Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial regulation of AMPK signaling revealed by a sensitive kinase activity reporter
Spatial regulation of AMPK signaling revealed by a sensitive kinase activity reporter
AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a master regulator of cellular metabolism, but how AMPK activity is spatiotemporally regulated remains unclear. Here, Schmitt et al develop a sensitive biosensor for AMPK, which they use to uncover mechanisms for AMPK activity in the lysosome and nucleus.
- Danielle L. Schmitt
- , Stephanie D. Curtis
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of LIG1 that engage with mutagenic mismatches inserted by polβ in base excision repair
Structures of LIG1 that engage with mutagenic mismatches inserted by polβ in base excision repair
Ligase I seals two ends of DNA during DNA repair and replication. Here — solving structures of Ligase I with imperfect DNA harboring mismatches incorporated by DNA polymerase — the authors reveal how the repair proteins maintain fidelity at final ligation step.
- Qun Tang
- , Mitchell Gulkis
- & Melike Çağlayan
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent properties as by-products of prebiotic evolution of aminoacylation ribozymes
Emergent properties as by-products of prebiotic evolution of aminoacylation ribozymes
Complex biochemical systems exhibit traits that appear to be highly adapted. Studies of catalytic RNA demonstrate that adaptive traits, such as increased specificity and error tolerance, could originate as evolutionary by-products.
- Evan Janzen
- , Yuning Shen
- & Irene A. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Haloacid dehalogenase-like phosphatases are widespread across all domains of life and play a crucial role in the regulation of levels of sugar phosphate metabolites in cells. The authors report on the structure-guided engineering of phosphatases for dedicated substrate specificity for the conversion of sucrose and starch into fructose and mannose.
- Chaoyu Tian
- , Jiangang Yang
- & Yanhe Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Complete biosynthetic pathway to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
Complete biosynthetic pathway to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
The market demand for acarbose, a drug used for treatment of patients affected by type-2 diabetes, has increased. In this article, the authors report the acarbose complete biosynthetic pathway, clarifying previously unknown steps and identifying a pseudoglycosyltransferase enzyme, AcbS, a homologue of AcbI that catalyzes the formation of a non-glycosidic C-N bond.
- Takeshi Tsunoda
- , Arash Samadi
- & Taifo Mahmud
-
Article
| Open Access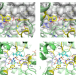 Structural basis of resistance to herbicides that target acetohydroxyacid synthase
Structural basis of resistance to herbicides that target acetohydroxyacid synthase
Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) is the target of more than 50 commercial herbicides, with many site-of-action resistance isolates identified in weeds. Here, the authors report the structural and kinetic characterizations to explain the effect AHAS mutations have on herbicide potency.
- Thierry Lonhienne
- , Yan Cheng
- & Luke W. Guddat
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of glycogen synthase inactivation and interaction with glycogenin
Mechanism of glycogen synthase inactivation and interaction with glycogenin
Glycogen is a major energy reserve in eukaryotes and is synthesised in part by glycogenin (GN) and glycogen synthase (GS). Here, authors describe the structural basis of GS regulation, specifically the mechanism of inactivation by phosphorylation.
- Laura Marr
- , Dipsikha Biswas
- & Elton Zeqiraj
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of EXTL3 helps to explain the different roles of bi-domain exostosins in heparan sulfate synthesis
The structure of EXTL3 helps to explain the different roles of bi-domain exostosins in heparan sulfate synthesis
Heparan sulphate (HS)—a common cell surface decoration—is a carbohydrate of alternating sugars assembled by bi-domain enzymes such as EXTL3. Here, authors present the structure of EXTL3, explain EXTL3 lost activity, and propose that HS extension is distributive.
- L. F. L. Wilson
- , T. Dendooven
- & P. Dupree
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into methionine S-methylation in diverse organisms
Insights into methionine S-methylation in diverse organisms
S-methyl methionine (SMM) is a key molecule in production of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), an important marine anti-stress compound, with roles in global nutrient cycling. Here, the authors determine the mechanism of SMM synthesis and uncover unexpected roles for SMM in archaea, CPR bacteria and animals.
