Featured
-
-
Article |
 Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Ion exchange is a powerful method to access metastable materials for energy storage, but identifying lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides remains challenging. Using such model materials, vacancy level and corresponding lithium preference are shown to be crucial for ion exchange pathway accessibility.
- Yu Han
- , Weihang Xie
- & Chong Liu
-
News & Views |
 Goosebumps drive microstructures
Goosebumps drive microstructures
Light-driven artificial goosebumps enable the simple yet precise actuation of microstructures.
- Jaeil Kim
- & Hoon Eui Jeong
-
Perspective |
 Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Potential and challenges of computing with molecular materials
Molecular materials for computing progress intensively but the performance and reliability still lag behind. Here the authors assess the current state of computing with molecular-based materials and describe two issues as the basis of a new computing technology: continued exploration of molecular electronic properties and process development for on-chip integration.
- R. Stanley Williams
- , Sreebrata Goswami
- & Sreetosh Goswami
-
Article |
 Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Limited datasets hinder the accurate prediction of DNA origami structures. A data-driven and physics-informed approach for model training is presented using a graph neural network to facilitate the rapid virtual prototyping of DNA-based nanostructures.
- Chien Truong-Quoc
- , Jae Young Lee
- & Do-Nyun Kim
-
Article |
 An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis
An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis
An intelligent DNA nanodevice, composed of DNA origami nanosheets and a thrombin-responsive DNA fastener, accurately delivers the appropriate dose of tissue plasminogen activator following activation by distinct thrombosis events.
- Jue Yin
- , Siyu Wang
- & Lianhui Wang
-
Article |
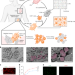 Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Implants made from patient-derived lyophilized lymph nodes loaded with chimeric antigen receptor T cells improve T cell delivery and inhibit tumour recurrence.
- Jiaqi Shi
- , Wei Wu
- & Zhen Gu
-
Article
| Open Access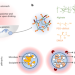 Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Sequential drinks of crosslinker and polymer solutions form a tough hydrogel in the stomach, enabling delivery of drugs and biologics in this harsh chemical environment.
- Gary W. Liu
- , Matthew J. Pickett
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
News & Views |
 Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Early detection of electrical degradation can be identified by colour change due to the chromogenic response of blended molecules in dielectric polymers.
- Gregory A. Sotzing
- & Pritish S. Aklujkar
-
Research Briefing |
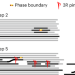 Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Metal monochalcogenides — a class of van der Waals layered semiconductors — can exhibit ultrahigh plasticity. Investigation of the deformation mechanism reveals that on mechanical loading, these materials undergo local phase transitions that, coupled with the concurrent generation of a microcrack network, give rise to the ultrahigh plasticity.
-
News & Views |
 Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Incorporating additives that contain hydrogen-bonding nanochannels creates nanoconfined polymer gels that are highly stretchable, elastic and insensitive to notch propagation.
- Meixiang Wang
- & Michael D. Dickey
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
News & Views |
 Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Using an electrochemical continuous flow cell, nitrogen reduction to ammonia is rigorously demonstrated through a calcium-mediated approach.
- Michael A. Yusov
- & Karthish Manthiram
-
Article |
 Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of 2D materials-based electronics towards ultimate edge computing solutions
Monolithic 3D integration of electronics based on fully 2D materials is demonstrated in the performance of artificial intelligence tasks.
- Ji-Hoon Kang
- , Heechang Shin
- & Sang-Hoon Bae
-
Article |
 Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Autonomous indication of electrical degradation in polymers
Early detection of electrical degradation in dielectric polymers is crucial but remains challenging. A general strategy of blending the polymer with chromogenic molecules is reported, which generates a visually discernible colour change as chemically activated by oxygen radicals generated in situ, indicating the early stage of electrical degradation in polymers.
- Xiaoyan Huang
- , Shuai Zhang
- & Jinliang He
-
Research Briefing |
 Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
Physical reservoir computers that can adapt to perform different tasks
A traditional physical-reservoir device has limited flexibility and cannot perform well across a range of computing tasks, owing to the fixed reservoir properties of the physical system. However, by exploiting the rich magnetic phase spaces of a single chiral magnet, reservoir properties can be reconfigured. This control enables on-demand optimization of computational performance across diverse machine-learning tasks.
