Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering spatial domains from spatially resolved transcriptomics with an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder
Deciphering spatial domains from spatially resolved transcriptomics with an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder
Breakthrough technologies for spatially resolved transcriptomics have enabled genome-wide profiling of gene expressions in captured locations. Here the authors integrate gene expressions and spatial locations to identify spatial domains using an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder.
- Kangning Dong
- & Shihua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering interpretable potential confounders in electronic medical records
Uncovering interpretable potential confounders in electronic medical records
Randomized clinical trials are often plagued by selection bias, and expert-selected covariates may insufficiently adjust for confounding factors. Here, the authors develop a framework based on natural language processing to uncover interpretable potential confounders from text.
- Jiaming Zeng
- , Michael F. Gensheimer
- & Ross D. Shachter
-
Article
| Open Access DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
The authors present DeepRank, a deep learning framework for the data mining of large sets of 3D protein-protein interfaces (PPI). They use DeepRank to address two challenges in structural biology: distinguishing biological versus crystallographic PPIs in crystal structures, and secondly the ranking of docking models.
- Nicolas Renaud
- , Cunliang Geng
- & Li C. Xue
-
Article
| Open Access A high-risk retinoblastoma subtype with stemness features, dedifferentiated cone states and neuronal/ganglion cell gene expression
A high-risk retinoblastoma subtype with stemness features, dedifferentiated cone states and neuronal/ganglion cell gene expression
Retinoblastoma is the most frequent intraocular paediatric malignancy whose molecular basis remains poorly understood. Here, the authors perform multi-omic analysis and identify two subtypes; one in a cone differentiated state and one more aggressive showing cone dedifferentiation and expressing neuronal markers.
- Jing Liu
- , Daniela Ottaviani
- & François Radvanyi
-
Article
| Open Access Peak learning of mass spectrometry imaging data using artificial neural networks
Peak learning of mass spectrometry imaging data using artificial neural networks
The high dimensional and complex nature of mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) data poses challenges to downstream analyses. Here the authors show an application of artificial intelligence in mining MSI data revealing biologically relevant metabolomic and proteomic information from data acquired on different mass spectrometry platforms.
- Walid M. Abdelmoula
- , Begona Gimenez-Cassina Lopez
- & Nathalie Y. R. Agar
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-species behavior analysis with attention-based domain-adversarial deep neural networks
Cross-species behavior analysis with attention-based domain-adversarial deep neural networks
Comparing changes in behaviour across various species is not always trivial, especial across significantly divergent species. Here, the authors develop a deep learning framework that allows them to map changes in locomotion demonstrated on dopamine-deficient humans, mice and worms.
- Takuya Maekawa
- , Daiki Higashide
- & Susumu Takahashi
-
Article
| Open Access Automatically disambiguating medical acronyms with ontology-aware deep learning
Automatically disambiguating medical acronyms with ontology-aware deep learning
Disambiguating abbreviations is important for automated clinical note processing; however, deploying machine learning for this task is restricted by lack of good training data. Here, the authors show novel data augmentation methods that use biomedical ontologies to improve abbreviation disambiguation in many datasets.
- Marta Skreta
- , Aryan Arbabi
- & Michael Brudno
-
Article
| Open Access The concurrence of DNA methylation and demethylation is associated with transcription regulation
The concurrence of DNA methylation and demethylation is associated with transcription regulation
The global pattern of the mammalian methylome is formed by changes in methylation and demethylation. Here the authors describe a metric methylation concurrence that measures the ratio of unmethylated CpGs inside the partially methylated reads and show that methylation concurrence is associated with epigenetically regulated tumour suppressor genes.
- Jiejun Shi
- , Jianfeng Xu
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Global spread of Salmonella Enteritidis via centralized sourcing and international trade of poultry breeding stocks
Global spread of Salmonella Enteritidis via centralized sourcing and international trade of poultry breeding stocks
Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis is a pathogen of poultry that can cause outbreaks in humans. Here the authors use genomic and trade data to investigate a pandemic in the 1980s, finding evidence that international trade of breeding stocks led to global spread of the pathogen.
- Shaoting Li
- , Yingshu He
- & Xiangyu Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting base editing outcomes with an attention-based deep learning algorithm trained on high-throughput target library screens
Predicting base editing outcomes with an attention-based deep learning algorithm trained on high-throughput target library screens
Base editors enable precise genetic alterations but vary in efficiency at different loci. Here the authors analyse ABEs and CBEs at over 28,000 integrated sequences to train BE-DICT, a machine learning model capable of predicting base editing outcomes.
