Analysis
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rainforest transformation reallocates energy from green to brown food webs
Rainforest transformation reallocates energy from green to brown food webs
Conversion of rainforest to plantations in Sumatra leads to higher energetic losses in animal food webs aboveground than belowground, with the belowground energy being reallocated from diverse arthropod communities to invasive earthworms.
- Anton M. Potapov
- , Jochen Drescher
- & Stefan Scheu
-
Article |
 Top-predator recovery abates geomorphic decline of a coastal ecosystem
Top-predator recovery abates geomorphic decline of a coastal ecosystem
Sea otters recolonizing an estuary in California indirectly reduce erosion by reducing burrowing crab abundance, suggesting that restoring predators could be a key mechanism to improve the stability of coastal wetlands and other ecosystems.
- Brent B. Hughes
- , Kathryn M. Beheshti
- & Brian R. Silliman
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent patterns of common species across tropical tree communities
Consistent patterns of common species across tropical tree communities
Inventory data from more than 1 million trees across African, Amazonian and Southeast Asian tropical forests suggests that, despite their high diversity, just 1,053 species, representing a consistent ~2.2% of tropical tree species in each region, constitute half of Earth’s 800 billion tropical trees.
- Declan L. M. Cooper
- , Simon L. Lewis
- & Stanford Zent
-
Article
| Open Access Global methane emissions from rivers and streams
Global methane emissions from rivers and streams
A spatially explicit global estimate reveals that land–water connections are important for regulating methane supply to running waters, and that these connections are vulnerable to both climate change and direct human modifications of the land.
- Gerard Rocher-Ros
- , Emily H. Stanley
- & Ryan A. Sponseller
-
Article
| Open Access The global wildland–urban interface
The global wildland–urban interface
A global assessment shows that the wildland–urban interface occurs on all continents, showing its broad-scale patterns and providing a basis for future research on dynamics and socioeconomic and biophysical processes.
- Franz Schug
- , Avi Bar-Massada
- & Volker C. Radeloff
-
Matters Arising |
 The importance of trait selection in ecology
The importance of trait selection in ecology
- Alexandra Weigelt
- , Liesje Mommer
- & M. Luke McCormack
-
Article
| Open Access Tree islands enhance biodiversity and functioning in oil palm landscapes
Tree islands enhance biodiversity and functioning in oil palm landscapes
A large-scale, five-year study in Indonesia finds that enriching oil palm-dominated landscapes with patches of trees bolsters biodiversity and ecosystem functioning without impairing oil palm yields but should not replace forest protection.
- Delphine Clara Zemp
- , Nathaly Guerrero-Ramirez
- & Holger Kreft
-
Article |
 The carbon sink of secondary and degraded humid tropical forests
The carbon sink of secondary and degraded humid tropical forests
Analysis of satellite-based data on recovering degraded and secondary forests in three tropical moist forest regions quantifies the amount of aboveground carbon accumulated, which counterbalanced one quarter of carbon emissions from old-growth forest loss between 1984 and 2018.
- Viola H. A. Heinrich
- , Christelle Vancutsem
- & Luiz E. O. C. Aragão
-
Article
| Open Access Coastal phytoplankton blooms expand and intensify in the 21st century
Coastal phytoplankton blooms expand and intensify in the 21st century
Satellite observations reveal global increases in the extent and frequency of phytoplankton blooms between 2003 and 2020 and provide insights into the relationship between blooms, ocean circulation and sea surface temperature.
- Yanhui Dai
- , Shangbo Yang
- & Lian Feng
-
Review Article |
 River ecosystem metabolism and carbon biogeochemistry in a changing world
River ecosystem metabolism and carbon biogeochemistry in a changing world
A review of current river ecosystem metabolism research quantifies the organic and inorganic carbon flux from land to global rivers and demonstrates that the carbon balance can be influenced by a changing world.
