Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates ILC2-dependent airway hyperreactivity
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates ILC2-dependent airway hyperreactivity
Airway hyperreactivity is driven by type 2 cytokines produced by ILC2 and Th2 cells. Here the authors show that an α7-nicotinic receptor agonist (GTS-21) inhibits ILC2 responses and is therapeutic against Alternaria-induced airway hyperreactivity in a humanized mouse model.
- Lauriane Galle-Treger
- , Yuzo Suzuki
- & Omid Akbari
-
Article
| Open Access Glucocorticoid regulation of ATP release from spinal astrocytes underlies diurnal exacerbation of neuropathic mechanical allodynia
Glucocorticoid regulation of ATP release from spinal astrocytes underlies diurnal exacerbation of neuropathic mechanical allodynia
Neuropathic pain hypersensitivity is known to undergo diurnal variations, although the underlying mechanisms are not clear. Using a sciatic nerve-injury mouse model, the authors find such diurnal changes are mediated by glucocorticoid induced enhancement of ATP release from astrocytes via pannexin-1 hemichannels.
- Satoru Koyanagi
- , Naoki Kusunose
- & Shigehiro Ohdo
-
Article
| Open Access Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis
Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis
Bmal1 is a key transcription factor that controls rhythmicity of diverse biological functions. Here, Pan et al. show that Bmal1 deficiency in mice increases lipoprotein secretion and reduces cholesterol excretion to bile, and decipher the molecular mechanisms underlying hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis promoted by the lack of Bmal1.
- Xiaoyue Pan
- , Christopher A. Bradfield
- & M. Mahmood Hussain
-
Article
| Open Access ANGPTL2 activity in cardiac pathologies accelerates heart failure by perturbing cardiac function and energy metabolism
ANGPTL2 activity in cardiac pathologies accelerates heart failure by perturbing cardiac function and energy metabolism
Heart responds to increased workload by enlarging cardiomyocytes to preserve function, but in pathologies hypertrophy leads to heart failure. Here the authors show that ANGPTL2 activity in the heart is critical for determining beneficial vs. pathological hypertrophy via its effect on AKT-SERCA2a signaling and myocardial energy.
- Zhe Tian
- , Keishi Miyata
- & Yuichi Oike
-
Article
| Open Access Irreversible inhibitors of the 3C protease of Coxsackie virus through templated assembly of protein-binding fragments
Irreversible inhibitors of the 3C protease of Coxsackie virus through templated assembly of protein-binding fragments
Molecular fragments are useful tools in drug-discovery but they might be hard to identify due to their weak affinity to the targets. Here, the authors use a protein-templated assembly to design high affinity inhibitors of Coxsackie virus 3C protease, a pharmacological target against enteroviral infections.
- Daniel Becker
- , Zuzanna Kaczmarska
- & Jörg Rademann
-
Article
| Open Access A cholinergic-sympathetic pathway primes immunity in hypertension and mediates brain-to-spleen communication
A cholinergic-sympathetic pathway primes immunity in hypertension and mediates brain-to-spleen communication
Immune system participates in the development of high blood pressure. Here the authors show that cholinergic-sympathetic pathway mediated by the α7nAChR receptor and the activation of splenic T cells prime immunity during hypertension and that selective splenic denervation protects against the onset of hypertension in mice.
- Daniela Carnevale
- , Marialuisa Perrotta
- & Giuseppe Lembo
-
Article
| Open Access Structure–function insights reveal the human ribosome as a cancer target for antibiotics
Structure–function insights reveal the human ribosome as a cancer target for antibiotics
The ribosome of bacteria and other unicellular pathogens is a common target for antibiotic drugs. Here the authors determine a structure of the human ribosome bound to the translation inhibitor cycloheximide, and provide evidence that targeting the ribosome is a promising avenue for cancer therapy.
- Alexander G. Myasnikov
- , S. Kundhavai Natchiar
- & Bruno P. Klaholz
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for CD36 binding by the malaria parasite
The structural basis for CD36 binding by the malaria parasite
Targeting of the CD36 scavenger receptor by the malaria parasite effector PfEMP1 prevents splenic clearance of infected erythrocytes. Here, the authors propose that diverse PfEMP1 achieve this by binding to a conserved phenylalanine residue in CD36 that is also required for lipoprotein binding.