-
Article |
 Pro-regenerative biomaterials recruit immunoregulatory dendritic cells after traumatic injury
Pro-regenerative biomaterials recruit immunoregulatory dendritic cells after traumatic injury
Pro-regenerative biomaterials for the treatment of muscle injury induce the proliferation of a dendritic cell population associated with cross-presentation and self-tolerance, promoting a pro-regenerative immune environment to aid muscle wound healing.
- Ravi Lokwani
- , Aditya Josyula
- & Kaitlyn Sadtler
-
Article |
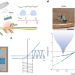 Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials for remote neural stimulation and motor function restoration
Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials for remote neural stimulation and motor function restoration
Self-rectifying magnetoelectric metamaterials with nonlinear responses generate electrical pulse sequences that enable precisely timed remote neural stimulation and restoration of sensory motor responses in vivo.
- Joshua C. Chen
- , Gauri Bhave
- & Jacob T. Robinson
-
News & Views |
 Resistance to fatigue
Resistance to fatigue
An additively manufactured AlSi10Mg alloy shows high fatigue strength, even close to its tensile strength, for micro-sized samples. The fine cells in its inherent three-dimensional network are considered as cages to limit damage accumulation.
- Christopher Hutchinson
-
News & Views |
 Bioelectronics goes vertical
Bioelectronics goes vertical
Remotely powered vertical electrochemical transistors are demonstrated to track subtle nerve-cell activity even when the transistor core is fully shielded from the biological environment.
- C. Eckel
- & R. T. Weitz
-
Article
| Open Access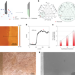 Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick films of metal–organic frameworks with ordered porosity would be attractive for membrane applications as these thin systems combine large molecular flux with high selectivity. Here crystalline ZIF films are grown on a crystalline substrate with high H2/N2 gas separation performance.
- Qi Liu
- , Yurun Miao
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Perspective |
 Colloidal robotics
Colloidal robotics
This Perspective provides an overview on the emergent field of colloidal robotics, discussing recent developments on colloidal and micrometre-sized particles that can perform functions such as sensing, communication, computation and motion.
- Albert Tianxiang Liu
- , Marek Hempel
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
An ultrahigh fatigue-resistant AlSi10Mg alloy is achieved by additive manufacturing, with its three-dimensional dual-phase cellular nanostructure acting as a strong volumetric nanocage to inhibit fatigue damage accumulation.
- Chengyi Dan
- , Yuchi Cui
- & Jian Lu
-
Article |
 Scalable integration of hybrid high-κ dielectric materials on two-dimensional semiconductors
Scalable integration of hybrid high-κ dielectric materials on two-dimensional semiconductors
A van der Waals buffer layer of Sb2O3 enables the integration of high-κ dielectric layer with sub-1 nm equivalent oxide thickness on two-dimensional semiconductors, resulting in high performance of two-dimensional field-effect transistors.
- Yongshan Xu
- , Teng Liu
- & Tianyou Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access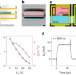 Integrated internal ion-gated organic electrochemical transistors for stand-alone conformable bioelectronics
Integrated internal ion-gated organic electrochemical transistors for stand-alone conformable bioelectronics
Organic electronic devices enhance biocompatibility, but have to rely on silicon-based technologies to improve limited speed and integration. This problem is overcome by creating a stand-alone, wireless, conformable, fully organic bioelectronic device with high electronic performance, scalability, stability and conformability in physiologic media.
- Claudia Cea
- , Zifang Zhao
- & Dion Khodagholy
-
News & Views |
 Better electronics from immiscibility
Better electronics from immiscibility
A bicontinuous conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrical conductivity, stretchability and fracture toughness in physiological environments achieves high-fidelity monitoring and effective stimulation of tissues and organs.
- Youdi Liu
- , Faheem Ershad
- & Cunjiang Yu
-
News & Views |
 A defensive blanket against viral infection of the lungs
A defensive blanket against viral infection of the lungs
A safe, inhalable formulation of mucin-interacting hydrogel microparticles creates a dense protective network in the lungs against viral infections.
