Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access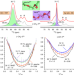 Conformational fitting of a flexible oligomeric substrate does not explain the enzymatic PET degradation
Conformational fitting of a flexible oligomeric substrate does not explain the enzymatic PET degradation
- Ren Wei
- , Chen Song
- & Wolfgang Zimmermann
-
Article
| Open Access Two-tiered enforcement of high-fidelity DNA ligation
Two-tiered enforcement of high-fidelity DNA ligation
DNA ligases catalyze the joining of DNA strands to complete DNA replication, recombination and repair transactions. Here the authors present X-ray structures and kinetic analyses of LIG1 complexes with undamaged and oxidatively damaged DNA that unveil determinants of LIG1 substrate recognition and enzymatic fidelity.
- Percy P. Tumbale
- , Thomas J. Jurkiw
- & R. Scott Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Homologous bd oxidases share the same architecture but differ in mechanism
Homologous bd oxidases share the same architecture but differ in mechanism
Cytochrome bd oxidases couple quinol oxidation and the release of protons to the periplasmic side with proton uptake from the cytoplasmic side to reduce dioxygen to water and they are the terminal reductases in bacterial and archaeal respiratory chains. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of Escherichia coli bd oxidase and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Alexander Theßeling
- , Tim Rasmussen
- & Thorsten Friedrich
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase nucleoprotein complex
Cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase nucleoprotein complex
Bacterial DNA gyrase is the only type II DNA topoisomerase capable of introducing negative supercoils into DNA and is of interest as a drug target. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase bound to a 180 bp double-stranded DNA and the antibiotic gepotidacin, which reveals the connections between the functional domains and their spatial organization.
- Arnaud Vanden Broeck
- , Christophe Lotz
- & Valérie Lamour
-
Article
| Open Access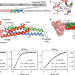 Structural insights of human mitofusin-2 into mitochondrial fusion and CMT2A onset
Structural insights of human mitofusin-2 into mitochondrial fusion and CMT2A onset
Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) is a dynamin-like GTPase that plays a central role in regulating mitochondrial fusion and cell metabolism. Here, authors report crystal structures of truncated human MFN2 in different nucleotide-loading states and show that MFN2 forms sustained dimers even after GTP hydrolysis.
- Yu-Jie Li
- , Yu-Lu Cao
- & Song Gao
-
Article
| Open Access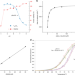 Inverting family GH156 sialidases define an unusual catalytic motif for glycosidase action
Inverting family GH156 sialidases define an unusual catalytic motif for glycosidase action
Sialidases are glycoside hydrolases that cleave sialosides. Here the authors define the 3-D structure, alone and in complex with products and inhibitors, of the CAZy family GH156 sialidase, EnvSia156, showing it displays a catalytical (β/α) 8-barrel domain distinct from other sialidases and allowing description of its inverting catalytic mechanism.
- Pedro Bule
- , Léa Chuzel
- & Gideon J. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access The free energy landscape of retroviral integration
The free energy landscape of retroviral integration
Retroviral integration of DNA into the host genome is a point of no return in the replication cycle but how efficient integration can take place remains unclear. Here the authors demonstrate that consecutive nucleoprotein intermediates are increasingly stable, resulting in a net forward rate.
- Willem Vanderlinden
- , Tine Brouns
- & Jan Lipfert
-
Article
| Open Access Acetyl-CoA-mediated activation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyase 2
Acetyl-CoA-mediated activation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyase 2
Isocitrate lyase (ICL) isoforms 1 and 2 are enzymes in the glyoxylate and methylcitrate cycles that enable Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) to use lipids as a carbon source. Here the authors present the ligand-free Mtb ICL2 and acetyl-CoA bound ICL2 crystal structures, which reveal a structural reorganisation upon acetyl-CoA binding that leads to an activation of its isocitrate lyase and methylcitrate lyase activities.
- Ram Prasad Bhusal
- , Wanting Jiao
- & Ivanhoe K. H. Leung
-
Article
| Open Access The cell cycle-regulated DNA adenine methyltransferase CcrM opens a bubble at its DNA recognition site
The cell cycle-regulated DNA adenine methyltransferase CcrM opens a bubble at its DNA recognition site
CcrM is a cell cycle-regulated DNA methyltransferase that methylates an adenine within a specific sequence following replication in the gram negative bacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Here the authors present a crystal structure of DNA-bound CcrM that reveals the molecular mechanism leading to sequence-specific methylation.