- Fu-Lien Hsieh
- , Louise Turner
- & Matthew K. Higgins
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved influenza A virus nucleoprotein code controls specific viral genome packaging
A conserved influenza A virus nucleoprotein code controls specific viral genome packaging
The nucleotide sequence of the eight genomic RNA segments of influenza A virus provides essential packaging signals, but how these sequences are recognized is unknown. Here, Moreira et al. identify conserved amino acids in the viral nucleoprotein that regulate packaging of RNA segments.
- Étori Aguiar Moreira
- , Anna Weber
- & Mindaugas Juozapaitis
-
Article
| Open Access A broadly neutralizing anti-influenza antibody reveals ongoing capacity of haemagglutinin-specific memory B cells to evolve
A broadly neutralizing anti-influenza antibody reveals ongoing capacity of haemagglutinin-specific memory B cells to evolve
A major goal of vaccine design is to protect against a broad range of pathogen strains. Here the authors isolate a new broadly neutralizing antibody against influenza haemagglutinin from human memory B cells, and identify mutations that increase and broaden the neutralization towards H5 HA subtype.
- Ying Fu
- , Zhen Zhang
- & Wayne A. Marasco
-
Article
| Open Access Broad activation of latent HIV-1 in vivo
Broad activation of latent HIV-1 in vivo
Treatment of HIV-1 infected patients with latency-reversing agents (LRA) induces transcription of proviruses in CD4 T cells. Using single-genome sequencing, the authors show that the LRA-induced CD4 T cell-associated HIV RNA is genetically diverse and contains a high proportion of defective RNA.
- Kirston Barton
- , Bonnie Hiener
- & Sarah Palmer
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming metabolic pathways in vivo with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to treat hereditary tyrosinaemia
Reprogramming metabolic pathways in vivo with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to treat hereditary tyrosinaemia
Hereditary tyrosinaemia type I is caused by a gene defect that leads to a lethal accumulation of toxic metabolites in the liver. Here the authors use CRISPR/Cas9 to 'cure' the disease in mice by inactivating another gene, rather than targeting the disease-causing gene itself, to reroute hepatic tyrosine catabolism.
- Francis P. Pankowicz
- , Mercedes Barzi
- & Karl-Dimiter Bissig
-
Article
| Open Access Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a3 defines a subset of failing pancreatic β cells in diabetic mice
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a3 defines a subset of failing pancreatic β cells in diabetic mice
Diabetes is associated with the de-differentiation of β-cells into a more progenitor-like cell type. Here, the authors identify Aldh3 as a marker of de-differentiating β-cell in animal models of diabetes, and show Aldh3+cells have impaired insulin secretion and mitochondrial dysfunction.
- Ja Young Kim-Muller
- , Jason Fan
- & Domenico Accili
-
Article
| Open Access RNF168 and USP10 regulate topoisomerase IIα function via opposing effects on its ubiquitylation
RNF168 and USP10 regulate topoisomerase IIα function via opposing effects on its ubiquitylation
The E3 ligase RNF168 is essential for the signalling of DNA double strand break and its mutations are associated with the RIDDLE syndrome. Here the authors identify TOP2a as substrate for RNF168 and USP10; providing a link between the RNF168/USP10 axis, TOP2a and the response to anti-cancer drugs that target TOP2.
- Kiran Kumar Naidu Guturi
- , Miyuki Bohgaki
- & Razqallah Hakem
-
Article
| Open Access Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans
Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans
Circular RNAs are widely expressed in eukaryotic cells but their functions and mechanisms of action are still being elucidated. Here the authors show that circANRILmodulates rRNA maturation and confers protection again atherosclerosis.
- Lesca M. Holdt
- , Anika Stahringer
- & Daniel Teupser
-
Article
| Open Access Novel gene function revealed by mouse mutagenesis screens for models of age-related disease
Novel gene function revealed by mouse mutagenesis screens for models of age-related disease
Random mutagenesis can uncover novel genes involved in phenotypic traits. Here the authors perform a large-scale phenotypic screen on over 100 mouse strains generated by ENU mutagenesis to identify mice with age-related diseases, which they attribute to specific mutations revealed by whole-genome sequencing.
