Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Zinc-finger BED domains drive the formation of the active Hermes transpososome by asymmetric DNA binding
Zinc-finger BED domains drive the formation of the active Hermes transpososome by asymmetric DNA binding
Hermes is a member of the eukaryotic hAT DNA transposon superfamily. Its transposase forms a ring-shaped tetramer of dimers to provide sufficient number of DNA binding BED domains to locate its transposon left-end in genomic DNA and facilitate the subsequent interaction with the right-end.
- Laurie Lannes
- , Christopher M. Furman
- & Fred Dyda
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor that selectively blocks DNA-binding by Trypanosoma brucei replication protein A1
Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor that selectively blocks DNA-binding by Trypanosoma brucei replication protein A1
The authors identify a small molecule inhibitor targeting the ssDNA-binding function of T. brucei Replication Protein A1 without affecting the host ortholog. They confirm the key residue in TbRPA1 involved in the species-specific selectivity of the chemical probe.
- Aditi Mukherjee
- , Zakir Hossain
- & Hee-Sook Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Autophagy receptor NDP52 alters DNA conformation to modulate RNA polymerase II transcription
Autophagy receptor NDP52 alters DNA conformation to modulate RNA polymerase II transcription
An autophagy receptor, NDP52, is recruited to the nucleus where it can bind DNA. The authors show this promotes changes in chromatin accessibility which supports transcription initiation, providing a direct link between autophagy and transcription regulation.
- Ália dos Santos
- , Daniel E. Rollins
- & Christopher P. Toseland
-
Article
| Open Access Replication fork binding triggers structural changes in the PriA helicase that govern DNA replication restart in E. coli
Replication fork binding triggers structural changes in the PriA helicase that govern DNA replication restart in E. coli
The mechanism of replication restart initiation by the bacterial DNA replication restart proteins PriA and PriB is resolved, revealing a switch-like restructuring of PriA triggered by replication fork binding that mediates PriA/PriB complex assembly.
- Alexander T. Duckworth
- , Peter L. Ducos
- & James L. Keck
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand-specific changes in conformational flexibility mediate long-range allostery in the lac repressor
Ligand-specific changes in conformational flexibility mediate long-range allostery in the lac repressor
Using hydrogen-deuterium exchange, the authors propose a model explaining how a classic transcription factor undergoes changes in its conformational ensemble in response to different ligands.
- Anum Glasgow
- , Helen T. Hobbs
- & Tanja Kortemme
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of a RecT/Redβ family recombinase in complex with a duplex intermediate of DNA annealing
Structure of a RecT/Redβ family recombinase in complex with a duplex intermediate of DNA annealing
Specific ssDNA binding proteins promote the annealing of complementary strands. Here the authors reveal an intermediate of annealing in which a duplex DNA is bound in an unusual conformation that is highly extended and unwound for the ssDNA binding protein Redβ from bacteriophage λ.
- Brian J. Caldwell
- , Andrew S. Norris
- & Charles E. Bell
-
Article
| Open Access The role of auxiliary domains in modulating CHD4 activity suggests mechanistic commonality between enzyme families
The role of auxiliary domains in modulating CHD4 activity suggests mechanistic commonality between enzyme families
CHD4 is an essential chromatin remodelling enzyme in complex organisms. Here the authors demonstrate that CHD4 activity is regulated both positively and negatively by distinct auxiliary domains, revealing parallels with other chromatin remodellers.
- Yichen Zhong
- , Hakimeh Moghaddas Sani
- & Joel P. Mackay
-
Article
| Open Access Smc5/6’s multifaceted DNA binding capacities stabilize branched DNA structures
Smc5/6’s multifaceted DNA binding capacities stabilize branched DNA structures
Using single-molecule visualization and manipulation, Chang et al. show that the eukaryotic Smc5/6 complex preferentially binds to and stabilizes ssDNA-dsDNA junctions, which could serve as the molecular basis for its diverse roles in genome maintenance.