- Kim F. Marquart
- , Ahmed Allam
- & Gerald Schwank
-
Article
| Open Access Genome dependent Cas9/gRNA search time underlies sequence dependent gRNA activity
Genome dependent Cas9/gRNA search time underlies sequence dependent gRNA activity
The link between gRNA sequence and Cas9 activity is well established but the mechanism underlying this relationship is not well understood. Here the authors show that gRNA sequence primarily influences activity by dictating the time it takes for Cas9 to find the target site in a species-specific manner.
- E. A. Moreb
- & M. D. Lynch
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of the cross-strand chimeric RNAs generated by fusions of bi-directional transcripts
Identification of the cross-strand chimeric RNAs generated by fusions of bi-directional transcripts
Gene fusion, trans-splicing or transcription read-through contributes to generation of chimeric RNA. Here the authors develop a pipeline to identify non-canonical type of chimeric RNAs called cross-strand chimeric RNA (cscRNA), which are fused between two precursor RNAs transcribed from the opposite DNA strands.
- Yuting Wang
- , Qin Zou
- & Xuerui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a fixed module repertoire for the analysis and interpretation of blood transcriptome data
Development of a fixed module repertoire for the analysis and interpretation of blood transcriptome data
The blood transcriptome of human subjects can be profiled on an almost routine basis in translational research settings. Here the authors show that a fixed and well-characterized repertoire of transcriptional modules can be employed as a reusable framework for the analysis, visualization and interpretation of such data
- Matthew C. Altman
- , Darawan Rinchai
- & Damien Chaussabel
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning connects DNA traces to transcription to reveal predictive features beyond enhancer–promoter contact
Deep learning connects DNA traces to transcription to reveal predictive features beyond enhancer–promoter contact
Recent advances in super-resolution microscopy have made it possible to measure chromatin 3D structure and transcription in thousands of single cells. Here, authors present a deep learning-based approach to characterise how chromatin structure relates to transcriptional state of individual cells and determine which structural features of chromatin regulation are important for gene expression state.
- Aparna R. Rajpurkar
- , Leslie J. Mateo
- & Alistair N. Boettiger
-
Article
| Open Access Model-based analysis uncovers mutations altering autophagy selectivity in human cancer
Model-based analysis uncovers mutations altering autophagy selectivity in human cancer
Although autophagy has been linked to tumourigenesis, it is unclear how genomic alterations affect autophagy selectivity in tumours. Here, the authors establish a pipeline that integrates computational and experimental approaches to show that altered autophagy selectivity is frequent in cancer cells and link glycogen autophagy with tumourigenesis.
- Zhu Han
- , Weizhi Zhang
- & Da Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
Current genome mining methods predict many putative non-ribosomal peptides (NRPs) from their corresponding biosynthetic gene clusters, but it remains unclear which of those exist in nature and how to identify their post-assembly modifications. Here, the authors develop NRPminer, a modification-tolerant tool for the discovery of NRPs from large genomic and mass spectrometry datasets, and use it to find 180 NRPs from different environments.
- Bahar Behsaz
- , Edna Bode
- & Hosein Mohimani
-
Article
| Open Access Permutation-based identification of important biomarkers for complex diseases via machine learning models
Permutation-based identification of important biomarkers for complex diseases via machine learning models
Study of human disease remains challenging due to convoluted disease etiologies and complex molecular mechanisms at genetic, genomic, and proteomic levels. Here, the authors propose a computationally efficient Permutation-based Feature Importance Test to assist interpretation and selection of individual features in complex machine learning models for complex disease analysis.
- Xinlei Mi
- , Baiming Zou
- & Jianhua Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of machine learning and genome-scale metabolic modeling identifies multi-omics biomarkers for radiation resistance
Integration of machine learning and genome-scale metabolic modeling identifies multi-omics biomarkers for radiation resistance
Personalized prediction of tumor radiosensitivity would facilitate development of precision medicine workflows for cancer treatment. Here, the authors integrate machine learning and genome-scale metabolic modeling approaches to identify multi-omics biomarkers predictive of radiation response.
- Joshua E. Lewis
- & Melissa L. Kemp
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupling epithelial-mesenchymal transitions from stromal profiles by integrative expression analysis
Decoupling epithelial-mesenchymal transitions from stromal profiles by integrative expression analysis
Epithelial cancer cells can transition into a mesenchymal phenotype to enable invasion and metastasis. Here, the authors use previously published single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing datasets to decouple the mesenchymal expression profiles of cancer and stromal cells.