- Ming Peng
- , Chun-Yang Li
- & Yu-Zhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of nucleotide discrimination by the translesion synthesis polymerase Rev1
Mechanism of nucleotide discrimination by the translesion synthesis polymerase Rev1
Rev1 is a specialized translesion synthesis DNA polymerase involved in the bypass DNA damage during DNA replication. Here, the authors determine the structural basis for preferential incorporation of dCTP by Rev1 during bypass of DNA damage.
- Tyler M. Weaver
- , Timothy H. Click
- & Bret D. Freudenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into biogenesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor proteins
Molecular insights into biogenesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor proteins
GPI-T catalyzes the committed step in GPI anchor protein biogenesis. Here, Xu et al. report the cryo-EM structure of the human GPI-T, revealing critical elements within an elongated, shared active site which is topologically arranged for substrate specificity.
- Yidan Xu
- , Guowen Jia
- & Dianfan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and characterization of a terpene biosynthetic pathway featuring a norbornene-forming Diels-Alderase
Discovery and characterization of a terpene biosynthetic pathway featuring a norbornene-forming Diels-Alderase
Pericyclase enzymes are an expanding family of enzymes. Here, the authors identify the norbornene synthase SdnG, a pericyclase for the intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction between a cyclopentadiene and an olefinic dienophile to form the sordaricin norbornene structure, and reconstitute the sordaricin biosynthesis.
- Zuodong Sun
- , Cooper S. Jamieson
- & Yi Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Radical SAM-dependent ether crosslink in daropeptide biosynthesis
Radical SAM-dependent ether crosslink in daropeptide biosynthesis
Darobactin is a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide featuring a unique scaffold and potent activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Here, the authors identify darobactin synthase DarE as responsible for the bicyclic scaffold formation and propose the name daropeptide for this growing class of enzymes.
- Sijia Guo
- , Shu Wang
- & Qi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A structural exposé of noncanonical molecular reactivity within the protein tyrosine phosphatase WPD loop
A structural exposé of noncanonical molecular reactivity within the protein tyrosine phosphatase WPD loop
Inositol pyrophosphates (PP-IPs) regulate immunity and phosphate homeostasis. Here, the authors’ structural dissection of an Arabidopsis thaliana PP-IP phosphatase reveals that substrates drive their own hydrolysis and identifies a highly elusive metaphosphate-like reaction intermediate.
- Huanchen Wang
- , Lalith Perera
- & Stephen B. Shears
-
Article
| Open Access Cyclic 5-membered disulfides are not selective substrates of thioredoxin reductase, but are opened nonspecifically
Cyclic 5-membered disulfides are not selective substrates of thioredoxin reductase, but are opened nonspecifically
Cyclic five-membered disulfides (1,2-dithiolanes) have been reported either as nonspecific redox motifs, or as highly specific cellular probes for thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). Here the authors show that 1,2-dithiolane probes are nonspecifically reduced by a range of thiol reductants and are not sensitive to TrxR modulation, thus they are unsuitable as cellular probes for TrxR.
- Jan G. Felber
- , Lena Poczka
- & Oliver Thorn-Seshold
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Zong and coworkers combine computational and experimental methods to decipher in detail the mechanism of action of glucuronoyl esterases, enzymes with significant biotechnological potential for decoupling lignin from polysaccharides in biomass.
- Zhiyou Zong
- , Scott Mazurkewich
- & Leila Lo Leggio
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Lysine benzoylation (Kbz) is a recently discovered histone modification. Here, the authors characterize writers, erasers and readers of histone Kbz in S. cerevisiae and identify non-histone proteins bearing Kbz, laying foundations to dissect the roles of Kbz in diverse cellular processes.
- Duo Wang
- , Fuxiang Yan
- & Yong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning discovery of missing links that mediate alternative branches to plant alkaloids
Machine learning discovery of missing links that mediate alternative branches to plant alkaloids
Producing plant secondary metabolites by microbes is limited by the known enzymatic reactions. Here, the authors apply machine learning to predict missing link enzymes of benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) biosynthesis in Papaver somniferum, and validate the specialized activities through heterologous production.
