Nature Podcast |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved
Marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved
A parachute-like skin membrane, the patagium, evolved independently in several marsupial species. Genomic analysis suggests that this trait came about through different changes to the regulation of the same gene.
- Darío G. Lupiáñez
-
Article
| Open Access Emx2 underlies the development and evolution of marsupial gliding membranes
Emx2 underlies the development and evolution of marsupial gliding membranes
Patagia—the mammalian gliding membrane—repeatedly originated through a process of convergent genomic evolution, whereby the regulation of Emx2 was altered by distinct cis-regulatory elements in independently evolved species.
- Jorge A. Moreno
- , Olga Dudchenko
- & Ricardo Mallarino
-
World View |
 Ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork
Ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork
Amid the data deluge provided by lab-based techniques, such as environmental-DNA analysis, true connection still comes only in the outdoors.
- Chris Mantegna
-
News & Views |
 Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
A therapeutic strategy that alters gene expression in a rare and severe neurodevelopmental condition has been tested in stem-cell-based models of the disease, and has been shown to correct genetic and cellular defects.
- Silvia Velasco
-
News & Views |
 Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
Genetic pedigrees spanning nine generations uncover the social organization of a nomadic empire that dominated much of central and eastern Europe from the sixth to the early ninth century.
- Lara M. Cassidy
-
News & Views |
 Tumours form without genetic mutations
Tumours form without genetic mutations
Researchers find that brief and reversible inhibition of a gene-silencing mechanism leads to irreversible tumour formation in fruit flies, challenging the idea that cancer is caused only by permanent changes to DNA.
- Anne-Kathrin Classen
-
News |
 DNA from ancient graves reveals the culture of a mysterious nomadic people
DNA from ancient graves reveals the culture of a mysterious nomadic people
Hundreds of genomes shed light on the marriage habits and social norms of the Avar people of central Europe.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis reveals context-dependent, cell-level selection of mtDNA
Single-cell analysis reveals context-dependent, cell-level selection of mtDNA
A new method for tracking single-cell heteroplasmy, called SCI-LITE, is combined with mitochondrial DNA base editing to reveal principles of heteroplasmy dynamics in dividing cells.
- Anna V. Kotrys
- , Timothy J. Durham
- & Vamsi K. Mootha
-
Article
| Open Access Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
A transient perturbation of transcriptional silencing mediated by Polycomb proteins is sufficient to induce an epigenetic cancer cell fate in Drosophila in the absence of driver mutations.
- V. Parreno
- , V. Loubiere
- & G. Cavalli
-
Article
| Open Access Phylogenomics and the rise of the angiosperms
Phylogenomics and the rise of the angiosperms
Phylogenomic analysis of 7,923 angiosperm species using a standardized set of 353 nuclear genes produced an angiosperm tree of life dated with 200 fossil calibrations, providing key insights into evolutionary relationships and diversification.
- Alexandre R. Zuntini
- , Tom Carruthers
- & William J. Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Network of large pedigrees reveals social practices of Avar communities
Network of large pedigrees reveals social practices of Avar communities
Analysis of ancient DNA from 424 individuals in the Avar period, from the sixth to the ninth century AD, reveals population movement from the steppe and the prolonged existence of a steppe nomadic descent system centred around patrilineality and female exogamy in central Europe.
- Guido Alberto Gnecchi-Ruscone
- , Zsófia Rácz
- & Zuzana Hofmanová
-
Research Highlight |
 Dozens of genes are linked to post-traumatic stress disorder
Dozens of genes are linked to post-traumatic stress disorder
Findings underscore that genetic factors contribute to development of the condition after a traumatic incident.
-
News & Views |
 Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
Mating between different species has often been considered an evolutionary dead end, but a study in longwing butterflies suggests that such hybridization could underlie the origins of a new species.
- Megan E. Frayer
- & Jenn M. Coughlan
-
Analysis
| Open Access Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success
Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success
Human genetic evidence increases the success rate of drugs from clinical development to approval but we are still far from reaching peak genetic insights to aid the discovery of targets for more effective drugs.