- Paul K. Potter
- , Michael R. Bowl
- & Steve D. M. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features
Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features
Diagnosis of lung cancer through manual histopathology evaluation is insufficient to predict patient survival. Here, the authors use computerized image processing to identify diagnostically relevant image features and use these features to distinguish lung cancer patients with different prognoses.
- Kun-Hsing Yu
- , Ce Zhang
- & Michael Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access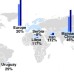 Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040
Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040
The socioeconomic burden of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is high, but the projected number of cases in the upcoming years is unclear. Here, the authors estimate the number and distribution of ALS cases to 2040, and show that cases are projected to increase, particularly in developing nations.
- Karissa C. Arthur
- , Andrea Calvo
- & Bryan J. Traynor
-
Article
| Open Access Fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome and protect against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent models
Fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome and protect against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent models
NSAID-induced analgesia is typically induced by inhibition of COX enzymes. Here the authors show instead that fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the Nlrp3 inflammasome via an effect on volume-regulated anion channel function and also repurpose these drugs for therapeutic effect in rodent models of Alzheimer disease.
- Michael J. D. Daniels
- , Jack Rivers-Auty
- & David Brough
-
Article
| Open Access The severity of hereditary porphyria is modulated by the porphyrin exporter and Lan antigen ABCB6
The severity of hereditary porphyria is modulated by the porphyrin exporter and Lan antigen ABCB6
Accumulation of intermediates of haem biosynthesis, porphyrins, is harmful and usually inherited, but it is unclear how the same mutation may make some individuals more ill than others. Here, the authors show that a porphyrin transporter ABCB6 is a modulator of porphyria, and that patients with functionally defective ABCB6 show more severe symptoms.
- Yu Fukuda
- , Pak Leng Cheong
- & John D. Schuetz
-
Article
| Open Access ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells promotes monocyte expansion and atherosclerosis progression
ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells promotes monocyte expansion and atherosclerosis progression
Angiopoietin-like 4 protein (ANGPTL4) is a regulator of lipoprotein metabolism whose role in atherosclerosis has been controversial. Here the authors show that ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells increases atherogenesis by promoting myeloid progenitor cell expansion and differentiation, foam cell formation and vascular inflammation.
- Binod Aryal
- , Noemi Rotllan
- & Carlos Fernández-Hernando
-
Article
| Open Access Common variants upstream of KDR encoding VEGFR2 and in TTC39B associate with endometriosis
Common variants upstream of KDR encoding VEGFR2 and in TTC39B associate with endometriosis
Endometriosis is a common gynaecological disease but the underlying pathogenesis is poorly understood, however there is a strong familial component. Here the authors conduct a genome wide association study and identify a novel susceptibility locus that correlates with disease severity.
- Valgerdur Steinthorsdottir
- , Gudmar Thorleifsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of claudin/zonula occludens-1 complexes by hetero-claudin interactions
Regulation of claudin/zonula occludens-1 complexes by hetero-claudin interactions
Alcohol abuse is a risk factor for acute respiratory distress syndrome, flooding of the lungs due to compromised barrier function. Here the authors report that alcohol upregulates claudin-5 that is then recruited to tight junctions in alveolar epithelial cells, causing the displacement of claudin-18 from ZO-1 and diminished barrier function.
- Barbara Schlingmann
- , Christian E. Overgaard
- & Michael Koval
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated genomic and transcriptomic survey of mucormycosis-causing fungi
An integrated genomic and transcriptomic survey of mucormycosis-causing fungi
Fungi of the order Mucorales can cause life-threatening infections. Here, Chibucos et al. present genomic and transcriptomic analyses of a diverse set of Mucorales fungi, shedding light on their evolution and identifying potential therapeutic targets in the pathogens and the host.
- Marcus C. Chibucos
- , Sameh Soliman
- & Vincent M. Bruno
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple capsid-stabilizing interactions revealed in a high-resolution structure of an emerging picornavirus causing neonatal sepsis
Multiple capsid-stabilizing interactions revealed in a high-resolution structure of an emerging picornavirus causing neonatal sepsis
Human parechovirus 3 (HPeV3) can cause severe central nervous system infections and is a major cause of neonatal sepsis. Here the authors determine the structure of HPeV3 that provides a high-resolution view of the capsid’s organization and shows multiple interactions of the RNA genome with coat proteins.