- Michael Tyler
- & Itay Tirosh
-
Article
| Open Access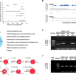 Presence of complete murine viral genome sequences in patient-derived xenografts
Presence of complete murine viral genome sequences in patient-derived xenografts
Patient-derived xenografts are widely used for drug development, but the impact of murine viral infection remains underexplored. Here, the authors demonstrate the extensive existence of murine viral sequences in patient-derived xenografts and significant expression change of crucial genes in samples with high virus load.
- Zihao Yuan
- , Xuejun Fan
- & W. Jim Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access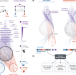 Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome
Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome
Most diseases disrupt multiple proteins, and drugs treat such diseases by restoring the functions of the disrupted proteins; how drugs restore these functions, however, is often unknown. Here, the authors develop the multiscale interactome, a powerful approach to explain disease treatment.
- Camilo Ruiz
- , Marinka Zitnik
- & Jure Leskovec
-
Article
| Open Access Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Kinases drive fundamental changes in cell state, but predicting kinase activity based on substrate-level changes can be challenging. Here the authors introduce a computational framework that utilizes similarities between substrates to robustly infer kinase activity.
- Serhan Yılmaz
- , Marzieh Ayati
- & Mehmet Koyutürk
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based cross-classifications reveal conserved spatial behaviors within tumor histological images
Deep learning-based cross-classifications reveal conserved spatial behaviors within tumor histological images
Histopathological images are a rich but incompletely explored data type for studying cancer. Here the authors show that convolutional neural networks can be systematically applied across cancer types, enabling comparisons to reveal shared spatial behaviors.
- Javad Noorbakhsh
- , Saman Farahmand
- & Jeffrey H. Chuang
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning uncovers independently regulated modules in the Bacillus subtilis transcriptome
Machine learning uncovers independently regulated modules in the Bacillus subtilis transcriptome
The systems-level regulatory structure underlying gene expression in bacteria can be inferred using machine learning algorithms. Here we show this structure for Bacillus subtilis, present five hypotheses gleaned from it, and analyse the process of sporulation from its perspective.
- Kevin Rychel
- , Anand V. Sastry
- & Bernhard O. Palsson
-
Article
| Open Access Interactive analysis of single-cell epigenomic landscapes with ChromSCape
Interactive analysis of single-cell epigenomic landscapes with ChromSCape
Bulk approaches fail to capture the cell-to-cell heterogeneity of chromatin landscapes, while single-cell approaches provide low coverage datasets. Here, the authors present ChromSCape, a user-friendly interactive application that processes single-cell epigenomic data to assist the biological interpretation of chromatin landscapes within cell populations, as demonstrated in the context of cancer.
- Pacôme Prompsy
- , Pia Kirchmeier
- & Céline Vallot
-
Article
| Open Access Globally altered epigenetic landscape and delayed osteogenic differentiation in H3.3-G34W-mutant giant cell tumor of bone
Globally altered epigenetic landscape and delayed osteogenic differentiation in H3.3-G34W-mutant giant cell tumor of bone
The histone variant mutation H3.3-G34W occurs in the majority of giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB). By profiling patient-derived GCTB tumor cells, the authors show that this mutation associates with epigenetic alterations in heterochromatic and bivalent regions that contribute to an impaired osteogenic differentiation and the osteolytic phenotype of GCTB.
- Pavlo Lutsik
- , Annika Baude
- & Christoph Plass
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-assisted comparative analysis of animal trajectories with DeepHL
Deep learning-assisted comparative analysis of animal trajectories with DeepHL
Comparative analysis of animal behaviour using locomotion data such as GPS data is difficult because the large amount of data makes it difficult to contrast group differences. Here the authors apply deep learning to detect and highlight trajectories characteristic of a group across scales of millimetres to hundreds of kilometres.
- Takuya Maekawa
- , Kazuya Ohara
- & Ken Yoda
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated knowledge discovery from omics data by optimal experimental design
Accelerated knowledge discovery from omics data by optimal experimental design
How to design experiments that accelerate knowledge discovery on complex biological landscapes remains a tantalizing question. Here, the authors present OPEX, an optimal experimental design method to identify informative omics experiments for both experimental space exploration and model training.
- Xiaokang Wang
- , Navneet Rai
- & Ilias Tagkopoulos
-
Perspective
| Open Access The use of mobile phone data to inform analysis of COVID-19 pandemic epidemiology
The use of mobile phone data to inform analysis of COVID-19 pandemic epidemiology
In this Perspective, the authors review the different applications for mobile phone data to support COVID-19 pandemic response, the relevance of these applications for infectious disease transmission and control, and potential sources and implications of selection bias in mobile phone data.
- Kyra H. Grantz
- , Hannah R. Meredith
- & Amy Wesolowski
-
Article
| Open Access A clustering-independent method for finding differentially expressed genes in single-cell transcriptome data
A clustering-independent method for finding differentially expressed genes in single-cell transcriptome data
How cell clusters are defined in single-cell sequencing data has important consequences for downstream analyses and the interpretation of results, but is often not straightforward. Here, the authors present a new approach that enables the prediction of differentially expressed genes without relying on explicit clustering of cells.
- Alexis Vandenbon
- & Diego Diez
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning uncovers cell identity regulator by histone code
Machine learning uncovers cell identity regulator by histone code
Identification of genes that determine and regulate cell identity remains challenging. Here, the authors use machine learning to identify cell identity genes and master regulator transcription factors based on gene expression profiles and histone modifications.
- Bo Xia
- , Dongyu Zhao
- & Kaifu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma
Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma
Understanding the mechanisms that lead to lung adenocarcinoma metastasis is important for identifying new therapeutics. Here, the authors document the changes in the transcriptome of human lung adenocarcinoma using single-cell sequencing and link cancer cell signatures to immune cell dynamics.
- Nayoung Kim
- , Hong Kwan Kim
- & Hae-Ock Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent RNA sequencing contamination in GTEx and other data sets
Consistent RNA sequencing contamination in GTEx and other data sets
Sample contamination has been reported in high throughput RNA sequencing. Here the authors analyze the RNA sequencing data from the Genotype-Tissue Expression project and describe how highly expressed, tissue specific genes contaminate across samples, which is corroborated in other data sets.
- Tim O. Nieuwenhuis
- , Stephanie Y. Yang
- & Marc K. Halushka
-
Article
| Open Access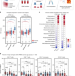 Sexual-dimorphism in human immune system aging
Sexual-dimorphism in human immune system aging
Whether the immune system aging differs between men and women is barely known. Here the authors characterize gene expression, chromatin state and immune subset composition in the blood of healthy humans 22 to 93 years of age, uncovering shared as well as sex-unique alterations, and create a web resource to interactively explore the data.
- Eladio J. Márquez
- , Cheng-han Chung
- & Duygu Ucar
-
Article
| Open Access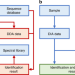 In silico spectral libraries by deep learning facilitate data-independent acquisition proteomics
In silico spectral libraries by deep learning facilitate data-independent acquisition proteomics
Data-independent acquisition (DIA) is an emerging technology in proteomics but it typically relies on spectral libraries built by data-dependent acquisition (DDA). Here, the authors use deep learning to generate in silico spectral libraries directly from protein sequences that enable more comprehensive DIA experiments than DDA-based libraries.
- Yi Yang
- , Xiaohui Liu
- & Liang Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Dissection of gene expression datasets into clinically relevant interaction signatures via high-dimensional correlation maximization
Dissection of gene expression datasets into clinically relevant interaction signatures via high-dimensional correlation maximization
Identification of clinically relevant gene expression signatures for cancer stratification remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a flexible nonlinear signal superposition model that enables dissection of large gene expression data sets into signatures and extraction of gene interactions.
- Michael Grau
- , Georg Lenz
- & Peter Lenz
-
Article
| Open Access A network-based approach to identify deregulated pathways and drug effects in metabolic syndrome
A network-based approach to identify deregulated pathways and drug effects in metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by complex phenotypes that increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Here the authors’ integrative network analysis suggests BTK inhibitor ibrutinib to be a promising treatment through its obesity-associated inflammation lowering effect.
- Karla Misselbeck
- , Silvia Parolo
- & Corrado Priami
-
Article
| Open Access Democratized image analytics by visual programming through integration of deep models and small-scale machine learning
Democratized image analytics by visual programming through integration of deep models and small-scale machine learning
Deep learning approaches for image preprocessing and analysis offer important advantages, but these are rarely incorporated into user-friendly software. Here the authors present an easy-to-use visual programming toolbox integrating deep-learning and interactive data visualization for image analysis.
- Primož Godec
- , Matjaž Pančur
- & Blaž Zupan
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of cell lines as models of primary tumors across 22 tumor types
Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of cell lines as models of primary tumors across 22 tumor types
Cell lines are used ubiquitously in cancer research but how well they represent the tumor type they were derived from is variable. Here, the authors compare transcriptomic profiles of 22 tumor types and cell lines and propose a new comprehensive cell line panel for pan-cancer studies.
