Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Portable bioluminescent platform for in vivo monitoring of biological processes in non-transgenic animals
Portable bioluminescent platform for in vivo monitoring of biological processes in non-transgenic animals
Bioluminescence imaging tends to rely on transgenic luciferase-expressing cells and animals. Here the authors report a portable bioluminescent system to non-invasively measure intra- and extracellular enzymes in vivo in non-transgenic animals which do not express luciferase.
- Aleksey Yevtodiyenko
- , Arkadiy Bazhin
- & Elena A. Goun
-
Article
| Open Access Selective and noncovalent targeting of RAS mutants for inhibition and degradation
Selective and noncovalent targeting of RAS mutants for inhibition and degradation
Most oncogenic RAS mutants remain undruggable. Here, the authors developed monobodies that selectively recognize the active state of KRAS(G12V) and KRAS(G12C) and demonstrated their utility in inhibiting RAS functions through inhibition and degradation.
- Kai Wen Teng
- , Steven T. Tsai
- & Shohei Koide
-
Article
| Open Access Selective inhibition of cullin 3 neddylation through covalent targeting DCN1 protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity
Selective inhibition of cullin 3 neddylation through covalent targeting DCN1 protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity
Activation of cullin-RING ligases can be inhibited by targeting DCN1, but selective DCN1 inhibitors with in vivo activity are lacking. Here, the authors develop covalent DCN1 inhibitors that selectively and potently inhibit cullin-3 activation and downstream functions in cells and in mice.
- Haibin Zhou
- , Jianfeng Lu
- & Shaomeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Naturally-occurring spinosyn A and its derivatives function as argininosuccinate synthase activator and tumor inhibitor
Naturally-occurring spinosyn A and its derivatives function as argininosuccinate synthase activator and tumor inhibitor
Arginine addiction induced by argininosuccinate synthase (ASSN1) deficiency has been exploited to treat ASS1-deficient cancers. Here, the authors show an alternative therapeutic approach where ASS1 activity is increased by the pesticide spinosyn A and is shown to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation.
- Zizheng Zou
- , Xiyuan Hu
- & Zhiyong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying therapeutic drug targets using bidirectional effect genes
Identifying therapeutic drug targets using bidirectional effect genes
Prioritising genes as potential drug targets is challenging and often unsuccessful once testing efficacy in humans. Here, the authors propose an approach to identifying drug targets that uses evidence from gain- or loss-of-function mutations associated with bidirectional effects on phenotypes.
- Karol Estrada
- , Steven Froelich
- & Lon R. Cardon
-
Article
| Open Access SLPI is a critical mediator that controls PTH-induced bone formation
SLPI is a critical mediator that controls PTH-induced bone formation
The mechanism by which parathyroid hormone mediates the switch from bone resorption to bone formation is unclear. Here, the authors show that SLPI regulates the communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts to promote the anabolic effect of parathyroid hormone.
- Akito Morimoto
- , Junichi Kikuta
- & Masaru Ishii
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of a Cortistatin analogue with immunomodulatory activity in models of inflammatory bowel disease
Structure-based design of a Cortistatin analogue with immunomodulatory activity in models of inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is caused by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and disturbed immune responses. Here the authors present examination of Cortistatin analogues that display enhanced half-life stability whilst maintaining immunomodulatory functionality.
- Álvaro Rol
- , Toni Todorovski
- & Maria J. Macias
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of V-ATPase inhibition by bafilomycin A1
Molecular basis of V-ATPase inhibition by bafilomycin A1
Bafilomycin A1, a member of macrolide antibiotics and an autophagy inhibitor, serves as a specific and potent V-ATPases inhibitor. Here authors report the cryo-EM structure of bafilomycin A1-bound V-ATPase with six bafilomycin A1 molecules bound to the c-ring and reveal the molecular basis for Bafilomycin A1 inhibition of the V-ATPase.
- Rong Wang
- , Jin Wang
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing human recombinant antibodies selected from pre-pandemic healthy donors binding at RBD-ACE2 interface
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing human recombinant antibodies selected from pre-pandemic healthy donors binding at RBD-ACE2 interface
Antibodies targeting the spike protein of coronaviruses are potential candidates for therapeutic development. Here, Bertoglio et al. use phage display to select anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike antibodies from the human naïve universal antibody gene libraries HAL9/10 that block interaction with ACE2 receptor to inhibit infection.