- Shabih Shakeel
- , Brenda M. Westerhuis
- & Sarah J. Butcher
-
Article
| Open Access A whole-genome sequence and transcriptome perspective on HER2-positive breast cancers
A whole-genome sequence and transcriptome perspective on HER2-positive breast cancers
Breast cancer is separated into multiple subtypes based on the expression of HER2 and hormone receptors. Here, the authors report the whole genome sequence of 64 HER2 positive tumours and show that these can be further separated into four groups with different gene expression profiles and genomic features.
- Anthony Ferrari
- , Anne Vincent-Salomon
- & Gilles Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access The FANCD2–FANCI complex is recruited to DNA interstrand crosslinks before monoubiquitination of FANCD2
The FANCD2–FANCI complex is recruited to DNA interstrand crosslinks before monoubiquitination of FANCD2
FANCD2 and FANCI are essential components of the Fanconi anaemia DNA damage repair pathway. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the FANCD2-FANCI complex, providing insight into how the complex is recruited to stalled replication forks.
- Chih-Chao Liang
- , Zhuolun Li
- & Martin A. Cohn
-
Article
| Open Access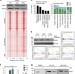 ERRα mediates metabolic adaptations driving lapatinib resistance in breast cancer
ERRα mediates metabolic adaptations driving lapatinib resistance in breast cancer
Despite initial benefits in treating HER2-positive breast cancer patients with lapatinib, resistance is prevalent. Here the authors show that lapatinib resistance can be ascribed to mTOR-mediated re-activation of ERRα and to the consequent induction of a metabolic adaptation.
- Geneviève Deblois
- , Harvey W. Smith
- & Vincent Giguère
-
Article
| Open Access Treatment of ongoing autoimmune encephalomyelitis with activated B-cell progenitors maturing into regulatory B cells
Treatment of ongoing autoimmune encephalomyelitis with activated B-cell progenitors maturing into regulatory B cells
Evidence of how functional Bregs develop in vivo has been lacking. Here the authors show that proB cells exposed in vivoto CpG differentiate into distinct Breg subsets that inhibit autoimmunity by arresting T cells in the lymph nodes via CCL19 and by producing IL-10 at the site of immunopathology.
- Sarantis Korniotis
- , Christophe Gras
- & Flora Zavala
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative functional genomics identifies regulatory mechanisms at coronary artery disease loci
Integrative functional genomics identifies regulatory mechanisms at coronary artery disease loci
Coronary heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide with multiple environmental and genetic risk factors. Here the authors integrate genomic, epigenomic and transcriptomic mapping to elucidate causal variation and mechanisms of known genetic associations.
- Clint L. Miller
- , Milos Pjanic
- & Thomas Quertermous
-
Article
| Open Access MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta
MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is genetically linked to autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive mutations. Here, Marini et al. describe two families with X-chromosome-linked OI with mutations in MBTPS2 that alter regulated intramembrane proteolysis and subsequent defects in collagen crosslinking and osteoblast function.
- Uschi Lindert
- , Wayne A. Cabral
- & Vorasuk Shotelersuk
-
Article
| Open Access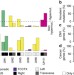 Patients with genetically heterogeneous synchronous colorectal cancer carry rare damaging germline mutations in immune-related genes
Patients with genetically heterogeneous synchronous colorectal cancer carry rare damaging germline mutations in immune-related genes
Some individuals present with multiple synchronous colorectal tumours, but the genetic understanding of this is unclear. Here, the authors use a sequencing strategy to show that the synchronous tumours are genetically independent and the patients harbour rare germline damaging mutations in genes associated with the immune system.
- Matteo Cereda
- , Gennaro Gambardella
- & Francesca D. Ciccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish
Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish
Hypoxia has diverse effects on aquatic life. Wang et al.show that reproductive defects resulting from hypoxia are epigenetically heritable in Japanese rice fish, and that this intergenerational inheritance is accompanied by differential methylation and gene expression in sperm.
