Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
The natural hallucinogen psilocybin — produced by so-called magic mushrooms — holds promise for the treatment of depression and other mental health conditions. Here, the authors provide a structural and biochemical analysis of the Psilocybe methyl transferase PsiM that provides mechanistic insight into the last step of psilocybin biosynthesis.
- Jesse Hudspeth
- , Kai Rogge
- & Sebastiaan Werten
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted sampling of natural product space to identify bioactive natural product-like polyketide macrolides
Targeted sampling of natural product space to identify bioactive natural product-like polyketide macrolides
Polyketide macrolides are of interest for drug discovery but their inherent structural and stereochemical complexity hinders the exploration of related regions of chemical space more broadly. Here, the authors designed in silico and synthesized a library of tetrahydrofuran-containing polyketide macrolides, and screened them against a panel of biological assays, identifying biologically active library members.
- Darryl M. Wilson
- , Daniel J. Driedger
- & Robert A. Britton
-
Article
| Open Access Design of target specific peptide inhibitors using generative deep learning and molecular dynamics simulations
Design of target specific peptide inhibitors using generative deep learning and molecular dynamics simulations
Here the authors report a computational approach which integrates deep learning and structural modelling to design target-specific peptides. They apply this to β-catenin and NF-κB essential modulator, resulting in improved binding, highlighting the efficacy of this strategy.
- Sijie Chen
- , Tong Lin
- & Xiaolin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Total syntheses of Tetrodotoxin and 9-epiTetrodotoxin
Total syntheses of Tetrodotoxin and 9-epiTetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin and congeners are specific voltage-gated sodium channel blockers that exhibit remarkable anesthetic and analgesic effects but total synthesis procedures are often limited by the scale. Here, the authors present a scalable asymmetric syntheses of Tetrodotoxin and 9-epiTetrodotoxin from the abundant chemical feedstock furfuryl alcohol.
- Peihao Chen
- , Jing Wang
- & Xiangbing Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist as a clinical candidate for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Discovery of a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist as a clinical candidate for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), an advanced form of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), can progress to liver fibrosis. Here, the authors develop a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist for the treatment of MASLD and MASH.
- Haushabhau S. Pagire
- , Suvarna H. Pagire
- & Jin Hee Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive Minisci late stage functionalization with transfer learning
Predictive Minisci late stage functionalization with transfer learning
Regioselectivity prediction for many reactions remains a challenging target for a priori prediction. Here, the authors develop a machine learning model that predicts the outcomes of Minisci reactions.
- Emma King-Smith
- , Felix A. Faber
- & Alpha A. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Late-stage synthesis of heterobifunctional molecules for PROTAC applications via ruthenium-catalysed C‒H amidation
Late-stage synthesis of heterobifunctional molecules for PROTAC applications via ruthenium-catalysed C‒H amidation
PROTACs are uniquely powerful therapeutic agents, but their synthetic tractability significantly limit drug discovery programs. Here, the authors developed a single step synthesis of PROTAC conjugates via late stage ruthenium-catalysed C–H amidation.
- Daniele Antermite
- , Stig D. Friis
- & Magnus J. Johansson
-
Article
| Open Access Modular access to alkylgermanes via reductive germylative alkylation of activated olefins under nickel catalysis
Modular access to alkylgermanes via reductive germylative alkylation of activated olefins under nickel catalysis
While carbon-introducing difunctionalization of C-C double bonds is well established, the analogous difunctionalization for introducing germanium group and other functionalities remains elusive. Here, the authors describe a nickel-catalyzed germylative alkylation of activated olefins with easily accessible primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl bromides and chlorogermanes as the electrophiles to form C-Ge and C-Calkyl bonds simultaneously.
- Rui Gu
- , Xiujuan Feng
- & Xuan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Bifunctionality of dirhodium tetracarboxylates in metallaphotocatalysis
Bifunctionality of dirhodium tetracarboxylates in metallaphotocatalysis
Traditional metallaphotocatalysis often requires two or more separate catalysts and is considered to be costly and not tolerant towards a wide substrate scope. Here the authors realize metallaphotocatalysis with a bifunctional dirhodium tetracarboxylate as single catalyst component to merge carbenoid chemistry and 1O2 chemistry.
