Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access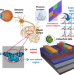 Programmable ferroelectric bionic vision hardware with selective attention for high-precision image classification
Programmable ferroelectric bionic vision hardware with selective attention for high-precision image classification
Selective attention is an efficient processing strategy to allocate computational resources for pivotal optical information. Here, the authors propose a bionic vision hardware to emulate the behavior, showing a potential in image classification.
- Rengjian Yu
- , Lihua He
- & Huipeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Three-to-one analog signal modulation with a single back-bias-controlled reconfigurable transistor
Three-to-one analog signal modulation with a single back-bias-controlled reconfigurable transistor
Designing efficient reconfigurable field effect transistors remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a transistor with three distinct operation modes, realized directly on an industrial 22nm FDSOI platform, demonstrating a reconfigurable analog circuit element with signal follower, phase shifter, and frequency doubler operation.
- Maik Simon
- , Halid Mulaosmanovic
- & Jens Trommer
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip generation and dynamic piezo-optomechanical rotation of single photons
On-chip generation and dynamic piezo-optomechanical rotation of single photons
Hybrid quantum technologies synergistically combine different types of systems with complementary strengths. Here, the authors show monolithic integration and control of quantum dots and the emitted single photons in a surface acoustic wave-driven GaAs integrated quantum photonic circuit.
- Dominik D. Bühler
- , Matthias Weiß
- & Hubert J. Krenner
-
Article
| Open Access High-lying valley-polarized trions in 2D semiconductors
High-lying valley-polarized trions in 2D semiconductors
Here, the authors observe tightly bound, valley-polarized, UV-emissive trions in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide transistors. These are quasiparticles composed of an electron from a high-lying conduction band with negative effective mass, a hole from the first valence band, and an additional charge from a band-edge state.
- Kai-Qiang Lin
- , Jonas D. Ziegler
- & John M. Lupton
-
Article
| Open Access Unimon qubit
Unimon qubit
While transmon is the most widely used superconducting qubit, the search for alternative qubit designs with improved characteristic is ongoing. Hyyppä et al. demonstrate a novel superconducting qubit, the unimon, that combines high anharmonicity and protection against low-frequency charge noise and flux noise.
- Eric Hyyppä
- , Suman Kundu
- & Mikko Möttönen
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous universal conductance as a hallmark of non-locality in a Majorana-hosted superconducting island
Anomalous universal conductance as a hallmark of non-locality in a Majorana-hosted superconducting island
The ability to detect the non-local nature of topological states in electron transport is highly desirable for topological quantum computation. Hao et al. propose a two-terminal transport scheme to detect the non-locality of a topological superconducting island via anomalous scaling of the tunnelling conductance.
- Yiru Hao
- , Gu Zhang
- & Dong E. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Stokes meta-hologram toward optical cryptography
Stokes meta-hologram toward optical cryptography
Achieving optical cryptography scheme with both high capacity and security is highly desirable. Here, authors report a Stokes meta-hologram with a hierarchical encryption strategy that allows vector encryptions to produce depth-masked ciphertexts.
- Xuyue Guo
- , Peng Li
- & Jianlin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Nanophotonic light sources with programmable emission spectrum are important building blocks for integrated photonics, sensing and optical computing. Here the authors tune the complex laser spectrum of a network laser achieving selective lasing of a single, two or more modes.
- Dhruv Saxena
- , Alexis Arnaudon
- & Riccardo Sapienza
-
Article
| Open Access The gate injection-based field-effect synapse transistor with linear conductance update for online training
The gate injection-based field-effect synapse transistor with linear conductance update for online training
The conventional von Neumann computing architecture is ill suited to data intensive tasks as data must be repeated moved between the separated processing and memory units. Here, Seo et al propose a CMOS compatible, highly linear gate injection field-effect transistor where data can be both stored and processed.
- Seokho Seo
- , Beomjin Kim
- & Shinhyun Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic Pseudo-Spin-Hall effect in acoustic metamaterials
Synthetic Pseudo-Spin-Hall effect in acoustic metamaterials
Controlling emission and propagation of acoustic waves offers new design opportunities for acoustic devices. Here the authors demonstrate such controls thanks to the emergence of a synthetic pseudo-spin in two-dimensional acoustic metamaterial.