- Thomas Crouzier
-
Article |
 Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Strong yet releasable metamaterial adhesives are fabricated using nonlinear cut architectures to achieve control of the crack propagation interface for programmable, directional and spatially selective adhesion.
- Dohgyu Hwang
- , Chanhong Lee
- & Michael D. Bartlett
-
Article |
 3D printable high-performance conducting polymer hydrogel for all-hydrogel bioelectronic interfaces
3D printable high-performance conducting polymer hydrogel for all-hydrogel bioelectronic interfaces
A bi-continuous hydrogel prepared from phase-separated PEDOT:PSS and polyurethane is 3D printed into soft biolelectronic devices with high electrical conductivity, stretchability and toughness for long-term in vivo electrophysiological monitoring and stimulation.
- Tao Zhou
- , Hyunwoo Yuk
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article |
 ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
Membranes formed from porous adsorbents can improve the economics of industrially difficult separations but require support materials that reduce gas permeance. Here an amorphous glassy foam membrane without a support is formed from ZIF-62 that shows high selectivity and permeance for CH4/N2 separations.
- Zibo Yang
- , Youssef Belmabkhout
- & Chongli Zhong
-
Article |
 Observation of anti-damping spin–orbit torques generated by in-plane and out-of-plane spin polarizations in MnPd3
Observation of anti-damping spin–orbit torques generated by in-plane and out-of-plane spin polarizations in MnPd3
The authors address spin–orbit torques and magnetization switching in MnPd3/CoFeB hetrostructures.
- Mahendra DC
- , Ding-Fu Shao
- & Shan X. Wang
-
News & Views |
 Artificial neuron transmits chemical signals
Artificial neuron transmits chemical signals
An artificial neuron architecture based on antiambipolar organic electrochemical transistors shows responses to biological ions and neurotransmitters akin to real neurons with comparable speed. The soft and more biocompatible nature of organic semiconductors could enable applications in brain–machine interfaces and in vivo sensing.
- Shinya E. Chen
- , Rajiv Giridharagopal
- & David S. Ginger
-
Review Article |
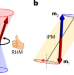 Coherent antiferromagnetic spintronics
Coherent antiferromagnetic spintronics
This Review discusses the field of antiferromagnetic spintronics with a focus on coherent effects.
- Jiahao Han
- , Ran Cheng
- & Shunsuke Fukami
-
Article |
 Combinatorial treatment rescues tumour-microenvironment-mediated attenuation of MALT1 inhibitors in B-cell lymphomas
Combinatorial treatment rescues tumour-microenvironment-mediated attenuation of MALT1 inhibitors in B-cell lymphomas
A hydrogel-based modular lymphoma organoid identifies how lymphoid microenvironment cues dampen the effect of MALT1 inhibitors and informs effective combination therapies to rescue the treatment response
- Shivem B. Shah
- , Christopher R. Carlson
- & Ankur Singh
-
News & Views |
 A bioadhesive robot to activate muscles
A bioadhesive robot to activate muscles
Soft actuators composed of a tough bioadhesive/elastomer shell encapsulating a stimuli-responsive metallic spring provide in situ mechanical stimulation of skeletal muscles to promote muscle tissue rehabilitation and prevent atrophy.
- Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Ion-tunable antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers enables biorealistic organic electrochemical neurons
Ion-tunable antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers enables biorealistic organic electrochemical neurons
Silicon-based complementary metal-oxide semiconductors or negative differential resistance device circuits can emulate neural features, yet are complicated to fabricate and not biocompatible. Here, the authors report an ion-modulated antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers demonstrating capability of sensing, spiking, emulating the most critical biological neural features, and stimulating biological nerves in vivo.
- Padinhare Cholakkal Harikesh
- , Chi-Yuan Yang
- & Simone Fabiano
-
-
-
Article |
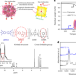 Advanced carbon molecular sieve membranes derived from molecularly engineered cross-linkable copolyimide for gas separations
Advanced carbon molecular sieve membranes derived from molecularly engineered cross-linkable copolyimide for gas separations
Carbon molecular sieves (CMS) are formed from pyrolysis of polymeric precursors, forming complex morphologies that enable gas separations. Here, by combining kinked and cross-linkable structures in the precursor, CMS membranes are reported that enable a broad spectrum of challenging gas separations.
