Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A globally relevant stock of soil nitrogen in the Yedoma permafrost domain
A globally relevant stock of soil nitrogen in the Yedoma permafrost domain
A climate sensitive permafrost region (Yedoma domain) was found to contain globally relevant N stock of >40 Gt nitrogen, of which 4 to 16 Gt of the N could become available by thaw until 2100. This study increases the current estimates by nearly 50%.
- Jens Strauss
- , Christina Biasi
- & Guido Grosse
-
Article
| Open Access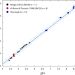 Marine phosphate availability and the chemical origins of life on Earth
Marine phosphate availability and the chemical origins of life on Earth
Phosphate is critical for all life on Earth but its origins have remained enigmatic. Experiments indicate that phosphate may have been abundant in ancient Fe-rich seawater, providing a crucial ingredient for the origins of life on Earth.
- Matthew P. Brady
- , Rosalie Tostevin
- & Nicholas J. Tosca
-
Article
| Open Access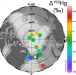 Mercury isotope evidence for Arctic summertime re-emission of mercury from the cryosphere
Mercury isotope evidence for Arctic summertime re-emission of mercury from the cryosphere
Arctic warming thaws permafrost, leading to enhanced soil mercury transport to the Arctic Ocean. Mercury isotope signatures in arctic rivers, ocean and atmosphere suggest that permafrost mercury is buried in marine sediment and not emitted to the global atmosphere
- Beatriz Ferreira Araujo
- , Stefan Osterwalder
- & Jeroen E. Sonke
-
Article
| Open Access Warming and redistribution of nitrogen inputs drive an increase in terrestrial nitrous oxide emission factor
Warming and redistribution of nitrogen inputs drive an increase in terrestrial nitrous oxide emission factor
Soil nitrogen isotopic composition is used to drive the IsoTONE model, which is constrained with measurements of tropospheric nitrous oxide isotopic composition. The model results reveal causes of rising mean global nitrous oxide emission factor.
- E. Harris
- , L. Yu
- & P. Rayner
-
Article
| Open Access Estuarine plastisphere as an overlooked source of N2O production
Estuarine plastisphere as an overlooked source of N2O production
The roles of marine plastisphere in global nitrogen cycling are largely unknown. Here, the authors indicate that the plastisphere could act as a potential source of N2O production, which is mainly regulated by the biotic denitrification
- Xiaoxuan Su
- , Leyang Yang
- & Yong-guan Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access 86Kr excess and other noble gases identify a billion-year-old radiogenically-enriched groundwater system
86Kr excess and other noble gases identify a billion-year-old radiogenically-enriched groundwater system
Noble gases confirm billion-year groundwater residence times and external fluxes in deep crustal settings globally with implications for subsurface habitability and economic reservoir formation over planetary timescales both on Earth and beyond
- O. Warr
- , C. J. Ballentine
- & B. Sherwood Lollar
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: Evidence confirms an anthropic origin of Amazonian Dark Earths
Reply to: Evidence confirms an anthropic origin of Amazonian Dark Earths
- Lucas C. R. Silva
- , Rodrigo Studart Corrêa
- & Roberto Ventura Santos
-
Article
| Open Access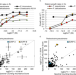 Adaptive responses of marine diatoms to zinc scarcity and ecological implications
Adaptive responses of marine diatoms to zinc scarcity and ecological implications
Here the authors identify two zinc/cobalt responsive proteins (ZCRPs) in marine diatoms, determining their functional roles in trace metal transport and homeostasis, as well as their application as an indicator of oceanic Zn stress.
- Riss M. Kellogg
- , Mark A. Moosburner
- & Mak A. Saito
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of the soil microbiome underlying N2O emissions from global wetlands
Structure and function of the soil microbiome underlying N2O emissions from global wetlands
The wetland soil microbiome has a major impact on greenhouse gas emissions. Here the authors characterize how a group of archaea contribute to N2O emissions and find that climate and land use changes could promote these organisms.