- Matthew Weiner
- , Xiang Ni
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article
| Open Access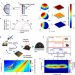 Spray-coated perovskite hemispherical photodetector featuring narrow-band and wide-angle imaging
Spray-coated perovskite hemispherical photodetector featuring narrow-band and wide-angle imaging
Hemispherical photodetectors allow wide sight angle without the complex optical paths of fisheye lenses. Here, Wei et al, report a spray-coated quasi-two-dimensional perovskite hemispherical photodetector with wavelength selective response from the visible to the near-infrared.
- Xiaopeng Feng
- , Yuhong He
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Standardized measurement of dielectric materials’ intrinsic triboelectric charge density through the suppression of air breakdown
Standardized measurement of dielectric materials’ intrinsic triboelectric charge density through the suppression of air breakdown
Determining the triboelectric charge and energy density of dielectric materials is generally limited by many factors, failing to reflect their intrinsic behaviour. Here, a standardized strategy is proposed employing contact-separation TENG and supressing air-breakdown to assess max triboelectric charge and energy densities leading to an updated triboelectric series.
- Di Liu
- , Linglin Zhou
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access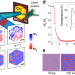 All-optical control of spin in a 2D van der Waals magnet
All-optical control of spin in a 2D van der Waals magnet
The use of light in driving the magnetization of materials has great technological potential, as well as allowing for insights into the fast dynamics of magnetic systems. Here, the authors combine CrI3, a van der Waals magnet, with WSe2, and demonstrate all optical switching of the resulting heterostructure.
- Maciej Da̧browski
- , Shi Guo
- & Robert J. Hicken
-
Article
| Open Access Two-particle time-domain interferometry in the fractional quantum Hall effect regime
Two-particle time-domain interferometry in the fractional quantum Hall effect regime
Excitations of the fractional quantum Hall states are of great interest because they obey anyonic statistics, but electronic interferometers give contrasting results about their quantum coherence. Here the authors use novel two-particle time-domain interferometry to show that quantum coherence is indeed preserved.
- I. Taktak
- , M. Kapfer
- & D. C. Glattli
-
Article
| Open Access Transition metal dichalcogenide metaphotonic and self-coupled polaritonic platform grown by chemical vapor deposition
Transition metal dichalcogenide metaphotonic and self-coupled polaritonic platform grown by chemical vapor deposition
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) are interesting for nanophotonic applications due to their high refractive index and excitonic properties. Here, the authors report a scalable bottom-up fabrication method to realize arrays of TMDC metastructures showing dielectric optical modes and self-coupled exciton-polaritons.
- Fuhuan Shen
- , Zhenghe Zhang
- & Zefeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Growth of bilayer MoTe2 single crystals with strong non-linear Hall effect
Growth of bilayer MoTe2 single crystals with strong non-linear Hall effect
2D transition metal ditellurides exhibit nontrivial topological phases, but the controlled bottom-up synthesis of these materials is still challenging. Here, the authors report the layer-by-layer growth of large-area bilayer and trilayer 1T’ MoTe2 films, showing thickness-dependent ferroelectricity and nonlinear Hall effect.
- Teng Ma
- , Hao Chen
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access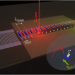 Flying electron spin control gates
Flying electron spin control gates
Spin qubits are a platform for quantum computing. There are many advantages for quantum information processing if the spin qubit can move. Here, Helgers et al. use a surface acoustic wave to define a moving quantum dot and demonstrate the magneticfield-free control of the spin precession, bringing “flying” spin qubits a step closer.
- Paul L. J. Helgers
- , James A. H. Stotz
- & Paulo V. Santos
-
Article
| Open Access Simulating hyperbolic space on a circuit board
Simulating hyperbolic space on a circuit board
Spaces with negative curvature are difficult to realise and investigate experimentally, but they can be emulated with synthetic matter. Here, the authors show how to do this using an electric circuit network, and present a method to characterize and verify the hyperbolic nature of the implemented model.
- Patrick M. Lenggenhager
- , Alexander Stegmaier
- & Tomáš Bzdušek
-
Article
| Open Access Prolonging valley polarization lifetime through gate-controlled exciton-to-trion conversion in monolayer molybdenum ditelluride
Prolonging valley polarization lifetime through gate-controlled exciton-to-trion conversion in monolayer molybdenum ditelluride
Here, the authors devise a strategy for prolonging the valley polarization lifetime in monolayer MoTe2 by converting excitons to trions through gate control, and by taking advantage of the longer valley polarization lifetime of trions.