- K. Yu
- , B. Chen
- & M. Sirota
-
Article
| Open Access A machine-compiled database of genome-wide association studies
A machine-compiled database of genome-wide association studies
Most databases of genotype-phenotype associations are manually curated. Here, Kuleshov et al. describe a machine curation system that extracts such relationships from the GWAS literature and synthesizes them into a structured knowledge base called GWASkb that can complement manually curated databases.
- Volodymyr Kuleshov
- , Jialin Ding
- & Michael Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic signatures of heterokaryosis in the oomycete pathogen Bremia lactucae
Genomic signatures of heterokaryosis in the oomycete pathogen Bremia lactucae
The oomycete Bremia lactucae is a highly variable pathogen that causes lettuce downy mildew. Here, the authors generate a high-quality genome assembly for B. lactucae, detect a high prevalence of heterokaryosis, and investigate its pathogenic consequences.
- Kyle Fletcher
- , Juliana Gil
- & Richard Michelmore
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing single-cell heterogeneity via data fusion improves image-based profiling
Capturing single-cell heterogeneity via data fusion improves image-based profiling
A challenge with single-cell resolution methods is that cell heterogeneity should be captured while allowing for comparisons between populations. Here the authors fuse information from the dispersion profiles with the average profiles at the level of profiles’ similarity matrices for single cell imaging data.
- Mohammad H. Rohban
- , Hamdah S. Abbasi
- & Anne E. Carpenter
-
Article
| Open Access Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
With the increasing obtainability of multi-OMICs data comes the need for easy to use data analysis tools. Here, the authors introduce Metascape, a biologist-oriented portal that provides a gene list annotation, enrichment and interactome resource and enables integrated analysis of multi-OMICs datasets.
- Yingyao Zhou
- , Bin Zhou
- & Sumit K. Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-task convolutional deep neural network for variant calling in single molecule sequencing
A multi-task convolutional deep neural network for variant calling in single molecule sequencing
Single Molecule Sequencing (SMS) technologies generate long but noisy reads data. Here, the authors develop Clairvoyante, a deep neural network-based method for variant calling with SMS reads such as PacBio and ONT data.
- Ruibang Luo
- , Fritz J. Sedlazeck
- & Michael C. Schatz
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-cancer characterisation of microRNA across cancer hallmarks reveals microRNA-mediated downregulation of tumour suppressors
Pan-cancer characterisation of microRNA across cancer hallmarks reveals microRNA-mediated downregulation of tumour suppressors
miRNAs have emerged as regulators of diverse biological processes including cancer. Here the authors present an extended pan-cancer analysis of the miRNAs in 15 epithelial cancers; integrating methylation, transcriptomic and mutation data they reveal alternative mechanisms of tumour suppressors’ regulation in absence of mutation, methylation or copy number alterations.
- Andrew Dhawan
- , Jacob G. Scott
- & Francesca M. Buffa
-
Article
| Open Access Patchwork of contrasting medication cultures across the USA
Patchwork of contrasting medication cultures across the USA
Health care in the United States is heterogeneous with respect to factors like disease incidence, treatment choices and health care spending. Here, the authors use insurance claims data from over 150 million patients to compare prescription rates of over 600 drugs, and uncover patterns of geographical variation that suggest an influence of race, health care laws and wealth.
- Rachel D. Melamed
- & Andrey Rzhetsky
-
Article
| Open Access Dereplication of microbial metabolites through database search of mass spectra
Dereplication of microbial metabolites through database search of mass spectra
New natural products can be identified via mass spectrometry by excluding all known ones from the analysis, a process called dereplication. Here, the authors extend a previously published dereplication algorithm to different classes of secondary metabolites.
- Hosein Mohimani
- , Alexey Gurevich
- & Pavel A. Pevzner
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the evolution of Escherichia coli by a data-driven approach
Predicting the evolution of Escherichia coli by a data-driven approach
How reproducible evolutionary processes are remains an important question in evolutionary biology. Here, the authors compile a compendium of more than 15,000 mutation events for Escherichia coli under 178 distinct environmental settings, and develop an ensemble of predictors to predict evolution at a gene level.
- Xiaokang Wang
- , Violeta Zorraquino
- & Ilias Tagkopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Network enhancement as a general method to denoise weighted biological networks
Network enhancement as a general method to denoise weighted biological networks
Technical noise in experiments is unavoidable, but it introduces inaccuracies into the biological networks we infer from the data. Here, the authors introduce a diffusion-based method for denoising undirected, weighted networks, and show that it improves the performances of downstream analyses.
- Bo Wang
- , Armin Pourshafeie
- & Jure Leskovec

 Learning meaningful representations of protein sequences
Learning meaningful representations of protein sequences