- Mohammad Bahram
- , Mikk Espenberg
- & Ülo Mander
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidative metabolisms catalyzed Earth’s oxygenation
Oxidative metabolisms catalyzed Earth’s oxygenation
How Earth’s atmosphere became oxygenated remains enigmatic. Here the authors use mathematical and phylogenetic analyses to find that Earth’s oxygenation is induced by the interactions of microbial oxidative metabolites with sediment minerals.
- Haitao Shang
- , Daniel H. Rothman
- & Gregory P. Fournier
-
Article
| Open Access Superlinear scaling of riverine biogeochemical function with watershed size
Superlinear scaling of riverine biogeochemical function with watershed size
River networks play an important role in biogeochemical processes of the earth system. Here the authors show that cumulative river network function increases faster than watershed size for many biogeochemical processes, particularly at higher river flow, indicating large rivers contribute disproportionately to network function in the Earth System.
- Wilfred M. Wollheim
- , Tamara K. Harms
- & Jacques C. Finlay
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpectedly minor nitrous oxide emissions from fluvial networks draining permafrost catchments of the East Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Unexpectedly minor nitrous oxide emissions from fluvial networks draining permafrost catchments of the East Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Permafrost soils can be substantial sources of nitrous oxide (N2O) to the atmosphere, but no data exist on the N2O footprints of permafrost rivers. Here, the authors show that alpine permafrost rivers are unexpectedly small sources of atmospheric N2O at present.
- Liwei Zhang
- , Sibo Zhang
- & Emily H. Stanley
-
Article
| Open Access Retention of deposited ammonium and nitrate and its impact on the global forest carbon sink
Retention of deposited ammonium and nitrate and its impact on the global forest carbon sink
A study using paired 15N tracers shows atmospheric N deposited in oxidized form is more likely retained by trees, while the reduced form is retained in soil. The authors argue that this is a greater contribution of deposited N to the global forest C sink than previously reported.
- Geshere Abdisa Gurmesa
- , Ang Wang
- & Yunting Fang
-
Article
| Open Access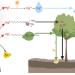 Amazon forests capture high levels of atmospheric mercury pollution from artisanal gold mining
Amazon forests capture high levels of atmospheric mercury pollution from artisanal gold mining
The Peruvian Amazon is facing the highest known input of mercury pollution of any ecosystem globally. Intact forests located near artisanal gold mining are particularly at risk from this toxin.
- Jacqueline R. Gerson
- , Natalie Szponar
- & Emily S. Bernhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Low N2O and variable CH4 fluxes from tropical forest soils of the Congo Basin
Low N2O and variable CH4 fluxes from tropical forest soils of the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin is home to the second largest stretch of continuous tropical forest, but the magnitude of greenhouse fluxes are poorly understood. Here the authors analyze gas samples and find the region is not actually a hotspot of N2O emissions.
- Matti Barthel
- , Marijn Bauters
- & Johan Six
-
Article
| Open Access Application of copper(II)-based chemicals induces CH3Br and CH3Cl emissions from soil and seawater
Application of copper(II)-based chemicals induces CH3Br and CH3Cl emissions from soil and seawater
Halogenated compounds impact stratospheric ozone. This study suggests agricultural application of Cu(II) chemicals induces abiotic production of methyl bromide and methyl chloride from soil and seawater, contributing to the atmospheric halogen load.
- Yi Jiao
- , Wanying Zhang
- & Robert C. Rhew
-
Article
| Open Access Thawing Yedoma permafrost is a neglected nitrous oxide source
Thawing Yedoma permafrost is a neglected nitrous oxide source
During permafrost thaw, nitrogen can be released as the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide, but the magnitude of this flux is unknown. Nitrous oxide emissions from ice-rich permafrost deposits are reported here, showing that emissions increase after thawing and stabilization and could represent an unappreciated positive climate feedback in the Arctic.
- M. E. Marushchak
- , J. Kerttula
- & C. Biasi
-
Article
| Open Access Substantial oxygen consumption by aerobic nitrite oxidation in oceanic oxygen minimum zones
Substantial oxygen consumption by aerobic nitrite oxidation in oceanic oxygen minimum zones
Oxygen is fundamental for marine life, yet it is absent from large areas of the ocean. Here the authors demonstrate that microbial nitrite oxidation effectively consumes oxygen where oxygen concentrations are low, playing a pivotal role in these regions.