- Qiyao Zhang
- , Hao Sun
- & Cun-Zheng Ning
-
Article
| Open Access Electric-field control of nonlinear THz spintronic emitters
Electric-field control of nonlinear THz spintronic emitters
Spintronic terahertz (THz) emitters are a class of magnetic heterostructure where femtosecond laser excitations generate THz radiation emission. While they have great potential, electric field control of spintronic emitter remains a challenge. Here, by combining a spintronic emitter with a piezoelectric substrate, Agarwal et al. demonstrate electric field control of THz emission through induced piezostrain.
- Piyush Agarwal
- , Lisen Huang
- & Ranjan Singh
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow-voltage operation of light-emitting diodes
Ultralow-voltage operation of light-emitting diodes
Light emission from 17 types of LEDs is observed at record-low voltages of 36–60% of the bandgaps, which cannot be explained by earlier theories. The electroluminescence-voltage curves reveal a unified mechanism for ultralow-voltage LED operation.
- Yaxiao Lian
- , Dongchen Lan
- & Dawei Di
-
Article
| Open Access General recipe to realize photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers with 100-W-to-1-kW single-mode operation
General recipe to realize photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers with 100-W-to-1-kW single-mode operation
Here, the authors analytically derive the general conditions for 100-W-to-1-kW-class single-mode operation in ultra-large-area (3~10 mm) photonic crystal lasers. Such high power single-mode semiconductor lasers will bring innovation to a wide variety of fields.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Masahiro Yoshida
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article
| Open Access Traps and transport resistance are the next frontiers for stable non-fullerene acceptor solar cells
Traps and transport resistance are the next frontiers for stable non-fullerene acceptor solar cells
Long operational stability is essential to commercialisation of organic solar cells. Here, the authors investigate the thermal degradation of inverted photovoltaic devices based on PM6:Y6 non-fullerene system to reveal that trap-induced transport resistance is primarily responsible for the drop in fill factor.
- Christopher Wöpke
- , Clemens Göhler
- & Carsten Deibel
-
Article
| Open Access Passive mode-locking and terahertz frequency comb generation in resonant-tunneling-diode oscillator
Passive mode-locking and terahertz frequency comb generation in resonant-tunneling-diode oscillator
The authors report passive mode-locking and frequency-comb generation induced by optical feedback in the resonant-tunneling-diode terahertz oscillator, a semiconductor-based oscillator covering the frequency range of 0.1 to 2 THz.
- Tomoki Hiraoka
- , Yuta Inose
- & Koichiro Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Light-intensity-dependent photoresponse time of organic photodetectors and its molecular origin
Light-intensity-dependent photoresponse time of organic photodetectors and its molecular origin
Understanding the charge trapping mechanism in organic semiconductors is crucial to design molecules for high-performance organic photodetectors. Labanti et al. systematically investigate the impact of donor molecular structure on the energetic disorder that affects both shallow and deep trap formation.
- Chiara Labanti
- , Jiaying Wu
- & Ji-Seon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Third harmonic characterization of antiferromagnetic heterostructures
Third harmonic characterization of antiferromagnetic heterostructures
Harmonic measurements have been used extensively in ferromagnetic/heavy metal heterostructures to characterize the magnetization dynamic; however, it has remained unclear about whether such techniques could be applied to antiferromagnetic devices. Here, Cheng et al demonstrate such a harmonic measurement approach in an antiferromagnet.
- Yang Cheng
- , Egecan Cogulu
- & Fengyuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced self-switching of perpendicular magnetization in CoPt single layer
Current-induced self-switching of perpendicular magnetization in CoPt single layer
One challenge for spin-based electronics is the controlled and reliable switching of magnetization without magnetic fields. Here, Liu et al investigate a variety of compositions of CoPt, and determine the specific composition to maximize switching performance, potentially simplifying device design.
- Liang Liu
- , Chenghang Zhou
- & Jingsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Topological phonon transport in an optomechanical system
Topological phonon transport in an optomechanical system
To realize the full promise of topological mechanical vibrations, they have to be controlled successfully at the nanoscale. Here the authors report topological phonon transport in an optomechanical array. This unlocks the full toolbox of cavity optomechanics, coupling light to motion, for the area of topological phononics.
- Hengjiang Ren
- , Tirth Shah
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article
| Open Access Beam steering at the nanosecond time scale with an atomically thin reflector
Beam steering at the nanosecond time scale with an atomically thin reflector
Andersen et al. have demonstrated a new type of beam steering device based on the excitonic response of an atomically thin semiconductor. Using electrostatic gates, the authors achieved tunable steering with switching times on the nanosecond scale.
