Featured
-
-
Article |
 Coordination of cohesin and DNA replication observed with purified proteins
Coordination of cohesin and DNA replication observed with purified proteins
We study the interplay between cohesin and replication by reconstituting a functional replisome using purified proteins, showing how cohesin initially responds to replication and providing a molecular model for the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion.
- Yasuto Murayama
- , Shizuko Endo
- & Hiroyuki Araki
-
Article
| Open Access MRE11 liberates cGAS from nucleosome sequestration during tumorigenesis
MRE11 liberates cGAS from nucleosome sequestration during tumorigenesis
The double-strand break sensor MRE11 is identified as a pivotal mediator of cGAS activation in response to multiple types of DNA damage.
- Min-Guk Cho
- , Rashmi J. Kumar
- & Gaorav P. Gupta
-
Article |
 Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Polymerase delta is required for multiple steps in polymerase theta-dependent repair of chromosome breaks, a pathway targeted in cancer therapy.
- Susanna Stroik
- , Juan Carvajal-Garcia
- & Dale A. Ramsden
-
Article |
 Intricate 3D architecture of a DNA mimic of GFP
Intricate 3D architecture of a DNA mimic of GFP
X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy analyses of Lettuce—a DNA mimic of GFP—bound to various fluorophores reveal previously unknown structures of DNA that rival analogous RNAs in complexity.
- Luiz F. M. Passalacqua
- , Michael T. Banco
- & Adrian R. Ferré-D’Amaré
-
Article |
 Break-induced replication orchestrates resection-dependent template switching
Break-induced replication orchestrates resection-dependent template switching
Break-induced telomere synthesis initiates recruitment of the SNM1A nuclease, which promotes DNA end resection that in turn allows template switching to enable bypass of lesions.
- Tianpeng Zhang
- , Yashpal Rawal
- & Roger A. Greenberg
-
Article
| Open Access CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is sufficient to block loop extruding cohesin in a DNA tension dependent manner, and induces loop extrusion direction switching and loop shrinkage.
- Iain F. Davidson
- , Roman Barth
- & Jan-Michael Peters
-
Article |
 Establishment and function of chromatin organization at replication origins
Establishment and function of chromatin organization at replication origins
Genome-scale in vitro reconstitution of DNA replication through chromatin establishes a crucial role for the origin recognition complex in organizing nucleosome arrays that are crucial for the initiation of replication.
- Erika Chacin
- , Karl-Uwe Reusswig
- & Christoph F. Kurat
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the transposon-associated TnpB enzyme
Cryo-EM structure of the transposon-associated TnpB enzyme
Cryo-electron microscopy analysis of the Deinococcus radiodurans ISDra2 TnpB in complex with its cognate ωRNA and target DNA provides insights into the mechanism of TnpB function and the evolution of CRISPR–Cas12 effectors.
- Ryoya Nakagawa
- , Hisato Hirano
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structural studies of the CRISPR-associated transposon comprising Cas12k, TnsC, TnsB and TniQ from Scytonema hofmannii using cryo-electron microscopy reveal insights into the architecture and mechanism of RNA-guided DNA transposition.
- Jung-Un Park
- , Amy Wei-Lun Tsai
- & Elizabeth H. Kellogg
-
Article
| Open Access R-loop formation and conformational activation mechanisms of Cas9
R-loop formation and conformational activation mechanisms of Cas9
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 in multiple DNA-bound states provide insights on the mechanism of Cas9 activation by target DNA.
- Martin Pacesa
- , Luuk Loeff
- & Martin Jinek
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST
Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST
The Polα–primase-associated CST complex organizes telomeric C-strand DNA synthesis, and, in combination with telomerase, it carries out complete replication of the single-stranded DNA overhang found at human telomeres.
- Arthur J. Zaug
- , Karen J. Goodrich
- & Thomas R. Cech
-
Article |
 Molecular basis for the initiation of DNA primer synthesis
Molecular basis for the initiation of DNA primer synthesis
The molecular determinants for primer synthesis are identified within the catalytic domain of primase-polymerase enzymes, elucidating the mechanisms underlying initiation of primer synthesis.
- Arthur W. H. Li
- , Katerina Zabrady
- & Aidan J. Doherty
-
Article |
 Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Using high-resolution NMR characterization, the kinetics and dynamics of the catalytic function of a DNAzyme are shown.
- Jan Borggräfe
- , Julian Victor
- & Manuel Etzkorn
-
Article |
 Activation of homologous recombination in G1 preserves centromeric integrity
Activation of homologous recombination in G1 preserves centromeric integrity
Centromeres are able to recruit the homologous recombination machinery during G1 via CENP-A and HJURP, thereby preserving centromeric integrity even in the absence of a sister chromatid.
