Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating social vulnerability into high-resolution global flood risk mapping
Integrating social vulnerability into high-resolution global flood risk mapping
The study introduces a method of integrating gridded estimates of social vulnerability into high-resolution global flood risk maps demonstrating new insights into the geography of flood risk within and between countries.
- Sean Fox
- , Felix Agyemang
- & Jeffrey Neal
-
Article
| Open Access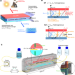 Thermodiffusive desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination
Current desalination technologies are energy intensive and suffer from membrane degradation and fouling. Here, authors propose and explore the potential of thermodiffusion as a means of membrane-free, single-phase thermal desalination. A pathway towards a feasible thermodiffusive desalination is provided.
- Shuqi Xu
- , Alice J. Hutchinson
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Comment
| Open Access Integrating science and the arts to deglobalise climate change adaptation
Integrating science and the arts to deglobalise climate change adaptation
Setting goals that are context-specific, relevant, and collectively shared is critical in adaptation. As necessary elements in target setting, imaginaries for adaptation and the language connected to them remain vague. Visuals produced through art-science collaborations can be great allies to (de)construct imaginaries and deglobalise discourses of adaptation.
- Marta Olazabal
- , Maria Loroño-Leturiondo
- & Josune Urrutia
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of a political crisis on performance of community forests and protected areas in Madagascar
The effect of a political crisis on performance of community forests and protected areas in Madagascar
The effectiveness of community-based land protection compared to traditional top-down protection is debated. Here, the authors show that both community-managed forests and traditional protected areas in Madagascar experienced deforestation during a political crisis but the former were especially vulnerable in the post-crisis period.
- Rachel A. Neugarten
- , Ranaivo A. Rasolofoson
- & Amanda D. Rodewald
-
Article
| Open Access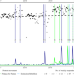 Increase in concerns about climate change following climate strikes and civil disobedience in Germany
Increase in concerns about climate change following climate strikes and civil disobedience in Germany
Climate movements aim to raise public awareness of climate change through protests, but their efficacy is debated. Here, the authors show that concerns about climate change increased in Germany after climate strikes and non-violent acts of civil disobedience.
- Johannes Brehm
- & Henri Gruhl
-
Article
| Open Access Substantially reducing global PM2.5-related deaths under SDG3.9 requires better air pollution control and healthcare
Substantially reducing global PM2.5-related deaths under SDG3.9 requires better air pollution control and healthcare
Reducing PM2.5 air pollution from biomass burning, transport, energy, and manufacturing, in combination with improvements in healthcare, especially in emerging economies like India and China, will be crucial to meeting SDG3.9
- Huanbi Yue
- , Chunyang He
- & Brett A. Bryan
-
Perspective
| Open Access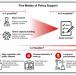 Engineering biology and climate change mitigation: Policy considerations
Engineering biology and climate change mitigation: Policy considerations
Engineering biology is a dynamic field that uses gene editing, synthesis, assembly, and engineering to design new or modified biological systems. Here the authors discuss the policy considerations and interventions needed to support a role for engineering biology in climate change mitigation.
- Jonathan Symons
- , Thomas A. Dixon
- & Isak S. Pretorius
-
Article
| Open Access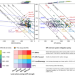 Trade-offs in land-based carbon removal measures under 1.5 °C and 2 °C futures
Trade-offs in land-based carbon removal measures under 1.5 °C and 2 °C futures
This study demonstrates how land-based carbon removals and the market-mediated responses are sensitive to mitigation policy strength and scope, illustrating that, despite trade-offs, both forestation and BECCS are integral to cost-effective 2 °C pathways.
- Xin Zhao
- , Bryan K. Mignone
- & Haewon C. McJeon
-
Article
| Open Access The atlas of unburnable oil for supply-side climate policies
The atlas of unburnable oil for supply-side climate policies
The global atlas of unburnable oil shows that the most socio-environmentally sensitive areas, such as protected areas or biodiversity hotspots, need to be kept entirely off-limits to oil extraction in order to keep global warming under 1.5 °C.