- John R. Horton
- , Clayton B. Woodcock
- & Xiaodong Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase forms a high-order spirosome architecture critical for its activity
Aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase forms a high-order spirosome architecture critical for its activity
Aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhE) converts acetyl-CoA to ethanol and plays an important role in bacterial fermentation. Here the authors present the 3.5 Å cryo-EM structure of full-length E. coli AdhE, which reveals a right-handed helical spirosome structure and they show that the helical structure is required for AdhE activity.
- Gijeong Kim
- , Liyana Azmi
- & Ji-Joon Song
-
Article
| Open Access A tri-ionic anchor mechanism drives Ube2N-specific recruitment and K63-chain ubiquitination in TRIM ligases
A tri-ionic anchor mechanism drives Ube2N-specific recruitment and K63-chain ubiquitination in TRIM ligases
The E3 ligase TRIM21 targets a broad range of pathogenic proteins using a unique mechanism. Here, the authors combine structural, biochemical and cell biological approaches to elucidate how TRIM21 selectively recruits its canonical E2 partner enzyme Ube2N and catalyzes ubiquitination.
- Leo Kiss
- , Jingwei Zeng
- & Leo C. James
-
Article
| Open Access The ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 interferes with SUMO activation
The ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 interferes with SUMO activation
FAT10 is an ubiquitin-like modifier that targets proteins to proteasomal degradation. Here, the authors show that FAT10 also regulates SUMO activation in vitro and in cells, providing evidence for functional crosstalk between two ubiquitin-like modifiers.
- Annette Aichem
- , Carolin Sailer
- & Marcus Groettrup
-
Article
| Open Access Retroviral integration into nucleosomes through DNA looping and sliding along the histone octamer
Retroviral integration into nucleosomes through DNA looping and sliding along the histone octamer
Retroviral integrases catalyze the insertion of viral DNA into the host cell DNA and can use nucleosomes as substrates for integration. Here the authors present the 3.9 Å cryo-EM structure of prototype foamy virus integrase after strand transfer into nucleosomal DNA, which together with single-molecule FRET measurements provides evidence for a DNA looping and sliding mechanism of integrases.
- Marcus D. Wilson
- , Ludovic Renault
- & Alessandro Costa
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of a bound peptide phosphonate reveals the mechanism of nocardicin bifunctional thioesterase epimerase-hydrolase half-reactions
Structure of a bound peptide phosphonate reveals the mechanism of nocardicin bifunctional thioesterase epimerase-hydrolase half-reactions
NocTE is a nonribosomal peptide synthetase thioesterase that completes the biosynthesis of pro-nocardicin G, the precursor for nocardicin β-lactam antibiotics. Here the authors provide mechanistic insights into NocTE by determining its crystal structures in the ligand-free form and covalently linked to a fluorophosphonate substrate mimic.
- Ketan D. Patel
- , Felipe B. d’Andrea
- & Andrew M. Gulick
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Cullin 2 RING E3 ligase regulation by the COP9 signalosome
Structural basis of Cullin 2 RING E3 ligase regulation by the COP9 signalosome
The COP9 signalosome (CSN) regulates Cullin-RING Ligase 2 (CRL2) but the molecular basis for their interaction is unknown. Here the authors use structural mass spectrometry and cryo-EM approaches to assess the structures and dynamics of CSN-CRL2 complexes.
- Sarah V. Faull
- , Andy M. C. Lau
- & Argyris Politis
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of amine dehydrogenases with increased catalytic performance and substrate scope from ε-deaminating L-Lysine dehydrogenase
Generation of amine dehydrogenases with increased catalytic performance and substrate scope from ε-deaminating L-Lysine dehydrogenase
Amine dehydrogenases (AmDHs) catalyse the conversion of ketones into amines. Here, the authors created AmDH variants, the best of which showing a substrate-dependent stereo-switchable selectivity, affording either S- or R-configured amine products with up to >99.9% enantiomeric excess.