- Simon Yuan Wang
- , Karen Lau
- & Rudolf Shiu-Sun Wu
-
Article
| Open Access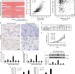 COPS5 amplification and overexpression confers tamoxifen-resistance in ERα-positive breast cancer by degradation of NCoR
COPS5 amplification and overexpression confers tamoxifen-resistance in ERα-positive breast cancer by degradation of NCoR
The corepressor NCoR is required for tamoxifen-mediated ERα-dependent transcriptional repression. Here, the authors show that COPS5 confers tamoxifen-resistance through the degradation of NCOR, the recruitment of the co-activator PCAF to ERα binding sites and the subsequent ERα transcriptional activity.
- Renquan Lu
- , Xiaobo Hu
- & Lin Guo
-
Article
| Open Access The landscape of chromosomal aberrations in breast cancer mouse models reveals driver-specific routes to tumorigenesis
The landscape of chromosomal aberrations in breast cancer mouse models reveals driver-specific routes to tumorigenesis
Genetically engineered mouse models of cancer are useful in identifying oncogenes and tumour suppressors. Here, the authors use gene expression profiles to generate a catalogue of copy number aberrations in 45 mouse models, and compare mouse and human tumours to identify additional drivers of tumorigenesis.
- Uri Ben-David
- , Gavin Ha
- & Todd R. Golub
-
Article
| Open Access miR-93 regulates Msk2-mediated chromatin remodelling in diabetic nephropathy
miR-93 regulates Msk2-mediated chromatin remodelling in diabetic nephropathy
Podocyte injury is central to kidney dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. Here the authors show that Msk2 is a target of miR-93 and this interaction mediates pathogenic chromatin remodelling in diabetic nephropathy.
- Shawn S. Badal
- , Yin Wang
- & Farhad R. Danesh
-
Article
| Open Access PACAP suppresses dry eye signs by stimulating tear secretion
PACAP suppresses dry eye signs by stimulating tear secretion
Dry eye disease is a complex condition with limited treatments. Here the authors show that mice lacking a multi-functional peptide PACAP develop dry eye-like signs that can be topically treated with PACAP peptide that stimulates tearing in mice, suggesting a possible therapy in humans with dry eyes.
- Tomoya Nakamachi
- , Hirokazu Ohtaki
- & Seiji Shioda
-
Article
| Open Access MicroRNA-125b-5p mimic inhibits acute liver failure
MicroRNA-125b-5p mimic inhibits acute liver failure
miR125b-5p has been associated with acute liver failure. Here the authors show that this miRNA targets Keap1 and activates Nrf2 to inhibit liver cell death after APAP or FAS toxicity, plus they show that a miR125b-5p mimic can inhibit ALF in mice.
- Dakai Yang
- , Qinggong Yuan
- & Amar Deep Sharma
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of the RNA-binding protein TACO1 causes late-onset mitochondrial dysfunction in mice
Loss of the RNA-binding protein TACO1 causes late-onset mitochondrial dysfunction in mice
Mutations in the translational activator of cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (TACO1) causes cytochrome c oxidase deficiency and Leigh Syndrome in patients. Here, the authors characterize mice with a mutation that causes lack of TACO1 expression, identifying a mouse model that could be useful for preclinical trials.
- Tara R. Richman
- , Henrik Spåhr
- & Aleksandra Filipovska
-
Article
| Open Access Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients
Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients
EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer is routinely treated with EGFR inhibitors, although resistance inevitably develops. Here, the authors sequence circulating tumour DNA and show that resistance to the third-generation inhibitor rociletinib is heterogeneous and recurrently involves somatic alterations of MET, EGFR, PIK3CA, ERRB2, and KRAS.
- Jacob J. Chabon
- , Andrew D. Simmons
- & Maximilian Diehn
-
Article
| Open Access SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation
SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation
Clinical RNA-seq datasets can predict clinical outcomes. Here, Shen et al. report a statistical method for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation using clinical RNA-seq datasets, and the identified isoform based survival predictors outperform gene expression based survival predictors using TCGA data on six cancer types.
- Shihao Shen
- , Yuanyuan Wang
- & Yi Xing
-
Article
| Open Access GPRC5A suppresses protein synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum to prevent radiation-induced lung tumorigenesis
GPRC5A suppresses protein synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum to prevent radiation-induced lung tumorigenesis
GPRC5A is a retinoic acid inducible gene that is preferentially expressed in lung tissue. Here the authors report that GPRC5A suppresses the translation of EGFR by interfering with the eIF4F complex assembly, thereby limiting lung tumorigenesis, particularly radiation-induced lung tumorigenesis.