- Lorenzo Pellegrini
- , Murat Arsel
- & Martí Orta-Martínez
-
Article
| Open Access Cost-effectiveness uncertainty may bias the decision of coal power transitions in China
Cost-effectiveness uncertainty may bias the decision of coal power transitions in China
China’s use of coal is complex to establish a clean and low-carbon transition for the country. With an uncertainty assessment framework, this study displays the risks of missing opportunities in obtaining cumulative positive net benefits and identifying an optimal transition strategy.
- Xizhe Yan
- , Dan Tong
- & Yu Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Strategies for robust renovation of residential buildings in Switzerland
Strategies for robust renovation of residential buildings in Switzerland
Building renovation is an urgent requirement to reduce the environmental impact associated with the building stock. In this paper, authors identify strategies for robust renovation considering uncertainties on the future and provide recommendations for the residential buildings in Switzerland.
- Alina Galimshina
- , Maliki Moustapha
- & Guillaume Habert
-
Article
| Open Access Policy and market forces delay real estate price declines on the US coast
Policy and market forces delay real estate price declines on the US coast
Subsidies for coastal management and tax advantages for high-income property owners dampen the negative effects of climate risks on coastal property values. Without subsidies or tax advantages market prices better reflect climate risks, but coastal gentrification could accelerate.
- Dylan E. McNamara
- , Martin D. Smith
- & Craig E. Landry
-
Article
| Open Access Limited impact of hydrogen co-firing on prolonging fossil-based power generation under low emissions scenarios
Limited impact of hydrogen co-firing on prolonging fossil-based power generation under low emissions scenarios
Effects of hydrogen and ammonia co-firing with fossil power generation on decarbonization scenario are assessed. Co-fired generation is limited to <1% because of higher cost of hydrogen. It will not delay the phase-out of fossil-based generators.
- Ken Oshiro
- & Shinichiro Fujimori
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Conventional blue denim dyeing has both environmental and health-related consequences. Here, Bidart et al. use enzyme engineering to develop a viable method for the bulk production of indican and demonstrate dying processes which could significantly reduce the negative consequences of this billion-dollar industry.
- Gonzalo Nahuel Bidart
- , David Teze
- & Ditte Hededam Welner
-
Article
| Open Access CCl4 emissions in eastern China during 2021–2022 and exploration of potential new sources
CCl4 emissions in eastern China during 2021–2022 and exploration of potential new sources
The Montreal Protocol globally phased out ozone-layer depleting CCl4 by 2010. However, atmospheric measurements show eastern China emitted ~7.6 gigagrams/year in 2021–2022. Further, industrial sources of ongoing CCL4 emissions are identified.
- Bowei Li
- , Jiahuan Huang
- & Xuekun Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Xu and colleagues find that the average trophic level of aquatic food items in the human diet is declining (from 3.42 to 3.18) because of the considerable increase in low-trophic level aquaculture species output relative to that of capture fisheries since 1976. Additionally they find that trade has contributed to increasing the availability and trophic level of aquatic foods in >60% of the world’s countries.
- Kangshun Zhao
- , Steven D. Gaines
- & Jun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Avoiding ecosystem and social impacts of hydropower, wind, and solar in Southern Africa’s low-carbon electricity system
Avoiding ecosystem and social impacts of hydropower, wind, and solar in Southern Africa’s low-carbon electricity system
Avoiding the most damaging land use and freshwater impacts of solar PV, wind, and hydropower development while halving carbon emissions by 2040 in the Southern Africa region is not only possible but incurs only modest (3-6%) system cost increases.
- Grace C. Wu
- , Ranjit Deshmukh
- & Kudakwashe Ndhlukula
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring negative emission potential of biochar to achieve carbon neutrality goal in China
Exploring negative emission potential of biochar to achieve carbon neutrality goal in China
Authors analyze the potential of biochar in China, revealing it could sequester up to 0.92 billion tons of CO2 per year with an average net cost of US$90 per ton of CO2 in a sustainable manner, supporting carbon neutrality goal by 2060.
- Xu Deng
- , Fei Teng
- & Pan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Stringent sustainability regulations for global supply chains are supported across middle-income democracies
Stringent sustainability regulations for global supply chains are supported across middle-income democracies
Citizens in middle-income countries (Brazil, India, Indonesia) support aligning local sustainability rules with new laws originating in OECD nations. People favor stricter regulations, driven by optimistic expectations of the benefits outweighing potential costs.