- Jeremy T-H. Chang
- , Shibai Li
- & Shixin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access MutS functions as a clamp loader by positioning MutL on the DNA during mismatch repair
MutS functions as a clamp loader by positioning MutL on the DNA during mismatch repair
MutS and MutL homologs are thought to form a stable complex to execute mismatch repair. This work shows that E. coli MutS only acts as a mismatch-dependent clamp-loader that assembles the MutL sliding clamp.
- Xiao-Wen Yang
- , Xiao-Peng Han
- & Jiaquan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A monomeric mycobacteriophage immunity repressor utilizes two domains to recognize an asymmetric DNA sequence
A monomeric mycobacteriophage immunity repressor utilizes two domains to recognize an asymmetric DNA sequence
Bacteriophage repressor proteins downregulate viral lytic gene expression. Herein, the authors present the X-ray crystal structure of a monomeric repressor that binds an asymmetric DNA sequence using two independent domains.
- Reliza J. McGinnis
- , Chad A. Brambley
- & Jamie R. Wallen
-
Article
| Open Access ComFC mediates transport and handling of single-stranded DNA during natural transformation
ComFC mediates transport and handling of single-stranded DNA during natural transformation
The ComFC protein is essential for natural transformation, a process that plays a major role in the spread of antibiotic resistance genes. Here the authors show that ComFC is a membrane-associated protein that participates in the transport of DNA through the cell membrane and the handling of the single-stranded DNA once delivered into the cytoplasm.
- Prashant P. Damke
- , Louisa Celma
- & J. Pablo Radicella
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
Many bacteria can take up exogenous DNA, in a process that often requires surface appendages composed of thousands of protein subunits called pilins. Here, Braus et al. show that a minor pilin binds directly to DNA and is important for DNA uptake in the pathogen Legionella pneumophila.
- Sebastian A. G. Braus
- , Francesca L. Short
- & Manuela K. Hospenthal
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
Cryo-EM structures of S. cerevisiae ORC bound to DNA and Cdc6 reveal an autoinhibited conformation and suggest a mechanism of origin licensing control in response to CDK phosphorylation.
- Jan Marten Schmidt
- , Ran Yang
- & Franziska Bleichert
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
UvrD is a model helicase from the non-hexameric Superfamily 1. Here, the authors use optical tweezers to measure directly the stepwise translocation of UvrD along a DNA hairpin, and propose a mechanism in which UvrD moves one base pair at a time, but sequesters the nascent single strands, releasing them after a variable number of ATP hydrolysis cycles.
- Sean P. Carney
- , Wen Ma
- & Yann R. Chemla
-
Article
| Open Access Zinc finger protein ZNF384 is an adaptor of Ku to DNA during classical non-homologous end-joining
Zinc finger protein ZNF384 is an adaptor of Ku to DNA during classical non-homologous end-joining
Classical non-homologous end-joining (cNHEJ) is the dominant pathway used by human cells to repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and maintain genome stability. Here the authors show that PARP1-driven chromatin expansion allows the recruitment of ZNF384, which in turn recruits Ku70/Ku80 to facilitate cNHEJ.
- Jenny Kaur Singh
- , Rebecca Smith
- & Haico van Attikum
-
Article
| Open Access Crosstalk between CST and RPA regulates RAD51 activity during replication stress
Crosstalk between CST and RPA regulates RAD51 activity during replication stress
During replication stress, the RPA protein complex coats single-stranded DNA to preclude RAD51 loading. Here, the authors show how RPA and CST crosstalk to regulate RAD51 activity.
- Kai-Hang Lei
- , Han-Lin Yang
- & Peter Chi
-
Article
| Open Access A complex of BRCA2 and PP2A-B56 is required for DNA repair by homologous recombination
A complex of BRCA2 and PP2A-B56 is required for DNA repair by homologous recombination
BRCA2 plays a central role in facilitating DNA repair by homologous recombination (HR). Here the authors describe how BRCA2 forms a complex with the protein phosphatase PP2A-B56 in response to DNA damage, which is required for HR.