- J. M. Beman
- , S. M. Vargas
- & S. D. Wankel
-
Article
| Open Access An abiotic source of Archean hydrogen peroxide and oxygen that pre-dates oxygenic photosynthesis
An abiotic source of Archean hydrogen peroxide and oxygen that pre-dates oxygenic photosynthesis
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has been proposed as an electron donor for photosynthesis before water, however, the amount of H2O2 available on early Earth was thought to be limited. Here the authors propose a new abiotic pathway wherein abrasion of quartz surfaces would have provided enough H2O2.
- Hongping He
- , Xiao Wu
- & Kurt O. Konhauser
-
Article
| Open Access Forest defoliator outbreaks alter nutrient cycling in northern waters
Forest defoliator outbreaks alter nutrient cycling in northern waters
Defoliating insects disrupt nutrient cycling of boreal catchments by redistributing carbon and nitrogen from forests to lakes. The resulting shift in lake biogeochemistry exceeds broader between-year trends observed across the boreal and north temperate region.
- Samuel G. Woodman
- , Sacha Khoury
- & Andrew J. Tanentzap
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of intensifying nitrogen limitation on ocean net primary production is fingerprinted by nitrogen isotopes
Impact of intensifying nitrogen limitation on ocean net primary production is fingerprinted by nitrogen isotopes
Projected declines in marine primary production are underpinned by a slowdown in nitrogen supplied to surface waters. Here the authors detail a new means to detect this slowdown and describe major shifts in the 21st century oceanic nitrogen cycle.
- Pearse J. Buchanan
- , Olivier Aumont
- & Alessandro Tagliabue
-
Article
| Open Access Antarctic ozone hole modifies iodine geochemistry on the Antarctic Plateau
Antarctic ozone hole modifies iodine geochemistry on the Antarctic Plateau
The Antarctic ozone hole has had far-reaching impacts, but effects on geochemical cycles in polar regions is still unknown. Iodine records from the interior of Antarctica provide evidence for human alteration of the natural geochemical cycle of this essential element.
- Andrea Spolaor
- , François Burgay
- & Alfonso Saiz-Lopez
-
Article
| Open Access Fire-derived phosphorus fertilization of African tropical forests
Fire-derived phosphorus fertilization of African tropical forests
Nowhere is biomass burning more abundant than on the African continent, but the biogeochemical impacts on forests are poorly understood. Here the authors show that biomass burning leads to high phosphorus deposition in the Congo basin, which scales with forest age as a result of increasing canopy complexity.
- Marijn Bauters
- , Travis W. Drake
- & Pascal Boeckx
-
Article
| Open Access Methane from microbial hydrogenolysis of sediment organic matter before the Great Oxidation Event
Methane from microbial hydrogenolysis of sediment organic matter before the Great Oxidation Event
Microbial CH4 kept the early Earth warm under the faint young sun, but clear records are lacking. Here the authors present isotopic evidence that CH4 seepage in the Canadian shield is from hydrogen biodegradation in a Neoarchean ecosystem rather than an abiotic synthesis product.
- Xinyu Xia
- & Yongli Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 via molybdenum-nitrogenase in a low molybdenum Proterozoic ocean analogue
Purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 via molybdenum-nitrogenase in a low molybdenum Proterozoic ocean analogue
N2 fixation was key to the expansion of life on Earth, but which organisms fixed N2 and if Mo-nitrogenase was functional in the low Mo early ocean is unknown. Here, the authors show that purple sulfur bacteria fix N2 using Mo-nitrogenase in a Proterozoic ocean analogue, despite low Mo conditions.
- Miriam Philippi
- , Katharina Kitzinger
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
-
Article
| Open Access Transporter characterisation reveals aminoethylphosphonate mineralisation as a key step in the marine phosphorus redox cycle
Transporter characterisation reveals aminoethylphosphonate mineralisation as a key step in the marine phosphorus redox cycle
Here the authors show that 2-aminoethylphosphonate (2AEP) mineralisation is widespread in the global ocean, operating independently of exogenous inorganic phosphate concentration. They propose 2AEP may be a major route for the regeneration of phosphate required to support marine primary production.
