Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access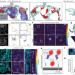 Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
High-speed molecular tracking is integrated with three-dimensional electron microscopy to map the diffusion distribution and ultrastructure of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contact sites, revealing the ability of high-speed single-molecule imaging to map contact site interface structures and corresponding diffusion landscapes.
- Christopher J. Obara
- , Jonathon Nixon-Abell
- & Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access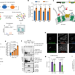 Ubiquitination regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of endoplasmic reticulum
Ubiquitination regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of endoplasmic reticulum
Ubiquitination of the receptor FAM134B regulates ER-phagy and remodelling of the endoplasmic reticulum in response to cellular demands.
- Alexis González
- , Adriana Covarrubias-Pinto
- & Ivan Dikić
-
Article
| Open Access Heteromeric clusters of ubiquitinated ER-shaping proteins drive ER-phagy
Heteromeric clusters of ubiquitinated ER-shaping proteins drive ER-phagy
The membrane-shaping protein ARL6IP1 is involved in the selective degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum, and this process depends on its ubiquitination and interaction with other membrane-shaping proteins such as FAM134B.
- Hector Foronda
- , Yangxue Fu
- & Christian A. Hübner
-
Article |
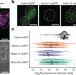 In situ architecture of the ER–mitochondria encounter structure
In situ architecture of the ER–mitochondria encounter structure
Integrative structural biology combining quantitative live imaging, cryo-correlative microscopy, subtomogram averaging and molecular modelling enables in situ determination of the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria encounter complex in yeast.
- Michael R. Wozny
- , Andrea Di Luca
- & Wanda Kukulski
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of translation and protein biogenesis at the ER membrane
Visualization of translation and protein biogenesis at the ER membrane
Structural studies of the ribosome-associated endoplasmic reticulum translocon complex based on cryo-electron tomography and molecular modelling reveal multiple intermediate states and interactions between the components of the complex and its cofactors.
- Max Gemmer
- , Marten L. Chaillet
- & Friedrich Förster
-
Article |
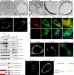 CLSTN3β enforces adipocyte multilocularity to facilitate lipid utilization
CLSTN3β enforces adipocyte multilocularity to facilitate lipid utilization
An adipocyte-selective product of the Clstn3 locus (CLSTN3β) facilitates the use of stored triglyceride by limiting lipid droplet (LD) expansion, defining a molecular mechanism that regulates LD form and function to facilitate lipid utilization in thermogenic adipocytes.
- Kevin Qian
- , Marcus J. Tol
- & Peter Tontonoz
-
Article |
 Mechanism of an intramembrane chaperone for multipass membrane proteins
Mechanism of an intramembrane chaperone for multipass membrane proteins
Biochemical and structural analysis of intermediates during multipass membrane protein biogenesis showed how an intramembrane chaperone guides nascent membrane proteins to a semi-enclosed lipid-filled cavity where they are inserted and folded correctly.
- Luka Smalinskaitė
- , Min Kyung Kim
- & Ramanujan S. Hegde
-
Article
| Open Access Substrate-driven assembly of a translocon for multipass membrane proteins
Substrate-driven assembly of a translocon for multipass membrane proteins
Biochemical reconstitution and functional analysis reveal how newly synthesized multipass membrane proteins dynamically remodel the translocon to facilitate their successful biogenesis.
- Arunkumar Sundaram
- , Melvin Yamsek
- & Robert J. Keenan
-
Article |
 A phosphoinositide signalling pathway mediates rapid lysosomal repair
A phosphoinositide signalling pathway mediates rapid lysosomal repair
Lysosomal membrane damage triggers a lipid signalling pathway that repairs lysosomes via lipid transport at newly established endoplasmic reticulum–lysosomal membrane contact sites.
- Jay Xiaojun Tan
- & Toren Finkel
-
Article |
 The role of NSP6 in the biogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2 replication organelle
The role of NSP6 in the biogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2 replication organelle
The non-structural protein NSP6 in SARS-CoV-2 has a key role in viral replication by zippering the endoplasmic reticulum membrane to establish connectors between the double-membrane vesicles of the viral replication organelle and the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Simona Ricciardi
- , Andrea Maria Guarino
- & Maria Antonietta De Matteis
-
Article
| Open Access ER proteins decipher the tubulin code to regulate organelle distribution
ER proteins decipher the tubulin code to regulate organelle distribution
The endoplasmic reticulum proteins CLIMP63, kinectin and p180 bind preferentially to subsets of microtubules with different post-translational modifications, thereby linking the ‘tubulin code’ to the intracellular distribution of membrane organelles.