- Vasilis Tseliou
- , Tanja Knaus
- & Francesco G. Mutti
-
Article
| Open Access The essential elements for the noncovalent association of two DNA ends during NHEJ synapsis
The essential elements for the noncovalent association of two DNA ends during NHEJ synapsis
During a process termed synapsis, the two DNA ends at a double-strand break (DSB) are brought together into physical proximity. Here, the authors use a single-molecule FRET approach with purified proteins to investigate the mechanism of synapsis in DSB repair by non-homologous DNA end joining (NHEJ).
- Bailin Zhao
- , Go Watanabe
- & Michael R. Lieber
-
Article
| Open Access A switch element in the autophagy E2 Atg3 mediates allosteric regulation across the lipidation cascade
A switch element in the autophagy E2 Atg3 mediates allosteric regulation across the lipidation cascade
Autophagy mediated by the conjugation pathway for ubiquitin-like proteins plays a key role in controlling homeostasis in eukaryotic cells. Here the authors provide a molecular basis for allosteric activation of the E2 ligase Atg3, uncovering the mechanism underlying Atg8 lipidation and a novel mechanism regulating E1-E2-E3-mediated ubiquitin-like protein conjugation.
- Yumei Zheng
- , Yu Qiu
- & Brenda A. Schulman
-
Article
| Open Access Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
The mechanism of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors develop a physiologically relevant in vitro model of Fe-S cluster assembly, allowing them to elucidate the sequence of Fe-S cluster synthesis along with the respective roles of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin.
- Sylvain Gervason
- , Djabir Larkem
- & Benoit D’Autréaux
-
Article
| Open Access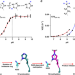 Structural basis for the target specificity of actin histidine methyltransferase SETD3
Structural basis for the target specificity of actin histidine methyltransferase SETD3
SETD3 is the first known metazoan protein histidine methyltransferase but the molecular basis for its target specificity is unclear. Here, the authors elucidate the structural and molecular determinants for the histidine specificity of SETD3.
- Shaobo Dai
- , John R. Horton
- & Xiaodong Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for the binding and selective dephosphorylation of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 by calcineurin
Molecular basis for the binding and selective dephosphorylation of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 by calcineurin
The mechanism by which Ser/Thr protein phosphatases specifically recruit and dephosphorylate their substrates is largely unclear. Hear, the authors elucidate how the Ser/Thr protein phosphatase calcineurin is recruited to its substrate NHE1 and how site-specific dephosphorylation is achieved.
- Ruth Hendus-Altenburger
- , Xinru Wang
- & Wolfgang Peti
-
Article
| Open Access A one-gate elevator mechanism for the human neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2
A one-gate elevator mechanism for the human neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2
How the human Alanine Serine Cysteine Transporter 2 (ASCT2) binds its substrates, neutral amino acids, and releases them on the cytoplasmic side remains unclear. Here authors present an inward-open structure of the human ASCT2 which shows that a hairpin serves as a gate in the inward-facing state.
- Alisa A. Garaeva
- , Albert Guskov
- & Cristina Paulino
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into E1 recognition and the ubiquitin-conjugating activity of the E2 enzyme Cdc34
Structural insights into E1 recognition and the ubiquitin-conjugating activity of the E2 enzyme Cdc34
The E2 enzyme Cdc34 plays a critical role in cell cycle progression but the structural bases for its activities are unknown. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Cdc34 alone, in complex with E1, and in complex with Ub that provide insights into the mechanism of Cdc34 activity in the cell.
- Katelyn M. Williams
- , Shuo Qie
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Acetylation regulates ribonucleotide reductase activity and cancer cell growth
Acetylation regulates ribonucleotide reductase activity and cancer cell growth
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) catalyzes the de novo synthesis of deoxyribonucleoside diphosphates to provide dNTP precursors for DNA synthesis. Here the authors show that the availability of dNTPs, DNA replication, and cellular proliferation, are modulated by acetylation and deacetylation of RRM2 by KAT7 and Sirt2 respectively.
- Guo Chen
- , Yin Luo
- & Xingming Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrophobic recognition allows the glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 to catalyze its substrate in two orientations
Hydrophobic recognition allows the glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 to catalyze its substrate in two orientations
UGT76G1 is an UDP-glucose dependent glycosyltransferase and a component of the biosynthesis pathway for the natural sugar substitute steviol glycoside. Here, the authors present substrate bound crystal structures of UGT76G1 and provide insights into substrate recognition and catalysis by the enzyme.
