Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Colliding heavy nuclei take multiple identities on the path to fusion
Colliding heavy nuclei take multiple identities on the path to fusion
Superheavy nuclei are synthesized in the laboratory through the fusion of lighter nuclei. Here the authors study multinucleon transfer and interactions during the early stages of nuclear fusion in the collision of 40Ca and 208Pb nuclei showing early onset of complexity.
- Kaitlin J. Cook
- , Dominic C. Rafferty
- & Suzana Szilner
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the nature of the proton radioactivity and branching ratio on the first proton emitter discovered 53mCo
Elucidating the nature of the proton radioactivity and branching ratio on the first proton emitter discovered 53mCo
Since the discovery of proton radioactivity in 53mCo, there has been no direct measurement of its branching ratio. Here the authors report the first measurement of the weak proton decay in 53mCo by combining results from advanced detection systems.
- Luis G. Sarmiento
- , Thomas Roger
- & Annika Voss
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental confirmation of driving pressure boosting and smoothing for hybrid-drive inertial fusion at the 100-kJ laser facility
Experimental confirmation of driving pressure boosting and smoothing for hybrid-drive inertial fusion at the 100-kJ laser facility
In laser-driven inertial fusion, finding optimal driving pressure is a major challenge. Here, the authors use a 100 kJ SG laser and a hybrid-drive scheme to demonstrate such driving pressure with the help of the direct-drive laser such that the indirect-drive radiation ablation pressure is turned into a well-smoothed hybrid-drive pressure much greater than the radiation ablation pressure.
- Ji Yan
- , Jiwei Li
- & Shaoping Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Search for 22Na in novae supported by a novel method for measuring femtosecond nuclear lifetimes
Search for 22Na in novae supported by a novel method for measuring femtosecond nuclear lifetimes
The authors report a particle-particle correlation and velocity-difference profile method to measure nuclear lifetime. The results obtained for excited states of 23Mg are used to constrain the production of 22Na in the astrophysical novae explosions.
- Chloé Fougères
- , François de Oliveira Santos
- & Magdalena Zielińska
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding the limits of nuclear stability at finite temperature
Expanding the limits of nuclear stability at finite temperature
It is interesting and important to understand how the properties of nuclei and their stability change with temperature. Here the authors report their theoretical study of hot nuclei and the drip lines that limit the nuclear existence at finite temperature.
- Ante Ravlić
- , Esra Yüksel
- & Nils Paar
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent geometry and duality in the carbon nucleus
Emergent geometry and duality in the carbon nucleus
Carbon (12C) nucleus has interesting characteristics including the existence of the Hoyle state. Here the authors discuss the structure of the nuclear states of 12C by using nuclear lattice effective field theory.
- Shihang Shen
- , Serdar Elhatisari
- & Ulf-G. Meißner
-
Article
| Open Access Breakup of the proton halo nucleus 8B near barrier energies
Breakup of the proton halo nucleus 8B near barrier energies
Halo-structured nuclei are examples of many-body open quantum system. Here the authors use a complete kinematics measurement and find an elastic breakup of proton halo nucleus 8B.
- L. Yang
- , C. J. Lin
- & F. P. Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access α-Clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state character
α-Clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state character
Alpha particles are considered the building blocks for some nuclei in alpha-clustering. Here the authors discuss quantum many-body simulations with nucleon-nucleon interaction to characterize the Hoyle state, the first excited 0+ state of the 12C nucleus, and find complexity in its alpha-clustering.
- T. Otsuka
- , T. Abe
- & H. Ueno
-
Article
| Open Access Precision measurements on oxygen formation in stellar helium burning with gamma-ray beams and a Time Projection Chamber
Precision measurements on oxygen formation in stellar helium burning with gamma-ray beams and a Time Projection Chamber
Presence of oxygen in the universe can provide information to stellar mass evolution. Here the authors report their method for the measurements of carbon to oxygen ratio and cross-section of the reaction-capture of helium-4 by carbon-12, to produce oxygen-16.
- R. Smith
- , M. Gai
- & M. W. Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access Testing CPT symmetry in ortho-positronium decays with positronium annihilation tomography
Testing CPT symmetry in ortho-positronium decays with positronium annihilation tomography
CPT violation could manifest itself in annihilating positronium events, but searching for this effect would require to know the spin of the annihilating system. Here, the authors do this using a positron-emission tomography scanner, finding no violation with a statistical precision of 10−4.