- Tom J. Battin
- , Ronny Lauerwald
- & Pierre Regnier
-
Article
| Open Access Logged tropical forests have amplified and diverse ecosystem energetics
Logged tropical forests have amplified and diverse ecosystem energetics
Logged forests in Borneo have higher energy flow from vegetation to and broad range of bird and mammal species relative to old-growth forests and oil palm plantations, showing that they can be diverse and ecologically vibrant ecosystems.
- Yadvinder Malhi
- , Terhi Riutta
- & Matthew J. Struebig
-
Article
| Open Access A function-based typology for Earth’s ecosystems
A function-based typology for Earth’s ecosystems
The International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Global Ecosystem Typology has been developed to provide a systematic framework for data on all of Earth’s ecosystems in a unified theoretical context to support biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
- David A. Keith
- , José R. Ferrer-Paris
- & Richard T. Kingsford
-
Article |
 Anticyclonic eddies aggregate pelagic predators in a subtropical gyre
Anticyclonic eddies aggregate pelagic predators in a subtropical gyre
Using a large-scale fishery dataset in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre, a pervasive pattern of increased pelagic predator catch inside anticyclonic eddies relative to cyclones and non-eddy areas is shown.
- Martin C. Arostegui
- , Peter Gaube
- & Camrin D. Braun
-
Article |
 Warm springs alter timing but not total growth of temperate deciduous trees
Warm springs alter timing but not total growth of temperate deciduous trees
Warmer spring temperatures affect the timing of stem diameter growth of temperate deciduous trees but have little effect on annual growth.
- Cameron Dow
- , Albert Y. Kim
- & Kristina J. Anderson-Teixeira
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence for recovery of mercury-contaminated fish populations
Experimental evidence for recovery of mercury-contaminated fish populations
In a 15-year whole-ecosystem, single-factor experiment, stopping experimental mercury loading results in rapid decreases in methylmercury contamination of fish populations and almost complete recovery within the timeframe of the study.
- Paul J. Blanchfield
- , John W. M. Rudd
- & Michael T. Tate
-
Article |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: A constraint on historic growth in global photosynthesis due to increasing CO2
RETRACTED ARTICLE: A constraint on historic growth in global photosynthesis due to increasing CO2
An emergent constraint combining biosphere models and carbon budget estimates suggests that the increase in the global terrestrial carbon sink is caused largely by a CO2-induced increase in photosynthesis.
- T. F. Keenan
- , X. Luo
- & S. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access The three major axes of terrestrial ecosystem function
The three major axes of terrestrial ecosystem function
Three key axes of variation of ecosystem functional changes and their underlying causes are identified from a dataset of surface gas exchange measurements across major terrestrial biomes and climate zones.
- Mirco Migliavacca
- , Talie Musavi
- & Markus Reichstein
-
Article |
 The contribution of insects to global forest deadwood decomposition
The contribution of insects to global forest deadwood decomposition
Multi-year field experiments across six continents suggest that insects have an important contribution to decomposition and carbon release from forest deadwood.
- Sebastian Seibold
- , Werner Rammer
- & Jörg Müller
-
Article |
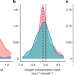 Widespread deoxygenation of temperate lakes
Widespread deoxygenation of temperate lakes
Analysis of temperate lakes finds a widespread decline in dissolved oxygen concentrations in surface and deep waters, which is associated with reduced solubility at warmer surface water temperatures and increased stratification at depth.
- Stephen F. Jane
- , Gretchen J. A. Hansen
- & Kevin C. Rose
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: Old-growth forest carbon sinks overestimated
- Sebastiaan Luyssaert
- , E.-Detlef Schulze
- & John Grace
-
Article |
 A trade-off between plant and soil carbon storage under elevated CO2
A trade-off between plant and soil carbon storage under elevated CO2
A synthesis of elevated carbon dioxide experiments reveals that when plant biomass is strongly stimulated by elevated carbon dioxide levels, soil carbon storage declines, and where biomass is weakly stimulated, soil carbon accumulates.