- Ting Yang
- , Jinzhu Zhang
- & Xiaofeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of tubulin detyrosination by VASH2/SVBP heterodimer
Structural basis of tubulin detyrosination by VASH2/SVBP heterodimer
The VASH2/SVBP heterodimer catalyzes the detyrosination of the α-tubulin C-terminus. Here the authors provide insights into the tubulin detyrosination mechanism by determining the crystal structures of VASH2/SVBP and VASH2/SVBP in complex with a tubulin tail peptide.
- Chen Zhou
- , Ling Yan
- & Zhu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial cysteine-lipases with high activity and altered catalytic mechanism created by laboratory evolution
Artificial cysteine-lipases with high activity and altered catalytic mechanism created by laboratory evolution
Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) is a serine lipase. Here, the authors use directed evolution to exchange serine with cysteine in the catalytic triad of the enzyme, thereby obtaining a highly active CALB variant that — unlike the wild type — accommodates bulky substrates.
- Yixin Cen
- , Warispreet Singh
- & Manfred T. Reetz
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-lock inhibitory mechanism for fine-tuning enzyme activities of the HECT family E3 ligases
A multi-lock inhibitory mechanism for fine-tuning enzyme activities of the HECT family E3 ligases
HECT type E3 ligases are key regulators of cell growth and proliferation. Here the authors present the crystal structures of the Nedd4 family E3 ligase WWP1 in a closed and semi-open state and in combination with mutagenesis experiments identify a multi-lock regulatory mechanism that allows the fine-tuning of activities of Nedd4 family E3 ligases.
- Zhen Wang
- , Ziheng Liu
- & Wenyu Wen
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanism of RNA duplex recognition and unwinding by DEAD-box helicase DDX3X
The mechanism of RNA duplex recognition and unwinding by DEAD-box helicase DDX3X
DEAD-box helicases (DDXs) function in an ATP-dependent, non-processive manner and the conserved helicase core is composed of two RecA-like domains D1 and D2. Here the authors present the crystal structure of the D1D2 core from human DDX3X bound to a 23-base pair dsRNA in the pre-unwound state and discuss the implications for helicase mechanism.
- He Song
- & Xinhua Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based mechanism for activation of the AAA+ GTPase McrB by the endonuclease McrC
Structure-based mechanism for activation of the AAA+ GTPase McrB by the endonuclease McrC
McrBC is a bacterial antiphage defense system that cleaves methylated DNA and is composed of the AAA+ GTPase motor McrB and the endonuclease McrC. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of E. coli McrBC that reveals how McrC inserts a stalk-like structure into the pore of the ring-shaped McrB hexamer and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Neha Nirwan
- , Yuzuru Itoh
- & Kayarat Saikrishnan
-
Article
| Open Access Kistamicin biosynthesis reveals the biosynthetic requirements for production of highly crosslinked glycopeptide antibiotics
Kistamicin biosynthesis reveals the biosynthetic requirements for production of highly crosslinked glycopeptide antibiotics
Kistamicin is a structurally divergent glycopeptide antibiotic (GPA) that contains a unique 15-membered A-O-B ring. Here, the authors obtained a crystal structure of the kistamicin OxyA/X-domain complex and analysed the cyclisation cascade leading to the formation of the A-O-B ring.
- Anja Greule
- , Thierry Izoré
- & Max J. Cryle
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanism to prevent production of reactive oxygen species by Escherichia coli respiratory complex I
A mechanism to prevent production of reactive oxygen species by Escherichia coli respiratory complex I
Respiratory complex I plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism coupling NADH oxidation to proton translocation. Here, the authors report the structure of the electron input part of Aquifex aeolicus complex I at up to 1.8 Å resolution with bound substrates in the reduced and oxidized states.
