Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access De novo diploid genome assembly using long noisy reads
De novo diploid genome assembly using long noisy reads
Most existing assemblers failed to generate high-quality phased assemblies using long noisy reads. Here, the authors present PECAT, a Phased Error Correction and Assembly Tool, for reconstructing diploid genomes from long noisy reads.
- Fan Nie
- , Peng Ni
- & Jianxin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access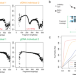 FinaleMe: Predicting DNA methylation by the fragmentation patterns of plasma cell-free DNA
FinaleMe: Predicting DNA methylation by the fragmentation patterns of plasma cell-free DNA
DNA methylation from cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can be profiled using whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS). Here, the authors develop a computational method, FinaleMe, that predicts DNA methylation and tissues of-origin in cfDNA and validate its performance using paired deep and shallow-coverage whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and WGBS data.
- Yaping Liu
- , Sarah C. Reed
- & Manolis Kellis
-
Article
| Open Access Tradeoffs in alignment and assembly-based methods for structural variant detection with long-read sequencing data
Tradeoffs in alignment and assembly-based methods for structural variant detection with long-read sequencing data
Long-read sequencing can greatly improve detection of genomic structural variants (SVs), and numerous methods have been developed to identify SVs using long-read data. Here the authors compare the performance of these methods and provide guidelines to aid users in selecting the most suitable tools for various scenarios.
- Yichen Henry Liu
- , Can Luo
- & Xin Maizie Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access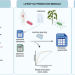 bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
Many bacteria live in close association with eukaryotic hosts, exhibiting detrimental, neutral or beneficial effects on host growth and health. Here, the authors present a streamlined computational workflow for bacterial genome annotation, large-scale comparative genomics, and prediction of genes potentially involved in niche adaptation.
- Guillermo Guerrero-Egido
- , Adrian Pintado
- & Víctor J. Carrión
-
Article
| Open Access TFvelo: gene regulation inspired RNA velocity estimation
TFvelo: gene regulation inspired RNA velocity estimation
Most RNA velocity models extract dynamics from the phase delay between unspliced and spliced mRNA for each gene. Here, authors propose TFvelo, broadening RNA velocity beyond splicing information to include gene regulation. TFvelo accurately models genes dynamics and infers cell pseudo-time from RNA abundance data.
- Jiachen Li
- , Xiaoyong Pan
- & Hong-Bin Shen
-
Review Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of autoimmunity seen through the lens of T cell functional traits
The genetic basis of autoimmunity seen through the lens of T cell functional traits
Genetic risk variants for autoimmune diseases are largely enriched in T cell-specific regulatory regions. In this review, Raychaudhuri and colleagues summarise the findings of recent studies evaluating the genetic regulation of T cell molecular and functional traits in these diseases.
- Kaitlyn A. Lagattuta
- , Hannah L. Park
- & Soumya Raychaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access Unzipped genome assemblies of polyploid root-knot nematodes reveal unusual and clade-specific telomeric repeats
Unzipped genome assemblies of polyploid root-knot nematodes reveal unusual and clade-specific telomeric repeats
Telomeres protect the extremities of linear chromosomes and are involved in ageing, senescence and genome stability. Here, the authors have identified peculiar and specific telomeric DNA repeats in the genomes of devastating plant-parasitic nematodes, opening new perspectives for their control.
- Ana Paula Zotta Mota
- , Georgios D. Koutsovoulos
- & Etienne G. J. Danchin
-
Article
| Open Access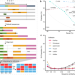 A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
Existing tools for structural variations (SVs) calling and merging often lead to fragmented SVs and the potential of introducing unnecessary errors. Here, the authors report the PanPop pipeline to address these issues by implementing sequence-aware SV merging algorithm to efficiently merge SVs of various types.
