Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Diverging co-translational protein complex assembly pathways are governed by interface energy distribution
Diverging co-translational protein complex assembly pathways are governed by interface energy distribution
Protein complex assembly can occur co-translationally. Here, the authors uncover diverging assembly pathways and hotspot disruptions in N-terminal acetyltransferases, enzymes implicated in neurodegenerative diseases. Their model predicts co-translational assembly based on interface energy distribution.
- Johannes Venezian
- , Hagit Bar-Yosef
- & Ayala Shiber
-
Article
| Open Access Developmental progression of DNA double-strand break repair deciphered by a single-allele resolution mutation classifier
Developmental progression of DNA double-strand break repair deciphered by a single-allele resolution mutation classifier
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired by a hierarchically regulated network of pathways. Here, authors develop ICP for deciphering somatic DSB repair patterns in multicellular organisms and discover developmental regulation in flies and mosquitoes, enabling tracking of mutant alleles and interhomolog copying of gene cassettes.
- Zhiqian Li
- , Lang You
- & Ethan Bier
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-omic integration of microbiome data for identifying disease-associated modules
Multi-omic integration of microbiome data for identifying disease-associated modules
Here, Muller et al. introduce MintTea, a method for analyzing multi-omic microbiome data and identifying disease-associated modules comprising mixed sets of features that collectively shift in disease, offering insights into microbiome-disease interactions.
- Efrat Muller
- , Itamar Shiryan
- & Elhanan Borenstein
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic architecture of multimodal human brain age
The genetic architecture of multimodal human brain age
The biological basis of brain aging is not well understood, but it has implications for human health. Here, the authors explore the genetic basis of human brain aging, finding genetic variants, genes and potential causal relationships with disease.
- Junhao Wen
- , Bingxin Zhao
- & Christos Davatzikos
-
Article
| Open Access InPACT: a computational method for accurate characterization of intronic polyadenylation from RNA sequencing data
InPACT: a computational method for accurate characterization of intronic polyadenylation from RNA sequencing data
Intronic polyadenylation (IPA) can produce transcripts with truncated coding regions and has been implicated in diverse biological processes and diseases. Here, the authors present a computational method for the accurate delineation of IPA events using RNA-sequencing data.
- Xiaochuan Liu
- , Hao Chen
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting nuclear G-quadruplex RNA-binding proteins with roles in transcription and phase separation
Predicting nuclear G-quadruplex RNA-binding proteins with roles in transcription and phase separation
RNA G-quadruplexes are important regulatory elements, yet our knowledge of their structure-based interactions is at present limited. Here the authors combine experimental and computational methods to develop a predictive tool, G4-FUNNIES, to estimate proteins’ RNA G4-binding propensities.
- Johanna Luige
- , Alexandros Armaos
- & Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom
-
Article
| Open Access Allele-specific transcriptional effects of subclonal copy number alterations enable genotype-phenotype mapping in cancer cells
Allele-specific transcriptional effects of subclonal copy number alterations enable genotype-phenotype mapping in cancer cells
Quantifying the impact of copy-number alterations (CNAs) on gene expression at the subclone level in cancer remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop TreeAlign, a method that integrates sample-matched single-cell DNA and RNA sequencing data to infer the impact of CNAs on subclonal gene expression.
- Hongyu Shi
- , Marc J. Williams
- & Sohrab P. Shah
-
Article
| Open Access Strong positive selection biases identity-by-descent-based inferences of recent demography and population structure in Plasmodium falciparum
Strong positive selection biases identity-by-descent-based inferences of recent demography and population structure in Plasmodium falciparum
Identity-by-descent (IBD) is used to infer malaria parasite population demography, but positive selection imposed by drug pressure can bias IBD estimates. This study shows that strong selection distorts IBD distributions impacting downstream inferences and presents an approach to correct these biases.
- Bing Guo
- , Victor Borda
- & Shannon Takala-Harrison
-
Article
| Open Access Balancing competing effects of tissue growth and cytoskeletal regulation during Drosophila wing disc development
Balancing competing effects of tissue growth and cytoskeletal regulation during Drosophila wing disc development
The authors integrate computational and quantitative approaches to elucidate how organ shape arises through the interplay between multiple growth pathways through regulation of both proliferation and the cytoskeleton.