- Federico Bertoglio
- , Doris Meier
- & Michael Hust
-
Article
| Open Access Tumor-penetrating therapy for β5 integrin-rich pancreas cancer
Tumor-penetrating therapy for β5 integrin-rich pancreas cancer
The iRGD tumor-penetrating peptide can achieve tumor specific drug delivery but whether and how it can penetrate into desmoplastic tumors is unknown. Here, the authors show that β5 integrin expression on tumor cells, mediated by CAFs-derived TGF-β, is required for iRGD penetration into the desmoplastic PDAC microenvironment and that iRGD-based combination therapy is effective in PDAC mouse models.
- Tatiana Hurtado de Mendoza
- , Evangeline S. Mose
- & Kazuki N. Sugahara
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-linking peptide and repurposed drugs inhibit both entry pathways of SARS-CoV-2
Cross-linking peptide and repurposed drugs inhibit both entry pathways of SARS-CoV-2
Until today effective antivirals for COVID-19 treatment are not widely available. Here, Zhao et al. characterize a dual-functional cross-linking peptide, 8P9R, that can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virus entry in vitro and suppresses viral replication in vivo in golden Syrian hamster.
- Hanjun Zhao
- , Kelvin K. W. To
- & Kwok-Yung Yuen
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic modulation reveals differentiation state specificity of oncogene addiction
Epigenetic modulation reveals differentiation state specificity of oncogene addiction
Epigenetic mechanisms associated with the differentiation state of cancer cells and their heterogeneity influence tumor responses to oncogene-targeted therapies. In this study, the authors perform an epigenetic compound screen and single-cell analysis in BRAF-mutant melanoma cells to identify compounds that block three distinct drug-tolerant epigenetic states associated with either one of the lysine-specific histone demethylases Kdm1a or Kdm4b, or BET proteins.
- Mehwish Khaliq
- , Mohan Manikkam
- & Mohammad Fallahi-Sichani
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of CD318, TSPAN8 and CD66c as target candidates for CAR T cell based immunotherapy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Identification of CD318, TSPAN8 and CD66c as target candidates for CAR T cell based immunotherapy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
There is an unmet clinical need to identify therapeutic options for the treatment of pancreatic cancer (PDAC). Here the authors present a systematic screening approach for the identification of potential PDAC cell surface target candidates for CAR-T cell based immunotherapy, followed by their functional validation in preclinical models.
- Daniel Schäfer
- , Stefan Tomiuk
- & Olaf Hardt
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating target deconvolution for therapeutic antibody candidates using highly parallelized genome editing
Accelerating target deconvolution for therapeutic antibody candidates using highly parallelized genome editing
Efficient deconvolution of antibody targets is needed for phenotype-based discovery. Here, the authors investigate a deconvolution approach based on pooled CRISPR Cas9 to achieve 97% deconvolution success rate.
- Jenny Mattsson
- , Ludvig Ekdahl
- & Björn Nilsson
-
Article
| Open Access Histamine H1 receptor deletion in cholinergic neurons induces sensorimotor gating ability deficit and social impairments in mice
Histamine H1 receptor deletion in cholinergic neurons induces sensorimotor gating ability deficit and social impairments in mice
Social impairment and anhedonia are common negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Here, the authors show that the histamine H1 receptor in cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain has a critical role in sensorimotor gating, social behaviour, and anhedonia-like behaviour in mice.
- Li Cheng
- , Cenglin Xu
- & Zhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Eltrombopag directly inhibits BAX and prevents cell death
Eltrombopag directly inhibits BAX and prevents cell death
The BCL-2 family protein BAX functions to regulate mitochondria-driven cell death. Here the authors show that the drug Eltrombopag inhibits BAX and prevents apoptosis induced by cytotoxic stimuli.
- Adam Z. Spitz
- , Emmanouil Zacharioudakis
- & Evripidis Gavathiotis
-
Article
| Open Access Biological and therapeutic implications of a unique subtype of NPM1 mutated AML
Biological and therapeutic implications of a unique subtype of NPM1 mutated AML
Molecular heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) across patients is a major challenge for prognosis and therapy. Here, the authors show that NPM1 mutated AML is a heterogeneous class, consisting of two subtypes which exhibit distinct molecular characteristics, differentiation state, patient survival and drug response.