- E. Keith Smith
- , Dennis Kolcava
- & Thomas Bernauer
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainability benefits of transitioning from current diets to plant-based alternatives or whole-food diets in Sweden
Sustainability benefits of transitioning from current diets to plant-based alternatives or whole-food diets in Sweden
The authors found that replacing animal source foods with plant-based alternatives would lead to substantial reductions in environmental impacts, while meeting most nutrition recommendations and being cost-competitive with the current average Swedish diet.
- Anne Charlotte Bunge
- , Rachel Mazac
- & Line Gordon
-
Article
| Open Access Greenhouse gas emissions from US irrigation pumping and implications for climate-smart irrigation policy
Greenhouse gas emissions from US irrigation pumping and implications for climate-smart irrigation policy
This study demonstrates the energy use of US pump irrigation produced 12.6 million tonnes CO2e in 2018, with spatial variability modulated by water source and fuel choice. These county-level estimates can inform strategic irrigation expansion and emissions reduction efforts.
- Avery W. Driscoll
- , Richard T. Conant
- & Nathaniel D. Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Global research has identified six critical transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030. Here, Allen et al model all six transformations in a national context and discuss implications for accelerating progress on the goals.
- Cameron Allen
- , Annabel Biddulph
- & Shirin Malekpour
-
Article
| Open Access An environmental justice analysis of air pollution emissions in the United States from 1970 to 2010
An environmental justice analysis of air pollution emissions in the United States from 1970 to 2010
Here the authors find socioeconomic and racial/ethnic disparities in county-level air pollution emissions reductions in the 40 years following the Clean Air Act (1970-2010) in the USA, particularly in emissions from energy generation and industry.
- Yanelli Nunez
- , Jaime Benavides
- & Marianthi-Anna Kioumourtzoglou
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
Towards optimizing the conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources in arid and semi-arid regions, here the authors propose a hybrid method involving moth-swarm and symbiotic organism search algorithms and artificial neural networks and demonstrate it for the HalīlRood basin.
- Saeid Akbarifard
- , Mohamad Reza Madadi
- & Mohammad Zounemat-Kermani
-
Article
| Open Access Global transboundary synergies and trade-offs among Sustainable Development Goals from an integrated sustainability perspective
Global transboundary synergies and trade-offs among Sustainable Development Goals from an integrated sustainability perspective
Domestic attempts to advance the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in a country can have synergistic and/or trade-off effects on the advancement of SDGs in other countries. Here the authors demonstrate that while high-income countries make up only 14% of the global population, they drive over 60% of worldwide SDG interactions.
- Huijuan Xiao
- , Sheng Bao
- & Jianguo Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A global analysis of how human infrastructure squeezes sandy coasts
A global analysis of how human infrastructure squeezes sandy coasts
In a first global analysis, researchers find that sandy shores are severely squeezed between human infrastructure and the rising sea, as on average, the first road or building is currently situated at just 390 meters distance from the shoreline.
- Eva M. Lansu
- , Valérie C. Reijers
- & Tjisse van der Heide
-
Article
| Open Access Managing urban development could halve nitrogen pollution in China
Managing urban development could halve nitrogen pollution in China
Here the authors demonstrate how managed urbanization in China could halve reactive nitrogen pollution to both the atmosphere and water resources. Investing 61 billion USD could provide 245 billion USD in benefits, while contributing to multiple SDG goals.
- Ouping Deng
- , Sitong Wang
- & Baojing Gu
-
Editorial
| Open AccessFeeding the future global population
Climate change is exacerbating challenges both for global food production and from its environmental impacts. Sustainable and socially responsible solutions for future world-wide food security are urgently needed.
-
Article
| Open Access Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health
Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health
Food production systems need to balance yield and sustainability. Here, the authors conduct 6 years long crop diversification field experiments in the North China Plain, showing that diversifying cereal monocultures with cash crops and legumes cand improve yield and reduce GHG emissions.