- Andrew R. J. Murphy
- , David J. Scanlan
- & Ian D. E. A. Lidbury
-
Article
| Open Access Plant mixture balances terrestrial ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry
Plant mixture balances terrestrial ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry
Plant and soil C:N:P ratios are critical to ecosystem functioning, but it remains uncertain how plant diversity affects terrestrial C:N:P. In this meta-analysis of 169 studies, the authors find that plant mixtures can balance plant and soil C:N:P ratios according to background soil C:N:P.
- Xinli Chen
- & Han Y. H. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Above- and belowground biodiversity jointly tighten the P cycle in agricultural grasslands
Above- and belowground biodiversity jointly tighten the P cycle in agricultural grasslands
Relationships between biodiversity and phosphorus cycling and the underlying processes are complex. Here the authors analyse a biodiversity manipulation experiment and an agricultural management gradient to show how plant and mycorrhizal fungal diversity promote phosphorus exploitation.
- Yvonne Oelmann
- , Markus Lange
- & Wolfgang Wilcke
-
Article
| Open Access Global distribution patterns of marine nitrogen-fixers by imaging and molecular methods
Global distribution patterns of marine nitrogen-fixers by imaging and molecular methods
Nitrogen fixation by diazotrophs is critical for marine primary production. Using Tara Oceans datasets, this study combines a quantitative image analysis pipeline with metagenomic mining to provide an improved global overview of diazotroph abundance, diversity and distribution.
- Juan José Pierella Karlusich
- , Eric Pelletier
- & Rachel A. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying nitrogen fixation by heterotrophic bacteria in sinking marine particles
Quantifying nitrogen fixation by heterotrophic bacteria in sinking marine particles
N2 fixation by heterotrophic bacteria has recently been found to take place on sinking marine particles, but an understanding of its regulation and importance is lacking. Here the authors develop a trait-based model for this N2 fixation, finding that this once overlooked process could have global importance.
- Subhendu Chakraborty
- , Ken H. Andersen
- & Lasse Riemann
-
Article
| Open Access Ecology of inorganic sulfur auxiliary metabolism in widespread bacteriophages
Ecology of inorganic sulfur auxiliary metabolism in widespread bacteriophages
Some bacteriophage encode auxiliary metabolic genes (AMGs) that impact host metabolism and biogeochemical cycling during infection. Here the authors identify hundreds of AMGs in environmental phage encoding sulfur oxidation genes and use their global distribution to infer phage-mediated biogeochemical impacts.
- Kristopher Kieft
- , Zhichao Zhou
- & Karthik Anantharaman
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomolar phosphate supply and its recycling drive net community production in the subtropical North Pacific
Nanomolar phosphate supply and its recycling drive net community production in the subtropical North Pacific
Primary productivity in the oligotrophic ocean sustains Earth’s ecosystems, but nutrient concentrations are vanishingly low. Here the authors measure nanomolar macronutrient concentrations in the North Pacific and find that net community production is sustained through high rates of phosphorus recycling.
- Fuminori Hashihama
- , Ichiro Yasuda
- & Masao Ishii
-
Article
| Open Access Lateral advection supports nitrogen export in the oligotrophic open-ocean Gulf of Mexico
Lateral advection supports nitrogen export in the oligotrophic open-ocean Gulf of Mexico
The middle of the Gulf of Mexico is stratified and highly oligotrophic, yet there are anomalously high fluxes of sinking particulate matter from the euphotic zone. Here the authors show that lateral advection of organic matter supports nitrogen export in the Gulf of Mexico’s open ocean.
- Thomas B. Kelly
- , Angela N. Knapp
- & Michael R. Stukel
-
Article
| Open Access Small sinking particles control anammox rates in the Peruvian oxygen minimum zone
Small sinking particles control anammox rates in the Peruvian oxygen minimum zone
Up to 40% of the ocean’s fixed nitrogen is lost in oxygen minimum zones (OMZs) by anammox, but despite the importance of this process, nitrogen loss patterns in OMZs are difficult to predict. Here the authors show that ammonium release from small particles is a major control of anammox in the Peruvian OMZ.