- Marius Schulte
- , Klaudia Frick
- & Thorsten Friedrich
-
Article
| Open Access Lysine 68 acetylation directs MnSOD as a tetrameric detoxification complex versus a monomeric tumor promoter
Lysine 68 acetylation directs MnSOD as a tetrameric detoxification complex versus a monomeric tumor promoter
The molecular mechanism by which acetylation regulates manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity and its oncogenicity is unclear. Here the authors show that an acetylation mimicking MnSOD mutant is a monomer, has peroxidase function and acts as a tumor promoting factor.
- Yueming Zhu
- , Xianghui Zou
- & David Gius
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of PCNA cycling on replicating DNA by RFC and RFC-like complexes
Regulation of PCNA cycling on replicating DNA by RFC and RFC-like complexes
Replication-Factor-C (RFC) and RFC-like complexes (RLCs) mediate chromatin engagement of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Here authors use biochemical and single molecule measurements to show that ATAD5-RLC has the most potent PCNA unloading activity and forms structurally distinct intermediates compared to RFC-PCNA.
- Mi-Sun Kang
- , Eunjin Ryu
- & Kyungjae Myung
-
Article
| Open Access The UbiX flavin prenyltransferase reaction mechanism resembles class I terpene cyclase chemistry
The UbiX flavin prenyltransferase reaction mechanism resembles class I terpene cyclase chemistry
The UbiD-UbiX decarboxylase system is required for the biosynthesis of quinone cofactors. Here, the authors combine structural and biochemical analyses to elucidate the UbiX reaction mechanism, showing that it resembles the mode of action of class I terpene cyclases.
- Stephen A. Marshall
- , Karl A. P. Payne
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of processive catalysis by an exo-hydrolase with a pocket-shaped active site
Discovery of processive catalysis by an exo-hydrolase with a pocket-shaped active site
Enzyme substrates and products often diffuse too rapidly to assess the catalytic implications of these movements. Here, the authors characterise the structural basis of product and substrate diffusion for an exo-hydrolase and discover a substrate-product assisted processive catalytic mechanism.
- Victor A. Streltsov
- , Sukanya Luang
- & Maria Hrmova
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the human frataxin-bound iron-sulfur cluster assembly complex provides insight into its activation mechanism
Structure of the human frataxin-bound iron-sulfur cluster assembly complex provides insight into its activation mechanism
The iron-sulfur cluster (ISC) assembly complex is activated by frataxin (FXN) and Friedreich’s ataxia is caused by FXN deficiency. Here the authors present the 3.2 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the human frataxin bound ISC complex and discuss how FXN activates enzymatic activity.
- Nicholas G. Fox
- , Xiaodi Yu
- & Seungil Han
-
Article
| Open Access Low potential enzymatic hydride transfer via highly cooperative and inversely functionalized flavin cofactors
Low potential enzymatic hydride transfer via highly cooperative and inversely functionalized flavin cofactors
The reduction of 2-naphtoyl-CoA to 5,6 dihydro-2-naphtoyl-CoA by 2-naphtoyl-CoA reductase is below the negative redox limit usually encountered in biological hydride transfer. Here, via X-ray crystallography and spectroscopic analysis, the authors elucidated the mechanism behind this.
- Max Willistein
- , Dominique F. Bechtel
- & Matthias Boll
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism-based tuning of insect 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde synthase for synthetic bioproduction of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
Mechanism-based tuning of insect 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde synthase for synthetic bioproduction of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
Bioproduction of tetrahydropapaveroline (THP) is limited by the specificity of monoamine oxidase (MAO). Here, the authors identify an insect 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde synthase (DHPAAS) that can bypass MAO for direct aldehyde production and demonstrate bifunctional switching of DHPAAS for efficient THP production.
- Christopher J. Vavricka
- , Takanobu Yoshida
- & Akihiko Kondo
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the plastic-degrading Ideonella sakaiensis MHETase bound to a substrate
Structure of the plastic-degrading Ideonella sakaiensis MHETase bound to a substrate
Plastic polymer PET degrading enzymes are of great interest for achieving sustainable plastics recycling. Here, the authors present the crystal structures of the plastic degrading bacterial enzymes PETase, MHETase in its apo-form and MHETase bound to a non-hydrolyzable substrate analog.