- Arvind Singh Mer
- , Emily M. Heath
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
Article
| Open Access Fast acting allosteric phosphofructokinase inhibitors block trypanosome glycolysis and cure acute African trypanosomiasis in mice
Fast acting allosteric phosphofructokinase inhibitors block trypanosome glycolysis and cure acute African trypanosomiasis in mice
Glycolytic enzymes are challenging drug targets due to their highly conserved active sites and phosphorylated substrates. Here, the authors identify fast acting allosteric inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei phosphofructokinase that block trypanosome glycolysis and provide cure evidence in murine model.
- Iain W. McNae
- , James Kinkead
- & Malcolm D. Walkinshaw
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning identifies candidates for drug repurposing in Alzheimer’s disease
Machine learning identifies candidates for drug repurposing in Alzheimer’s disease
Clinical trials of novel therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) have provided largely negative results, so far. Here, the authors present a machine learning framework that quantifies potential associations between the pathology of AD severity and gene-based molecular mechanisms to enable drug repurposing.
- Steve Rodriguez
- , Clemens Hug
- & Artem Sokolov
-
Article
| Open Access PRMT5 inhibition disrupts splicing and stemness in glioblastoma
PRMT5 inhibition disrupts splicing and stemness in glioblastoma
The arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 is over-expressed in cancer and has a role in the maintenance of stem cells. Here, the authors show that PRMT5 inhibitors can block the growth of patient derived glioblastoma stem cell cultures in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that PRMT5 inhibition may be a useful therapeutic strategy
- Patty Sachamitr
- , Jolene C. Ho
- & Peter B. Dirks
-
Article
| Open Access p53 dynamics vary between tissues and are linked with radiation sensitivity
p53 dynamics vary between tissues and are linked with radiation sensitivity
p53 mediates the response to irradiation, however, tissues with similar levels of p53 have different radiation sensitivities. Here, the authors show that the in vivo p53 dynamics varies in these tissues after radiation, and the use of Mdm2 inhibitor to sustain p53 activity enhances radiosensitivity.
- Jacob Stewart-Ornstein
- , Yoshiko Iwamoto
- & Galit Lahav
-
Article
| Open Access Variant-selective stereopure oligonucleotides protect against pathologies associated with C9orf72-repeat expansion in preclinical models
Variant-selective stereopure oligonucleotides protect against pathologies associated with C9orf72-repeat expansion in preclinical models
C9orf72 expansion mutations are the most common genetic cause of ALS and FTD, which have limited therapies. The authors generate stereopure oligonucleotides that selectively deplete expansion-containing transcripts and protect against expansion-associated pathologies in preclinical models.
- Yuanjing Liu
- , Jean-Cosme Dodart
- & Robert H. Brown Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput phenotypic screen and transcriptional analysis identify new compounds and targets for macrophage reprogramming
High-throughput phenotypic screen and transcriptional analysis identify new compounds and targets for macrophage reprogramming
Macrophages may polarize into different states with distinct regulatory functions for inflammation. Here the authors perform high-throughput in vitro screening of a library of ~4000 compounds to identify those with specific effects on human macrophage polarization, while RNAseq helps uncover the targets and pathways mediating these effects.
- Guangan Hu
- , Yang Su
- & Jianzhu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access 3D bioprinting of high cell-density heterogeneous tissue models through spheroid fusion within self-healing hydrogels
3D bioprinting of high cell-density heterogeneous tissue models through spheroid fusion within self-healing hydrogels
Cellular models are needed to study disease in vitro and to screen drugs for toxicity and efficacy. Here the authors develop a bioprinting approach to transfer spheroids into self-healing support hydrogels at high resolution, which enables their patterning and fusion into high-cell density microtissues of prescribed spatial organization.
- Andrew C. Daly
- , Matthew D. Davidson
- & Jason A. Burdick
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared nanospectroscopy reveals the molecular interaction fingerprint of an aggregation inhibitor with single Aβ42 oligomers
Infrared nanospectroscopy reveals the molecular interaction fingerprint of an aggregation inhibitor with single Aβ42 oligomers
Our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying pathological protein aggregation remains incomplete. Here, single molecule infrared nanospectroscopy (AFM-IR) offers insight into the structure of Aβ42 oligomeric and fibrillar species and their interaction with an aggregation inhibitor, paving the way for single molecule drug discovery studies.