- Jian Wang
- , Alton B. Farris
- & Ya Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Th2 and eosinophil responses suppress inflammatory arthritis
Th2 and eosinophil responses suppress inflammatory arthritis
Type 2 immune responses are viewed as opposites of Type 1 and 17 responses. Here the authors show that activation of Type 2 immunity by helminth infection counteracts the development of inflammatory arthritis, a type 17-mediated pathology, via IL-4/IL-13- STAT6 signalling and eosinophil activation.
- Zhu Chen
- , Darja Andreev
- & Aline Bozec
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of ETV6-RUNX1-like and DUX4-rearranged subtypes in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Identification of ETV6-RUNX1-like and DUX4-rearranged subtypes in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
The fusion of two genes during the pathogenesis of cancer can create oncogenes. In this study, the authors screen pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia samples for the presence of fusion genes and describe fusion genes that define new molecular subtypes of the disease
- Henrik Lilljebjörn
- , Rasmus Henningsson
- & Thoas Fioretos
-
Article
| Open Access Tenascin-C drives persistence of organ fibrosis
Tenascin-C drives persistence of organ fibrosis
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a fibrotic disease affecting multiple organs. Here the authors use patient samples plus mouse studies to show a central role for tenascin C as a TLR4 activator responsible for persistence of fibrosis in the context of SSc and SSc-like disease.
- Swati Bhattacharyya
- , Wenxia Wang
- & John Varga
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-specific Crmp2 deletion leads to neuronal development deficits and behavioural impairments in mice
Brain-specific Crmp2 deletion leads to neuronal development deficits and behavioural impairments in mice
The in vivo function of CRMP2 is unclear. Zhang et al. generate and characterize brain-specific Crmp2knockout mice. These mice show impairments in hippocampal neurogenesis, neuronal maturation and synaptic transmission, and exhibit schizophrenia-related behavioral deficits.
- Hongsheng Zhang
- , Eunchai Kang
- & Zhiheng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Suppressor of IKKɛ is an essential negative regulator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy
Suppressor of IKKɛ is an essential negative regulator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy
Identifying pathways that cause pathological cardiac hypertrophy holds great therapeutic potential. Here the authors discover one such pathway and show that SIKE, an inhibitor of interferon signalling, prevents pathological but not physiological cardiac hypertrophy by interacting with TBK1 and modulating the TBK1/AKT signalling in rodents and monkeys.
- Ke-Qiong Deng
- , Aibing Wang
- & Hongliang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies 8p21.3 associated with persistent hepatitis B virus infection among Chinese
Genome-wide association study identifies 8p21.3 associated with persistent hepatitis B virus infection among Chinese
This genome-wide association study on persistent hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection among Chinese confirms previously associated genetic loci while discovering a novel protective locus at 8p21.3. The study also demonstrates the nearby gene INST10 suppresses HBV replication in vitro.
- Yuanfeng Li
- , Lanlan Si
- & Gangqiao Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic changes in neural circuitry during adolescence are associated with persistent attenuation of fear memories
Dynamic changes in neural circuitry during adolescence are associated with persistent attenuation of fear memories
Flexible fear-related responses may be advantageous in adolescence. Here the authors use microprisms to image prefrontal cortical spine maturation across development and report that plasticity in adolescent fear extinction responses is associated with dynamic reorganization in the amygdalahippocampal-PFC circuit.
- Siobhan S. Pattwell
- , Conor Liston
- & Francis S. Lee
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Dental diseases
- Endocrine system and metabolic diseases
- Eye diseases
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Haematological diseases
- Immunological disorders
- Infectious diseases
- Kidney diseases
- Metabolic disorders
- Neurological disorders
- Nutrition disorders
- Oral diseases
- Psychiatric disorders
- Reproductive disorders
- Respiratory tract diseases
- Rheumatic diseases
- Skin diseases
- Trauma
- Urogenital diseases

 25-hydroxycholesterol contributes to cerebral inflammation of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy through activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
25-hydroxycholesterol contributes to cerebral inflammation of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy through activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome