Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access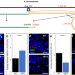 Bisection of the X chromosome disrupts the initiation of chromosome silencing during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Bisection of the X chromosome disrupts the initiation of chromosome silencing during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
During meiosis, sex chromosomes show silenced gene expression that is disrupted when translocated to autosomes. Here, the authors engineer C. elegans with bisected X chromosomes and see active transcription in gonads, indicating continuity of sex chromosomes promotes silencing.
- Yisrael Rappaport
- , Hanna Achache
- & Yonatan B. Tzur
-
Article
| Open Access The developing mouse coronal suture at single-cell resolution
The developing mouse coronal suture at single-cell resolution
The development of the coronal suture remains incompletely understood. Here the authors perform scRNA-seq and expression validation to uncover the cellular diversity within the murine embryonic coronal suture, thus revealing possible mechanisms for its loss in craniosynostosis.
- D’Juan T. Farmer
- , Hana Mlcochova
- & Stephen R. F. Twigg
-
Article
| Open Access The chromatin, topological and regulatory properties of pluripotency-associated poised enhancers are conserved in vivo
The chromatin, topological and regulatory properties of pluripotency-associated poised enhancers are conserved in vivo
Poised enhancers (PEs) in embryonic stem cells have accessible chromatin, are bound by repressive Polycomb Group proteins, and interact with their targets prior to activation. However, whether this is recapitulated in vivo is unknown. Here the authors show PEs display these features in mouse embryos, are prevalent across vertebrates, and are required for developmental gene expression.
- Giuliano Crispatzu
- , Rizwan Rehimi
- & Alvaro Rada-Iglesias
-
Article
| Open Access Endometrial receptivity and implantation require uterine BMP signaling through an ACVR2A-SMAD1/SMAD5 axis
Endometrial receptivity and implantation require uterine BMP signaling through an ACVR2A-SMAD1/SMAD5 axis
Building on the known role of BMP signalling in implantation, the authors define the role of uterine ACVR2A and ALK3 (via SMAD1/5) in vivo in regulating murine endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation.
- Diana Monsivais
- , Takashi Nagashima
- & Martin M. Matzuk
-
Article
| Open Access Cryptic genetic variation in a heat shock protein modifies the outcome of a mutation affecting epidermal stem cell development in C. elegans
Cryptic genetic variation in a heat shock protein modifies the outcome of a mutation affecting epidermal stem cell development in C. elegans
How the genetic background modifies the expression of mutations is a key question that is addressed in this study in the context of seam cell development in Caenorhabditis elegans isolates. One amino acid deletion in a conserved heat shock protein is sufficient to shape phenotype expressivity upon mutation of a GATA transcription factor.
- Sneha L. Koneru
- , Mark Hintze
- & Michalis Barkoulas
-
Article
| Open Access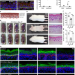 High proliferation and delamination during skin epidermal stratification
High proliferation and delamination during skin epidermal stratification
How the developing skin epidermis is transformed from a simple single-layered epithelium to a complex and stratified barrier is still an open question. Here, the authors provide a model based on high proliferation and delamination of the keratinocyte progenitors that support the stratification process.
- Mareike Damen
- , Lisa Wirtz
- & Hisham Bazzi
-
Article
| Open Access EMX2-GPR156-Gαi reverses hair cell orientation in mechanosensory epithelia
EMX2-GPR156-Gαi reverses hair cell orientation in mechanosensory epithelia
Sensory hair cells develop an asymmetric architecture to restrict stimulus detection to a single axis. Here the authors identify GPR156 as directing a 180-degree reversal in hair cell orientation through Gαi, downstream of EMX2 in the mouse inner ear and zebrafish lateral line.
- Katie S. Kindt
- , Anil Akturk
- & Basile Tarchini
-
Article
| Open Access Differential chromatin binding of the lung lineage transcription factor NKX2-1 resolves opposing murine alveolar cell fates in vivo
Differential chromatin binding of the lung lineage transcription factor NKX2-1 resolves opposing murine alveolar cell fates in vivo
How transcription factors regulate cell fates in native tissues is unclear. Here, the authors report that differential chromatin binding of NKX2-1 determines opposing alveolar cell fates in the murine lung, showing loss of YAP/TAZ directs NKX2-1 to alternative binding sites leading to cell fate conversion.