- Eric Vallabh Minikel
- , Jeffery L. Painter
- & Matthew R. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits
Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits
Genomic studies of Heliconius butterflies provide evidence that Heliconius elevatus is a hybrid species, and that its speciation was driven by introgression of traits from Heliconius melpomene into the other parent, an ancestor of Heliconius pardalinus.
- Neil Rosser
- , Fernando Seixas
- & Kanchon K. Dasmahapatra
-
Research Briefing |
 Genetic risk variants lead to type 2 diabetes development through different pathways
Genetic risk variants lead to type 2 diabetes development through different pathways
The largest genome-wide association study for type 2 diabetes so far, which included several ancestry groups, led to the identification of eight clusters of genetic risk variants. The clusters capture different biological pathways that contribute to the disease, and some clusters are associated with vascular complications.
-
Nature Podcast |
 The ‘ghost roads’ driving tropical deforestation
The ‘ghost roads’ driving tropical deforestation
Researchers find that a huge number of roads that don’t appear on official maps, and the protein that could determine whether someone is left-handed.
- Nick Petrić Howe
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
Article |
 Cell-type-resolved mosaicism reveals clonal dynamics of the human forebrain
Cell-type-resolved mosaicism reveals clonal dynamics of the human forebrain
Using mosaic variant barcode analysis, clonal dynamics of specific cell types are deconvolved in the human forebrain.
- Changuk Chung
- , Xiaoxu Yang
- & Joseph G. Gleeson
-
Comment |
 AI can help to tailor drugs for Africa — but Africans should lead the way
AI can help to tailor drugs for Africa — but Africans should lead the way
Computational models that require very little data could transform biomedical and drug development research in Africa, as long as infrastructure, trained staff and secure databases are available.
- Gemma Turon
- , Mathew Njoroge
- & Kelly Chibale
-
Research Highlight |
 Advanced CRISPR system fixes a deadly mutation in cells
Advanced CRISPR system fixes a deadly mutation in cells
Applying a ‘base editor’ allows cells to crank out increased levels of a vital metabolic enzyme.
-
Research Briefing |
 Five steps to connect genetic risk variants to disease
Five steps to connect genetic risk variants to disease
Genetic variants contribute to the risk of developing certain diseases, but identifying the genes and molecular pathways under their control has been difficult. Now, a systematic approach to pinpointing these factors yields insights into how a specific pathway in endothelial cells influences the risk of coronary artery disease.
-
Nature Podcast |
 Pregnancy’s effect on ‘biological’ age, polite birds, and the carbon cost of home-grown veg
Pregnancy’s effect on ‘biological’ age, polite birds, and the carbon cost of home-grown veg
We round up some recent stories from the Nature Briefing.
- Benjamin Thompson
- , Noah Baker
- & Flora Graham
-
Article
| Open Access The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres
The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres
A comparison of two complete sets of human centromeres reveals that the centromeres show at least a 4.1-fold increase in single-nucleotide variation compared with their unique flanks, and up to 3-fold variation in size, resulting from an accelerated mutation rate.
- Glennis A. Logsdon
- , Allison N. Rozanski
- & Evan E. Eichler
-
Article
| Open Access Improving prime editing with an endogenous small RNA-binding protein
Improving prime editing with an endogenous small RNA-binding protein
Genome-scale genetic screens identify the small RNA-binding protein La as a strong mediator of prime editing.
- Jun Yan
- , Paul Oyler-Castrillo
- & Britt Adamson
-
News |
 Right- or left-handed? Protein in embryo cells might help decide
Right- or left-handed? Protein in embryo cells might help decide
Gene that codes for structural protein could determine the dominant side of the human brain.
- Sumeet Kulkarni
-
Article |
Complexity of avian evolution revealed by family-level genomes
- Josefin Stiller
- , Shaohong Feng
- & Guojie Zhang
-
News |
 Scientists made a six-legged mouse embryo — here’s why
Scientists made a six-legged mouse embryo — here’s why
A rodent with two extra limbs instead of genitals shows the crucial role of a gene pathway in determining the fate of a primordial structure.