- Taoda Shi
- , Tianyuan Zhang
- & Wenhao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Selective activator of human ClpP triggers cell cycle arrest to inhibit lung squamous cell carcinoma
Selective activator of human ClpP triggers cell cycle arrest to inhibit lung squamous cell carcinoma
Chemo-activation of mitochondrial ClpP exhibits promising anticancer properties. Here, the authors develop a potent activator ZK53 that is highly selective on human ClpP but inactive toward bacterial ClpP proteins, and show that ZK53 causes cell cycle arrest via ClpP on lung squamous cell carcinoma cells and exhibits therapeutic effects in animal models.
- Lin-Lin Zhou
- , Tao Zhang
- & Cai-Guang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A pharmacophore-guided deep learning approach for bioactive molecular generation
A pharmacophore-guided deep learning approach for bioactive molecular generation
Designing novel molecules with desired bioactivity is a critical challenge in drug discovery, particularly for novel or understudied targets. The authors propose a pharmacophore-guided deep learning approach PGMG to generate diverse active-like molecules with limited activity data.
- Huimin Zhu
- , Renyi Zhou
- & Min Li
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic enantioselective reductive alkynylation of amides enables one-pot syntheses of pyrrolidine, piperidine and indolizidine alkaloids
Catalytic enantioselective reductive alkynylation of amides enables one-pot syntheses of pyrrolidine, piperidine and indolizidine alkaloids
Saturated α-alkyl aza-heterocycles are found in a wide array of bioactive molecules. Here, the authors disclosed a one-pot, catalytic enantioselective synthesis of pyrrolidine, piperidine and indolizidine alkaloids from amides and alkynes.
- Fang-Fang Xu
- , Jin-Quan Chen
- & Pei-Qiang Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Retrosynthesis prediction with an interpretable deep-learning framework based on molecular assembly tasks
Retrosynthesis prediction with an interpretable deep-learning framework based on molecular assembly tasks
Automating retrosynthesis prediction in organic chemistry is a major application of ML. Here the authors present RetroExplainer, which offers a high-performance, transparent and interpretable deep-learning framework providing valuable insights for drug development.
- Yu Wang
- , Chao Pang
- & Leyi Wei
-
Article
| Open Access 2-Oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane as a new bioisostere of the phenyl ring
2-Oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane as a new bioisostere of the phenyl ring
The phenyl ring is a basic structural element in chemistry. Here, the authors show the design, synthesis, and validation of 2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane as a new saturated bioisostere with improved physicochemical properties
- Vadym V. Levterov
- , Yaroslav Panasiuk
- & Pavel K. Mykhailiuk
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting Toll-like receptor-driven systemic inflammation by engineering an innate structural fold into drugs
Targeting Toll-like receptor-driven systemic inflammation by engineering an innate structural fold into drugs
In this work, the authors report a drug class based on an ancient innate defense fold. Inspired by Nature’s anti-infective strategies, this peptide-based drug targets systemic inflammation via multiple molecular interactions, enhancing effectiveness
- Ganna Petruk
- , Manoj Puthia
- & Artur Schmidtchen
-
Article
| Open Access A Bischler-Napieralski and homo-Mannich sequence enables diversified syntheses of sarpagine alkaloids and analogues
A Bischler-Napieralski and homo-Mannich sequence enables diversified syntheses of sarpagine alkaloids and analogues
The Mannich reaction is a well-established method for the synthesis of β-amino carbonyl compounds while the analogous reactions of homo-enol or its equivalents with imines or iminium ions are much less explored. Here, the authors describe a homo-Mannich reaction of cyclopropanol with imines generated via a Bischler-Napieralski reaction.
- Hanyue Qiu
- , Xinghai Fei
- & Min Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent access to 5,6,7-perifused cycles
Divergent access to 5,6,7-perifused cycles
The lack of efficient and diverse synthesis strategy has hindered the study of perifused cycles. Here, the authors report a metal-catalyzed cascade electrocyclization to access 5,6,7-perifused cycles, and demonstrated the versatility of this protocol in the late-stage modification of pharmaceuticals.