- C. Terrer
- , R. P. Phillips
- & R. B. Jackson
-
Article |
 Warming impairs trophic transfer efficiency in a long-term field experiment
Warming impairs trophic transfer efficiency in a long-term field experiment
In artificial ponds exposed to seven years of experimental warming, energy transfer between two trophic levels of freshwater plankton decreased by 56% and the biomass of both levels was reduced.
- Diego R. Barneche
- , Chris J. Hulatt
- & Gabriel Yvon-Durocher
-
Article |
 Environmental drivers of megafauna and hominin extinction in Southeast Asia
Environmental drivers of megafauna and hominin extinction in Southeast Asia
Stable isotope data for Southeast Asian mammals across the Quaternary period shed light on environmental change from the Early Pleistocene to the Holocene epoch, contextualizing hominin evolution and megafauna extinction in the region.
- Julien Louys
- & Patrick Roberts
-
Article |
 Mapping carbon accumulation potential from global natural forest regrowth
Mapping carbon accumulation potential from global natural forest regrowth
A one-kilometre-resolution map of aboveground carbon accumulation rates of forest regrowth shows 100-fold variation across the globe, with rates 32% higher on average than IPCC estimates.
- Susan C. Cook-Patton
- , Sara M. Leavitt
- & Bronson W. Griscom
-
Article |
 Soil carbon loss by experimental warming in a tropical forest
Soil carbon loss by experimental warming in a tropical forest
When tropical forest soils are warmed in situ, they release more CO2 than predicted by theory, creating a potentially substantial positive feedback to climate change.
- Andrew T. Nottingham
- , Patrick Meir
- & Benjamin L. Turner
-
Article |
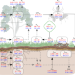 The fate of carbon in a mature forest under carbon dioxide enrichment
The fate of carbon in a mature forest under carbon dioxide enrichment
Carbon dioxide enrichment of a mature forest resulted in the emission of the excess carbon back into the atmosphere via enhanced ecosystem respiration, suggesting that mature forests may be limited in their capacity to mitigate climate change.
- Mingkai Jiang
- , Belinda E. Medlyn
- & David S. Ellsworth
-
Article |
 Asynchronous carbon sink saturation in African and Amazonian tropical forests
Asynchronous carbon sink saturation in African and Amazonian tropical forests
Unlike Amazonian forests, African forests have maintained their carbon sink until recently but by 2030 the African carbon sink will have shrunk by 14 per cent and the Amazonian sink will reach almost zero.
- Wannes Hubau
- , Simon L. Lewis
- & Lise Zemagho
-
Letter |
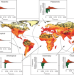 Wilderness areas halve the extinction risk of terrestrial biodiversity
Wilderness areas halve the extinction risk of terrestrial biodiversity
Wilderness areas with minimal levels of human disturbance promote the persistence of biodiversity by acting as buffers against species loss, and therefore represent key targets for environmental protection.
- Moreno Di Marco
- , Simon Ferrier
- & James E. M. Watson
-
Letter |
 Increasing wildfires threaten historic carbon sink of boreal forest soils
Increasing wildfires threaten historic carbon sink of boreal forest soils
Soil radiocarbon dating reveals that combusted ‘legacy carbon’—soil carbon that escaped burning during previous fires—could shift the carbon balance of boreal ecosystems, resulting in a positive climate feedback.
- Xanthe J. Walker
- , Jennifer L. Baltzer
- & Michelle C. Mack
-
Letter |
 Global warming impairs stock–recruitment dynamics of corals
Global warming impairs stock–recruitment dynamics of corals
A regional-scale shift in the relationships between adult stock and recruitment of corals occurred along the Great Barrier Reef, following mass bleaching events in 2016 and 2017 caused by global warming.