- P. Moskal
- , A. Gajos
- & W. Wiślicki
-
Article
| Open Access 4D-imaging of drip-line radioactivity by detecting proton emission from 54mNi pictured with ACTAR TPC
4D-imaging of drip-line radioactivity by detecting proton emission from 54mNi pictured with ACTAR TPC
Proton radioactivity is useful for studying nuclear structure. Here the authors report two proton emission branches from the 10+ state isomer of 54mNi by using a time projection chamber.
- J. Giovinazzo
- , T. Roger
- & M. Versteegen
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of a sudden increase in the nuclear size of proton-rich silver-96
Evidence of a sudden increase in the nuclear size of proton-rich silver-96
Laser spectroscopic measurements of isotopes near the doubly-magic 100-Sn are challenging due to difficulties in their production. Here the authors measure the ground state charge radius of the proton-rich 96-Ag isotope and find a discontinuity in the nuclear size when crossing the neutron number N equal to 50.
- M. Reponen
- , R. P. de Groote
- & I. D. Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of the neutron charge radius and the role of its constituents
Measurement of the neutron charge radius and the role of its constituents
The charge radius of nucleons provides information about their structure. Here the authors present a method, based values of neutron electric form factors, to determine the charge radius of the neutron and provide information on improving the uncertainty of neutron charge radius measurements
- H. Atac
- , M. Constantinou
- & N. Sparveris
-
Article
| Open Access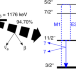 Electromagnetic character of the competitive γγ/γ-decay from 137mBa
Electromagnetic character of the competitive γγ/γ-decay from 137mBa
Second order effects can play an important role in highlighting nuclear structure properties. Here, the authors show how the second-order nuclear transitions in the form of double-gamma decay in 137Ba help understanding atomic nuclei.
- P.-A. Söderström
- , L. Capponi
- & T. Petruse
-
Article
| Open Access A physically cryptographic warhead verification system using neutron induced nuclear resonances
A physically cryptographic warhead verification system using neutron induced nuclear resonances
Inspection and authentication of warheads is important for nuclear safety and security. Here the authors report experimental scheme for the verification of nuclear warheads using the neutron resonance transmission analysis of a reference and candidate objects while preserving the sensitive information.
- Ezra M. Engel
- & Areg Danagoulian
-
Article
| Open Access The observation of vibrating pear-shapes in radon nuclei
The observation of vibrating pear-shapes in radon nuclei
Octupole deformation in nuclei is important to understand nuclear structure and electric dipole moments of heavy atoms. Here the authors measure energies of excited quantum states in radon isotopes and find that these isotopes do not provide favourable conditions in the search for CP-violation.
- P. A. Butler
- , L. P. Gaffney
- & M. Zielinska
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental limit on an exotic parity-odd spin- and velocity-dependent interaction using an optically polarized vapor
Experimental limit on an exotic parity-odd spin- and velocity-dependent interaction using an optically polarized vapor
Symmetry breaking is an important process in fundamental understanding of matter and dark matter. Here the authors discuss an experimental bound on an exotic parity odd spin- and velocity-dependent interaction between electron and nucleon by using a sensitive spin-exchange relaxation-free atomic magnetometer.
- Young Jin Kim
- , Ping-Han Chu
- & Shaun Newman
-
Article
| Open Access Stand-off nuclear reactor monitoring with neutron detectors for safeguards and non-proliferation applications
Stand-off nuclear reactor monitoring with neutron detectors for safeguards and non-proliferation applications
Nuclear power reactors need to be monitored for safety and security while in operation. Here the authors discuss monitoring and safeguarding research reactors and small modular reactors using detection of neutrons up to a hundred meters away from the reactor shielding.
- B. M. van der Ende
- , L. Li
- & B. Sur
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong nanocrystalline steel with exceptional thermal stability and radiation tolerance
Ultrastrong nanocrystalline steel with exceptional thermal stability and radiation tolerance
Weaker ferritic/matensitic steels rather than stronger austenitic steels are usually candidates for nuclear reactors since they do not easily swell under irradiation. Here, the authors make an ultrastrong lanthanum-doped nanocrystalline austenitic steel that is thermally stable and radiation-tolerant.