- Danielle R. Little
- , Anne M. Lynch
- & Jichao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access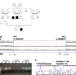 Deletion of CTCF sites in the SHH locus alters enhancer–promoter interactions and leads to acheiropodia
Deletion of CTCF sites in the SHH locus alters enhancer–promoter interactions and leads to acheiropodia
Acheiropodia is associated with homozygous deletions in the LMBR1 gene around ZRS, an enhancer regulating SHH during limb development, but how these deletions lead to this phenotype is unknown. Here the authors use whole-genome sequencing, ChIP-seq, 4C-seq and DNA FISH to show that alterations in CTCF motifs are responsible via altered enhancer–promoter interactions.
- Aki Ushiki
- , Yichi Zhang
- & Nadav Ahituv
-
Article
| Open Access Role of Hakai in m6A modification pathway in Drosophila
Role of Hakai in m6A modification pathway in Drosophila
Drosophila m6A writer complex regulates alternative splicing of the Sex-lethal gene. Here the authors show that a potential E3 ligase Hakai interacts with the fly m6A writer complex and that m6A level is reduced in Hakai mutant flies.
- Yanhua Wang
- , Lifeng Zhang
- & Dong Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Defective dystrophic thymus determines degenerative changes in skeletal muscle
Defective dystrophic thymus determines degenerative changes in skeletal muscle
Immune cells are known to aggravate the inflammatory impact of Duchene muscular dystrophy. Here, the authors describe impaired thymic development and suggest thymic involution in this model of disease is linked to disease acceleration due to impaired immunological tolerance.
- Andrea Farini
- , Clementina Sitzia
- & Yvan Torrente
-
Article
| Open Access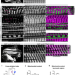 Myofibril and mitochondria morphogenesis are coordinated by a mechanical feedback mechanism in muscle
Myofibril and mitochondria morphogenesis are coordinated by a mechanical feedback mechanism in muscle
Mitochondria produce high amounts of ATP to power myosin motors and sustained muscle contraction. Here, the authors show that during development, muscles coordinate the morphogenesis of their myofibrils directly with their mitochondria to optimize both for the physiological needs of each muscle-type.
- Jerome Avellaneda
- , Clement Rodier
- & Frank Schnorrer
-
Article
| Open Access Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Sclerosing bone disorder (SBD) includes a broad spectrum of monogenic diseases characterised by increased bone density. Here, the authors describe a previously unknown SBD in four families caused by mutations in TMEM53 and demonstrate the role this protein plays in BMP signalling during bone formation.
- Long Guo
- , Aritoshi Iida
- & Shiro Ikegawa
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of BAF and MLL4 promotes cell type-specific enhancer activation
Interplay of BAF and MLL4 promotes cell type-specific enhancer activation
The SWI/SNF complex BAF and the histone H3K4 methyltransferase MLL4 (KMT2D) play critical roles in enhancer activation, however the interplay between them has remained unclear. Here the authors show that BAF and MLL4 are interdependent in promoting enhancer activation by lineage-determining transcription factors during adipogenesis.
- Young-Kwon Park
- , Ji-Eun Lee
- & Kai Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic sex chromosome expression in Drosophila male germ cells
Dynamic sex chromosome expression in Drosophila male germ cells
Sex chromosome gene content and expression is unusual. Here the authors use single cell RNA-Seq on Drosophila larvae to demonstrate that the single X and pair of 4th chromosomes are specifically inactivated in primary spermatocytes, while genes on the single Y chromosome become maximally active in primary spermatocytes.
- Sharvani Mahadevaraju
- , Justin M. Fear
- & Brian Oliver
-
Article
| Open Access PQM-1 controls hypoxic survival via regulation of lipid metabolism
PQM-1 controls hypoxic survival via regulation of lipid metabolism
Animals respond to hypoxic stress by adjusting metabolic processes to balance survival and reproduction. Here the authors identify the transcription factor PQM-1 as a metabolic regulator that balances hypoxic lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in C. elegans to limit somatic integrity and promote progeny survival.
- Thomas Heimbucher
- , Julian Hog
- & Coleen T. Murphy
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin remodeling in bovine embryos indicates species-specific regulation of genome activation
Chromatin remodeling in bovine embryos indicates species-specific regulation of genome activation
Preimplantation embryos undergo extensive transcriptomic and epigenomic remodeling. Here the authors assay open chromatin in bovine oocytes, embryos, and embryonic stem cells, and compare the transcriptomes and epigenomes of cattle, human and mouse embryos, revealing species-specific regulation of genome activation.