- Jingpeng Han
- , Yongjian Yang
- & Baosheng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Diversity-oriented synthesis encoded by deoxyoligonucleotides
Diversity-oriented synthesis encoded by deoxyoligonucleotides
Most DNA-encoded library (DEL) syntheses are limited by the presence of sensitive DNA-based constructs. Here, the authors develop DOSEDO, a diverse 3.7 million compound DEL, generated through diversity-oriented synthesis that provides enhanced scaffold and exit vector diversity and gives validated binding hits for multiple protein targets.
- Liam Hudson
- , Jeremy W. Mason
- & Karin Briner
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BDK) inhibitors with opposing effects on BDK protein levels
Small molecule branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BDK) inhibitors with opposing effects on BDK protein levels
Branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BDK) inhibits the activity of branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase and branched chain amino acid degradation, implicated in several diseases. Here, the authors discover a BDK inhibitor and degrader that shows efficacy in rodent metabolism and heart failure models, as well as another class of BDK inhibitors that stabilizes BDK.
- Rachel J. Roth Flach
- , Eliza Bollinger
- & Kevin J. Filipski
-
Article
| Open Access DNA framework-engineered chimeras platform enables selectively targeted protein degradation
DNA framework-engineered chimeras platform enables selectively targeted protein degradation
The lack of a universal platform for PROTAC development remains a major bottleneck. Here, the authors report modular DNA framework-based PROTACs (DbTACs) that enable precise control of the linker length and selective degradation of diverse targets in different cellular compartments using various warheads.
- Li Zhou
- , Bin Yu
- & Yi Ma
-
Article
| Open Access HypoRiPPAtlas as an Atlas of hypothetical natural products for mass spectrometry database search
HypoRiPPAtlas as an Atlas of hypothetical natural products for mass spectrometry database search
A gap exists between large-scale genome mining and mass spectral datasets for natural product discovery. Here the authors bridge the gap by developing HypoRiPPAtlas, an Atlas of hypothetical natural product structures, which is ready-to-use for in silico database search of tandem mass spectra.
- Yi-Yuan Lee
- , Mustafa Guler
- & Hosein Mohimani
-
Article
| Open Access Non-covalent inhibitors of thioredoxin glutathione reductase with schistosomicidal activity in vivo
Non-covalent inhibitors of thioredoxin glutathione reductase with schistosomicidal activity in vivo
Only praziquantel is available for treating schistosomiasis, a disease affecting >200 million people. Here, the authors identify compounds active against schistosome infections meeting the criteria for lead progression indicated by WHO with better activity against juvenile worms than praziquantel.
- Valentina Z. Petukhova
- , Sammy Y. Aboagye
- & Pavel A. Petukhov
-
Article
| Open Access USP25 regulates KEAP1-NRF2 anti-oxidation axis and its inactivation protects acetaminophen-induced liver injury in male mice
USP25 regulates KEAP1-NRF2 anti-oxidation axis and its inactivation protects acetaminophen-induced liver injury in male mice
The redox status of a cell is regulated through a number of mechanisms, chief among these is the KEAP1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of NRF2. Here the authors show that KEAP1 itself is ubiquitinated and degraded in a process that is opposed by the ubiquitin-specific protease USP25.
- Changzhou Cai
- , Huailu Ma
- & Jiewei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access From a drug repositioning to a structure-based drug design approach to tackle acute lymphoblastic leukemia
From a drug repositioning to a structure-based drug design approach to tackle acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Deoxycytidine kinase is the rate-limiting enzyme of the salvage pathway and it has recently emerged as a target for antiproliferative therapies for cancers where it is essential. Here, the authors develop a potent inhibitor applying an iterative multidisciplinary approach, which relies on computational design coupled with experimental evaluations.
- Magali Saez-Ayala
- , Laurent Hoffer
- & Xavier Morelli
-
Article
| Open Access Potent and selective covalent inhibition of the papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2
Potent and selective covalent inhibition of the papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2
The development of direct-acting antivirals to combat COVID-19 remains an important goal. Here the authors design covalent inhibitors that target the papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2. The most promising inhibitor blocks viral replication in mammalian cells.