- Pengli Zheng
- , Christopher J. Obara
- & Craig Blackstone
-
Article |
 An intramembrane chaperone complex facilitates membrane protein biogenesis
An intramembrane chaperone complex facilitates membrane protein biogenesis
The PAT complex, an intermembrane chaperone complex comprising the ER-resident membrane proteins CCDC47 and Asterix, directly interacts with nascent transmembrane domains to facilitate the biogenesis of multi-spanning membrane proteins.
- Patrick J. Chitwood
- & Ramanujan S. Hegde
-
Article |
 Nitrosative stress drives heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Nitrosative stress drives heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
iNOS-driven dysregulation of the IRE1α–XBP1 pathway leads to cardiomyocyte dysfunction in mice and recapitulates the systemic and cardiovascular features of human heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
- Gabriele G. Schiattarella
- , Francisco Altamirano
- & Joseph A. Hill
-
Letter |
 Cryo-EM structure of the protein-conducting ERAD channel Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3
Cryo-EM structure of the protein-conducting ERAD channel Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3
The structure of yeast Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3 shows that Hrd1 forms an aqueous cavity with a lateral seal within the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, shedding light on how misfolded proteins are transported out of the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Stefan Schoebel
- , Wei Mi
- & Maofu Liao
-
Letter |
 Reconstitution of the tubular endoplasmic reticulum network with purified components
Reconstitution of the tubular endoplasmic reticulum network with purified components
In the presence of GTP, a tubular endoplasmic reticulum network can be reconstituted with only two purified membrane proteins.
- Robert E. Powers
- , Songyu Wang
- & Tom A. Rapoport
-
Letter |
 The SND proteins constitute an alternative targeting route to the endoplasmic reticulum
The SND proteins constitute an alternative targeting route to the endoplasmic reticulum
Experiments in yeast cells show that three proteins—Snd1, Snd2 and Snd3—provide an alternative pathway for targeting of cellular proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Naama Aviram
- , Tslil Ast
- & Maya Schuldiner
-
Letter |
 Receptor-mediated selective autophagy degrades the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus
Receptor-mediated selective autophagy degrades the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus
In yeast, the novel protein Atg40 is enriched in the cortical and cytoplasmic endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and loads these ER subdomains into autophagosomes to facilitate ER autophagy; Atg39 localizes to the perinuclear ER and induces autophagic sequestration of part of the nucleus, thus ensuring cell survival under nitrogen-deprived conditions.
- Keisuke Mochida
- , Yu Oikawa
- & Hitoshi Nakatogawa
-
Letter |
 Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum turnover by selective autophagy
Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum turnover by selective autophagy
The protein FAM134B is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident receptor that facilitates ER autophagy, and downregulation of this protein (mutations of which are also known to cause sensory neuropathy in humans) results in expanded ER structures and degeneration of mouse sensory neurons.
- Aliaksandr Khaminets
- , Theresa Heinrich
- & Ivan Dikic
-
Letter |
 Repeated ER–endosome contacts promote endosome translocation and neurite outgrowth
Repeated ER–endosome contacts promote endosome translocation and neurite outgrowth
Repeated contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and a subset of endosomes called late endosomes (LEs) is shown to promote microtubule-dependent translocation of LEs to the cell periphery and their subsequent fusion with the plasma membrane to induce outgrowth of neuronal protrusions.
- Camilla Raiborg
- , Eva M. Wenzel
- & Harald Stenmark
-
Letter |
 The unfolded protein response governs integrity of the haematopoietic stem-cell pool during stress
The unfolded protein response governs integrity of the haematopoietic stem-cell pool during stress
Molecular, pharmacological and functional data show that haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are predisposed to ER-stress-mediated apoptosis compared to closely related progenitors; a framework for understanding how stress signalling is coordinated within the hematopoietic hierarchy and integrated with stemness is provided, and may have implications for the improvement of clinical transplantation of HSCs.
- Peter van Galen
- , Antonija Kreso
- & John E. Dick
-
Article |
 Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of COPII coat size and function
Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of COPII coat size and function
The size of COPII vesicles is shown to be controlled by monoubiquitylation, with potential implications for cranio-lenticulo-sutural dysplasia and chylomicron retention disease.
- Lingyan Jin
- , Kanika Bajaj Pahuja
- & Michael Rape
-
Letter |
 Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
- Suneng Fu
- , Ling Yang
- & Gökhan S. Hotamisligil

 The UFM1 E3 ligase recognizes and releases 60S ribosomes from ER translocons
The UFM1 E3 ligase recognizes and releases 60S ribosomes from ER translocons