Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
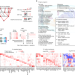 Convergence of coronary artery disease genes onto endothelial cell programs
Convergence of coronary artery disease genes onto endothelial cell programs
Variant-to-gene-to-program is a new approach to building maps of genome function to link risk variants to disease genes and to convergent signalling pathways in an unbiased manner; its strength is demonstrated in coronary artery disease.
- Gavin R. Schnitzler
- , Helen Kang
- & Jesse M. Engreitz
-
Article |
 Base-editing mutagenesis maps alleles to tune human T cell functions
Base-editing mutagenesis maps alleles to tune human T cell functions
Massive-scale mutational screening across 385 genes reveals a wide spectrum of alleles that govern tunable T cell functions, including cytokine production and cytotoxicity.
- Ralf Schmidt
- , Carl C. Ward
- & Alexander Marson
-
Article
| Open Access A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
Using single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, human embryonic limb development across space and time and the diversification and cross-species conservation of cells are demonstrated.
- Bao Zhang
- , Peng He
- & Sarah A. Teichmann
-
Article |
 Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
Integration of multiomics data with functional analysis of pancreatic tissues from individuals with early-stage type 2 diabetes indicates that the genetic risk converges on RFX6, which regulates chromatin architecture at multiple risk loci.
- John T. Walker
- , Diane C. Saunders
- & Marcela Brissova
-
Perspective |
 Functional genomics and systems biology in human neuroscience
Functional genomics and systems biology in human neuroscience
Technical developments and large collaborative research networks in neurogenomics promise rapid progress in neuroscience, but translation of results from model systems to human brains is limited by sample availability, technical challenges and ethical issues.
- Genevieve Konopka
- & Aparna Bhaduri
-
Perspective |
 The status of the human gene catalogue
The status of the human gene catalogue
Although the catalogue of human protein-coding genes is nearing completion, the number of non-coding RNA genes remains highly uncertain, and for all genes much work remains to be done to understand their functions.
- Paulo Amaral
- , Silvia Carbonell-Sala
- & Steven L. Salzberg
-
Article
| Open Access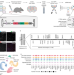 Transcriptional linkage analysis with in vivo AAV-Perturb-seq
Transcriptional linkage analysis with in vivo AAV-Perturb-seq
An in vivo single-cell CRISPR screening method identifies transcriptional phenotypes of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome associated with a broad dysregulation of a class of disease susceptibility genes that are important for RNA processing and synaptic function.
- Antonio J. Santinha
- , Esther Klingler
- & Randall J. Platt
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway
Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway
Triacylglycerols are an energy source produced in humans by DGAT1 and DGAT2, but disrupting these enzymes reveals a noncanonical pathway involving the protein DIESL (formerly TMEM68) and its regulator TMX1, which is important during lipid scarcity.
- Gian-Luca McLelland
- , Marta Lopez-Osias
- & Thijn R. Brummelkamp
-
Article
| Open Access Organization of the human intestine at single-cell resolution
Organization of the human intestine at single-cell resolution
Intestinal cell types are organized into distinct neighbourhoods and communities within the healthy human intestine, with distinct immunological niches.
- John W. Hickey
- , Winston R. Becker
- & Michael Snyder
-
Article |
 An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
A machine learning approach is used to analyse multi-omics (proteomics, metabolomics and transcriptomics) data, producing genetic scores for more than 17,000 biomolecular traits in human blood, and identifying possible associations with disease.
- Yu Xu
- , Scott C. Ritchie
- & Michael Inouye
-
Article
| Open Access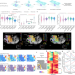 Spatial epigenome–transcriptome co-profiling of mammalian tissues
Spatial epigenome–transcriptome co-profiling of mammalian tissues
The authors present two technologies for spatially resolved, genome-wide, joint profiling of the epigenome and transcriptome by cosequencing chromatin accessibility and gene expression, or histone modifications and gene expression on the same tissue section at near-single-cell resolution.
- Di Zhang
- , Yanxiang Deng
- & Rong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals
The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals
Evolutionary analyses of single-nucleus transcriptome data for testes from 11 species are reported, illuminating the molecular evolution of spermatogenesis and associated forces, and providing a resource for investigating the testis across mammals.
- Florent Murat
- , Noe Mbengue
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
Article
| Open Access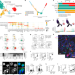 Active eosinophils regulate host defence and immune responses in colitis
Active eosinophils regulate host defence and immune responses in colitis
Single-cell transcriptomic profiling and functional assays are used to identify subpopulations of eosinophils that are present in the mouse gastrointestinal tract and provide insight into the role of these cells in inflammatory bowel diseases in humans.
- Alessandra Gurtner
- , Costanza Borrelli
- & Isabelle C. Arnold
-
Article |
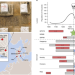 Evolution of immune genes is associated with the Black Death
Evolution of immune genes is associated with the Black Death
Klunk and colleagues identify signatures of natural selection imposed by Yersinia pestis and demonstrate their effect on genetic diversity and susceptibility to certain diseases in the present day.
- Jennifer Klunk
- , Tauras P. Vilgalys
- & Luis B. Barreiro
-
Article
| Open Access Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq, a single-cell transcriptome profiling approach that preserves cell viability during RNA extraction using fluidic force microscopy, can address a range of biological questions by transforming scRNA-seq from an end-point to a temporal analysis approach.
- Wanze Chen
- , Orane Guillaume-Gentil
- & Bart Deplancke
-
Article |
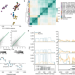 Transcriptome variation in human tissues revealed by long-read sequencing
Transcriptome variation in human tissues revealed by long-read sequencing
To understand the contribution of variants to transcript expression regulation, long-read transcriptome data are generated from the GTEx resource, and a new software package to perform allele-specific analysis is developed.
- Dafni A. Glinos
- , Garrett Garborcauskas
- & Beryl B. Cummings
-
Article |
 Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Retro-Cascorder, a system for time-ordered recording of transcriptional output, uses retrons as a tag to mediate DNA barcode acquisition in a CRISPR array.
- Santi Bhattarai-Kline
- , Sierra K. Lear
- & Seth L. Shipman
-
Article
| Open Access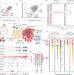 The renal lineage factor PAX8 controls oncogenic signalling in kidney cancer
The renal lineage factor PAX8 controls oncogenic signalling in kidney cancer
The lineage transcription factor PAX8 is shown to play a pivotal part in determining cancer risk in clear cell renal cell carcinoma, providing insights into how genetic mutations lead to specific types of cancer.
- Saroor A. Patel
- , Shoko Hirosue
- & Sakari Vanharanta
-
Article |
 Differential cofactor dependencies define distinct types of human enhancers
Differential cofactor dependencies define distinct types of human enhancers
The systematic categorization of human enhancers by their cofactor dependencies provides a conceptual framework to understand the sequence and chromatin diversity of enhancers and their roles in different gene-regulatory programmes.
- Christoph Neumayr
- , Vanja Haberle
- & Alexander Stark
-
Article |
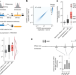 Compatibility rules of human enhancer and promoter sequences
Compatibility rules of human enhancer and promoter sequences
A new high-throughput assay applied to 1,000 enhancers and 1,000 promoters in human cells reveals how different classes of enhancers and promoters control RNA expression.
- Drew T. Bergman
- , Thouis R. Jones
- & Jesse M. Engreitz
-
Article |
 Somatic genomic changes in single Alzheimer’s disease neurons
Somatic genomic changes in single Alzheimer’s disease neurons
Analyses of single-cell whole-genome sequencing data show that somatic mutations are increased in the brain of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared to neurotypical individuals, with a pattern of genomic damage distinct from that of normal ageing.
- Michael B. Miller
- , August Yue Huang
- & Christopher A. Walsh
-
Article
| Open Access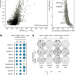 CCNE1 amplification is synthetic lethal with PKMYT1 kinase inhibition
CCNE1 amplification is synthetic lethal with PKMYT1 kinase inhibition
Genome-scale CRISPR–Cas9-based synthetic lethality screens identify PKMYT1 as a potential therapeutic target in tumours with CCNE1 amplification.
- David Gallo
- , Jordan T. F. Young
- & Daniel Durocher
-
Article |
 A genome-scale screen for synthetic drivers of T cell proliferation
A genome-scale screen for synthetic drivers of T cell proliferation
A genome-scale gain-of-function screen using overexpression of nearly 12,000 open reading frames (ORFs) identifies positive regulators of human T cell function and suggests that ORF-based screens could be applied clinically to improve T cell therapies.
- Mateusz Legut
- , Zoran Gajic
- & Neville E. Sanjana
-
Article
| Open Access Early prediction of preeclampsia in pregnancy with cell-free RNA
Early prediction of preeclampsia in pregnancy with cell-free RNA
Analyses of circulating cell-free RNA (cfRNA) in blood samples from pregnant mothers identify changes in gene expression that could be used in liquid biopsy tests to identify and monitor individuals who are at risk of preeclampsia.
- Mira N. Moufarrej
- , Sevahn K. Vorperian
- & Stephen R. Quake
-
Article |
 AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
Using time-controlled CRISPR screens, the authors identify AKIRIN2 as a factor involved in the nuclear import of the proteasome.