- Christopher J. Vavricka
- , Shunsuke Takahashi
- & Tomohisa Hasunuma
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically unveiling the structure-activity relationship of biomacromolecule-metal-organic frameworks symbiotic crystal
Atomically unveiling the structure-activity relationship of biomacromolecule-metal-organic frameworks symbiotic crystal
Biomolecule-metal-organic-frameworks allow for the creation of hybrid materials with desired biological and chemical function. Here, the authors refine the structure-function relationship by identifying the atomic-layer structure of the hybrids and show differences in structure upon different crystallisation pathways.
- Linjing Tong
- , Siming Huang
- & Gangfeng Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstituting the complete biosynthesis of D-lysergic acid in yeast
Reconstituting the complete biosynthesis of D-lysergic acid in yeast
The ergot alkaloids are a class of natural products known for their pharmacologically privileged molecular structure that are used in the treatment of neurological ailments. Here the authors report on the production of the ergot (fungus)-derived therapeutic precursor, D-lysergic acid (DLA), in baker’s yeast.
- Garrett Wong
- , Li Rong Lim
- & Wen Shan Yew
-
Article
| Open Access The toposiomerase IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex orients human Bloom’s syndrome helicase for efficient disruption of D-loops
The toposiomerase IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex orients human Bloom’s syndrome helicase for efficient disruption of D-loops
Human Bloom’s syndrome (BLM) helicase has a role in DNA repair, and BLM deficiency in humans is associated with chromosomal abnormalities. Here the authors employ solution biophysical assays to show BLM maintains a balance for disruption and stabilization of oligonucleotide-based D-loops. Interaction with the Topoisomerase IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex orients the activity toward D-loop disruption.
- Gábor M. Harami
- , János Pálinkás
- & Mihály Kovács
-
Article
| Open Access A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
The drug AT-527 targets the SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery. Here the authors use Cryo-EM to show how AT-527 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 polymerase by acting as an immediate RNA chain terminator and stably binding in a NiRAN active-site pocket; impeding an essential nucleotide-transfer activity.
- Ashleigh Shannon
- , Véronique Fattorini
- & Bruno Canard
-
Article
| Open Access Structures and function of a tailoring oxidase in complex with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module
Structures and function of a tailoring oxidase in complex with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases work with additional enzymes to synthesise secondary metabolites and therapeutics. Here, the authors explore bacillamide D synthesis and show the oxidase action is done while the intermediate is attached to the synthetase and replicate this with an oxidase bound synthetase for bioengineering applications.
- Camille Marie Fortinez
- , Kristjan Bloudoff
- & T. Martin Schmeing
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA methyltransferase METTL8 installs m3C32 in mitochondrial tRNAsThr/Ser(UCN) to optimise tRNA structure and mitochondrial translation
The RNA methyltransferase METTL8 installs m3C32 in mitochondrial tRNAsThr/Ser(UCN) to optimise tRNA structure and mitochondrial translation
RNA modifications are key regulators of RNA functions. Here, the authors identify METTL8 as the enzyme installing m3C32 in mitochondrial tRNAThr/Ser(UCN). Lack of these modifications affects tRNA structure and impairs mitochondrial translation.
- Nicole Kleiber
- , Nicolas Lemus-Diaz
- & Markus T. Bohnsack
-
Article
| Open Access Transglutaminase 3 crosslinks the secreted gel-forming mucus component Mucin-2 and stabilizes the colonic mucus layer
Transglutaminase 3 crosslinks the secreted gel-forming mucus component Mucin-2 and stabilizes the colonic mucus layer
The colonic mucus layer is an organized system providing a physical barrier against pathogens and simultaneously harbouring the commensal flora. Here the authors report that transglutaminase 3 activity contributes to homeostasis of the colonic mucus layer and the lack of this enzymatic activity leads to increased susceptibility against DSS-induced colitis in mice.