- Francesco Simone Ruggeri
- , Johnny Habchi
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Many next-generation antibody therapeutics have enhanced potency but the risk of adverse events. Here the authors develop a conditionally activated, single-module CAR.
- Spencer Park
- , Edward Pascua
- & Javier Chaparro-Riggers
-
Article
| Open Access DutaFabs are engineered therapeutic Fab fragments that can bind two targets simultaneously
DutaFabs are engineered therapeutic Fab fragments that can bind two targets simultaneously
Bispecific antibodies can bind to two distinct targets though the fusion of two different Fv regions. In this study, the authors develop DutaFabs that present two separated and independent antigen binding sites within the same Fv region, giving rise to bispecific Fab fragments.
- Roland Beckmann
- , Kristian Jensen
- & Hubert Kettenberger
-
Article
| Open Access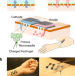 Transdermal electroosmotic flow generated by a porous microneedle array patch
Transdermal electroosmotic flow generated by a porous microneedle array patch
Transdermal delivery has emerged as a preferred method of drug delivery. Here, the authors report on the application of porous polymer microneedles coupled with electroosmosis powered by enzymatic batteries for the transport of small and large molecules through the skin.
- Shinya Kusama
- , Kaito Sato
- & Matsuhiko Nishizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic nanoparticle amyloid corona for screening Aβ oligomeric aggregate-degrading drugs
Plasmonic nanoparticle amyloid corona for screening Aβ oligomeric aggregate-degrading drugs
Effective screening of drugs to treat amyloid oligomeric aggregates associated with Alzheimer’s is needed for drug development. Here the authors report on the creation of an amyloid corona around a plasmonic nanoparticle to monitor amyloid degradation when exposed to potential drugs and demonstrate application.
- Dongtak Lee
- , Dongsung Park
- & Dae Sung Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access The complex structure of GRL0617 and SARS-CoV-2 PLpro reveals a hot spot for antiviral drug discovery
The complex structure of GRL0617 and SARS-CoV-2 PLpro reveals a hot spot for antiviral drug discovery
The SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) is of interest as a drug target. Here, the authors identify GRL0617 as a PPI (protein–protein interaction) inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro that inhibits its deISGylating activity and present the mechanism of action of the compound through the GRL0617-bound PLpro crystal structure and NMR studies.
- Ziyang Fu
- , Bin Huang
- & Hao Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting aberrant DNA methylation in mesenchymal stromal cells as a treatment for myeloma bone disease
Targeting aberrant DNA methylation in mesenchymal stromal cells as a treatment for myeloma bone disease
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been shown to support multiple myeloma (MM) development. Here, MSCs isolated from the bone marrow of MM patients are shown to have altered DNA methylation patterns and a methyltransferase inhibitor reverts MM-associated bone loss and reduces tumour burden in MM murine models.
- Antonio Garcia-Gomez
- , Tianlu Li
- & Esteban Ballestar
-
Article
| Open Access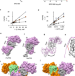 Structural basis of malaria parasite phenylalanine tRNA-synthetase inhibition by bicyclic azetidines
Structural basis of malaria parasite phenylalanine tRNA-synthetase inhibition by bicyclic azetidines
Bicyclic azetidine inhibitors are promising antimalarials that target the Plasmodium cytosolic phenylalanine tRNAsynthetase (cFRS). Here, Sharma et al. provide the biochemical and structural basis of its mechanism using co-crystal structure of PvcFRS with BRD1389.
- Manmohan Sharma
- , Nipun Malhotra
- & Amit Sharma
-
Article
| Open Access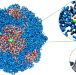 Cryo-EM structure of Helicobacter pylori urease with an inhibitor in the active site at 2.0 Å resolution
Cryo-EM structure of Helicobacter pylori urease with an inhibitor in the active site at 2.0 Å resolution
Infection by Helicobacter pylori is associated with peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. H. pylori urease is required for colonization of the stomach and thus an attractive antimicrobial drug target. Cryo-EM analyses of the H. pylori urease with inhibitors bound reveal structural details useful in rational drug design.