- Duygu Yilmaz
- , Audrey Furst
- & Evi Soutoglou
-
Article |
 Target site selection and remodelling by type V CRISPR-transposon systems
Target site selection and remodelling by type V CRISPR-transposon systems
Structural studies on Scytonema hofmanni CRISPR-associated transposon protein complexes indicate a mechanism for RNA-guided DNA transposition involving Cas12k, TnsC and TnsB.
- Irma Querques
- , Michael Schmitz
- & Martin Jinek
-
Article |
 eccDNAs are apoptotic products with high innate immunostimulatory activity
eccDNAs are apoptotic products with high innate immunostimulatory activity
By developing a new eccDNA purification and profiling method, the study revealed close-to-random genomic origination, mechanism of biogenesis and function of eccDNAs.
- Yuangao Wang
- , Meng Wang
- & Yi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Transposon-associated TnpB is a programmable RNA-guided DNA endonuclease
Transposon-associated TnpB is a programmable RNA-guided DNA endonuclease
The RNA-directed nuclease TnpB from Deinococcus radiodurans can be reprogrammed to cleave DNA target sites in human cells.
- Tautvydas Karvelis
- , Gytis Druteika
- & Virginijus Siksnys
-
Article |
 RNA transcripts stimulate homologous recombination by forming DR-loops
RNA transcripts stimulate homologous recombination by forming DR-loops
RNA transcripts stimulate homologous recombination through the formation of DR-loops, intermediate structures that contain both DNA–DNA and DNA–RNA hybrids.
- Jian Ouyang
- , Tribhuwan Yadav
- & Lee Zou
-
Article |
 Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
A high-throughput, chromosome-wide analysis of DNA looping reveals its contribution to the organization of chromatin, and provides insight into how nucleosomes are deposited and organised de novo.
- Aakash Basu
- , Dmitriy G. Bobrovnikov
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article |
 DNA mismatches reveal conformational penalties in protein–DNA recognition
DNA mismatches reveal conformational penalties in protein–DNA recognition
A high-throughput assay that introduces mismatched base pairs into the DNA sequence shows that mismatches can increase transcription factor binding affinity by prepaying some of the energetic cost of distorting the DNA.
- Ariel Afek
- , Honglue Shi
- & Raluca Gordân
-
Article |
 Regulation of the MLH1–MLH3 endonuclease in meiosis
Regulation of the MLH1–MLH3 endonuclease in meiosis
Reconstitution of the activation of the MLH1–MLH3 endonuclease shows how crossovers are formed during meiosis.
- Elda Cannavo
- , Aurore Sanchez
- & Petr Cejka
-
Article
| Open Access Occupancy maps of 208 chromatin-associated proteins in one human cell type
Occupancy maps of 208 chromatin-associated proteins in one human cell type
ChIP–seq and CETCh–seq data are used to analyse binding maps for 208 transcription factors and other chromatin-associated proteins in a single human cell type, providing a comprehensive catalogue of the transcription factor landscape and gene regulatory networks in these cells.
- E. Christopher Partridge
- , Surya B. Chhetri
- & Eric M. Mendenhall
-
Article |
 Alcohol-derived DNA crosslinks are repaired by two distinct mechanisms
Alcohol-derived DNA crosslinks are repaired by two distinct mechanisms
DNA interstrand crosslinks induced by acetaldehyde are repaired by both the Fanconi anaemia pathway and by a second, excision-independent repair mechanism.
- Michael R. Hodskinson
- , Alice Bolner
- & Puck Knipscheer
-
Article |
 A bacteriophage nucleus-like compartment shields DNA from CRISPR nucleases
A bacteriophage nucleus-like compartment shields DNA from CRISPR nucleases
The jumbo phage ΦKZ constructs a proteinaceous nucleus-like compartment around its genome that protects phage DNA from degradation by DNA-targeting immune effectors of the host, including CRISPR–Cas and restriction enzymes.
- Senén D. Mendoza
- , Eliza S. Nieweglowska
- & Joseph Bondy-Denomy
-
Article |
 Mechanism of head-to-head MCM double-hexamer formation revealed by cryo-EM
Mechanism of head-to-head MCM double-hexamer formation revealed by cryo-EM
Time-resolved electron microscopy reveals the mechanism by which the origin recognition complex loads pairs of MCM helicases around DNA prior to bidirectional replication.
- Thomas C. R. Miller
- , Julia Locke
- & Alessandro Costa
-
Article |
 Transposon-encoded CRISPR–Cas systems direct RNA-guided DNA integration
Transposon-encoded CRISPR–Cas systems direct RNA-guided DNA integration
A programmable transposase integrates donor DNA at user-defined genomic target sites with high fidelity, revealing a new approach for genetic engineering that obviates the need for DNA double-strand breaks and homologous recombination.