- Xiaolin Yang
- , Jinran Xiong
- & Klaus Butterbach-Bahl
-
Article
| Open Access Flood exposure and pregnancy loss in 33 developing countries
Flood exposure and pregnancy loss in 33 developing countries
Flooding impacts billions globally and indirect health effects are not sufficiently examined, especially for women in developing countries. Here, the authors show that flood exposure during pregnancy correlates with a higher risk of pregnancy loss, particularly for marginalized women, revealing increased health disparities in a changing climate.
- Cheng He
- , Yixiang Zhu
- & Haidong Kan
-
Article
| Open Access Waste milk humification product can be used as a slow release nano-fertilizer
Waste milk humification product can be used as a slow release nano-fertilizer
The growth in global milk demand has been accompanied by an increase in waste milk disposal. Here, the authors transform waste milk through humification and incorporate the product into attapulgite creating a nano-fertiliser that benefits for plants growing in pots.
- Yanping Zhu
- , Yuxuan Cao
- & Dongqing Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Approaching national climate targets in China considering the challenge of regional inequality
Approaching national climate targets in China considering the challenge of regional inequality
Aggressive or uniform actions on climate targets may exacerbate regional inequality and induce economic losses in China. The proposed collaborative strategy for carbon neutrality can avoid up to 1.54% of GDP losses while 90% of provinces would gain.
- Biying Yu
- , Zihao Zhao
- & Hua Liao
-
Q&A
| Open Access A conversation about cultivated meat
A conversation about cultivated meat
Summary: Cultivated or cultured meat is promising to revolutionize the food industry in the coming years to decades, helping to resolve concerns related to the environmental impact and ethical implications linked to conventional meat production. We talked to Dr. Sandhya Sriram, the Group CEO and Co-founder of Shiok Meats Pte. Ltd., Singapore; Prof. Shulamit Levenberg, the former Dean of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the Technion, current Director of the Technion Center for 3D Bioprinting and The Rina & Avner Schneur Center for Diabetes Research, as well as the Co-founder and Chief Scientific Adviser of Aleph Farms, Israel; and Dr. Timothy Olsen, Head of Cultured Meat in the Life Science business at Merck KGaA, Germany; about this relatively new and quickly developing sector. They explain what their teams are working on, including the biggest recent accomplishments, speak about the main challenges facing the field and how they can be resolved, and share their visions about the future of cultivated meat, aiming to provide more equitable and sustainable access to nutritious food for the growing world population.
-
Article
| Open Access Uncertainties in deforestation emission baseline methodologies and implications for carbon markets
Uncertainties in deforestation emission baseline methodologies and implications for carbon markets
This study reveals high variability in deforestation emission baselines typically used to derive carbon credits, with median error at 0.778 times the actual rate. It underscores the need for enhanced methods to improve carbon market accuracy and reliability.
- Hoong Chen Teo
- , Nicole Hui Li Tan
- & Lian Pin Koh
-
Article
| Open Access Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
The rapid deployment of low-carbon measures is urgently needed to reduce cement emissions as cement CO2 emissions from developing countries will almost deplete the remaining cement emissions budget within climate targets.
- Danyang Cheng
- , David M. Reiner
- & Dabo Guan
-
Article
| Open Access Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
The geographic distribution of dengue has been expanding in recent decades, and Vietnam is one of the most severely affected countries. In this study, the authors use Bayesian hierarchical modelling to investigate the socio-environmental and climatic drivers of dengue incidence in Vietnam and how they vary across the country.
- Rory Gibb
- , Felipe J. Colón-González
- & Rachel Lowe
-
Article
| Open Access Deploying green hydrogen to decarbonize China’s coal chemical sector
Deploying green hydrogen to decarbonize China’s coal chemical sector
The coal chemical sector uses coal to produce chemicals and emits substantial greenhouse gases, which are hard to abate by electrification alone. Deploying green H2 for China’s coal chemical plants can reduce ~50% of emissions at a low cost.
- Yang Guo
- , Liqun Peng
- & Denise L. Mauzerall
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Unsorted retired batteries pose recycling challenges due to diverse cathodes. Here, the authors propose a privacy-preserving machine learning system that enables accurate sorting with minimal data, important for a sustainable battery recycling industry.