- Sara M. Ambjørn
- , Julien P. Duxin
- & Jakob Nilsson
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional characterization of the bacterial biofilm activator RemA
Structural and functional characterization of the bacterial biofilm activator RemA
Biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis requires expression of matrix production genes, which are upregulated by transcriptional activator RemA. Here, the authors show that RemA forms octameric rings with the potential to form a 16-meric superstructure, suggesting that the protein can wrap DNA through a LytTR-related domain.
- Tamara Hoffmann
- , Devid Mrusek
- & Gert Bange
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive deletion landscape of CRISPR-Cas9 identifies minimal RNA-guided DNA-binding modules
Comprehensive deletion landscape of CRISPR-Cas9 identifies minimal RNA-guided DNA-binding modules
Proteins evolve through the modular rearrangement of domains. Here the authors introduce MISER, a minimization by iterative size-exclusion and recombination method to make all possible deletions of a protein, uncovering functions for Cas9 domains involved in DNA binding.
- Arik Shams
- , Sean A. Higgins
- & David F. Savage
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleotide proofreading functions by nematode RAD51 paralogs facilitate optimal RAD51 filament function
Nucleotide proofreading functions by nematode RAD51 paralogs facilitate optimal RAD51 filament function
A RAD51 paralog complex, RFS-1/RIP-1, is shown to control ssDNA binding and dissociation by RAD-51 differentially in the presence and absence of nucleotide cofactors. These nucleotide proofreading activities drive a preferential accumulation of RAD-51-ssDNA complexes with optimal nucleotide content.
- Mário Špírek
- , Martin R. G. Taylor
- & Lumir Krejci
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for allosteric regulation of Human Topoisomerase IIα
Structural basis for allosteric regulation of Human Topoisomerase IIα
Type 2 DNA topoisomerases (Top2) regulates DNA topology during DNA replication, transcription, and chromosome segregation. Here the authors describe a complete structure of the catalytic core of the human Topo IIα bound to DNA and etoposide, providing insight into the regulation of Topo IIα activities and how opening of the DNA-gate is spatially connected to the ATPase domain.
- Arnaud Vanden Broeck
- , Christophe Lotz
- & Valérie Lamour
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically encoded formaldehyde sensors inspired by a protein intra-helical crosslinking reaction
Genetically encoded formaldehyde sensors inspired by a protein intra-helical crosslinking reaction
In order to understand the role of formaldehyde in living systems, real-time monitoring is required. Here the authors report a genetically encoded, reaction-based formaldehyde sensor (FAsor) that enables visualisation of formaldehyde in mammalian cells and tissues.
- Rongfeng Zhu
- , Gong Zhang
- & Peng R. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Potent DNA gyrase inhibitors bind asymmetrically to their target using symmetrical bifurcated halogen bonds
Potent DNA gyrase inhibitors bind asymmetrically to their target using symmetrical bifurcated halogen bonds
The mechanism of DNA gyrase inhibitor stabilization of single-strand DNA cleavage breaks by DNA gyrase has been hypothetical. Here, the authors show experimental evidence of the mechanism using a library of inhibitors with improved binding and employ crystal analysis to show bifurcated halogen bonding.
- Anja Kolarič
- , Thomas Germe
- & Marko Anderluh
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic protein-binding DNA sponge as a tool to tune gene expression and mitigate protein toxicity
Synthetic protein-binding DNA sponge as a tool to tune gene expression and mitigate protein toxicity
Decoy binding sites are natural regulators of gene expression. Here the authors design synthetic DNA sponges that fine tune the performance of synthetic gene circuits in a simple yet systematic manner, expanding the synthetic biology toolkit for gene regulation.
- Xinyi Wan
- , Filipe Pinto
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural asymmetry governs the assembly and GTPase activity of McrBC restriction complexes
Structural asymmetry governs the assembly and GTPase activity of McrBC restriction complexes
The bacterial defense system McrBC is a two-component motor-driven nuclease complex that cleaves foreign DNA. Here, the authors present the structures of the GTP-specific AAA + motor protein McrB and two McrBC complexes and discuss the molecular mechanism of how McrC binding stimulates McrB GTP hydrolysis.