- Brian C. Sanders
- , Suman Pokhrel
- & Jerry M. Parks
-
Article
| Open Access Wavelength engineerable porous organic polymer photosensitizers with protonation triggered ROS generation
Wavelength engineerable porous organic polymer photosensitizers with protonation triggered ROS generation
Engineering excitation wavelength of photosensitizers allows to enhanced reactive oxygen species but controlling the wavelength corresponding to operating conditions remains challenging. Here, the authors implement a wavelength-engineerable imidazolium-based porous organic polymer and demonstrate tuning of the optimal wavelength for maximum performance by modifying the linker system.
- Jinwoo Shin
- , Dong Won Kang
- & Chang Seop Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Trio-pharmacophore DNA-encoded chemical library for simultaneous selection of fragments and linkers
Trio-pharmacophore DNA-encoded chemical library for simultaneous selection of fragments and linkers
Dual-pharmacophore DNA-Encoded Libraries (DELs) can generate large libraries, but linker optimisation is challenging. Here, the authors report a trio-pharmacophore DEL (T-DEL) for both de novo fragment identification and linker optimization of known fragment pairs.
- Meiying Cui
- , Dzung Nguyen
- & Yixin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and biosynthesis of karnamicins as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Discovery and biosynthesis of karnamicins as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Treatment of hypertension entails use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Here, the authors show a series of karnamicins with significant inhibitory activity and identify two unusual flavoprotein hydroxylases involved in the assembly of the fully-substituted hydroxypyridine core of karnamicins.
- Zhiyin Yu
- , Jian-Ping Huang
- & Sheng-Xiong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning models to accelerate the design of polymeric long-acting injectables
Machine learning models to accelerate the design of polymeric long-acting injectables
Polymer-based long-acting injectable drugs are a promising therapeutic strategy for chronic diseases. Here the authors use machine learning to inform the data-driven development of advanced drug formulations.
- Pauric Bannigan
- , Zeqing Bao
- & Christine Allen
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of macrocyclic nucleoside antibacterials and their interactions with MraY
Synthesis of macrocyclic nucleoside antibacterials and their interactions with MraY
MraY is a membrane enzyme required for bacterial cell wall synthesis. Here, the authors modify sphaerimicins as antibacterials targeting it via structure-based design and synthesis through two key reactions, showing a platform for further development of MraY inhibitors as antibacterials.
- Takeshi Nakaya
- , Miyuki Yabe
- & Satoshi Ichikawa
-
Article
| Open Access DeepPROTACs is a deep learning-based targeted degradation predictor for PROTACs
DeepPROTACs is a deep learning-based targeted degradation predictor for PROTACs
The rational design of PROTACs is difficult due to their obscure structure-activity relationship. Here the authors present a deep neural network model - DeepPROTACs - for predicting the degradation capacity of a proposed PROTAC molecule.
- Fenglei Li
- , Qiaoyu Hu
- & Fang Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Generative deep learning enables the discovery of a potent and selective RIPK1 inhibitor
Generative deep learning enables the discovery of a potent and selective RIPK1 inhibitor
Retrieval of a new starting active compound with a novel scaffold during early drug development is an important but challenging task. Here, the authors propose a generative deep learning model and by applying this model they discover a potent and highly selective RIPK1 inhibitor with a previously unreported scaffold.
- Yueshan Li
- , Liting Zhang
- & Shengyong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Lysyl-tRNA synthetase, a target for urgently needed M. tuberculosis drugs
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase, a target for urgently needed M. tuberculosis drugs
Tuberculosis is a major cause of mortality, and the rise of drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis requires the urgent development of safe and effective treatments. In this work, the authors develop a compound against lysyl-tRNA synthetase, demonstrating on-target mechanism of action and efficacy in vivo.
- Simon R. Green
- , Susan H. Davis
- & Laura A. T. Cleghorn
-
Article
| Open Access Insight into mode-of-action and structural determinants of the compstatin family of clinical complement inhibitors
Insight into mode-of-action and structural determinants of the compstatin family of clinical complement inhibitors
Therapeutic modulation of the complement system has gained interest over the past two decades. Here, the authors provide molecular-level insight into the mode-of-action, target selectivity and species specificity of the compstatin family of complement inhibitors, which entered the clinic in 2021.
