waals heterostructures.
- Zihan Liang
- , Xin Zhou
- & Xiaolong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access 3D hierarchical graphene matrices enable stable Zn anodes for aqueous Zn batteries
3D hierarchical graphene matrices enable stable Zn anodes for aqueous Zn batteries
Uncontrolled dendrite growth and severe side reactions at high capacities and rates impede its practical application for zinc metal anodes. Here, the authors propose a composite zinc anode with 3D hierarchical graphene matrix as a multifunctional host to regulate zinc deposition for aqueous zinc batteries.
- Yongbiao Mu
- , Zheng Li
- & Lin Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Local spectroscopy of a gate-switchable moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Local spectroscopy of a gate-switchable moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Twisted moiré heterostructures offer a highly tunable solid-state platform for exploring fundamental condensed matter physics. Here, the authors use scanning tunnelling microscopy to investigate the local electronic structure of the gate-controlled quantum anomalous Hall insulator state in twisted monolayer–bilayer graphene.
- Canxun Zhang
- , Tiancong Zhu
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
Article
| Open Access Fast synthesis of large-area bilayer graphene film on Cu
Fast synthesis of large-area bilayer graphene film on Cu
Bilayer graphene (BLG) is promising for optoelectronic applications due to its tunable bandgap, but its large-area growth on Cu substrates is still challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the fast synthesis of high-coverage meter-scale BLG on commercial Cu foils by introducing CO2 during the growth.
- Jincan Zhang
- , Xiaoting Liu
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Structural superlubricity (SSL) is a state of nearly zero friction and no wear between two contacted solid surfaces. Here, authors show that, by preventing edge contact with the substrate, a microscale graphite flake can achieve robust SSL against nanostructured silicon surfaces under ambient condition.
- Xuanyu Huang
- , Tengfei Li
- & Quanshui Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Ising superconductivity induced from spin-selective valley symmetry breaking in twisted trilayer graphene
Ising superconductivity induced from spin-selective valley symmetry breaking in twisted trilayer graphene
Superconductivity has been observed experimentally in twisted trilayer graphene. Here, the authors show theoretically that extended electron-electron Coulomb interaction induces breakdown of spin-selective valley symmetry in twisted trilayer graphene, which leads to Ising superconductivity.
- J. González
- & T. Stauber
-
Article
| Open Access Strong second-harmonic generation by sublattice polarization in non-uniformly strained monolayer graphene
Strong second-harmonic generation by sublattice polarization in non-uniformly strained monolayer graphene
Nanostructured platforms for efficient nonlinear optics are the building block of next generation integrated photonic devices. Here the authors provide a straightforward method to engineer the lattice symmetry of monolayer graphene, boosting the SHG signal at low temperature.
- Kunze Lu
- , Manlin Luo
- & Donguk Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry-broken Josephson junctions and superconducting diodes in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Symmetry-broken Josephson junctions and superconducting diodes in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Correlated electronic states in moiré matter are of great fundamental and technological interest. Here, the authors demonstrate a Josephson junction in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene with a correlated insulator weak link, showing magnetism and programmable superconducting diode behaviour.
- J. Díez-Mérida
- , A. Díez-Carlón
- & Dmitri K. Efetov
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional correlated insulator in CrOCl-interfaced Bernal bilayer graphene
Unconventional correlated insulator in CrOCl-interfaced Bernal bilayer graphene
Here, the authors report evidence of unconventional correlated insulating states in bilayer graphene/CrOCl heterostructures over wide doping ranges and demonstrate their application for the realization of low-temperature logic inverters.
- Kaining Yang
- , Xiang Gao
- & Zheng Han
-
Article
| Open Access Staggered circular nanoporous graphene converts electromagnetic waves into electricity
Staggered circular nanoporous graphene converts electromagnetic waves into electricity
The electromagnetic (EM) energy released by electronic devices in the environment is largely wasted and contributes to EM pollution. Here, the authors report the synthesis of staggered circular nanoporous graphene enabling the absorption and conversion of EM waves into electricity via the thermoelectric effect.
- Hualiang Lv
- , Yuxing Yao
- & Xiaoguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of hot carriers and hot phonons in the re-entrant metallic and semiconducting states of Moiré-gapped graphene
Signatures of hot carriers and hot phonons in the re-entrant metallic and semiconducting states of Moiré-gapped graphene
Significant attention has been devoted to understanding the low-electric-field properties of carriers in moiré graphene, but high-electric-field transport has not been as well explored. Here, the authors find non-monotonic transport behavior at moiré minigaps due to competition between inter-band tunneling and coupling to out-of-equilibrium phonons.
- Jubin Nathawat
- , Ishiaka Mansaray
- & Jonathan P. Bird
-
Comment
| Open AccessResearch on scalable graphene faces a reproducibility gap
More than a decade after the first demonstration of large-scale graphene synthesis by chemical vapor deposition, the commercialization of graphene products is limited not only by price, but also by consistency, reproducibility, and predictability. Here, the author discusses the reproducibility issues in the field and proposes possible solutions to improve the reliability of published results.
- Peter Bøggild
-
Article
| Open Access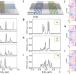 Twisted bilayer zigzag-graphene nanoribbon junctions with tunable edge states
Twisted bilayer zigzag-graphene nanoribbon junctions with tunable edge states
Twisted 2D materials have recently emerged as a controllable quantum simulator platform. Here, the authors apply the same approach to tune the edge states of zigzag graphene nanoribbons, showing a unique degree of freedom represented by the lateral stacking offset of the 1D nanostructures.
- Dongfei Wang
- , De-Liang Bao
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access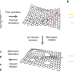 Microwave-assisted design of nanoporous graphene membrane for ultrafast and switchable organic solvent nanofiltration
Microwave-assisted design of nanoporous graphene membrane for ultrafast and switchable organic solvent nanofiltration
Layered 2D materials can be used for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) membrane fabrication due to precise molecular sieving by the interlayer structure and stability in harsh conditions. Here authors synthesise sp2-enriched nanoporous graphene by microwave treatment and demonstrate its excellent OSN performance.
- Junhyeok Kang
- , Yeongnam Ko
- & Dae Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
While porous graphene oxide with nm-sized pores can be of great interest to biofluidic and energy storage applications, achieving precisely controlled porosity remains a technical challenge. Here, the authors exploit swift heavy ions to create uniform nanoholes and ultralong straight nanochannels in GO films.
- Andrzej Olejniczak
- & Ruslan A. Rymzhanov
-
Article
| Open Access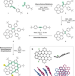 Synthesis of precisely functionalizable curved nanographenes via graphitization-induced regioselective chlorination in a mechanochemical Scholl Reaction
Synthesis of precisely functionalizable curved nanographenes via graphitization-induced regioselective chlorination in a mechanochemical Scholl Reaction
The synthesis of functionalizable nanographenes remains challenging. Here, the authors report that mechanochemical Scholl reaction allows access to regioselectively modifiable curved nanographenes in a high-yielding and general manner.
- Jovana Stanojkovic
- , Ronny William
- & Mihaiela C. Stuparu

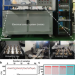 Continuous and low-carbon production of biomass flash graphene
Continuous and low-carbon production of biomass flash graphene