- Clarissa Karthäuser
- , Soeren Ahmerkamp
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
-
Article
| Open Access Global health effects of future atmospheric mercury emissions
Global health effects of future atmospheric mercury emissions
Mercury is a neurotoxin and pollutant with enhanced emissions from anthropogenic activities. Here, the authors develop a global emissions, transport, and human risk model and find substantial future losses in revenue and public health if emission reductions proposed by the Minamata Convention are delayed.
- Yanxu Zhang
- , Zhengcheng Song
- & Ping Li
-
Article
| Open Access Nutrient content and stoichiometry of pelagic Sargassum reflects increasing nitrogen availability in the Atlantic Basin
Nutrient content and stoichiometry of pelagic Sargassum reflects increasing nitrogen availability in the Atlantic Basin
The macroalgae Sargassum has grown for centuries in the oligotrophic North Atlantic supported by natural nutrient sources and cycling. Here the authors show that changes in tissue nutrient contents since the 1980s reflect global anthropogenic nitrogen enrichment, causing blooms in the wider Atlantic basin.
- B. E. Lapointe
- , R. A. Brewton
- & P. L. Morton
-
Article
| Open Access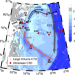 The 79°N Glacier cavity modulates subglacial iron export to the NE Greenland Shelf
The 79°N Glacier cavity modulates subglacial iron export to the NE Greenland Shelf
A large fraction of ice sheet discharge enters the ocean subsurface from underneath large floating ice-tongues. Here the authors show that associated nutrient export may be governed by shelf circulation and, especially for Fe, particle-dissolved phase exchanges, which is largely independent from freshwater Fe content.
- Stephan Krisch
- , Mark James Hopwood
- & Eric Pieter Achterberg
-
Article
| Open Access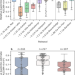 The kaolinite shuttle links the Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events
The kaolinite shuttle links the Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events
Expanded phosphorus availability possibly triggered a marine bioproduction boom after 2.3 billion years ago, but its delivery mechanisms remain unclear. Here we propose a kaolinite shuttle which efficiently adsorbs phosphorus in continental weathering settings and releases it under marine conditions.
- Weiduo Hao
- , Kaarel Mänd
- & Kurt O. Konhauser
-
Article
| Open Access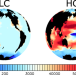 Zooplankton grazing of microplastic can accelerate global loss of ocean oxygen
Zooplankton grazing of microplastic can accelerate global loss of ocean oxygen
Microplastic pollution is a major threat to marine food webs, but the wider ranging impacts on global ocean biogeochemistry are poorly understood. Here the authors use an Earth system model to determine that zooplankton grazing on microplastics could exacerbate trends in ocean oxygen loss.
- K. Kvale
- , A. E. F. Prowe
- & A. Oschlies
-
Article
| Open Access A committed fourfold increase in ocean oxygen loss
A committed fourfold increase in ocean oxygen loss
Ocean warming and changing circulation as a result of climate change are driving down oxygen levels and threatening ecosystems. Here the author shows that though immediate cessation of anthropogenic CO2 emissions would halt upper ocean oxygen loss, it would continue in the deep ocean for 100 s of years.
- Andreas Oschlies
-
Article
| Open Access Bomb 137Cs in modern honey reveals a regional soil control on pollutant cycling by plants
Bomb 137Cs in modern honey reveals a regional soil control on pollutant cycling by plants
Radioactive 137Cs is a fission product remaining in the environment from mid-20th century nuclear testing. Here the authors show that vegetation thousands of kilometers from testing sites continues to cycle 137Cs, and consequently, bees magnify this contaminant in honey in regions with low soil potassium.
- J. M. Kaste
- , P. Volante
- & A. J. Elmore
-
Article
| Open Access Lightning strikes as a major facilitator of prebiotic phosphorus reduction on early Earth
Lightning strikes as a major facilitator of prebiotic phosphorus reduction on early Earth
Determining the origins of life on Earth is confounded by the fact that the sources of nutrients necessary to create early life forms remain mysterious. Here the authors show that lightning strikes could have supplied a major source of essential phosphorus on early Earth.