- Jack D. A. Sharpen
- , Brendan Dolan
- & Christian V. Recktenwald
-
Article
| Open Access Aminoacyl chain translocation catalysed by a type II thioesterase domain in an unusual non-ribosomal peptide synthetase
Aminoacyl chain translocation catalysed by a type II thioesterase domain in an unusual non-ribosomal peptide synthetase
Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases (NRPSs) are responsible for the construction of many types of natural products. Here the authors characterize a key type II thioesterase domain that sheds light on the chain translocation processes of legonmycin NRPSs.
- Shan Wang
- , William D. G. Brittain
- & Hai Deng
-
Article
| Open Access The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1
The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1
TCPTP is a non-receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase involved in various signalling pathways. Here, the authors provide structural insights into TCPTP activation, showing that TCPTP is inhibited by its C-terminal tail, which can be displaced by the cytosolic tail of integrin-α1, leading to activation.
- Jai Prakash Singh
- , Yang Li
- & Tzu-Ching Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational changes in Lassa virus L protein associated with promoter binding and RNA synthesis activity
Conformational changes in Lassa virus L protein associated with promoter binding and RNA synthesis activity
The L protein of segmented, negative strand RNA viruses contains the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase essential for virus amplification. Here, the authors report cryoEM structures of the Lassa virus L protein in active, RNA-bound states, and provide mechanistic insights.
- Tomas Kouba
- , Dominik Vogel
- & Stephen Cusack
-
Article
| Open Access Structural evolution of a DNA repair self-resistance mechanism targeting genotoxic secondary metabolites
Structural evolution of a DNA repair self-resistance mechanism targeting genotoxic secondary metabolites
Microbial DNA glycosylases associated with the biosynthesis of DNA-damaging antibiotics have evolved self-resistance for their cognate natural products. Here, the authors provide evidence that cellular self-resistance is enabled by reduced affinity of the glycosylases for the excision products of the corresponding DNA lesions.
- Elwood A. Mullins
- , Jonathan Dorival
- & Brandt F. Eichman
-
Article
| Open Access Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX, a dehydrogenase/isomerase flavoprotein, is required for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis. Here, the authors characterize FabX substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism, and reveal that it contains an atypical [4Fe-4S] cluster, which is essential and participates in the catalytic cycle.
- Jiashen Zhou
- , Lin Zhang
- & Liang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM snapshots of a native lysate provide structural insights into a metabolon-embedded transacetylase reaction
Cryo-EM snapshots of a native lysate provide structural insights into a metabolon-embedded transacetylase reaction
How is acetyl-CoA produced in the context of the endogenous, eukaryotic pyruvate dehydrogenase complex metabolon? Here the authors dissect the embedded transacetylase reaction through biochemical, cryo-EM, HADDOCKing and molecular dynamics methods.
- Christian Tüting
- , Fotis L. Kyrilis
- & Panagiotis L. Kastritis
-
Article
| Open Access AGPAT2 interaction with CDP-diacylglycerol synthases promotes the flux of fatty acids through the CDP-diacylglycerol pathway
AGPAT2 interaction with CDP-diacylglycerol synthases promotes the flux of fatty acids through the CDP-diacylglycerol pathway
AGPATs (1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferases) catalyze the acylation of lysophosphatidic acid to form phosphatidic acid (PA), a key step in the synthesis of all glycerolipids. Here, the authors show that AGPAT2 and CDP-DAG synthases (CDS1 and CDS2) form functional complexes that promote further conversion of PA along the CDP-DAG pathway of phospholipid synthesis.
- Hoi Yin Mak
- , Qian Ouyang
- & Hongyuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
L-asparaginases catalyse the hydrolysis of L-asparagine to L-aspartic acid and ammonia. Here, the authors present high resolution crystal structures of Rhizobium etli L-asparaginase that contains a Zn2+ binding site without a catalytic role and discuss the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme.
- Joanna I. Loch
- , Barbara Imiolczyk
- & Mariusz Jaskolski
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens
Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens
The nucleotidyl cyclase toxin exoenzyme Y (ExoY), which is secreted by the human pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio vulnificus is activated by actin. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of PaExoY bound to F-actin and VvExoY in complex with G-actin-profilin. These structures together with molecular dynamics simulations and enzymatic assays provide insights into the activation mechanism for both bacterial cyclase toxin families that interact with either F- or G-actin.