- Trond I. Andersen
- , Ryan J. Gelly
- & Mikhail D. Lukin
-
Article
| Open Access Creating boundaries along a synthetic frequency dimension
Creating boundaries along a synthetic frequency dimension
The exploration of topological boundary effects is one of the important aspects that could foster the development of future topological photonics devices. Here the authors propose a straightforward method to construct sharp boundaries in synthetic dimensions using a modulated ring resonator strongly coupled to an auxiliary ring.
- Avik Dutt
- , Luqi Yuan
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-sensitive polarization-resolved black phosphorus homojunction photodetector defined by ferroelectric domains
Ultra-sensitive polarization-resolved black phosphorus homojunction photodetector defined by ferroelectric domains
Integrated polarization-sensitive photodetectors are important for sensing applications and optical communication. Here, the authors report the realization of 2D black phosphorus homojunction photodetectors defined by ferroelectric substrates, showing polarization ratios up to 288 and high responsivity in the near-infrared.
- Shuaiqin Wu
- , Yan Chen
- & Jianlu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks
Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks
High-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics has not been achieved before. Here, the authors leverage a room-temperature direct printing strategy to realize an all-MXene-printed integrated system capable of wireless communication, energy harvesting, and smart sensing.
- Yuzhou Shao
- , Lusong Wei
- & Jianfeng Ping
-
Article
| Open Access Optomechanical crystal with bound states in the continuum
Optomechanical crystal with bound states in the continuum
Unsuspended optomechanical systems might enable unique applications for quantum sensing and transduction. Here, the authors demonstrate a two-dimensional slab-on-substrate optomechanical crystal empowered by mechanical bound states in the continuum.
- Shengyan Liu
- , Hao Tong
- & Kejie Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Skyrmion pinning energetics in thin film systems
Skyrmion pinning energetics in thin film systems
Skyrmions, topological spin textures, can be pinned by defects present in the material that hosts them, influencing their motion. Here, Gruber et al show that the skyrmions are pinned at their boundary where the finite size of the skyrmions governs their pinning, and they demonstrate that certain pinning sites can switched on and off in-situ.
- Raphael Gruber
- , Jakub Zázvorka
- & Mathias Kläui
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical tensile structures with ultralow mechanical dissipation
Hierarchical tensile structures with ultralow mechanical dissipation
Low dissipation of fundamental mode is a determinant factor in nanomechanical resonator design. Here the authors realize soft clamping for the fundamental mode in a nanomechanical tensile structure achieving low loss, low mass, and low resonance frequency that render it a perfect force sensor.
- M. J. Bereyhi
- , A. Beccari
- & N. J. Engelsen
-
Article
| Open Access Brightening of a dark monolayer semiconductor via strong light-matter coupling in a cavity
Brightening of a dark monolayer semiconductor via strong light-matter coupling in a cavity
Here, the authors show brightening of dark excitons by strong coupling between cavity photons and high energy, spin-allowed, bright excitons in monolayer WSe2. In this regime, the commonly observed photoluminescence quenching stemming from the fast relaxation to the dark ground state is prevented.
- Hangyong Shan
- , Ivan Iorsh
- & Christian Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Neural sampling machine with stochastic synapse allows brain-like learning and inference
Neural sampling machine with stochastic synapse allows brain-like learning and inference
Neural sampling machines make use of noise to perform learning. Here, Dutta et al. present a hybrid stochastic synapse composed out of a ferroelectric transistor combined with a stochastic selector exhibiting multiplicative synaptic noise required for implementing a neural sample machine.
- Sourav Dutta
- , Georgios Detorakis
- & Suman Datta
-
Article
| Open Access Transmon platform for quantum computing challenged by chaotic fluctuations
Transmon platform for quantum computing challenged by chaotic fluctuations
Superconducting quantum processors need to balance intentional disorder (to protect qubits) and nonlinear resonator coupling (to manipulate qubits), while avoiding chaotic instabilities. Berke et al. use the techniques of many-body localization theory to study the stability of current platforms against quantum chaos.
- Christoph Berke
- , Evangelos Varvelis
- & David P. DiVincenzo
-
Article
| Open Access Implementing in-situ self-organizing maps with memristor crossbar arrays for data mining and optimization
Implementing in-situ self-organizing maps with memristor crossbar arrays for data mining and optimization
Self-organizing maps are data mining tools for unsupervised learning algorithms dealing with big data problems. The authors experimentally demonstrate a memristor-based self-organizing map that is more efficient in computing speed and energy consumption for data clustering, image processing and solving optimization problems.