- Congcong Du
- , Shenbao Jin
- & Tongde Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Extremely rapid isotropic irradiation of nanoparticles with ions generated in situ by a nuclear reaction
Extremely rapid isotropic irradiation of nanoparticles with ions generated in situ by a nuclear reaction
Mass production of nanoparticles containing well-controlled structural defects is a challenge. Here the authors demonstrate the feasibility of homogeneous ion irradiation generated in a nuclear reactor, for the preparation of fluorescent nanodiamonds and silicon carbide nanoparticles.
- Jan Havlik
- , Vladimira Petrakova
- & Petr Cigler
-
Article
| Open Access Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Mapping the distribution of magnetic fields inside bulk materials is challenging but crucial to understand and develop functional magnetic materials. Here the authors demonstrate the capability to visualize 3D vector magnetic fields inside materials using spin-polarized neutron tomography and tensorial reconstruction techniques.
- A. Hilger
- , I. Manke
- & J. Banhart
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal control theory enables homonuclear decoupling without Bloch–Siegert shifts in NMR spectroscopy
Optimal control theory enables homonuclear decoupling without Bloch–Siegert shifts in NMR spectroscopy
Bloch–Siegert shifts prevent the accurate observation of resonance frequencies in NMR experiments. Here the authors present a method for homonuclear decoupling that avoids inducing Bloch–Siegert shifts and improves the sensitivity and resolution of HNCA experiments.
- Paul W. Coote
- , Scott A. Robson
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for prevalent Z = 6 magic number in neutron-rich carbon isotopes
Evidence for prevalent Z = 6 magic number in neutron-rich carbon isotopes
Magic numbers are associated with the stability of atomic nuclei. Here, the authors analyse the proton radii, binding energies and electric quadrupole transition rates of neutron-rich carbon isotopes at proton number six and use nuclear structure models to support the magic number Z = 6.
- D. T. Tran
- , H. J. Ong
- & T. Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear disarmament verification via resonant phenomena
Nuclear disarmament verification via resonant phenomena
Authenticating a nuclear warhead without revealing its design is a challenge. Here the authors discuss a nuclear disarmament verification method based on neutron resonance analysis which is sensitive to the isotopic composition of the materials used in warheads.
- Jake J. Hecla
- & Areg Danagoulian
-
Article
| Open Access A glimpse of gluons through deeply virtual compton scattering on the proton
A glimpse of gluons through deeply virtual compton scattering on the proton
It remains a challenge to find the structure and the distribution of the constituents of nucleons. Here the authors use a scattering method to get information about the gluons and quarks inside a proton and separate the contribution of Bethe-Heitler from the deeply virtual Compton scattering process.
- M. Defurne
- , A. Martí Jiménez-Argüello
- & P. Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access High precision hyperfine measurements in Bismuth challenge bound-state strong-field QED
High precision hyperfine measurements in Bismuth challenge bound-state strong-field QED
Precision measurements provide a sensitive test of fundamental constants and their uncertainties. Here the authors precisely measure the hyperfine structure splitting in bismuth ions, and report significant discrepancy with the theoretical prediction of quantum electrodynamics.
- Johannes Ullmann
- , Zoran Andelkovic
- & Wilfried Nörtershäuser
-
Article
| Open Access Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
It is challenging to explore properties of heavy elements as they can only be produced artificially. Here, the authors demonstrate a high resolution spectroscopy method, studying the properties of actinium, which can be extended to the study of other elements located at the end of the periodic table.
- R. Ferrer
- , A. Barzakh
- & A. Zadvornaya
-
Article
| Open Access A physical zero-knowledge object-comparison system for nuclear warhead verification
A physical zero-knowledge object-comparison system for nuclear warhead verification
Zero-knowledge proofs can be used to prove that a statement is true without revealing why it is. Here the authors demonstrate a non-electronic fast neutron radiography technique to confirm that two objects are identical without revealing any details about their design or composition.
- Sébastien Philippe
- , Robert J. Goldston
- & Francesco d’Errico

 Discrete symmetries tested at 10−4 precision using linear polarization of photons from positronium annihilations
Discrete symmetries tested at 10−4 precision using linear polarization of photons from positronium annihilations