- Alexander Belyy
- , Felipe Merino
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure provides insights into the dimer arrangement of the O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT
Cryo-EM structure provides insights into the dimer arrangement of the O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT
The modification of proteins with O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (OGlcNAc) plays roles in regulation of numerous cellular functions while incorrect O-GlcNAcylation patterns are linked to disease. Here, the authors report a cryo-EM structure of full-length O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), the only enzyme responsible for O-GlcNAcylation.
- Richard W. Meek
- , James N. Blaza
- & Gideon J. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access 2-Oxoglutarate derivatives can selectively enhance or inhibit the activity of human oxygenases
2-Oxoglutarate derivatives can selectively enhance or inhibit the activity of human oxygenases
The human 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) oxygenases FIH and AspH are relevant drug targets. Here, the authors show that synthetic and naturally occurring 2OG derivatives can selectively modulate FIH and AspH activities, suggesting that these compounds may serve as a basis to develop 2OG oxygenase-targeting probes and drugs.
- Yu Nakashima
- , Lennart Brewitz
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Crosstalk between CST and RPA regulates RAD51 activity during replication stress
Crosstalk between CST and RPA regulates RAD51 activity during replication stress
During replication stress, the RPA protein complex coats single-stranded DNA to preclude RAD51 loading. Here, the authors show how RPA and CST crosstalk to regulate RAD51 activity.
- Kai-Hang Lei
- , Han-Lin Yang
- & Peter Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Arginine methylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk controls DNA end-resection and homologous recombination repair
Arginine methylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk controls DNA end-resection and homologous recombination repair
Post-translational modifications are critical for regulating the DNA damage response. Here, the authors identify a methylation-deubiquitination crosstalk between methyltransferase PRMT1 and deubiquitinase USP11, showing that the enzymes regulate each other’s functions in DNA repair.
- Maria Pilar Sanchez-Bailon
- , Soo-Youn Choi
- & Clare C. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of Clostridium difficile TcdA and TcdB toxins with transition state analogues
Inhibition of Clostridium difficile TcdA and TcdB toxins with transition state analogues
The Clostridium difficile virulence factors TcdA and TcdB contain a glucosyltransferase domain (GTD), which has both glucohydrolase (GH) and glucosyltransferase (GT) activities. Here, the authors characterize the transition state features of the TcdA and TcdB GH reactions by measuring kinetic isotope effects and they identify two transition state analogues, isofagomine and noeuromycin that inhibit TcdA and TcdB. They also present the crystal structures of TcdB-GTD bound to these inhibitors and the reaction product UDP.
- Ashleigh S. Paparella
- , Briana L. Aboulache
- & Vern L. Schramm
-
Article
| Open Access Sustained enzymatic activity and flow in crowded protein droplets
Sustained enzymatic activity and flow in crowded protein droplets
Living cells can harvest environmental energy to drive chemical processes. Here the authors design a minimal artificial system that achieves steady states at similar metabolic densities to microorganisms.
- Andrea Testa
- , Mirco Dindo
- & Paola Laurino
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for protein glutamylation by the Legionella pseudokinase SidJ
Structural basis for protein glutamylation by the Legionella pseudokinase SidJ
Legionella pneumophila (LP) employs the metaeffector SidJ to suppress the toxicity of SdeA and other LP SidE effector family members by catalysing the glutamylation of the catalytic Glu residue. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of SidJ in complex with SdeA in two different states, which together with mutagenesis analysis provide insights into the substrate recognition and the mechanism of protein glutamylation by SidJ.