- Zhongyun Liu
- , Wulin Qiu
- & William J. Koros
-
Review Article |
 Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
This Review discusses recent progress in bioinspired nanocomposite design, emphasizing the role of hierarchical structuring at distinct length scales to create multifunctional, lightweight and robust structural materials for diverse technological applications.
- Dhriti Nepal
- , Saewon Kang
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning heat capacities
Machine learning heat capacities
As metal–organic frameworks move towards practical application, data for an expanded range of physical properties are needed. Molecular-level modelling and data science can play an important role.
- Randall Q. Snurr
-
News & Views |
 Move imperceptibly
Move imperceptibly
Pine cones deform ultraslowly as humidity changes, which is mostly driven by the spring-shaped and square microtubular heterostructure of the vascular bundles. This mechanism inspires the development of soft actuators with imperceptible but efficient motion under environmental stimuli.
- Cecilia Laschi
- & Barbara Mazzolai
-
Article |
 Unperceivable motion mimicking hygroscopic geometric reshaping of pine cones
Unperceivable motion mimicking hygroscopic geometric reshaping of pine cones
The ultra-slow reshaping of pine cones is dominated by the unique spring/square heterostructure in their vascular bundles, with the velocity slowed by sclereids. Inspired by this motion, a soft actuator showing unperceivable motion was developed.
- Feilong Zhang
- , Man Yang
- & Shutao Wang
-
Article |
 Active tissue adhesive activates mechanosensors and prevents muscle atrophy
Active tissue adhesive activates mechanosensors and prevents muscle atrophy
An implantable tissue adhesive soft actuator adheres to muscle, generating mechanical stimulation, and activates mechanosensing pathways for prevention of atrophy in disuse muscles.
- Sungmin Nam
- , Bo Ri Seo
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 Unusual microstructures by 3D printing
Unusual microstructures by 3D printing
Additive manufacturing imparts defects in as-built titanium alloy microstructures, which form internally twinned nanoprecipitates with heat treatment to yield attractive mechanical properties.
- Amy J. Clarke
-
Article |
 A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
Heat capacity of nanoporous materials is important for processes such as carbon capture, as this can affect process design energy requirements. Here, a machine learning approach for heat capacity prediction, trained on density functional theory simulations, is presented and experimentally verified.
- Seyed Mohamad Moosavi
- , Balázs Álmos Novotny
- & Berend Smit
-
Article |
 Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Biohybrid microrobots consisting of nanoparticle-modified microalgae are constructed for active drug delivery in the lungs. In an acute bacterial pneumonia model, the microrobots effectively reduce bacterial burden and lessen animal mortality.
- Fangyu Zhang
- , Jia Zhuang
- & Joseph Wang
-
Article |
 Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Laser additive manufacturing can be exploited to generate unique internally twinned nanoprecipitates in commercial titanium alloys, paving the way to fabricate ultrastrong metallic materials with intricate shapes for broad applications.
- Yuman Zhu
- , Kun Zhang
- & Aijun Huang
-
Comment |
 Growing designability in structural materials
Growing designability in structural materials
Structural materials are critical components for our daily lives and industries. This Comment highlights the emerging concepts in structural materials over the past two decades, particularly the multi-principal element alloys, heterostructured materials and additive manufacturing that enables the fabrication of complex architectures.
- Robert O. Ritchie
- & Xiaoyu Rayne Zheng
-
Article |
 Transient nuclear deformation primes epigenetic state and promotes cell reprogramming
Transient nuclear deformation primes epigenetic state and promotes cell reprogramming
Mechanical confinement of fibroblasts into micrometre-sized channels deforms the cell nucleus, leading to temporary nuclear lamina destablization and disassembly, loss of lamina-associated domains in chromatin and a decrease in histone and DNA methylation. These mechanically induced alterations in chromatin boost the conversion of fibroblasts into neurons and pluripotent stem cells and thus can be explored for cell engineering applications.
- Yang Song
- , Jennifer Soto
- & Song Li

 Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors Floating artificial leaves
Floating artificial leaves A biopolymer to fight pancreatic cancer
A biopolymer to fight pancreatic cancer