- Terry P. Hughes
- , James T. Kerry
- & Rachael M. Woods
-
Letter |
 Climate–land-use interactions shape tropical mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions
Climate–land-use interactions shape tropical mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions
Elevational trends in biodiversity and ecosystem functions across natural and anthropogenic habitats on Mount Kilimanjaro show that the effects of land use are strongly mediated by climate.
- Marcell K. Peters
- , Andreas Hemp
- & Ingolf Steffan-Dewenter
-
Review Article |
 The future of hyperdiverse tropical ecosystems
The future of hyperdiverse tropical ecosystems
The immense biodiversity of tropical ecosystems is threatened by multiple interacting local and global stressors that can only be addressed by the concerted efforts of grassroots organizations, researchers, national governments and the international community.
- Jos Barlow
- , Filipe França
- & Nicholas A. J. Graham
-
Letter |
 Ecosystem restructuring along the Great Barrier Reef following mass coral bleaching
Ecosystem restructuring along the Great Barrier Reef following mass coral bleaching
Fish and invertebrate communities transformed across the span of the Great Barrier Reef following the 2016 bleaching event due to a decline in coral-feeding fishes resulting from coral loss, and because of different regional responses of key trophic groups to the direct effect of temperature.
- Rick D. Stuart-Smith
- , Christopher J. Brown
- & Graham J. Edgar
-
Letter |
 Seabirds enhance coral reef productivity and functioning in the absence of invasive rats
Seabirds enhance coral reef productivity and functioning in the absence of invasive rats
Productivity of coral reefs is enhanced near islands with no invasive rats, as populations of seabirds, which transfer nitrogen from deeper areas of ocean to the nearshore waters via their guano, are much larger than on rat-infested islands.
- Nicholas A. J. Graham
- , Shaun K. Wilson
- & M. Aaron MacNeil
-
Letter |
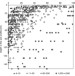 Atmosphere–soil carbon transfer as a function of soil depth
Atmosphere–soil carbon transfer as a function of soil depth
This study of whole-soil carbon dynamics finds that, of the atmospheric carbon that is incorporated into the topmost metre of soil over 50 years, just 19 per cent reaches the subsoil, in a manner that depends on land use and aridity.
- Jérôme Balesdent
- , Isabelle Basile-Doelsch
- & Christine Hatté
-
Letter |
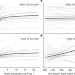 Pervasive phosphorus limitation of tree species but not communities in tropical forests
Pervasive phosphorus limitation of tree species but not communities in tropical forests
In lowland tropical forests in Panama, widespread species-level phosphorus limitation of tree growth is not reflected in community-wide growth or biomass owing to the presence of a few species tolerant of low phosphorus availability.
- Benjamin L. Turner
- , Tania Brenes-Arguedas
- & Richard Condit
-
Letter |
 Unexpectedly large impact of forest management and grazing on global vegetation biomass
Unexpectedly large impact of forest management and grazing on global vegetation biomass
Analyses of potential and actual biomass stocks indicate that trade-offs exist between conserving carbon stocks on managed land and raising the contribution of biomass to raw material and energy supply for the mitigation of climate change.
- Karl-Heinz Erb
- , Thomas Kastner
- & Sebastiaan Luyssaert
-
Letter |
 Large emissions from floodplain trees close the Amazon methane budget
Large emissions from floodplain trees close the Amazon methane budget
Methane fluxes from the stems of Amazonian floodplain trees indicate that the escape of soil gas through wetland trees is the dominant source of methane emissions in the Amazon basin.
- Sunitha R. Pangala
- , Alex Enrich-Prast
- & Vincent Gauci
-
Letter |
 Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity
Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity
A synthesis of 67 biodiversity studies shows that, after controlling for environmental covariates, the effects of biodiversity on biomass are stronger in nature than in experiments and are comparable to the effects of other drivers of productivity.