- Benjamin L. Hess
- , Sandra Piazolo
- & Jason Harvey
-
Article
| Open Access Potentially bioavailable iron produced through benthic cycling in glaciated Arctic fjords of Svalbard
Potentially bioavailable iron produced through benthic cycling in glaciated Arctic fjords of Svalbard
The impacts of a melting Arctic on the biogeochemistry of marine ecosystems are unknown. Here, the authors investigate glacial input of iron to Svalbard fjords finding that reworking of glacial iron in fjord sediment is important to make iron bioavailable, but could be susceptible to glacial retreat.
- Katja Laufer-Meiser
- , Alexander B. Michaud
- & Bo Barker Jørgensen
-
Article
| Open Access Active methanogenesis during the melting of Marinoan snowball Earth
Active methanogenesis during the melting of Marinoan snowball Earth
The deglaciation of Marinoan snowball Earth (~635 Myr ago) has been associated with potentially extensive CH4 emissions in relation to transient marine euxinia. Here, the authors find that active methanogenesis occurred during the termination of Marinoan snowball Earth, fueled by methyl sulfide production in sulfidic seawater.
- Zhouqiao Zhao
- , Bing Shen
- & Haoran Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Manganese co-limitation of phytoplankton growth and major nutrient drawdown in the Southern Ocean
Manganese co-limitation of phytoplankton growth and major nutrient drawdown in the Southern Ocean
Southern Ocean productivity is a crucial component of the carbon cycle, but phytoplankton there are thought to be limited by iron. Here the authors conduct trace metal incubation experiments across the Drake Passage, finding that manganese can play an unexpected role in restricting phytoplankton growth.
- Thomas J. Browning
- , Eric P. Achterberg
- & Edward Mawji
-
Article
| Open Access Anoxic chlorophyll maximum enhances local organic matter remineralization and nitrogen loss in Lake Tanganyika
Anoxic chlorophyll maximum enhances local organic matter remineralization and nitrogen loss in Lake Tanganyika
Enigmatic blooms of phytoplankton in aquatic oxygen-deficient zones could exacerbate depletion of nitrogen. Here the authors perform stable isotope experiments on the oxygen-deficient waters of Lake Tanganyika in Africa, finding that blooms drive down fixed nitrogen and could expand as a result of climate change.
- Cameron M. Callbeck
- , Benedikt Ehrenfels
- & Carsten J. Schubert
-
Article
| Open Access Mineral phosphorus drives glacier algal blooms on the Greenland Ice Sheet
Mineral phosphorus drives glacier algal blooms on the Greenland Ice Sheet
Melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet—a threat for sea level rise—is accelerated by ice algal blooms. Here the authors find a link between mineral phosphorus and glacier algae, indicating that dust-derived nutrients aid bloom development, thereby impacting ice sheet melting.
- Jenine McCutcheon
- , Stefanie Lutz
- & Liane G. Benning
-
Article
| Open Access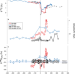 Upper limits on the extent of seafloor anoxia during the PETM from uranium isotopes
Upper limits on the extent of seafloor anoxia during the PETM from uranium isotopes
The expansion of oceanic anoxia during the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum has important implications for faunal turnover patterns and global biogeochemical cycles. Here the authors use uranium isotopes and a biogeochemical model to suggest that the areal expansion of anoxia must have been limited to 10-fold.
- Matthew O. Clarkson
- , Timothy M. Lenton
- & Derek Vance
-
Article
| Open Access A persistently low level of atmospheric oxygen in Earth’s middle age
A persistently low level of atmospheric oxygen in Earth’s middle age
Constraining the rise in atmospheric oxygen through the early Earth is important to understand the evolution of complex life. Here, the authors find that a major rise in atmospheric oxygen level occurred after the Great Oxidation Event, followed by pO2 within 1% of present atmospheric level through most of the Proterozoic Eon (2.4 to 0.65 Ga).
- Xiao-Ming Liu
- , Linda C. Kah
- & Robert M. Hazen

 Beaver dams overshadow climate extremes in controlling riparian hydrology and water quality
Beaver dams overshadow climate extremes in controlling riparian hydrology and water quality