- Sara Reardon
-
Nature Podcast |
 How climate change is affecting global timekeeping
How climate change is affecting global timekeeping
Melting polar ice could delay major time adjustment, and the strange connection between brain inflammation and memory.
- Elizabeth Gibney
- & Nick Petrić Howe
-
Article
| Open Access The complex polyploid genome architecture of sugarcane
The complex polyploid genome architecture of sugarcane
We build a polyploid reference genome for hybrid sugarcane cultivar R570, improving on its current ‘mosaic monoploid’ representation, enabling fine-grain description of genome architecture and the exploration of candidate genes underlying the Bru1 brown rust resistance locus.
- A. L. Healey
- , O. Garsmeur
- & A. D’Hont
-
Article |
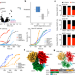 Targeting DCAF5 suppresses SMARCB1-mutant cancer by stabilizing SWI/SNF
Targeting DCAF5 suppresses SMARCB1-mutant cancer by stabilizing SWI/SNF
DCAF5 has a quality-control function for SWI/SNF complexes and promotes the degradation of incompletely assembled SWI/SNF complexes in the absence of SMARCB1.
- Sandi Radko-Juettner
- , Hong Yue
- & Charles W. M. Roberts
-
News |
 Pregnancy advances your ‘biological’ age — but giving birth turns it back
Pregnancy advances your ‘biological’ age — but giving birth turns it back
Carrying a baby creates some of the same epigenetic patterns on DNA seen in older people.
- Saima Sidik
-
Technology Feature |
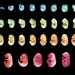 One year, three researchers, millions of cells: how a small team created the largest mouse-embryo atlas so far
One year, three researchers, millions of cells: how a small team created the largest mouse-embryo atlas so far
A map of mouse development from conception to birth tracks 12.4 million cells at single-cell resolution as they mature into organs and other tissues.
- Sara Reardon
-
Research Briefing |
 Neuron migration to brain regions key to memory and navigation continues into childhood
Neuron migration to brain regions key to memory and navigation continues into childhood
This study identifies a major migratory route for young neurons in the brains of young children. This route forms during pregnancy and links the birthplace of these nerve cells to their destination in highly interconnected brain regions that are responsible for memory and spatial processing.
-
News |
 Ancient malaria genome from Roman skeleton hints at disease’s history
Ancient malaria genome from Roman skeleton hints at disease’s history
Genetic information from ancient remains is helping to reveal how malaria has moved and evolved alongside people.
- Tosin Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access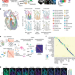 Spatially organized cellular communities form the developing human heart
Spatially organized cellular communities form the developing human heart
Combining single-cell RNA-sequencing with high-resolution multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization reveals in detail the cellular interactions and specialization of cardiac cell types that form and remodel the human heart.
- Elie N. Farah
- , Robert K. Hu
- & Neil C. Chi
-
Correspondence |
On the ethics of informed consent in genetic data collected before 1997
- Martin Zieger
- , Yann Joly
- & Maria Eugenia D’Amato
-
Article
| Open Access Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
Selfish conflict underlies RNA-mediated parent-of-origin effects
In Caenorhabditis tropicalis, selective expression of genetic alleles from one parent but not the other can arise from maternally inherited small transcripts acting via the PIWI-interacting RNA host defence pathway.
- Pinelopi Pliota
- , Hana Marvanova
- & Alejandro Burga
-
News & Views |
 Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
In experiments dubbed the Random Genome Project, researchers have integrated DNA strands with random sequences into yeast and mouse cells to find the default transcriptional state of their genomes.
- Sean R. Eddy
-
News |
 Oldest stone tools in Europe hint at ancient humans’ route there
Oldest stone tools in Europe hint at ancient humans’ route there
Dating of artefacts found at a site in western Ukraine suggests that archaic humans had entered Europe’s eastern gate by 1.4 million years ago.