- Sanne E. Klompe
- , Phuc L. H. Vo
- & Samuel H. Sternberg
-
Letter |
 TRAIP is a master regulator of DNA interstrand crosslink repair
TRAIP is a master regulator of DNA interstrand crosslink repair
The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAIP governs the choice between the NEIL3 or the Fanconi anaemia pathway for the repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks.
- R. Alex Wu
- , Daniel R. Semlow
- & Johannes C. Walter
-
Article |
 LHX2- and LDB1-mediated trans interactions regulate olfactory receptor choice
LHX2- and LDB1-mediated trans interactions regulate olfactory receptor choice
Specific interchromosomal contacts in olfactory sensory neurons form a super-enhancer that controls the expression of a single olfactory receptor in each neuron.
- Kevin Monahan
- , Adan Horta
- & Stavros Lomvardas
-
Article |
 The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
A method for systematically exploring interactions between the nucleosome and transcription factors identifies five major interaction patterns.
- Fangjie Zhu
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Article |
 Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II–DSIF–NELF
Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II–DSIF–NELF
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of a paused transcription elongation complex of RNA polymerase II bound to DRB sensitivity-inducing factor and negative elongation factor is reported at 3.2 Å resolution.
- Seychelle M. Vos
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article |
 Structure of activated transcription complex Pol II–DSIF–PAF–SPT6
Structure of activated transcription complex Pol II–DSIF–PAF–SPT6
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of an activated transcription elongation complex of RNA polymerase II bound to DRB sensitivity-inducing factor and the elongation factors PAF1 complex and SPT6 is reported at 3.1 Å resolution.
- Seychelle M. Vos
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Letter |
 53BP1–RIF1–shieldin counteracts DSB resection through CST- and Polα-dependent fill-in
53BP1–RIF1–shieldin counteracts DSB resection through CST- and Polα-dependent fill-in
53BP1 and shieldin recruit the CTC1–STN1–TEN1 complex and polymerase-α to sites of DNA damage to help control the repair of double-strand breaks.
- Zachary Mirman
- , Francisca Lottersberger
- & Titia de Lange
-
Letter |
 The mechanism of eukaryotic CMG helicase activation
The mechanism of eukaryotic CMG helicase activation
In vitro experiments, using purified proteins and an assay that detects DNA unwinding, reveal the mechanism of activation of eukaryotic DNA replication.
- Max E. Douglas
- , Ferdos Abid Ali
- & John F. X. Diffley
-
Article |
 Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
A kinetic model is proposed to predict the probability of dG•dT misincorporation across different polymerases, and provides mechanisms for sequence-dependent misincorporation.
- Isaac J. Kimsey
- , Eric S. Szymanski
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Article |
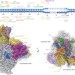 Structural basis of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation
Structural basis of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation
Detailed structures of yeast RNA polymerase III and its initiation complex shed light on how the transcription of essential non-coding RNAs begins and allow comparisons with other RNA polymerases.
- Guillermo Abascal-Palacios
- , Ewan Phillip Ramsay
- & Alessandro Vannini
-
Letter |
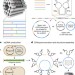 Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
All necessary strands for DNA origami can be created in a single scalable process by using bacteriophages to generate single-stranded precursor DNA containing the target sequences interleaved with self-excising DNA enzymes.
- Florian Praetorius
- , Benjamin Kick
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Article |
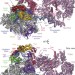 Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the yeast pre-initiation complex (PIC) and its complex with core Mediator provide insights into the opening of promoter DNA and the initiation of transcription.
- S. Schilbach
- , M. Hantsche
- & P. Cramer
-
Letter |
 Nucleosome–Chd1 structure and implications for chromatin remodelling
Nucleosome–Chd1 structure and implications for chromatin remodelling
A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the chromatin remodelling factor Chd1 bound to a nucleosome leads to a model for DNA translocation by its ATPase motor.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article |
 The transcription fidelity factor GreA impedes DNA break repair
The transcription fidelity factor GreA impedes DNA break repair
In Escherichia coli, the control of RNA polymerase backtracking by transcription elongation factors impairs DNA break repair by affecting RecBCD resection and consequently RecA loading at sites far removed from the original DNA break.
- Priya Sivaramakrishnan
- , Leonardo A. Sepúlveda
- & Christophe Herman
-
Article |
 BRCA1–BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing
BRCA1–BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing
The tumour suppressor complex BRCA1–BARD1, which facilitates the generation of a single-stranded DNA template during homologous recombination, also binds to the recombinase RAD51 and enhances its function.