- Zeyu Zheng
- , Mingjia Zhu
- & Yongzhi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access ContScout: sensitive detection and removal of contamination from annotated genomes
ContScout: sensitive detection and removal of contamination from annotated genomes
It is unclear whether naturally evolved de novo proteins have stable, folded structures. Here, systematic identification and structural modeling of de novo genes, this study reveals that a small subset of these proteins may have well-folded structures, and were likely born with these structures.
- Balázs Bálint
- , Zsolt Merényi
- & László G. Nagy
-
Article
| Open Access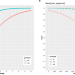 Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Using All of Us pilot data, the authors compared short- and long-read performance across medically relevant genes and showcased the utility of long reads to improve variant detection and phasing in easy and hard to resolve medically relevant genes.
- M. Mahmoud
- , Y. Huang
- & F. J. Sedlazeck
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning parameters for polygenic risk score methods using GWAS summary statistics from training data
Tuning parameters for polygenic risk score methods using GWAS summary statistics from training data
Some polygenic risk score (PRS) methods for predicting genetic risk for common diseases require an external individual-level dataset for parameter tuning, posing privacy-related concerns. Here, the authors present an empirical Bayes method that tunes PRS models using only summary statistics from the training data.
- Wei Jiang
- , Ling Chen
- & Hongyu Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access vcfdist: accurately benchmarking phased small variant calls in human genomes
vcfdist: accurately benchmarking phased small variant calls in human genomes
Accurately benchmarking small variant calling accuracy is critical for the continued improvement of human genome sequencing. Here, the authors show that current approaches are biased towards certain variant representations and develop a new approach to ensure consistent and accurate benchmarking, regardless of the original variant representations.
- Tim Dunn
- & Satish Narayanasamy
-
Article
| Open Access The PENGUIN approach to reconstruct protein interactions at enhancer-promoter regions and its application to prostate cancer
The PENGUIN approach to reconstruct protein interactions at enhancer-promoter regions and its application to prostate cancer
The authors reconstruct high fidelity networks of protein-protein interactions between promoters and enhancers in prostate cancer and demonstrate the potential of such an analytical framework to obtain actionable insights into the disease and potential therapeutic targets.
- Alexandros Armaos
- , François Serra
- & Gian Gaetano Tartaglia
-
Article
| Open Access Global pathogenomic analysis identifies known and candidate genetic antimicrobial resistance determinants in twelve species
Global pathogenomic analysis identifies known and candidate genetic antimicrobial resistance determinants in twelve species
A global analysis of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) across 27,155 genomes and 69 drugs reveals patterns in AMR gene transfer between species and identifies 142 AMR gene candidates, two of which were tested and confirmed as contributing to AMR.
- Jason C. Hyun
- , Jonathan M. Monk
- & Bernhard O. Palsson
-
Article
| Open Access Unistrand piRNA clusters are an evolutionarily conserved mechanism to suppress endogenous retroviruses across the Drosophila genus
Unistrand piRNA clusters are an evolutionarily conserved mechanism to suppress endogenous retroviruses across the Drosophila genus
To control transposable elements, fruit flies rely on distinct genomic regions called piRNA clusters. Here, new piRNA clusters were identified across diverse Drosophila species, displaying a conserved and specialised role in the control of endogenous retroviruses in ovarian somatic cells.
- Jasper van Lopik
- , Azad Alizada
- & Benjamin Czech Nicholson
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing cancer evolution and heterogeneity using Hi-C
Tracing cancer evolution and heterogeneity using Hi-C
It is challenging to analyse chromosomal rearrangements in heterogeneous solid cancers. Here the authors present HiDENSEC, a method to jointly infer absolute copy number, ploidy, tumor purity and large-scale rearrangements from Hi-C data. The increased statistical power afforded by joint inference enables novel insights into cancer genome evolution.
- Dan Daniel Erdmann-Pham
- , Sanjit Singh Batra
- & Dirk Hockemeyer
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic review and integrated data analysis reveal diverse pangolin-associated microbes with infection potential
Systematic review and integrated data analysis reveal diverse pangolin-associated microbes with infection potential
The diversity and spillover potential of pangolin-associated microbes are not fully understood. Here, the authors describe the distribution and spectrum of reported pangolin microbes by integrating data from multiple sources and assess their potential to emerge as human pathogens.