- Eva S. Cunha
- , Xiaorui Chen
- & Hartmut Luecke
-
Article
| Open Access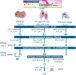 Multistage and transmission-blocking targeted antimalarials discovered from the open-source MMV Pandemic Response Box
Multistage and transmission-blocking targeted antimalarials discovered from the open-source MMV Pandemic Response Box
Here, Reader et al. screen the Medicines for Malaria Venture Pandemic Response Box in parallel against Plasmodiumasexual and liver stage parasites, stage IV/V gametocytes, gametes, oocysts and as endectocides. They identify two potent transmission-blocking drugs: a histone demethylase inhibitor ML324 and the antitubercular SQ109.
- Janette Reader
- , Mariëtte E. van der Watt
- & Lyn-Marié Birkholtz
-
Review Article
| Open Access Resilin-mimetics as a smart biomaterial platform for biomedical applications
Resilin-mimetics as a smart biomaterial platform for biomedical applications
Advances made in synthesis and analytical techniques has allowed the exploration and mimicry of natural materials. Resilin-mimetics have emerged from this advance as a biomaterial with a range of potential applications. Here, the authors review the history and current research on resilin-mimetics, providing a future perspective.
- Rajkamal Balu
- , Naba K. Dutta
- & Namita Roy Choudhury
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis CoaBC by targeting an allosteric site
Inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis CoaBC by targeting an allosteric site
The bifunctional enzyme CoaBC catalyses the second and third step in the Coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis pathway and is of interest as a M. tuberculosis drug target. Here, the authors present the full-length crystal structure of Mycobacterium smegmatis CoaBC, which is regulated by CoA and CoA thioesters and forms a dodecamer and by performing a high-throughput screen they identify selective inhibitors of M. tuberculosis CoaB that bind to an allosteric site within CoaB.
- Vitor Mendes
- , Simon R. Green
- & Tom L. Blundell
-
Article
| Open Access Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages
Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages
Adipose tissue macrophages are central to controlling inflammation in the context of obesity. Here the authors present a new infrared dye (IR-61) that accumulates in the mitochondria of these cells resulting in anti-inflammatory effects that counter obesity-associated pathology in mice.
- Yawei Wang
- , Binlin Tang
- & Chunmeng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Steroid hormones sulfatase inactivation extends lifespan and ameliorates age-related diseases
Steroid hormones sulfatase inactivation extends lifespan and ameliorates age-related diseases
Sul-2 is a steroid sulfatase in c.elegans. Here the authors show that, in the absence of sul-2 enzymatic activity, worm lifespan is increased, and that chemical inhibition ameliorates symptoms of neurodegenerative disorders in worms and mice.
- Mercedes M. Pérez-Jiménez
- , José M. Monje-Moreno
- & Manuel J. Muñoz
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the nuclear receptor RORα regulates TH17 driven inflammatory disorders
Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the nuclear receptor RORα regulates TH17 driven inflammatory disorders
Unlike RORα, which has been thought to be somewhat redundant, RORγt has been well characterized in its function and contribution to the development of Th17 cells. Here the authors show that RORα is important in Th17 differentiation and that RORα deletion or a small molecule inhibitor of RORα can reduce disease in EAE and colitis mouse models.
- Ran Wang
- , Sean Campbell
- & Laura A. Solt
-
Perspective
| Open AccessThe role of dissociation in ketamine’s antidepressant effects
Ketamine is associated with rapid antidepressant effects and temporary dissociative experiences, and this review examines whether these dissociative symptoms are necessary for antidepressant efficacy. Although the current literature does not support this relationship, further work is needed to explore possible associations at the molecular, biomarker, and psychological levels.
- Elizabeth D. Ballard
- & Carlos A. Zarate Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides broad preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite
A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides broad preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite
Snakebite is a life-threatening neglected tropical disease that is currently treated using different antibody-based antivenoms, each effective against bites of specific snake species, but not others. Here, the authors show that a combination of two toxin-inhibiting repurposed drugs provides broad protection in experimental animals against the lethal effects of snakebites from multiple snake species.