- Michelle M. Halstead
- , Xin Ma
- & Pablo J. Ross
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of NARS1 impairs progenitor proliferation in cortical brain organoids and leads to microcephaly
Loss of NARS1 impairs progenitor proliferation in cortical brain organoids and leads to microcephaly
Asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase1 (NARS1) is required for protein synthesis. Here, the authors identify biallelic NARS1 mutations in individuals with microcephaly and neurodevelopmental delay. Cortical brain organoid modeling recapitulates microcephaly characteristics and scRNA-seq reveals a role for NARS1 in radial glial cell proliferation.
- Lu Wang
- , Zhen Li
- & Joseph G. Gleeson
-
Article
| Open Access The netrin receptor UNC-40/DCC assembles a postsynaptic scaffold and sets the synaptic content of GABAA receptors
The netrin receptor UNC-40/DCC assembles a postsynaptic scaffold and sets the synaptic content of GABAA receptors
The netrin receptor UNC-40/DCC is required to recruit GABAAR at neuromuscular junctions in C. elegans. Here, the authors show that UNC-40/DCC assembles an intracellular synaptic scaffold, regulating the content of GABAAR and inhibitory neurotransmission.
- Xin Zhou
- , Marine Gueydan
- & Jean-Louis Bessereau
-
Article
| Open Access XPO5 promotes primary miRNA processing independently of RanGTP
XPO5 promotes primary miRNA processing independently of RanGTP
XPO5 mediates nuclear export of miRNA hairpin precursors (pre-miRNAs) through a RanGTP-dependent binding. Here the authors employ HITS-CLIP and biochemical analysis and show that XPO5 binds and promotes nuclear processing of clustered pri-miRNAs, with extensive double-stranded regions, independently of RanGTP.
- Jingjing Wang
- , Jerome E. Lee
- & Rui Yi
-
Article
| Open Access The secreted protease Adamts18 links hormone action to activation of the mammary stem cell niche
The secreted protease Adamts18 links hormone action to activation of the mammary stem cell niche
How hormonal signaling in the mammary epithelium controls the surrounding extracellular matrix is unclear. Here, the authors show that a secreted protease, Adamts18, induced by upstream estrogen-progesterone activated Wnt4 in myoepithelial cells, remodels the basement membrane and contributes to mammary epithelial stemness.
- Dalya Ataca
- , Patrick Aouad
- & Cathrin Brisken
-
Article
| Open Access The conserved microRNA miR-34 regulates synaptogenesis via coordination of distinct mechanisms in presynaptic and postsynaptic cells
The conserved microRNA miR-34 regulates synaptogenesis via coordination of distinct mechanisms in presynaptic and postsynaptic cells
Although micro(mi)RNA-based post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms have been implicated in the assembly and modulation of synaptic connections, few miRNAs have been identified that control synapse formation. Here, authors performed an unbiased screen for novel regulators of synapse morphogenesis at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction and discovered that miR-34 inhibits Nrx-IV to influence active zone formation, whereas, postsynaptic miR-34 inhibits Hts to regulate the initiation of bouton formation from presynaptic terminals.
- Elizabeth M. McNeill
- , Chloe Warinner
- & David Van Vactor
-
Article
| Open Access Klf5 acetylation regulates luminal differentiation of basal progenitors in prostate development and regeneration
Klf5 acetylation regulates luminal differentiation of basal progenitors in prostate development and regeneration
The role of the Klf5 in early and postnatal prostate development and in regeneration is unclear. Here, the authors show that Klf5 acetylation regulates and maintains luminal differentiation of prostate basal progenitors and is essential following androgen-induced regeneration.
- Baotong Zhang
- , Xinpei Ci
- & Jin-Tang Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Dstyk mutation leads to congenital scoliosis-like vertebral malformations in zebrafish via dysregulated mTORC1/TFEB pathway
Dstyk mutation leads to congenital scoliosis-like vertebral malformations in zebrafish via dysregulated mTORC1/TFEB pathway
Congenital scoliosis is a complex genetic disorder characterized by vertebral malformation. Here, the authors demonstrate that loss of dstyk leads to scoliosis in zebrafish due to dysregulated biogenesis of notochord vacuoles and that DSTYK is required for lysosome biogenesis through mTORC1 regulation.