- Run-Ze Ye
- , Xiao-Yang Wang
- & Wu-Chun Cao
-
Article
| Open Access De novo genome assembly depicts the immune genomic characteristics of cattle
De novo genome assembly depicts the immune genomic characteristics of cattle
The genomic organisation of the cattle genome has been assembled to a limited level of resolution. Here using long range nanopore sequencing the authors present a cattle genome assembly concentrating on characterising the immunogenomic loci, particularly T cell receptor (TR), immunoglobulin (IG) and MHC genes, from one animal.
- Ting-Ting Li
- , Tian Xia
- & Tao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of errors in draft genome assemblies at single-nucleotide resolution for quality assessment and improvement
Identification of errors in draft genome assemblies at single-nucleotide resolution for quality assessment and improvement
A high-quality genome assembly is essential for various genomic studies in life sciences. Here the authors develop CRAQ, a reference-free method that facilitates the evaluation and improvement of any de novo genome assembly with single nucleotide resolution.
- Kunpeng Li
- , Peng Xu
- & Yuannian Jiao
-
Article
| Open Access NeST: nested hierarchical structure identification in spatial transcriptomic data
NeST: nested hierarchical structure identification in spatial transcriptomic data
A wide variety of tissues exhibit nested hierarchical organisation of cells in gene expression and activities. Here, authors present NeST, a method for spatial transcriptomics to identify such structures and uncover their functions via ligand-receptor communication, in both two and three dimensions.
- Benjamin L. Walker
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Simulation of undiagnosed patients with novel genetic conditions
Simulation of undiagnosed patients with novel genetic conditions
Rare Mendelian disorders pose a major diagnostic challenge, but evaluation of automated tools that aim to uncover causal genes tools is limited. Here, the authors present a computational pipeline that simulates realistic clinical datasets to address this deficit.
- Emily Alsentzer
- , Samuel G. Finlayson
- & Isaac S. Kohane
-
Article
| Open Access Context-dependent perturbations in chromatin folding and the transcriptome by cohesin and related factors
Context-dependent perturbations in chromatin folding and the transcriptome by cohesin and related factors
Enhancer–promoter looping and topologically associating domain are at the base of chromatin structures. Here the authors present a computational workflow in which multi-omics datasets are compared systematically to explore how three-dimensional (3D) structure and gene expression are regulated by cohesin and related factors.
- Ryuichiro Nakato
- , Toyonori Sakata
- & Katsuhiko Shirahige
-
Article
| Open Access Circular RNAs in the human brain are tailored to neuron identity and neuropsychiatric disease
Circular RNAs in the human brain are tailored to neuron identity and neuropsychiatric disease
Dopamine neurons control movements while pyramidal neurons regulate memory and language. Here the authors show that circular RNAs production in these neurons appears tailored to neuron identity and genetically linked to neuropsychiatric disease such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Xianjun Dong
- , Yunfei Bai
- & Clemens R. Scherzer
-
Article
| Open Access A landscape of complex tandem repeats within individual human genomes
A landscape of complex tandem repeats within individual human genomes
Haplotype-resolved long, complex tandem repeats remain largely hidden despite their potential relevance to disease. Here, the authors reveal and analyze the genome-wide landscape of these repeats using a high-precision algorithm.
- Kazuki Ichikawa
- , Riki Kawahara
- & Shinichi Morishita
-
Article
| Open Access Extrachromosomal circular DNA and structural variants highlight genome instability in Arabidopsis epigenetic mutants
Extrachromosomal circular DNA and structural variants highlight genome instability in Arabidopsis epigenetic mutants
Epigenetic control of extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) compartment and the relationships between eccDNA and plant genome stability remain unclear. Here, the authors investigate eccDNA and structural variations in Arabidopsis epigenetic mutants to reveal the eccDNA repertoire and its impact on genome stability.