- Melanie de Almeida
- , Matthias Hinterndorfer
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Article
| Open Access A transcriptomic and epigenomic cell atlas of the mouse primary motor cortex
A transcriptomic and epigenomic cell atlas of the mouse primary motor cortex
The authors describe an integrated atlas of the diverse cell types in the mouse primary motor cortex.
- Zizhen Yao
- , Hanqing Liu
- & Eran A. Mukamel
-
Article |
 A gene–environment-induced epigenetic program initiates tumorigenesis
A gene–environment-induced epigenetic program initiates tumorigenesis
In mouse models of pancreatic cancer, a cooperative interaction between tissue damage and Kras gene mutation rapidly induces cancer-associated chromatin states in pre-malignant tissue, leading to gene dysregulation and neoplastic transformation.
- Direna Alonso-Curbelo
- , Yu-Jui Ho
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
Article |
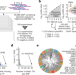 Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
An ultra-high-throughput multiplex protein–DNA binding assay is used to assess binding of 270 human transcription factors to 95,886 noncoding variants in the human genome, providing data to improve prediction of the effects of noncoding variants on transcription factor binding and thereby increase understanding of molecular pathways involved in diverse human traits and genetic diseases.
- Jian Yan
- , Yunjiang Qiu
- & Bing Ren
-
Article |
 Inherited causes of clonal haematopoiesis in 97,691 whole genomes
Inherited causes of clonal haematopoiesis in 97,691 whole genomes
Analysis of 97,691 high-coverage human blood DNA-derived whole-genome sequences enabled simultaneous identification of germline and somatic mutations that predispose individuals to clonal expansion of haematopoietic stem cells, indicating that both inherited and acquired mutations are linked to age-related cancers and coronary heart disease.
- Alexander G. Bick
- , Joshua S. Weinstock
- & Pradeep Natarajan
-
Article
| Open Access Expanded encyclopaedias of DNA elements in the human and mouse genomes
Expanded encyclopaedias of DNA elements in the human and mouse genomes
The authors summarize the data produced by phase III of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project, a resource for better understanding of the human and mouse genomes.
- Federico Abascal
- , Reyes Acosta
- & Zhiping Weng
-
Article
| Open Access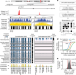 Global reference mapping of human transcription factor footprints
Global reference mapping of human transcription factor footprints
A high-density DNase I cleavage map from 243 human cell and tissue types provides a genome-wide, nucleotide-resolution map of human transcription factor footprints.
- Jeff Vierstra
- , John Lazar
- & John A. Stamatoyannopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Index and biological spectrum of human DNase I hypersensitive sites
Index and biological spectrum of human DNase I hypersensitive sites
High-resolution maps of DNase I hypersensitive sites from 733 human biosamples are used to identify and index regulatory DNA within the human genome.
- Wouter Meuleman
- , Alexander Muratov
- & John Stamatoyannopoulos
-
Article |
 A pathway coordinated by DELE1 relays mitochondrial stress to the cytosol
A pathway coordinated by DELE1 relays mitochondrial stress to the cytosol
Haploid genetic screening of cells under different types of mitochondrial perturbation shows that a pathway involving OMA1, DELE1 and the eIF2α kinase HRI communicates mitochondrial stress to the cytosol to trigger the integrated stress response.
- Evelyn Fessler
- , Eva-Maria Eckl
- & Lucas T. Jae
-
Review Article |
 Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease
Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease
This Review examines inflammatory bowel disease in the context of human genetics studies that help to identify pathways that regulate homeostasis of the mucosal immune system and discusses future prospects for disease-subtype classification and therapeutic intervention.
- Daniel B. Graham
- & Ramnik J. Xavier
-
Review Article |
 A brief history of human disease genetics
A brief history of human disease genetics
This Review describes progress in the study of human genetics, in which rapid advances in technology, foundational genomic resources and analytical tools have contributed to the understanding of the mechanisms responsible for many rare and common diseases and to preventative and therapeutic strategies for many of these conditions.
- Melina Claussnitzer
- , Judy H. Cho
- & Mark I. McCarthy
-
Letter |
 Genome editing retraces the evolution of toxin resistance in the monarch butterfly
Genome editing retraces the evolution of toxin resistance in the monarch butterfly
CRISPR–Cas9 engineering of the Drosophila Atpα gene (encoding the α-subunit of the sodium pump) is used to study the ability of mutations that evolved independently in several insect orders to confer resistance to keystone plant toxins.
- Marianthi Karageorgi
- , Simon C. Groen
- & Noah K. Whiteman
-
Article |
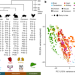 Gene expression across mammalian organ development
Gene expression across mammalian organ development
The transcriptomes of seven major organs across developmental stages from several mammalian species are used for comparative analyses of gene expression and evolution across organ development.