- Shengyu Tao
- , Haizhou Liu
- & Hongbin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
Ronco and colleagues analyze disaster-induced movements in the presence of floods, storms, and landslides during 2016–2021, providing empirical evidence that differential vulnerability exists and quantifying its extent. They achieve this by employing explainable machine learning techniques to model and understand internal displacement flows and patterns from observational data.
- Michele Ronco
- , José María Tárraga
- & Gustau Camps-Valls
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures
Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures
Most inhabited areas in the US have more mass in buildings and mobility networks than in plant biomass. Cities are comparably resource efficient, while high material intensity is found in rural areas. Migration reinforces this phenomenon as people leave while built structures remain.
- David Frantz
- , Franz Schug
- & Helmut Haberl
-
Article
| Open Access Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
A new study explores the global feasible supply of steel and cement within Paris-compliant carbon budgets, explicitly considering uncertainties in the deployment of infrastructure and it shows that feasible supply may fall short of expected global demand.
- Takuma Watari
- , André Cabrera Serrenho
- & Julian Allwood
-
Article
| Open Access The social costs of tropical cyclones
The social costs of tropical cyclones
The estimates of the societal costs of carbon currently used for policy evaluations may be too low due to an insufficient representation of tropical cyclone damage. Accounting for them substantially increases the estimated benefits of climate change mitigation measures.
- Hazem Krichene
- , Thomas Vogt
- & Christian Otto
-
Article
| Open Access Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
This study finds that flood insurance policy design affects economic development in floodplains and, consequently, flood risk in Europe. Therefore, the authors advocate for flood insurance design to be integrated in climate change adaptation policy.
- Max Tesselaar
- , W. J. Wouter Botzen
- & Jeroen C. J. H. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access A fish cartel for Africa
A fish cartel for Africa
Englander and Costello note that African coastal waters are among the world’s most biologically rich, but African countries earn much less than their peers from selling access to foreign fishers. They find forming a “fish cartel" would increase African fish biomass by 16% and profits by 23%.
- Gabriel Englander
- & Christopher Costello
-
Article
| Open Access Climate change beliefs and their correlates in Latin America
Climate change beliefs and their correlates in Latin America
The authors map beliefs in climate change and their correlates in Latin America. The study shows skepticism over the existence and anthropogenic origins of climate change to be limited, but identifies a high number of skeptics around the severity of its consequences. Results also show individualistic worldviews to be the most powerful driver of climate change beliefs in the region.
- Matias Spektor
- , Guilherme N. Fasolin
- & Juliana Camargo
-
Article
| Open Access Message framing to promote solar panels
Message framing to promote solar panels
Green technologies foster the use of green energy; however, large investment costs hinder adoption. In a large-scale field experiment, the authors show that message framing can promote a serious commitment to solar panels among the broader public.
- Dominik Bär
- , Stefan Feuerriegel
- & Markus Weinmann
-
Article
| Open Access Decarbonization potential of electrifying 50% of U.S. light-duty vehicle sales by 2030
Decarbonization potential of electrifying 50% of U.S. light-duty vehicle sales by 2030
Electric vehicle sales goals alone will not achieve light duty vehicle emissions targets. Other actions including decarbonizing the electric grid, mode shifting, vehicle downsizing, reducing travel demand, and accelerating fleet turnover, are needed.
- Maxwell Woody
- , Gregory A. Keoleian
- & Parth Vaishnav
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Health impact of air pollution is estimated using PM2.5 mass as exposure metric. Here authors show that the impacts on child health is underestimated in India using this metric relative to the cumulative impact of the various PM2.5 components.
- Ekta Chaudhary
- , Franciosalgeo George
- & Unnati Mehta
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Rapid adoption of zero-emission vehicles with a concurrent transition to clean electricity is essential to achieve U.S. transportation decarbonization goals. Managing travel demand can ease this transition by reducing the need for clean electricity supply. @cghoehne, @nrel, #NRELMobility
- Christopher Hoehne
- , Matteo Muratori
- & Ookie Ma

 Sustained increase in suspended sediments near global river deltas over the past two decades
Sustained increase in suspended sediments near global river deltas over the past two decades