- Yiming Niu
- , Hiroshi Suzuki
- & Joshua S. Chappie
-
Article
| Open Access An ambruticin-sensing complex modulates Myxococcus xanthus development and mediates myxobacterial interspecies communication
An ambruticin-sensing complex modulates Myxococcus xanthus development and mediates myxobacterial interspecies communication
Starvation induces cell aggregation and formation of spore-containing fruiting bodies in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. Here, the authors show that a different myxobacterial species produces a compound that inhibits the development of fruiting bodies in M. xanthus, by affecting the function of histidine kinases and major regulators.
- Francisco Javier Marcos-Torres
- , Carsten Volz
- & Rolf Müller
-
Article
| Open Access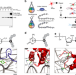 Analysis of protein-DNA interactions in chromatin by UV induced cross-linking and mass spectrometry
Analysis of protein-DNA interactions in chromatin by UV induced cross-linking and mass spectrometry
Cross-linking mass spectrometry (XLMS) allows mapping of protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions, but the analysis of protein-DNA complexes remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a UV light-based XLMS workflow to determine protein-DNA interfaces in reconstituted chromatin and isolated nuclei.
- Alexandra Stützer
- , Luisa M. Welp
- & Henning Urlaub
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-resolution mapping of transcription factor-DNA interactions by femtosecond laser crosslinking and mass spectrometry
Atomic-resolution mapping of transcription factor-DNA interactions by femtosecond laser crosslinking and mass spectrometry
Cross-linking mass spectrometry (MS) is an important tool in structural biology, but its application to protein-DNA complexes has been hampered by low cross-linking efficiency. Here, the authors develop a femtosecond UV-laser induced cross-linking MS workflow to map protein-DNA interactions in vitro and in cells.
- Alexander Reim
- , Roland Ackermann
- & Michael Wierer
-
Article
| Open Access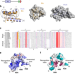 Structural basis for the complex DNA binding behavior of the plant stem cell regulator WUSCHEL
Structural basis for the complex DNA binding behavior of the plant stem cell regulator WUSCHEL
WUSCHEL is a homeodomain transcription factor that is essential for stem cell maintenance in the plant shoot apical meristem. Here, via structural and biochemical approaches, Sloan et al. show that strong WUSCHEL binding to preferential target motifs can be attributed to dimer formation that stabilizes DNA binding.
- Jeremy Sloan
- , Jana P. Hakenjos
- & Jan U. Lohmann
-
Article
| Open Access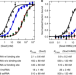 The Sox2 transcription factor binds RNA
The Sox2 transcription factor binds RNA
Some transcription factors have been proposed to functionally interact with RNA to facilitate proper regulation of gene expression. Here the authors demonstrate that human Sox2 interact directly and with high affinity to RNAs through its HMG DNA-binding domain.
- Zachariah E. Holmes
- , Desmond J. Hamilton
- & Robert T. Batey
-
Article
| Open Access DNA repair by Rad52 liquid droplets
DNA repair by Rad52 liquid droplets
Genome dynamics allow cells to repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are highly toxic DNA lesions. Here the authors reveal that in S. cerevisiae, Rad52 DNA repair proteins assemble in liquid droplets that work with dynamic nuclear microtubules to relocalize lesions to the nuclear periphery for repair.
- Roxanne Oshidari
- , Richard Huang
- & Karim Mekhail
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase nucleoprotein complex
Cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase nucleoprotein complex
Bacterial DNA gyrase is the only type II DNA topoisomerase capable of introducing negative supercoils into DNA and is of interest as a drug target. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the complete E. coli DNA gyrase bound to a 180 bp double-stranded DNA and the antibiotic gepotidacin, which reveals the connections between the functional domains and their spatial organization.
- Arnaud Vanden Broeck
- , Christophe Lotz
- & Valérie Lamour
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and functional implications of WYL domain-containing bacterial DNA damage response regulator PafBC
Structure and functional implications of WYL domain-containing bacterial DNA damage response regulator PafBC
The transcriptional activator PafBC is a regulator of mycobacterial DNA damage response and upregulates genes involved in DNA repair. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of Arthrobacter aurescens PafBC and suggest that PafBC might be activated by binding of a nucleic acid ligand, and bioinformatics analysis shows that its central WYL domain is a widespread feature in bacterial transcription factors.