- Xianding Sun
- , Yang Zhou
- & Lin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Renewed proliferation in adult mouse cochlea and regeneration of hair cells
Renewed proliferation in adult mouse cochlea and regeneration of hair cells
The adult mammalian inner ear cells cannot regenerate nor proliferate. Here, the authors show that co-activation of Myc and NOTCH pathways can stimulate proliferation of inner ear sensory epithelial cells, which can be induced to become hair cell-like cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Yilai Shu
- , Wenyan Li
- & Zheng-Yi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A reference map of murine cardiac transcription factor chromatin occupancy identifies dynamic and conserved enhancers
A reference map of murine cardiac transcription factor chromatin occupancy identifies dynamic and conserved enhancers
Mapping transcription factors (TFs) occupancy is essential for understanding transcriptional programs. Here the authors use biotinylated knockin alleles of key cardiac TFs (GATA4, NKX2-5, MEF2A, MEF2C, SRF, TBX5, TEAD1) to map their genome-wide occupancy in the fetal and adult mouse heart, providing insight into the cardiac transcriptional regulatory network.
- Brynn N. Akerberg
- , Fei Gu
- & William T. Pu
-
Article
| Open Access UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
Retrotransposons are silenced by an epigenetic mechanism and piRNA pathway in the mammalian germline. Here, the authors report that UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons by interacting with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins during spermatogenesis.
- Juan Dong
- , Xiaoli Wang
- & Shuiqiao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Ciliary exclusion of Polycystin-2 promotes kidney cystogenesis in an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease model
Ciliary exclusion of Polycystin-2 promotes kidney cystogenesis in an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease model
The molecular role of ciliary Polycystin-2 (PC2) in cyst formation and polycystic kidney disease (ADKPD) is unclear. Here, the authors identify a PC2 mutant lacking ciliary localisation but with active Ca2+ channel function in mice, that is sufficient to generate an ADPKD phenotype.
- Rebecca V. Walker
- , Jennifer L. Keynton
- & Dominic P. Norris
-
Article
| Open Access EZHIP constrains Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 activity in germ cells
EZHIP constrains Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 activity in germ cells
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) plays critical roles in transcriptional silencing during development. Here the authors identify EZHIP as a cofactor of PRC2 expressed predominantly in the gonads, finding that EZHIP limits the enzymatic activity of PRC2 in germ cells in mice.
- Roberta Ragazzini
- , Raquel Pérez-Palacios
- & Raphaël Margueron
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-type-specific genomics reveals histone modification dynamics in mammalian meiosis
Cell-type-specific genomics reveals histone modification dynamics in mammalian meiosis
Meiotic DSB formation, repair and recombination occur in a continuum of substages termed leptonema, zygonema, pachynema, and diplonema. Here, authors develop a method for isolating pure sub-populations of nuclei that allows for detailed study of meiotic substages.
- Kwan-Wood Gabriel Lam
- , Kevin Brick
- & R. Daniel Camerini-Otero
-
Article
| Open Access Pioneer and nonpioneer factor cooperation drives lineage specific chromatin opening
Pioneer and nonpioneer factor cooperation drives lineage specific chromatin opening
Pioneer transcription factor Pax7 specifies melanotrope cells, which then allows for the binding of Tpit transcription factor. Here, authors find that while binding of heterochromatin targeting by Pax7 is independent of Tpit, Pax7-dependent chromatin opening requires Tpit.
- Alexandre Mayran
- , Kevin Sochodolsky
- & Jacques Drouin
-
Article
| Open Access Hox11 expressing regional skeletal stem cells are progenitors for osteoblasts, chondrocytes and adipocytes throughout life
Hox11 expressing regional skeletal stem cells are progenitors for osteoblasts, chondrocytes and adipocytes throughout life
Prior evidence suggested mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) required for skeletal formation, maintenance, and repair arise postnatally. Here, the authors show that Hoxa11 lineage-marked cells give rise to all skeletal lineages from embryogenesis through adulthood and are upstream progenitors of LepR- and Osx-lineage MSCs
- Kyriel M. Pineault
- , Jane Y. Song
- & Deneen M. Wellik
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in SMARCB1 and in other Coffin–Siris syndrome genes lead to various brain midline defects
Mutations in SMARCB1 and in other Coffin–Siris syndrome genes lead to various brain midline defects
Why and how mutations in genes encoding BAF complex components lead to distinct disease entitites remains unresolved. In this study, authors establish the first Smarcb1 mutant mouse model with multiple brain abnormalities recapitulating human Coffin–Siris syndrome and show that one prominent midline abnormality, corpus callosum agenesis, is due to midline glia aberrations.
- Alina Filatova
- , Linda K. Rey
- & Ulrike A. Nuber
-
Article
| Open Access Common and distinct transcriptional signatures of mammalian embryonic lethality
Common and distinct transcriptional signatures of mammalian embryonic lethality
The transcriptional signature of embryonic lethality has not been defined. Here, the authors, as part of the Deciphering the Mechanisms of Developmental Disorders programme, define genes causing murine embryonic lethality around E9.5 and identify developmental delay transcriptional signatures.
- John E. Collins
- , Richard J. White
- & Elisabeth M. Busch-Nentwich
-
Article
| Open Access An asymmetric allelic interaction drives allele transmission bias in interspecific rice hybrids
An asymmetric allelic interaction drives allele transmission bias in interspecific rice hybrids
Our limited understanding of the hybrid sterility (HS) mechanism in Asian–African rice hybrids hampers utilization of the interspecific heterosis for rice production. Here, the authors identify S1-mediated HS-related tripartite gamete killer-protector system, and explore their evolutionary relationship.
- Yongyao Xie
- , Jintao Tang
- & Letian Chen
-
Article
| Open Access TORC1 modulation in adipose tissue is required for organismal adaptation to hypoxia in Drosophila
TORC1 modulation in adipose tissue is required for organismal adaptation to hypoxia in Drosophila
The hypoxia response pathway couples oxygen availability to physiological adaptations. Using the model system Drosophila melanogaster, here the authors show that hypoxia inhibits TORC1 signalling and increases lipid levels in the larval fat body and that these effects are required for development to adulthood.
- Byoungchun Lee
- , Elizabeth C. Barretto
- & Savraj S. Grewal
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved CCM complex promotes apoptosis non-autonomously by regulating zinc homeostasis
A conserved CCM complex promotes apoptosis non-autonomously by regulating zinc homeostasis
Cerebral Cavernous Malformations (CCM) are often caused by mutations in CCM1/KRIT1. Here, Chapman et al. elegantly show that the CCM complex promotes apoptosis by regulating zinc homeostasis and storage via a conserved mechanism that likely generates the pathological defects observed in CCM.
- Eric M. Chapman
- , Benjamin Lant
- & W. Brent Derry
-
Article
| Open Access Live imaging of alveologenesis in precision-cut lung slices reveals dynamic epithelial cell behaviour
Live imaging of alveologenesis in precision-cut lung slices reveals dynamic epithelial cell behaviour
The process of alveologenesis is incompletely understood, partly due to the lack of applicable real-time imaging methods. Here the authors describe the process of alveologenesis and the behaviour of epithelial cells in real-time, using widefield microscopy and image deconvolution in precision-cut lung slices, revealing the dominant role of epithelial cell migration.
- Khondoker M. Akram
- , Laura L. Yates
- & Charlotte H. Dean
-
Article
| Open Access BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes temporally and developmentally regulate the sheath to blade ratio of rice leaves
BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes temporally and developmentally regulate the sheath to blade ratio of rice leaves
Despite the importance of proximal-distal patterning of leaves in cereal productivity, the underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, the authors find that the ratio of sheath to blade in rice leaf shifts depends on the expression levels of BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes.
- Taiyo Toriba
- , Hiroki Tokunaga
- & Junko Kyozuka
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of a floral colour polymorphism by pollinator-mediated overdominance
Emergence of a floral colour polymorphism by pollinator-mediated overdominance
Examples of overdominance are usually explained by deleterious effects in homozygotes. Here, Kellenberger et al. describe a case of overdominance in the floral color of the Alpine orchid Gymnadenia rhellicani apparently maintained by pollinator preferences without deleterious effects in homozygotes.
- Roman T. Kellenberger
- , Kelsey J. R. P. Byers
- & Philipp M. Schlüter
-
Article
| Open Access Functional genomic analysis identifies miRNA repertoire regulating C. elegans oocyte development
Functional genomic analysis identifies miRNA repertoire regulating C. elegans oocyte development
Biogenesis and function of miRNAs in somatic cells is well characterized, but their role in the germline has not been established. Here the authors identify and characterize Drosha independent and dependent miRNAs during C. elegans oogenesis, revealing their roles in meiotic progression and oocyte development.
- Amanda L. Minogue
- , Michael R. Tackett
- & Swathi Arur
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial fine-mapping for gene-by-environment effects identifies risk hot spots for schizophrenia
Spatial fine-mapping for gene-by-environment effects identifies risk hot spots for schizophrenia
Schizophrenia (SCZ) risk is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Here, the authors develop a statistical method for analyzing gene-by-environment effects in SCZ risk across Denmark with fine spatial resolution.
- Chun Chieh Fan
- , John J. McGrath
- & Carsten Bøcker Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Kinesin-2 and IFT-A act as a complex promoting nuclear localization of β-catenin during Wnt signalling
Kinesin-2 and IFT-A act as a complex promoting nuclear localization of β-catenin during Wnt signalling
IFT-A proteins and Kinesin-2 modulate canonical Wnt/Wg-signalling independent of their ciliary role, but how is unclear. Here, the authors show that Kinesin-2 and IFT-A act as a complex to promote nuclear translocation of β-catenin in Drosophila and mouse MEF Wnt signalling independent of its ciliary role.
- Linh T. Vuong
- , Carlo Iomini
- & Marek Mlodzik
-
Article
| Open Access A non-canonical BRD9-containing BAF chromatin remodeling complex regulates naive pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells
A non-canonical BRD9-containing BAF chromatin remodeling complex regulates naive pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells
The BAF complex is a multi-subunit chromatin remodeling complex that plays important roles in transcription regulation. Here the authors provide evidence that BRD9 and GLTSCR1/BICRA or its paralog GLTSCR1-like/BICRAL define a non-canonical BAF complex that regulates naive pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells.
- Jovylyn Gatchalian
- , Shivani Malik
- & Diana C. Hargreaves
-
Article
| Open Access Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
During early embryogenesis, critical cardiac specification events occur. Here the authors isolate cardiac progenitor cells from early zebrafish embryos and characterize accessible chromatin regions specific to this cell population, finding that many of these regions overlap with conserved non-coding elements that are ortholgous to accessible chromatin regions in human.
- Xuefei Yuan
- , Mengyi Song
- & Michael D. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Oestrogen receptor α AF-1 and AF-2 domains have cell population-specific functions in the mammary epithelium
Oestrogen receptor α AF-1 and AF-2 domains have cell population-specific functions in the mammary epithelium
Oestrogen receptors α (ERα) are expressed in a subset of mammary epithelial cells. Here, the authors identify cells with low-ERα protein levels and show that distinct cell populations have distinct requirements for the AF1 and AF2 domains of the ERα, and ERα acts in a biphasic manner dependent on developmental stage.
- Stéphanie Cagnet
- , Dalya Ataca
- & Cathrin Brisken
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of embryonic neural crest derived cardiomyocytes causes adult onset hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in zebrafish
Loss of embryonic neural crest derived cardiomyocytes causes adult onset hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in zebrafish
A small percentage of cardiomyocytes (CM) are of neural crest origin but the function of such cells in the adult zebrafish is unclear. Here, the authors identify this CM subpopulation as expressing the Notch ligand jag2b and if deleted in the embryo, cause severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in adulthood.
- Sarah Abdul-Wajid
- , Bradley L. Demarest
- & H. Joseph Yost
-
Article
| Open Access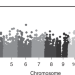 A missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis
A missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis
The majority of scoliosis is considered idiopathic with onset in adolescence (AIS) and has a genetic contribution. Here, the authors perform an exome wide association study of data from 457 severe AIS cases and 987 controls, and find a missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with AIS.
- Gabe Haller
- , Kevin McCall
- & Christina A. Gurnett
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of maternal care on gene expression and DNA methylation in a subsocial bee
The effect of maternal care on gene expression and DNA methylation in a subsocial bee
Development may be plastic and influenced by parental care. Here, the authors show that experimental reduction of maternal care in the small carpenter bee leads to extensive changes in gene expression and splicing, minor changes in methylation, and greater offspring aggression and social avoidance.
- Samuel V. Arsenault
- , Brendan G. Hunt
- & Sandra M. Rehan

 Developmental genetics of color pattern establishment in cats
Developmental genetics of color pattern establishment in cats