- J. Emmett Duffy
- , Casey M. Godwin
- & Bradley J. Cardinale
-
Perspective |
 Damming the rivers of the Amazon basin
Damming the rivers of the Amazon basin
The current and expected environmental consequences of built dams and proposed dam constructions in the Amazon basin are explored with the help of a Dam Environmental Vulnerability Index.
- Edgardo M. Latrubesse
- , Eugenio Y. Arima
- & Jose C. Stevaux
-
Letter |
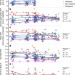 Elevation alters ecosystem properties across temperate treelines globally
Elevation alters ecosystem properties across temperate treelines globally
Examination of the ecosystem properties of treeline ecotones in seven temperate regions of the world shows that the reduction in temperature with increasing elevation does not affect tree leaf nutrient concentrations, but does reduce ground-layer community-weighted plant nitrogen levels, leading to a strong stoichiometric convergence of ground-layer plant community nitrogen to phosphorus ratios across all regions.
- Jordan R. Mayor
- , Nathan J. Sanders
- & David A. Wardle
-
Letter |
 A theoretical foundation for multi-scale regular vegetation patterns
A theoretical foundation for multi-scale regular vegetation patterns
Empirically validated mathematical models show that a combination of intraspecific competition between subterranean social-insect colonies and scale-dependent feedbacks between plants can explain the spatially periodic vegetation patterns observed in many landscapes, such as the Namib Desert ‘fairy circles’.
- Corina E. Tarnita
- , Juan A. Bonachela
- & Robert M. Pringle
-
Letter |
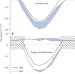 Seasonality of temperate forest photosynthesis and daytime respiration
Seasonality of temperate forest photosynthesis and daytime respiration
Climate models require an understanding of ecosystem-scale respiration and photosynthesis, yet there is no way of measuring these two fluxes directly; here, new instrumentation is used to determine these fluxes in a temperate forest, showing, for instance, that respiration is less during the day than at night.
- R. Wehr
- , J. W. Munger
- & S. R. Saleska
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Dry-season greening of Amazon forests
Dry-season greening of Amazon forests
- Scott R. Saleska
- , Jin Wu
- & Natalia Restrepo-Coupe
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Morton et al. reply
- Douglas C. Morton
- , Jyoteshwar Nagol
- & Peter R. J. North
-
Letter |
 Vast assembly of vocal marine mammals from diverse species on fish spawning ground
Vast assembly of vocal marine mammals from diverse species on fish spawning ground
Vocalizations were recorded for over eight distinct whale species as they converged on a shoal of herring to feed; the predators divided the shoal into overlapping but species-specific foraging sectors and the activities of the whales changed between day and night.
- Delin Wang
- , Heriberto Garcia
- & Purnima Ratilal
-
Letter |
 Sensitivity of global terrestrial ecosystems to climate variability
Sensitivity of global terrestrial ecosystems to climate variability
Using satellite data and a novel analytical approach, a new index of the sensitivity of vegetation to climate variability is developed, revealing areas of high sensitivity that include tundra, boreal forest, tropical forest and temperate grasslands.
- Alistair W. R. Seddon
- , Marc Macias-Fauria
- & Kathy J. Willis
-
Letter |
 Biomass resilience of Neotropical secondary forests
Biomass resilience of Neotropical secondary forests
An analysis of above-ground biomass recovery during secondary succession in forest sites and plots, covering the major environmental gradients in the Neotropics.
- Lourens Poorter
- , Frans Bongers
- & Danaë M. A. Rozendaal
-
Article |
 The global spectrum of plant form and function
The global spectrum of plant form and function
The authors found that the key elements of plant form and function, analysed at global scale, are largely concentrated into a two-dimensional plane indexed by the size of whole plants and organs on the one hand, and the construction costs for photosynthetic leaf area, on the other.
- Sandra Díaz
- , Jens Kattge
- & Lucas D. Gorné

 Critical transitions in the Amazon forest system
Critical transitions in the Amazon forest system