- Andreas U. Müller
- , Marc Leibundgut
- & Eilika Weber-Ban
-
Article
| Open Access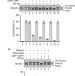 DNA requirement in FANCD2 deubiquitination by USP1-UAF1-RAD51AP1 in the Fanconi anemia DNA damage response
DNA requirement in FANCD2 deubiquitination by USP1-UAF1-RAD51AP1 in the Fanconi anemia DNA damage response
In the Fanconi anemia pathway, deubiquitination of FANCD2 is a fundamental regulatory step. Here, the authors have developed a set of biochemical tools to reconstitute FANCD2 deubiquitination by recombinant USP1-UAF1-RAD51AP1 and reveal critical mechanistic details of the process.
- Fengshan Liang
- , Adam S. Miller
- & Patrick Sung
-
Article
| Open Access A dual role in regulation and toxicity for the disordered N-terminus of the toxin GraT
A dual role in regulation and toxicity for the disordered N-terminus of the toxin GraT
The Pseudomonas putida toxin GraT and antitoxin GraA form a type II toxin-antoxin module. Here the authors present the crystal structures of the GraA dimer, GraTA and GraA-DNA complexes and show that GraT contains a functionally important N-terminal intrinsic disordered region that prevents the binding of the GraTA complex to the operator.
- Ariel Talavera
- , Hedvig Tamman
- & Remy Loris
-
Article
| Open Access PAXX and its paralogs synergistically direct DNA polymerase λ activity in DNA repair
PAXX and its paralogs synergistically direct DNA polymerase λ activity in DNA repair
PAXX functions as part of the nonhomologous end-joining pathway to repair double-strand DNA breaks. Here the authors show PAXX and its paralogs interact with polymerase lambda to promote joining of incompatible ends.
- Andrew Craxton
- , Deeksha Munnur
- & Michal Malewicz
-
Article
| Open Access UPF1-like helicase grip on nucleic acids dictates processivity
UPF1-like helicase grip on nucleic acids dictates processivity
UPF1 is a highly processive helicase that plays an essential role in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Here the authors use single molecule binding assays to establish a functionally important relationship between helicase grip to nucleic acids, binding lifetime and the duration of translocation.
- Joanne Kanaan
- , Saurabh Raj
- & Hervé Le Hir
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into antibiotic resistance - how a binding protein traps albicidin
Molecular insights into antibiotic resistance - how a binding protein traps albicidin
The potent antibacterial compound albicidin is synthesized by the plant-pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas albilineans. Here the authors employ a multidisciplinary approach and provide structural and mechanistic insights into how the drug-binding protein AlbA confers albicidin resistance to Klebsiella oxytoca.
- Lida Rostock
- , Ronja Driller
- & Roderich D. Süssmuth
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities using quantitative mass spectrometry
Global profiling of protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities using quantitative mass spectrometry
Quantitative mass spectrometry enables the proteome-wide assessment of biomolecular binding affinities. While previous approaches mainly focused on protein–small molecule interactions, the authors here present a method to probe protein–DNA and protein–nucleosome binding affinities at proteome scale.
- Matthew M. Makowski
- , Cathrin Gräwe
- & Michiel Vermeulen
-
Article
| Open Access The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development
The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development
BldC regulates the onset of differentiation in Streptomycetes by a yet unknown molecular mechanism. Using a combination of structural, biochemical and in vivo approaches, the authors show that BldC controls the transcription of several developmental regulators and unravel its DNA binding mode.
- Maria A. Schumacher
- , Chris D. den Hengst
- & Mark J. Buttner
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for TNA synthesis by an engineered TNA polymerase
Structural basis for TNA synthesis by an engineered TNA polymerase
The laboratory-evolved polymerase Kod-RI catalyzes α-L-threose nucleic acid (TNA) synthesis. Here, the authors present Kod-RI crystal structures that give insights into how TNA triphosphates are selected and extended in a template-dependent manner, which will help to engineer improved TNA polymerases for synthetic genetics applications.