- Panpan Zhang
- , Assane Mbodj
- & Marie Mirouze
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic dissection of endemic carbapenem resistance reveals metallo-beta-lactamase dissemination through clonal, plasmid and integron transfer
Genomic dissection of endemic carbapenem resistance reveals metallo-beta-lactamase dissemination through clonal, plasmid and integron transfer
Resistance to carbapenems, a class of last-line antibiotics, is a global health threat. This study analysed a two-decade history of carbapenem resistance and identified complex, multi-level (bacterial strain, plasmid, gene) transmission dynamics.
- Nenad Macesic
- , Jane Hawkey
- & Anton Y. Peleg
-
Article
| Open Access Mutational signature dynamics shaping the evolution of oesophageal adenocarcinoma
Mutational signature dynamics shaping the evolution of oesophageal adenocarcinoma
It is critical to understand what drives the progression of oesophageal adenocarcinoma (OAC) from a pre-cancerous state. Here, the authors use whole-genome sequencing to characterise the mutational processes and drivers of OAC progression from Barrett’s Oesophagus, as well as their prognostic associations.
- Sujath Abbas
- , Oriol Pich
- & Maria Secrier
-
Article
| Open Access High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors
High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors
There is a need for methods that allow the analysis of single-cell long-read sequencing data without depending on known barcode lists or short-read sequencing. Here, the authors develop scNanoGPS, a tool that can independently deconvolute long reads into single cells and single molecules, and apply it on tumour and cell line data.
- Cheng-Kai Shiau
- , Lina Lu
- & Ruli Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin alternates between A and B compartments at kilobase scale for subgenic organization
Chromatin alternates between A and B compartments at kilobase scale for subgenic organization
Ultra-deep mapping of genome organization uncovers precise nuclear compartments and diffuse CTCF loops. This work demonstrates that compartment domains segregate the 5′ and 3′ ends of genes and that CTCF loops create proximal structures.
- Hannah L. Harris
- , Huiya Gu
- & M. Jordan Rowley
-
Article
| Open Access INSurVeyor: improving insertion calling from short read sequencing data
INSurVeyor: improving insertion calling from short read sequencing data
Current methods for detecting insertions from short read sequencing data generally have low sensitivity. Here, the authors develop a new tool that runs quickly and detects significantly more true positive insertions compared to any combination of existing methods.
- Ramesh Rajaby
- , Dong-Xu Liu
- & Wing-Kin Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Transposon signatures of allopolyploid genome evolution
Transposon signatures of allopolyploid genome evolution
Assigning assembled chromosomes to subgenome in allopolypoid genome analysis is challenging. Here, the authors report a statistical formwork for identifying evolutionarily coherent subgneomes relying on transposable elements to group chromosomes into sets with shared ancestry and apply it in cyprinids, false flax and strawberry.
- Adam M. Session
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article
| Open Access Reference-free assembly of long-read transcriptome sequencing data with RNA-Bloom2
Reference-free assembly of long-read transcriptome sequencing data with RNA-Bloom2
Most existing long-read transcriptome assembly methods rely on reference genomes and transcript annotations, while reference-free methods remain scarce. Here, Nip et al. introduce RNA-Bloom2, a reference-free method that requires substantially less memory and runtime than other reference-free methods.
- Ka Ming Nip
- , Saber Hafezqorani
- & Inanc Birol
-
Article
| Open Access Linear time complexity de novo long read genome assembly with GoldRush
Linear time complexity de novo long read genome assembly with GoldRush
Current state-of-the-art de novo long read genome assemblers follow the Overlap-Layout-Consensus paradigm. GoldRush departs from this paradigm, generating highly contiguous assemblies with linear time complexity and using an order of magnitude less RAM than state-of-the-art methods.