- Christina Lamers
- , Xiaoguang Xue
- & Daniel Ricklin
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a binding site on soluble RANKL that can be targeted to inhibit soluble RANK-RANKL interactions and treat osteoporosis
Identification of a binding site on soluble RANKL that can be targeted to inhibit soluble RANK-RANKL interactions and treat osteoporosis
Huang et al. discover a binding site on soluble RANKL that is not found on its membrane-bound homologue. A drug screening identified a small molecule (S3-15) that can target this binding site and has anti-osteoporotic but not immunosuppressive effects.
- Dane Huang
- , Chao Zhao
- & Jun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the path to Plasmodium prolyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors that overcome halofuginone resistance
Elucidating the path to Plasmodium prolyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors that overcome halofuginone resistance
The development of antimalarials against the human liver and asexual blood stages is one of the top public health challenges. Here, the authors report a single-step biochemical assay for the characterization of prolyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors, and develop high-affinity inhibitors for the enzyme, including elusive triple-site ligands.
- Mark A. Tye
- , N. Connor Payne
- & Ralph Mazitschek
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 with a highly selective inhibitor for the treatment of prostate cancer
Targeting dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 with a highly selective inhibitor for the treatment of prostate cancer
The kinase DYRK2 is a known oncogene but its role in prostate cancer is unexplored. Here, the authors identify DYRK2 as a target for prostate cancer with a role in invasion and they discover a specific DYRK2 inhibitor that has good pharmacokinetics and efficacy in vivo.
- Kai Yuan
- , Zhaoxing Li
- & Peng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Foldamers reveal and validate therapeutic targets associated with toxic α-synuclein self-assembly
Foldamers reveal and validate therapeutic targets associated with toxic α-synuclein self-assembly
Inhibiting alpha-synuclein self-assembly into amyloid structures, associated with Parkinson’s disease, is a potential therapeutic intervention. Here, the authors identify the domains/sequences that are essential for alpha-synuclein aggregation and test the activity of foldamer-based antagonists to identify potential therapeutic targets.
- Jemil Ahmed
- , Tessa C. Fitch
- & Sunil Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic lipopeptide targeting top-priority multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens
A synthetic lipopeptide targeting top-priority multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens
Polymyxins are often the last therapeutic option for multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria, but have suboptimal safety and efficacy. Here the authors report the discovery and development of a synthetic lipopeptide with an improved safety and efficacy against top-priority MDR Gram-negative pathogens.
- Kade D. Roberts
- , Yan Zhu
- & Jian Li
-
Article
| Open Access A propolis-derived small molecule ameliorates metabolic syndrome in obese mice by targeting the CREB/CRTC2 transcriptional complex
A propolis-derived small molecule ameliorates metabolic syndrome in obese mice by targeting the CREB/CRTC2 transcriptional complex
Disruption of CREB/CRTC2, a key gluconeogenic transcriptional complex, has been shown to ameliorate insulin resistance in mice. Here, the authors show that the inhibitor artipllin C and the synthetic compound A57, which presents with higher inhibitory activity, improve insulin sensitivity in obese mice by inhibiting CREB-CRTC2 interaction.
- Yaqiong Chen
- , Jiang Wang
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Pyridylpiperazine-based allosteric inhibitors of RND-type multidrug efflux pumps
Pyridylpiperazine-based allosteric inhibitors of RND-type multidrug efflux pumps
Efflux transporters of the RND family confer resistance to multiple antibiotics in Gram-negative bacteria. Here, the authors identify pyridylpiperazine-based compounds that potentiate antibiotic activity in E. coli through allosteric inhibition of its primary RND transporter.
- Coline Plé
- , Heng-Keat Tam
- & Ruben C. Hartkoorn
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic prodrug design enables biocatalytic activation in mice to elicit tumor growth suppression
Synthetic prodrug design enables biocatalytic activation in mice to elicit tumor growth suppression
Considering the intrinsic toxicities of transition metals, their incorporation into drug therapies must operate at minimal amounts while ensuring adequate catalytic activity within complex biological systems. This study investigates the design of synthetic prodrugs that not only can be tuned to be harmless, but are robustly transformed in vivo to reach therapeutically relevant levels.