- Rui Wang
- , Tuo Shi
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Full 2π tunable phase modulation using avoided crossing of resonances
Full 2π tunable phase modulation using avoided crossing of resonances
Though active metasurfaces have been attractive for applications requiring control of optical wavefronts, realizing metasurfaces with full phase control remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a metasurface design strategy for enhanced dynamic phase modulation and tunability.
- Ju Young Kim
- , Juho Park
- & Min Seok Jang
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave-to-optical conversion with a gallium phosphide photonic crystal cavity
Microwave-to-optical conversion with a gallium phosphide photonic crystal cavity
A route to scalability for superconducting quantum computation is the modular approach, which however requires coherent microwave-to-optical conversion. Here the authors use gallium phosphide optomechanical crystal cavities for this task, exploiting their high refractive index and large OM coupling rate.
- Simon Hönl
- , Youri Popoff
- & Paul Seidler
-
Article
| Open Access Memristor-based analogue computing for brain-inspired sound localization with in situ training
Memristor-based analogue computing for brain-inspired sound localization with in situ training
Sound localization is one of the many learning tasks accomplished by the brain based on the binaural signals of the ears. Here, Wu et al demonstrate in-situ learning of sound localization function using a memristor array, with dramatic improvements in energy efficiency.
- Bin Gao
- , Ying Zhou
- & Huaqiang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access An adaptive synaptic array using Fowler–Nordheim dynamic analog memory
An adaptive synaptic array using Fowler–Nordheim dynamic analog memory
While great progress has been made in the applications of machine learning models, training them on conventional computing hardware is an energy intensive process. Here, Mehta et al present an adaptive synaptic array offering considerable improvements in the energy efficiency of training.
- Darshit Mehta
- , Mustafizur Rahman
- & Shantanu Chakrabartty
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced Néel order switching facilitated by magnetic phase transition
Current-induced Néel order switching facilitated by magnetic phase transition
Electrical manipulation of antiferromagnetic order is crucial for future memory devices, but existing switching schemes require a large current density. Here, the authors achieve record low current density switching in FeRh by taking advantage of its antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic phase transition.
- Hao Wu
- , Hantao Zhang
- & Kang L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ground state cooling of an ultracoherent electromechanical system
Ground state cooling of an ultracoherent electromechanical system
’Systems with long coherence times are extremely important for the processing of quantum information. To this end the authors present a system able to cool down a resonator to its quantum mechanical ground state harnessing the large coupling between an ultra-coherent mechanical resonator and a superconducting circuit.’
- Yannick Seis
- , Thibault Capelle
- & Albert Schliesser
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable black phosphorus image sensor for broadband optoelectronic edge computing
Programmable black phosphorus image sensor for broadband optoelectronic edge computing
2D materials represent a promising platform for machine vision and edge computing applications, although usually limited to ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. Here, the authors report the realization of a programmable image sensor based on black phosphorus, implementing multispectral imaging and analog in-memory computing functionalities in the near- to mid-infrared range.
- Seokhyeong Lee
- , Ruoming Peng
- & Mo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding lip language using triboelectric sensors with deep learning
Decoding lip language using triboelectric sensors with deep learning
Lip-language decoding systems are a promising technology to help people lacking a voice live a convenient life with barrier-free communication. Here, authors propose a concept of such system integrating self-powered triboelectric sensors and a well-trained dilated RNN model based on prototype learning.
- Yijia Lu
- , Han Tian
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralarge anti-Stokes lasing through tandem upconversion
Ultralarge anti-Stokes lasing through tandem upconversion
Constructing ultraviolet lasing is of great significance for basic research and medical use. Here the authors present a strategy for generating ultraviolet lasing through a tandem upconversion process with ultralarge anti-Stokes shift (1260 nm).
- Tianying Sun
- , Bing Chen
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Deep learning has an increasing impact to assist research. Here, authors show that a dynamical neural network, trained on a minimal amount of data, can predict the behaviour of spintronic devices with high accuracy and an extremely efficient simulation time.
- Xing Chen
- , Flavio Abreu Araujo
- & Damien Querlioz

 Quantum bath engineering of a high impedance microwave mode through quasiparticle tunneling
Quantum bath engineering of a high impedance microwave mode through quasiparticle tunneling