- Johnathan Wong
- , Lauren Coombe
- & Inanç Birol
-
Article
| Open Access Alternative promoters in CpG depleted regions are prevalently associated with epigenetic misregulation of liver cancer transcriptomes
Alternative promoters in CpG depleted regions are prevalently associated with epigenetic misregulation of liver cancer transcriptomes
The regulatory mechanisms of alternative promoters remain to be investigated. Here, the authors explore the sequence and epigenetics landscape of alternative promoters and how they regulate gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Chirag Nepal
- & Jesper B. Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Virus diversity, wildlife-domestic animal circulation and potential zoonotic viruses of small mammals, pangolins and zoo animals
Virus diversity, wildlife-domestic animal circulation and potential zoonotic viruses of small mammals, pangolins and zoo animals
Monitoring the diversity of viruses infecting animals is important for assessing zoonotic risk. Here, the authors use metatranscriptomics to characterise the viromes of small mammals, pangolins, and zoo animals in China to identify potentially zoonotic viruses.
- Xinyuan Cui
- , Kewei Fan
- & Yongyi Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying high-impact variants and genes in exomes of Ashkenazi Jewish inflammatory bowel disease patients
Identifying high-impact variants and genes in exomes of Ashkenazi Jewish inflammatory bowel disease patients
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is highly prevalent among the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Here, the authors identify novel IBD-associated variants and genes, validated by transcriptomic and phenome-wide associations.
- Yiming Wu
- , Kyle Gettler
- & Yuval Itan
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping genomic regulation of kidney disease and traits through high-resolution and interpretable eQTLs
Mapping genomic regulation of kidney disease and traits through high-resolution and interpretable eQTLs
Here, the authors discover over 15,000 eQTLs in human kidney samples by integrating single-nucleus open chromatin data, resulting in high resolution eQTLs, increased enrichment of GWAS heritability and colocalization, followed by downstream validation.
- Seong Kyu Han
- , Michelle T. McNulty
- & Matthew G. Sampson
-
Article
| Open Access An autoimmune pleiotropic SNP modulates IRF5 alternative promoter usage through ZBTB3-mediated chromatin looping
An autoimmune pleiotropic SNP modulates IRF5 alternative promoter usage through ZBTB3-mediated chromatin looping
Here the authors used an evidence-based strategy to prioritize causal pleiotropic variants of autoimmune diseases, and revealed that rs4728142 modulates aberrant IRF5 alternative promoter usage by ZBTB3-mediated chromatin looping.
- Zhao Wang
- , Qian Liang
- & Mulin Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access A thousand-genome panel retraces the global spread and adaptation of a major fungal crop pathogen
A thousand-genome panel retraces the global spread and adaptation of a major fungal crop pathogen
Zymoseptoria tritici is an important fungal pathogen of wheat which has spread globally. Here, the authors perform genomic analyses on a collection of ~1100 Z. tritici samples from 42 countries to describe its global spread and elucidate mechanisms of adaptation to different environmental conditions.
- Alice Feurtey
- , Cécile Lorrain
- & Daniel Croll
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular atlas reveals the tri-sectional spinning mechanism of spider dragline silk
A molecular atlas reveals the tri-sectional spinning mechanism of spider dragline silk
The genetic basis of spider major ampullate (Ma) gland silk production remains unknown. Hu et al. unveil a molecular atlas of this gland for the golden orb-weaving spider combining genome assembly and multiomics, revealing the single-cell spatial architecture of silk production in the Ma gland.
- Wenbo Hu
- , Anqiang Jia
- & Yi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Amniotes co-opt intrinsic genetic instability to protect germ-line genome integrity
Amniotes co-opt intrinsic genetic instability to protect germ-line genome integrity
Pachytene Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) expressed in mammalian germ lines are abundant, but their evolution and function are not fully understood. Here, the authors find that pachytene piRNA loci are hotspots of structural variation, which underlies rapid piRNA birth, divergence, and loss.