- Margarida Cardoso-Moreira
- , Jean Halbert
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional cofactors display specificity for distinct types of core promoters
Transcriptional cofactors display specificity for distinct types of core promoters
A screen of 23 transcriptional cofactors for their ability to activate 72,000 candidate core promoters in Drosophila melanogaster identified distinct compatibility groups, providing insight into mechanisms that underlie the selective activation of transcriptional programs.
- Vanja Haberle
- , Cosmas D. Arnold
- & Alexander Stark
-
Article |
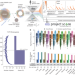 Prioritization of cancer therapeutic targets using CRISPR–Cas9 screens
Prioritization of cancer therapeutic targets using CRISPR–Cas9 screens
In a screen of 324 human cancer cell lines and utilising a systematic target prioritization framework, the Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase is shown to be a synthetic lethal target in tumours from multiple cancer types with microsatellite instability, providing a new target for cancer drug development.
- Fiona M. Behan
- , Francesco Iorio
- & Mathew J. Garnett
-
Article
| Open Access Amphioxus functional genomics and the origins of vertebrate gene regulation
Amphioxus functional genomics and the origins of vertebrate gene regulation
Genomic, epigenomic and transcriptomic data derived from the Mediterranean amphioxus (Branchiostoma lanceolatum) provide insights into the evolution of the genomic regulatory landscape of chordates.
- Ferdinand Marlétaz
- , Panos N. Firbas
- & Manuel Irimia
-
Article |
 Predictable and precise template-free CRISPR editing of pathogenic variants
Predictable and precise template-free CRISPR editing of pathogenic variants
The authors use a machine-learning algorithm to predict the spectrum of CRISPR–Cas9-nuclease-mediated DNA repair outcomes at human genomic target sites.
- Max W. Shen
- , Mandana Arbab
- & Richard I. Sherwood
-
Article |
 Gene expression variability across cells and species shapes innate immunity
Gene expression variability across cells and species shapes innate immunity
Comparison of transcriptomic data from immune-stimulated cells across different species sheds light on the architecture of the innate immune response.
- Tzachi Hagai
- , Xi Chen
- & Sarah A. Teichmann
-
Article |
 Single-cell transcriptomics of 20 mouse organs creates a Tabula Muris
Single-cell transcriptomics of 20 mouse organs creates a Tabula Muris
A ‘mouse atlas’, comprising single-cell transcriptomic data from more than 100,000 cells from 20 organs and tissues, has been created as a resource for cell biology.
- Nicholas Schaum
- , Jim Karkanias
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Article |
 The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
A method for systematically exploring interactions between the nucleosome and transcription factors identifies five major interaction patterns.
- Fangjie Zhu
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Article |
 Accurate classification of BRCA1 variants with saturation genome editing
Accurate classification of BRCA1 variants with saturation genome editing
Germline BRCA1 loss-of-function variants are associated with predisposition to early-onset breast and ovarian cancer; here the authors use CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to functionally assess thousands of BRCA1 variants in order to facilitate the clinical interpretation of these variants.
- Gregory M. Findlay
- , Riza M. Daza
- & Jay Shendure
-
Letter |
 CRISPR screens identify genomic ribonucleotides as a source of PARP-trapping lesions
CRISPR screens identify genomic ribonucleotides as a source of PARP-trapping lesions
Mutations in all three genes encoding ribonuclease H2 sensitize cells to poly(ADP–ribose) polymerase inhibitors by compromising ribonucleotide excision repair.
- Michal Zimmermann
- , Olga Murina
- & Daniel Durocher
-
Letter |
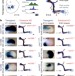 Enhancer redundancy provides phenotypic robustness in mammalian development
Enhancer redundancy provides phenotypic robustness in mammalian development
Gene enhancer knockout phenotypes and analysis of enhancer activity patterns show that developmental genes are regulated by multiple redundant enhancers in mouse embryos.
- Marco Osterwalder
- , Iros Barozzi
- & Len A. Pennacchio
-
Letter
| Open Access The impact of rare variation on gene expression across tissues
The impact of rare variation on gene expression across tissues
The authors show that rare genetic variants contribute to large gene expression changes across diverse human tissues and provide an integrative method for interpretation of rare variants in individual genomes.
- Xin Li
- , Yungil Kim
- & Stephen B. Montgomery
-
Article |
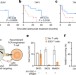 Identification of essential genes for cancer immunotherapy
Identification of essential genes for cancer immunotherapy
The authors describe a two-cell-type CRISPR screen to identify tumour-intrinsic genes that regulate the sensitivity of cancer cells to effector T cell function.
- Shashank J. Patel
- , Neville E. Sanjana
- & Nicholas P. Restifo

 Improving prime editing with an endogenous small RNA-binding protein
Improving prime editing with an endogenous small RNA-binding protein