- Nicholas Chim
- , Changhua Shi
- & John C. Chaput
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution of human shelterin complexes reveals unexpected stoichiometry and dual pathways to enhance telomerase processivity
Reconstitution of human shelterin complexes reveals unexpected stoichiometry and dual pathways to enhance telomerase processivity
The human shelterin complex protects telomere ends from being recognized as damaged DNA sites and regulates telomere length in conjunction with telomerase. Here the authors establish the stoichiometries of human shelterin complexes of various compositions and show shelterin provides dual pathways to stimulate telomerase processivity.
- Ci Ji Lim
- , Arthur J. Zaug
- & Thomas R. Cech
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering TAL effectors for 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine recognition
Deciphering TAL effectors for 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine recognition
Transcription activator-like effector proteins recognise specific DNA sequences via tandem repeats. Here the authors demonstrate TALEs can recognise the methylated bases 5mC and 5hmC, enabling them to detect epigenetic modifications.
- Yuan Zhang
- , Lulu Liu
- & Chengqi Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleolin directly mediates Epstein-Barr virus immune evasion through binding to G-quadruplexes of EBNA1 mRNA
Nucleolin directly mediates Epstein-Barr virus immune evasion through binding to G-quadruplexes of EBNA1 mRNA
Cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) express the virus-encoded EBNA1, which is essential for viral genome maintenance but also highly antigenic. Here the authors implicate nucleolin as a host factor that mediates the repression of EBNA1-derived antigenic peptides through binding of the G4-quadruplex structure present within the EBNA1 mRNA.
- María José Lista
- , Rodrigo Prado Martins
- & Marc Blondel
-
Article
| Open Access Specialized interfaces of Smc5/6 control hinge stability and DNA association
Specialized interfaces of Smc5/6 control hinge stability and DNA association
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) complexes maintain genome integrity by regulating the segregation of chromosomes. Here, Altet al. describe the structure of the heterodimeric Smc5/6-hinge from fission yeast and define functional features critical for Smc5/6’s cellular function.
- Aaron Alt
- , Hung Q. Dang
- & Antony W. Oliver
-
Article
| Open Access De-novo protein function prediction using DNA binding and RNA binding proteins as a test case
De-novo protein function prediction using DNA binding and RNA binding proteins as a test case
Identification of the function of proteins is difficult when there are no structurally or biochemically characterized homologs. Here, the authors present an approach that allows the prediction of nucleic-acid binding proteins based on sequence alone, and they are able to experimentally validate their method.
- Sapir Peled
- , Olga Leiderman
- & Yanay Ofran
-
Article
| Open Access Extremotolerant tardigrade genome and improved radiotolerance of human cultured cells by tardigrade-unique protein
Extremotolerant tardigrade genome and improved radiotolerance of human cultured cells by tardigrade-unique protein
Tardigrades are resistant to extreme environmental conditions including dehydration, radiation and the vacuum of space. Here the authors present a high-quality genome which displays minimal horizontal gene transfer, and identify the unique tardigrade protein Dsup which suppresses DNA damage.
- Takuma Hashimoto
- , Daiki D. Horikawa
- & Takekazu Kunieda
-
Article
| Open Access A second DNA binding site in human BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination
A second DNA binding site in human BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination
BRCA2 is a well-characterized central player in homologous recombination in which it functions as the RAD51 loader. Here the authors identify an N-terminal region of BRCA2 that binds DNA and promotes efficient DNA repair.
- Catharina von Nicolai
- , Åsa Ehlén
- & Aura Carreira
-
Article
| Open Access Sequences flanking the core-binding site modulate glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity
Sequences flanking the core-binding site modulate glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity
To modulate gene expression, the glucocorticoid receptor binds to response elements (RE) that vary in sequence. Here, the authors show that RE sequences can modulate glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity, which might provide regulatory specificity towards individual target genes.
- Stefanie Schöne
- , Marcel Jurk
- & Sebastiaan H. Meijsing

 Partition complex structure can arise from sliding and bridging of ParB dimers
Partition complex structure can arise from sliding and bridging of ParB dimers