- Yu H. Sun
- , Hongxiao Cui
- & Xin Zhiguo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the exact breakpoints of structural variations using long sequencing reads with DeBreak
Deciphering the exact breakpoints of structural variations using long sequencing reads with DeBreak
Long-read sequencing is promising for the detection of structural variants (SVs), which requires algorithms with high sensitivity and precision. Here, the authors develop DeBreak, an algorithm for comprehensive and accurate SV detection in long-read sequencing data across different platforms, which outperforms other SV callers.
- Yu Chen
- , Amy Y. Wang
- & Zechen Chong
-
Article
| Open Access GALA: a computational framework for de novo chromosome-by-chromosome assembly with long reads
GALA: a computational framework for de novo chromosome-by-chromosome assembly with long reads
Genomes usually contain multiple chromosomes. The paper reports on GALA, a computational framework for chromosome-based sequencing data separation and gap-free de novo assembly. It allows integration of different sources of data.
- Mohamed Awad
- & Xiangchao Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Thousands of human non-AUG extended proteoforms lack evidence of evolutionary selection among mammals
Thousands of human non-AUG extended proteoforms lack evidence of evolutionary selection among mammals
Analysis of a large number of Ribo-seq datasets and genomic alignments led to detection of novel non-AUG proteoforms. Unexpectedly the number of non-AUG proteoforms identified with Ribo-seq greatly exceeds those with strong phylogenetic support.
- Alla D. Fedorova
- , Stephen J. Kiniry
- & Pavel V. Baranov
-
Article
| Open Access Graph-based pangenomics maximizes genotyping density and reveals structural impacts on fungal resistance in melon
Graph-based pangenomics maximizes genotyping density and reveals structural impacts on fungal resistance in melon
The power of pangenomic graphs to improve genetic mapping is still unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate its value in identification of genetic variants associated with disease resistance traits in melon using PanPipes, a pangenome construction and low-coverage genotype-by-sequencing pipeline.
- Justin N. Vaughn
- , Sandra E. Branham
- & William P. Wechter
-
Article
| Open Access Reference panel guided topological structure annotation of Hi-C data
Reference panel guided topological structure annotation of Hi-C data
Predicting topological structures from Hi-C data provides insight into comprehending gene expression and regulation. Here, the authors present RefHiC, an attention-based deep learning framework that leverages a reference panel of Hi-C datasets to assist topological structure annotation from a given study sample.
- Yanlin Zhang
- & Mathieu Blanchette
-
Article
| Open Access Transposable element-mediated rearrangements are prevalent in human genomes
Transposable element-mediated rearrangements are prevalent in human genomes
Here the authors show that transposable element-mediated rearrangements impact more than 500 kbp of an average human genome, are a source of individual variation, a substrate for evolutionary change, and can occur through diverse mechanisms.
- Parithi Balachandran
- , Isha A. Walawalkar
- & Christine R. Beck
-
Article
| Open Access VeChat: correcting errors in long reads using variation graphs
VeChat: correcting errors in long reads using variation graphs
Consensus sequence-based methods for self-correction of long-read sequencing data are affected by biases that can mask true variants characterizing little-covered or low-frequency haplotypes. Here, to address this issue, the authors develop a variation graph-based method for performing haplotype-aware self-correction of long reads.
- Xiao Luo
- , Xiongbin Kang
- & Alexander Schönhuth
-
Article
| Open Access Strain level microbial detection and quantification with applications to single cell metagenomics
Strain level microbial detection and quantification with applications to single cell metagenomics
Here the authors develop CAMMiQ, a combinatorial optimization approach that utilizes variable length, “unique” and “doubly-unique” genomic segments, showing improves identification and quantification of distinct microbes in metagenomic sequence data.
- Kaiyuan Zhu
- , Alejandro A. Schäffer
- & S. Cenk Sahinalp

 Nonlinear DNA methylation trajectories in aging male mice
Nonlinear DNA methylation trajectories in aging male mice