- Michael Adams
- , Rahul Sharma
- & Sagar Bhogaraju
-
Article
| Open Access Palmitoylation targets the calcineurin phosphatase to the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase complex at the plasma membrane
Palmitoylation targets the calcineurin phosphatase to the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase complex at the plasma membrane
Calcineurin — the Ca2+ regulated phosphatase and target of immunosuppressants — regulates GPCR-mediated phospholipid signaling at the plasma membrane. Here the authors show that CNAβ1 (a poorly studied isoform of the calcineurin catalytic subunit) is targeted to the plasma membrane through palmitoylation to dephosphorylate and promote PI4KA complex activity.
- Idil Ulengin-Talkish
- , Matthew A. H. Parson
- & Martha S. Cyert
-
Article
| Open Access The δ subunit of F1Fo-ATP synthase is required for pathogenicity of Candida albicans
The δ subunit of F1Fo-ATP synthase is required for pathogenicity of Candida albicans
F1Fo-ATP synthase is a key enzyme for energy production in fungi. Here, the authors show that the δ subunit of the enzyme is required for Candida albicans lethal infection and represents a potential therapeutic target.
- Shuixiu Li
- , Yajing Zhao
- & Hong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Human cell based directed evolution of adenine base editors with improved efficiency
Human cell based directed evolution of adenine base editors with improved efficiency
Application of adenine base editors (ABE) has been precluded by low activity. Here the authors show the generation of a human cell based ABE directional screening system and identification of ABE variant (NG-ABEmax-KR) exhibiting a significant increase in activity for human and mouse genome manipulation.
- Junhao Fu
- , Qing Li
- & Feng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Thiocysteine lyases as polyketide synthase domains installing hydropersulfide into natural products and a hydropersulfide methyltransferase
Thiocysteine lyases as polyketide synthase domains installing hydropersulfide into natural products and a hydropersulfide methyltransferase
Enzymes installing an intact hydropersulfide (-SSH) group into natural products have so far not been identified. Here, the authors report the characterization of an S-adenosyl methionine-dependent hydropersulfide methyltransferase (GnmP) for guangnanmycin biosynthesis, and identification of three SH domains within several NRPS-PKS assembly lines as thiocysteine lyases.
- Song Meng
- , Andrew D. Steele
- & Ben Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Activation mechanism of human soluble guanylate cyclase by stimulators and activators
Activation mechanism of human soluble guanylate cyclase by stimulators and activators
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is a validated drug target for cardiovascular diseases. Here, the authors report structures of human sGC in complex with NO and sGC stimulators or activator, providing insight into the mechanism of sGC activation by pharmacological compounds.
- Rui Liu
- , Yunlu Kang
- & Lei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access UbiD domain dynamics underpins aromatic decarboxylation
UbiD domain dynamics underpins aromatic decarboxylation
Understanding the structure and dynamics of enzymes is important for a number of applications. Here, the authors report on the crystal structure of vanillic acid decarboxylase, and show how the dynamics of the UbiD superfamily enzymes relate to the covalent catalysis of aromatic (de)carboxylation.
- Stephen A. Marshall
- , Karl A. P. Payne
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Toward scalable biocatalytic conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by galactose oxidase using coordinated reaction and enzyme engineering
Toward scalable biocatalytic conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by galactose oxidase using coordinated reaction and enzyme engineering
5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) can be transformed to a range of industrially useful derivatives, such as 2,5-diformylfuran (DFF), but the reactions needed for efficient industrial production are hindered by several issues. Here, the authors perform reaction and enzyme engineering resulting in a galactose oxidase variant with high activity towards HMF, improved oxygen binding and high productivity.
- William R. Birmingham
- , Asbjørn Toftgaard Pedersen
- & Nicholas J. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access The six steps of the complete F1-ATPase rotary catalytic cycle
The six steps of the complete F1-ATPase rotary catalytic cycle
F1Fo ATP synthase works using a rotary catalysis mechanism. Here, the authors report cryo-EM structures of Bacillus PS3 F1-ATPase encompassing the complete set of six states taken up during the catalytic cycle, including the binding- and catalytic-dwell states.
- Meghna Sobti
- , Hiroshi Ueno
- & Alastair G. Stewart

 A cryptic third active site in cyanophycin synthetase creates primers for polymerization
A cryptic third active site in cyanophycin synthetase creates primers for polymerization