- Laura-Oana Albulescu
- , Chunfang Xie
- & Nicholas R. Casewell
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of protein glycosylation is a novel pro-angiogenic strategy that acts via activation of stress pathways
Inhibition of protein glycosylation is a novel pro-angiogenic strategy that acts via activation of stress pathways
Therapeutic angiogenesis has the potential of inducing and maintaining new blood vessels and thus improving outcomes in patients with ischemic disorders. Mannosamine functions as an endothelial cell mitogen/survival factor through activation of stress pathways and might be useful to protect and regenerate the vascular endothelium in a variety of disorders.
- Cuiling Zhong
- , Pin Li
- & Napoleone Ferrara
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitous selection for mecA in community-associated MRSA across diverse chemical environments
Ubiquitous selection for mecA in community-associated MRSA across diverse chemical environments
The mecA gene confers resistance to many β-lactam antibiotics in community-associated MRSA bacteria. Here, Snitser et al. show that mecA also provides broad selective advantage across diverse chemical environments in the presence of subinhibitory β-lactam concentrations, by protecting the bacteria against increased cell-envelope permeability.
- Olga Snitser
- , Dor Russ
- & Roy Kishony
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR based editing of SIV proviral DNA in ART treated non-human primates
CRISPR based editing of SIV proviral DNA in ART treated non-human primates
Removal of integrated HIV DNA remains a roadblock for HIV cure. Here, Mancuso et al. show that intravenous administration of an adeno-associated virus-based CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing construct to SIV-infected macaques results in excision of integrated proviral DNA from infected blood cells and tissues known to be viral reservoirs.
- Pietro Mancuso
- , Chen Chen
- & Kamel Khalili
-
Article
| Open Access Designed CXCR4 mimic acts as a soluble chemokine receptor that blocks atherogenic inflammation by agonist-specific targeting
Designed CXCR4 mimic acts as a soluble chemokine receptor that blocks atherogenic inflammation by agonist-specific targeting
The development of specific anti-cytokine/chemokine therapeutic strategies for atherosclerotic disease is challenging. Here, the authors have designed a peptide-based ectodomain mimic of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 that selectively targets MIF but not CXCL12 and blocks experimental atherosclerosis in vivo.
- Christos Kontos
- , Omar El Bounkari
- & Jürgen Bernhagen
-
Article
| Open Access Surveying biomolecular frustration at atomic resolution
Surveying biomolecular frustration at atomic resolution
The analysis of biomolecular frustration yielded insights into several aspects of protein behavior. Here the authors describe a framework to efficiently quantify and localize biomolecular frustration within proteins at atomic resolution, and observe that drug specificity is correlated with a minimally frustrated binding pocket leading to a funneled binding landscape.
- Mingchen Chen
- , Xun Chen
- & Peter G. Wolynes
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallographic structure of wild-type SARS-CoV-2 main protease acyl-enzyme intermediate with physiological C-terminal autoprocessing site
Crystallographic structure of wild-type SARS-CoV-2 main protease acyl-enzyme intermediate with physiological C-terminal autoprocessing site
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) is one of two cysteine proteases essential for viral replication. Here, the authors determine the crystal structure of an Mpro acyl intermediate with its native C-terminal autocleavage sequence and the structure of a product bound active site mutant (C145A), which are of interest for antiviral drug development.
- Jaeyong Lee
- , Liam J. Worrall
- & Natalie C. J. Strynadka
-
Article
| Open Access Computationally predicting clinical drug combination efficacy with cancer cell line screens and independent drug action
Computationally predicting clinical drug combination efficacy with cancer cell line screens and independent drug action
Computational models that can predict drug combination efficacy are often based on drug synergy. Here, the authors develop a different approach to computationally predict the efficacy of drug combinations using monotherapy data from high-throughput cancer cell line screens.
- Alexander Ling
- & R. Stephanie Huang
-
Comment
| Open Access Turning genes into medicines—what have we learned from gene therapy drug development in the past decade?
Turning genes into medicines—what have we learned from gene therapy drug development in the past decade?
Gene and cell therapy products approved over the past decade in Europe and North America have provided new therapeutic options for single gene disorders and for hematologic malignancies. Lessons learned, and limitations identified, are reviewed.
- Katherine A. High

 Characterization of an engineered live bacterial therapeutic for the treatment of phenylketonuria in a human gut-on-a-chip
Characterization of an engineered live bacterial therapeutic for the treatment of phenylketonuria in a human gut-on-a-chip