- Gottfried J. Palm
- , Lukas Reisky
- & Gert Weber
-
Article
| Open Access RdDM-independent de novo and heterochromatin DNA methylation by plant CMT and DNMT3 orthologs
RdDM-independent de novo and heterochromatin DNA methylation by plant CMT and DNMT3 orthologs
Whether plants have true DNMT3 orthologs and their role in establishing DNA methylation are still unclear. Here, the authors show that DNMT3s are persistent through plant evolution and mediates both de novo and heterochromatin DNA methylation in the early divergent land plant Physcomitrella patens.
- Rafael Yaari
- , Aviva Katz
- & Nir Ohad
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule characterization of extrinsic transcription termination by Sen1 helicase
Single-molecule characterization of extrinsic transcription termination by Sen1 helicase
Yeast’s Sen1 helicase is involved in the suppression of antisense transcription from bidirectional eukaryotic promoters. Here authors develop and utilize a quantitative single-molecule assay reporting on the kinetics of extrinsic eukaryotic transcription termination by the Sen1 helicase and a reaction intermediate in which the Pol II transcription bubble appears half-rewound.
- S. Wang
- , Z. Han
- & T. R. Strick
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and biochemical evidence supporting poly ADP-ribosylation in the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans
Structural and biochemical evidence supporting poly ADP-ribosylation in the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans
Poly-ADP-ribosylation (PARylation) is a well-known regulatory event in eukaryotes but has not yet been observed in bacteria. Here, the authors solve the structure of a bacterial PAR-glycohydrolase and provide evidence for a prokaryotic PARylation machinery involved in the response to genotoxic stress.
- Chao-Cheng Cho
- , Chia-Yu Chien
- & Chun-Hua Hsu
-
Comment
| Open Access The shape of human squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer
The shape of human squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer
- Andrew J. Brown
- , Ngee Kiat Chua
- & Nieng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access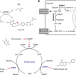 Design strategy for serine hydroxymethyltransferase probes based on retro-aldol-type reaction
Design strategy for serine hydroxymethyltransferase probes based on retro-aldol-type reaction
The enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) has been implicated in several diseases, however is hard to investigate. Here, the authors used a design strategy based on the retro-aldol-type reaction catalyzed by SHMT to develop SHMT-responsive fluorescence and 19F NMR molecular probes.
- Hiroshi Nonaka
- , Yuki Nakanishi
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article
| Open Access ASPP proteins discriminate between PP1 catalytic subunits through their SH3 domain and the PP1 C-tail
ASPP proteins discriminate between PP1 catalytic subunits through their SH3 domain and the PP1 C-tail
Serine/threonine phosphatases such as PP1 associate with a large array of subunit proteins, such as ASPP (apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53) to achieve selective targeting. Here authors solved the crystal structure of the human ASPP2/PP1 complex and explain how ASPP2 can distinguish between PP1 isoforms.
- M. Teresa Bertran
- , Stéphane Mouilleron
- & Nicolas Tapon
-
Article
| Open Access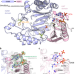 The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase
The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase
Elp3 is the catalytic subunit of the eukaryotic Elongator complex that catalyzes posttranscriptional tRNA modifications. Here the authors present the crystal structures of an acetyl-CoA analog bound bacterial Elp3 and a monomeric archaeal Elp3 and show that Elp3 functions as a tRNA modification enzyme in all domains of life.
- Ting-Yu Lin
- , Nour El Hana Abbassi
- & Sebastian Glatt
-
Article
| Open Access Copper amine oxidases catalyze the oxidative deamination and hydrolysis of cyclic imines
Copper amine oxidases catalyze the oxidative deamination and hydrolysis of cyclic imines
Little is known about the degradation pathway of cyclic imines that are frequently found in bioactive secondary metabolites. Here, the authors found and characterised a copper amine oxidase, HarA that catalyses a ring-opening reaction of cyclic imine in harmaline and oxidative deamination of amines.
- Toshiki Nagakubo
- , Takuto Kumano
- & Michihiko Kobayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are critical regulators of cellular processes by removing ubiquitin from specific targets. Here global kinetic modelling reveals the mechanism by which the low intrinsic activity of USP7 is substantially enhanced on a specific physiological target.
- Robbert Q. Kim
- , Paul P. Geurink
- & Titia K. Sixma

 Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory syncytial virus RNA polymerase
Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory syncytial virus RNA polymerase