- Giorgia Guglielmi
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers
Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for 233 circulating metabolites from 33 cohorts reveals more than 400 loci and suggests probable causal genes, providing insights into metabolic pathways and disease aetiology.
- Minna K. Karjalainen
- , Savita Karthikeyan
- & Johannes Kettunen
-
Article
| Open Access A concerted neuron–astrocyte program declines in ageing and schizophrenia
A concerted neuron–astrocyte program declines in ageing and schizophrenia
A synaptic neuron and astrocyte program (SNAP) varies among healthy humans, may shape interindividual differences in synapses and plasticity, and is undermined in schizophrenia and with advancing age.
- Emi Ling
- , James Nemesh
- & Steven A. McCarroll
-
Article
| Open Access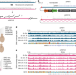 Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Introduction of a long synthetic DNA into yeast genomic loci results in high default transcriptional activity in yeast but low activity in mouse, suggesting distinct default levels of genomic activity in these organisms.
- Brendan R. Camellato
- , Ran Brosh
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
News |
 Genetics solves mystery of rare brown pandas after 40 years
Genetics solves mystery of rare brown pandas after 40 years
Chinese researchers find the gene responsible for the brown-and-white fur of a handful of giant pandas in China.
- Xiaoying You
-
News |
 Oldest known animal sex chromosome evolved in octopuses 380 million years ago
Oldest known animal sex chromosome evolved in octopuses 380 million years ago
Result reveals for the first time how some cephalopods determine sex.
- Carissa Wong
-
Nature Podcast |
 Could this one-time ‘epigenetic’ treatment control cholesterol?
Could this one-time ‘epigenetic’ treatment control cholesterol?
Regulating gene expression lowers blood cholesterol in mice, and how the Universe’s cosmic fog was lifted.
- Nick Petrić Howe
-
News |
 ‘Epigenetic’ editing cuts cholesterol in mice
‘Epigenetic’ editing cuts cholesterol in mice
Changes to chemical tags on DNA in mice dial down the activity of a gene without cuts to the genome.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Spotlight |
 Stealthy stem cells to treat disease
Stealthy stem cells to treat disease
Gene-editing strategies that allow stem cells to evade the immune system offer hope for universal cell-replacement therapies.
- Elie Dolgin
-
News & Views |
 A mobile DNA sequence could explain tail loss in humans and apes
A mobile DNA sequence could explain tail loss in humans and apes
The lack of a tail is one thing that separates apes — including humans — from other primates. Insertion of a short DNA sequence into a gene that controls tail development could explain tail loss in the common ancestor of apes.
- Miriam K. Konkel
- & Emily L. Casanova
-
Article
| Open Access Durable and efficient gene silencing in vivo by hit-and-run epigenome editing
Durable and efficient gene silencing in vivo by hit-and-run epigenome editing
Experiments in mice show that designed epigenome editors that contain domains of transcriptional repressors can enable stable epigenetic silencing of Pcsk9, a gene with a role in cholesterol homeostasis, without inducing DNA breaks.
- Martino Alfredo Cappelluti
- , Valeria Mollica Poeta
- & Angelo Lombardo
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agricultural genetics
- Animal breeding
- Behavioural genetics
- Cancer genetics
- Cancer genomics
- Clinical genetics
- Consanguinity
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- Cytogenetics
- Development
- Epigenetics
- Epigenomics
- Eukaryote
- Evolutionary biology
- Functional genomics
- Gene expression
- Gene regulation
- Genetic association study
- Genetic hybridization
- Genetic interaction
- Genetic linkage study
- Genetic markers
- Genome
- Genomic instability
- Genomics
- Genotype
- Haplotypes
- Heritable quantitative trait
- Immunogenetics
- Inbreeding
- Medical genetics
- Microbial genetics
- Mutation
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Plant breeding
- Plant genetics
- Polyploidy
- Population genetics
- Prokaryote
- Quantitative trait
- RNA splicing
- RNAi
- Sequencing

 How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’