- Weixing Zhao
- , Justin B. Steinfeld
- & Patrick Sung
-
Article |
 Type III CRISPR–Cas systems produce cyclic oligoadenylate second messengers
Type III CRISPR–Cas systems produce cyclic oligoadenylate second messengers
CRISPR-associated protein Csm6 is activated by a cyclic oligoadenylate second messenger generated by Cas10 activity in the CRISPR type III interference complex, representing a novel mechanism of CRISPR interference.
- Ole Niewoehner
- , Carmela Garcia-Doval
- & Martin Jinek
-
Letter |
 Cascading MutS and MutL sliding clamps control DNA diffusion to activate mismatch repair
Cascading MutS and MutL sliding clamps control DNA diffusion to activate mismatch repair
MutS and MutL—the highly conserved core proteins responsible for the repair of mismatched DNA—form sequential stable sliding clamps that together modulate one-dimensional diffusion along the DNA and, with MutH, facilitate the search for a distant excision initiation site.
- Jiaquan Liu
- , Jeungphill Hanne
- & Richard Fishel
-
Letter |
 The CRISPR-associated DNA-cleaving enzyme Cpf1 also processes precursor CRISPR RNA
The CRISPR-associated DNA-cleaving enzyme Cpf1 also processes precursor CRISPR RNA
The CRISPR-associated protein Cpf1 from Francisella novicida is a novel enzyme with specific, dual-endoribonuclease–endonuclease activities in precursor crRNA processing and crRNA-programmable cleavage of target DNA.
- Ines Fonfara
- , Hagen Richter
- & Emmanuelle Charpentier
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of the Rous sarcoma virus intasome
Crystal structure of the Rous sarcoma virus intasome
A crystal structure of the octameric integrase from Rous sarcoma virus in complex with viral and target DNAs.
- Zhiqi Yin
- , Ke Shi
- & Hideki Aihara
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for promiscuous PAM recognition in type I–E Cascade from E. coli
Structural basis for promiscuous PAM recognition in type I–E Cascade from E. coli
The structure of E. coli Cascade bound to foreign target DNA is presented, revealing the basis of the relaxed Cascade PAM recognition specificity, which results from its interaction with the minor groove, and demonstrating how a wedge in Cascade forces the directional pairing of the target strand with CRISPR RNA while stabilizing the non-target displaced strand.
- Robert P. Hayes
- , Yibei Xiao
- & Ailong Ke
-
Letter |
 DNA-dependent formation of transcription factor pairs alters their binding specificity
DNA-dependent formation of transcription factor pairs alters their binding specificity
A high-throughput analysis of DNA binding in over 9,000 interacting transcription factor pairs reveals that the interactions are often actively mediated by the DNA itself and the composite DNA sites recognized are different from the individual motifs of each transcription factor.
- Arttu Jolma
- , Yimeng Yin
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Letter |
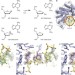 The DNA glycosylase AlkD uses a non-base-flipping mechanism to excise bulky lesions
The DNA glycosylase AlkD uses a non-base-flipping mechanism to excise bulky lesions
Crystal structures of the DNA glycosylase AlkD with DNA containing various modified bases show that neither substrate recognition nor catalysis use a base-flipping mechanism; instead, AlkD scans the phosphodeoxyribose backbone for increased cationic charge imparted by the alkylated base, and then uses the positive charge to facilitate cleavage of the glycosidic bond, thus explaining the specificity of AlkD for cationic lesions.
- Elwood A. Mullins
- , Rongxin Shi
- & Brandt F. Eichman
-
Article |
 The mechanism of DNA replication termination in vertebrates
The mechanism of DNA replication termination in vertebrates
This study describes a new model of eukaryotic replication termination in which converging leading strands pass each other unhindered and the replicative DNA helicase is unloaded late, after all strands have been ligated.
- James M. Dewar
- , Magda Budzowska
- & Johannes C. Walter
-
Letter |
 CDA directs metabolism of epigenetic nucleosides revealing a therapeutic window in cancer
CDA directs metabolism of epigenetic nucleosides revealing a therapeutic window in cancer
Enzymes of the nucleotide salvage pathway are shown to have substrate selectivity that protects newly synthesized DNA from random incorporation of epigenetically modified forms of cytosine; a subset of cancer cell lines that overexpress cytidine deaminase (CDA) are sensitive to treatment with 5hmdC or 5fdC (oxidized forms of 5-methyl-cytosine), which leads to DNA damage and cell death, indicating the chemotherapeutic potential of these nucleoside variants for CDA-overexpressing cancers.
- Melania Zauri
- , Georgina Berridge
- & Skirmantas Kriaucionis

 CST–polymerase α-primase solves a second telomere end-replication problem
CST–polymerase α-primase solves a second telomere end-replication problem