- Nilay Kumar
- , Jennifer Rangel Ambriz
- & Mark Alber
-
Article
| Open Access Tradeoffs in alignment and assembly-based methods for structural variant detection with long-read sequencing data
Tradeoffs in alignment and assembly-based methods for structural variant detection with long-read sequencing data
Long-read sequencing can greatly improve detection of genomic structural variants (SVs), and numerous methods have been developed to identify SVs using long-read data. Here the authors compare the performance of these methods and provide guidelines to aid users in selecting the most suitable tools for various scenarios.
- Yichen Henry Liu
- , Can Luo
- & Xin Maizie Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of glycopeptide fragment mass spectra by deep learning
Prediction of glycopeptide fragment mass spectra by deep learning
Deep learning has achieved a notable success in proteomics and is now emerging in glycoproteomics. Here, the authors develop a neural network-based method to predict mass spectra of intact glycopeptides and demonstrate its potential in data-dependent and data-independent acquisition glycoproteomics.
- Yi Yang
- & Qun Fang
-
Article
| Open Access The bone ecosystem facilitates multiple myeloma relapse and the evolution of heterogeneous drug resistant disease
The bone ecosystem facilitates multiple myeloma relapse and the evolution of heterogeneous drug resistant disease
Here, the authors develop a hybrid agent-based model to quantify the contributions of intrinsic cellular mechanisms and bone ecosystem factors to therapy resistance in multiple myeloma. They show that intrinsic mechanisms are essential for resistance, and that the bone microenvironment provides a protective niche that increases the likelihood.
- Ryan T. Bishop
- , Anna K. Miller
- & David Basanta
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate and rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing using a machine learning-assisted nanomotion technology platform
Accurate and rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing using a machine learning-assisted nanomotion technology platform
Sturm et. al developed a 2 to 4 h antibiotic susceptibility test based on bacterial vibrations. This diagnostic test applies to the most frequently found gram-negative bacteria in bloodstream infections and demonstrates its potential in contributing to faster treatment decisions.
- Alexander Sturm
- , Grzegorz Jóźwiak
- & Danuta Cichocka
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven prediction of colonization outcomes for complex microbial communities
Data-driven prediction of colonization outcomes for complex microbial communities
Predicting the colonization of exogenous species in complex communities is a challenge in ecology. Here, the authors propose a data-driven approach to predict colonization outcomes and perform validation experiments in human gut microbial communities.
- Lu Wu
- , Xu-Wen Wang
- & Lei Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Local prediction-learning in high-dimensional spaces enables neural networks to plan
Local prediction-learning in high-dimensional spaces enables neural networks to plan
The task of planning a sequence of actions, and dynamically adjusting the plan in dependence of unforeseen circumstances, remains challenging for artificial intelligence frameworks. The authors introduce a learning approach inspired by cognitive functions, that demonstrates high flexibility and generalization capability in planning tasks, suitable for on-chip learning.
- Christoph Stöckl
- , Yukun Yang
- & Wolfgang Maass
-
Article
| Open Access Charting cellular differentiation trajectories with Ricci flow
Charting cellular differentiation trajectories with Ricci flow
When stem cells develop into tissues intracellular signalling is rewired, errors in this process lead to cancer. Here, authors applied tools from differential geometry made by Albert Einstein’s General Relativity to understand and predict biological network rewiring in health and disease.
- Anthony Baptista
- , Ben D. MacArthur
- & Christopher R. S. Banerji
-
Article
| Open Access The decline of the 2022 Italian mpox epidemic: Role of behavior changes and control strategies
The decline of the 2022 Italian mpox epidemic: Role of behavior changes and control strategies
Mpox cases in Italy rapidly declined following a peak in summer 2022. Here, the authors investigate potential reasons for the decline in cases using an individual-based model of a sexual contact network of men who have sex with men.
- Giorgio Guzzetta
- , Valentina Marziano
- & Stefano Merler
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based prediction and characterization of photo-crosslinking in native protein–RNA complexes
Structure-based prediction and characterization of photo-crosslinking in native protein–RNA complexes
Feng et al. developed a computational method PxR3D-map to jointly analyze crosslinked nucleotides and amino acids in protein-RNA complexes, which revealed key structural features underlying photocrosslinking of protein and RNA in cells.