- Igor Nasibullin
- , Ivan Smirnov
- & Katsunori Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access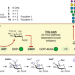 Fluorinated rhamnosides inhibit cellular fucosylation
Fluorinated rhamnosides inhibit cellular fucosylation
Aberrant expression of fucosylated glycans has been linked to several disease states. Control of fucose expression on live cells is needed to aid research and therapy development. Here the authors report on the development of a class of fucosylation metabolic prodrug inhibitors and demonstrated inhibition of cellular fucosylation.
- Johan F. A. Pijnenborg
- , Emiel Rossing
- & Thomas J. Boltje
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Bleeding complications limits the use of effective antithrombotics therapeutics. Here, the authors developed next-generation direct thrombin inhibitors with low bleeding risks as safe peri-percutaneous coronary intervention anticoagulants when used in combination with antiplatelets.
- Cho Yeow Koh
- , Norrapat Shih
- & Mark Y. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access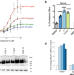 Compounds targeting OSBPL7 increase ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux preserving kidney function in two models of kidney disease
Compounds targeting OSBPL7 increase ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux preserving kidney function in two models of kidney disease
This study describes a class of small molecule compounds that promote ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux via a non-transcriptional mechanism, the identification of the molecular target by a chemical biology approach, and the potential of these agents for the treatment of chronic kidney diseases and potentially other diseases where lipid accumulation drives disease progression.
- Matthew B. Wright
- , Javier Varona Santos
- & Alessia Fornoni
-
Article
| Open Access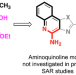 Tetrasubstituted imidazoles as incognito Toll-like receptor 8 a(nta)gonists
Tetrasubstituted imidazoles as incognito Toll-like receptor 8 a(nta)gonists
Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) plays essential roles in the innate immune response to viral single-stranded RNA (ssRNA), so small molecule modulators of TLR8 are of interest, however adverse effects limit their use. Here, the authors report a tetrasubstituted imidazole CU-CPD107 with dichotomous behaviour, which inhibits R848-induced TLR8 signaling, but shows synergistic activity in the presence of ssRNA, making it a potential antiviral agent.
- Yi Yang
- , Adam Csakai
- & Hang Yin
-
Article
| Open Access A novel RyR1-selective inhibitor prevents and rescues sudden death in mouse models of malignant hyperthermia and heat stroke
A novel RyR1-selective inhibitor prevents and rescues sudden death in mouse models of malignant hyperthermia and heat stroke
Mutations in ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1), a Ca2+ release channel in skeletal muscle, cause malignant hyperthermia (MH) and are involved in heat stroke. Here, the authors show that an oxolinic acid-derivative RyR1 inhibitor effectively prevents and treats MH and heat stroke in various MH mouse models.
- Toshiko Yamazawa
- , Takuya Kobayashi
- & Takashi Murayama
-
Review Article
| Open Access Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential
Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential
Natural products are an important source of bioactive compounds and have versatile applications in different fields, but their discovery is challenging. Here, the authors review the recent developments in genome mining for discovery of natural products, focusing on compounds from unconventional microorganisms and microbiomes.
- Kirstin Scherlach
- & Christian Hertweck
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring protein hotspots by optimized fragment pharmacophores
Exploring protein hotspots by optimized fragment pharmacophores
Fragment-based drug discovery employs screening of small polar compounds typically exhibiting low affinity towards protein targets. Here, the authors combine the use of protein-based binding pharmacophores with the theory of protein hotspots to develop a design protocol for fragment libraries, called SpotXplorer, and validate their approach on common and emerging drug targets.
- Dávid Bajusz
- , Warren S. Wade
- & György M. Keserű

 Late-stage meta-C–H alkylation of pharmaceuticals to modulate biological properties and expedite molecular optimisation in a single step
Late-stage meta-C–H alkylation of pharmaceuticals to modulate biological properties and expedite molecular optimisation in a single step