- Huijuan Feng
- , Xiang-Jun Lu
- & Chaolin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access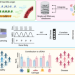 Cell type signatures in cell-free DNA fragmentation profiles reveal disease biology
Cell type signatures in cell-free DNA fragmentation profiles reveal disease biology
Deconvolution of cfDNA fragmentation benefits from cell type-specific reference data. Here, the authors create a disease agnostic cfDNA cell type of origin analysis and show it can successfully predict cell types of origin from plasma samples.
- Kate E. Stanley
- , Tatjana Jatsenko
- & Joris Robert Vermeesch
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic review and meta-analysis for a Global Patient co-Owned Cloud (GPOC)
Systematic review and meta-analysis for a Global Patient co-Owned Cloud (GPOC)
Use of cloud-based personal health records are increasing globally. Here, authors introduce the Global Patient co-Owned Cloud (GPOC) concept. The systematic review and meta-analysis examine factors like data security, efficiency, privacy, and cost. It aims to establish a scientific basis for a GPOC, which may disseminate global artificial intelligence for healthcare.
- Niklas Lidströmer
- , Joe Davids
- & Eric Herlenius
-
Article
| Open Access BASALT refines binning from metagenomic data and increases resolution of genome-resolved metagenomic analysis
BASALT refines binning from metagenomic data and increases resolution of genome-resolved metagenomic analysis
Binning is an essential step in genome-resolved metagenomic analysis in which assembled contigs originating from the same source population are clustered. However it is challenging, especially for low abundance microbial species. Here the authors introduce a toolkit that integrates multiple prominent binning tools and AI for efficient and high-resolution recovery of non-redundant bins from short- and long-read metagenomic sequencing datasets.
- Zhiguang Qiu
- , Li Yuan
- & Ke Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling large-scale screening of Barrett’s esophagus using weakly supervised deep learning in histopathology
Enabling large-scale screening of Barrett’s esophagus using weakly supervised deep learning in histopathology
Diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus depends on pathologist assessment of stained slides. Here, the authors utilise a deep learning approach to prioritize potential cases using diagnostic labels in two datasets, with the aim to improve Barrett’s screening capacity.
- Kenza Bouzid
- , Harshita Sharma
- & Javier Alvarez-Valle
-
Article
| Open Access AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics faces the challenge of processing vast data amounts. Here, the authors introduce AlphaPept, an open-source, Python-based framework that offers high speed analysis and easy integration for large-scale proteome analysis.
- Maximilian T. Strauss
- , Isabell Bludau
- & Matthias Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Drivers and impact of the early silent invasion of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha
Drivers and impact of the early silent invasion of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha
The SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant of concern emerged in the UK in late 2020 but spread internationally before it was detected. Here, the authors reconstruct the dynamics of dissemination of this variant out of the UK by combining extent of genomic sequencing, travel volume, and local epidemic dynamics in a Bayesian model.
- Benjamin Faucher
- , Chiara E. Sabbatini
- & Chiara Poletto
-
Article
| Open Access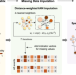 Interrogations of single-cell RNA splicing landscapes with SCASL define new cell identities with physiological relevance
Interrogations of single-cell RNA splicing landscapes with SCASL define new cell identities with physiological relevance
RNA splicing serves as a critical layer of gene expression regulation. Here, authors introduce SCASL for investigating the heterogeneity of RNA splicing landscapes at single-cell resolution, offering a novel scheme for classifying cell identities with physiological relevance.
- Xianke Xiang
- , Yao He
- & Xuerui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access The defensome of complex bacterial communities
The defensome of complex bacterial communities
Bacteria have evolved numerous innate and adaptive defence mechanisms. Here, Beavogui et al characterise the impact of biogeography, genetic mobility, and clustering in defense islands, on the defence systems of soil, marine, and human gut bacterial populations genomes.
- Angelina Beavogui
- , Auriane Lacroix
- & Pedro H. Oliveira
-
Article
| Open Access Viscosity-dependent control of protein synthesis and degradation
Viscosity-dependent control of protein synthesis and degradation
Xenopus egg extracts constitute a cell-like system for studying biochemical reactions. Here Chen and co-workers show that extract protein synthesis and degradation are differently affected by cytoplasmic concentration and viscosity.
- Yuping Chen
- , Jo-Hsi Huang
- & James E. Ferrell Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning predictor PSPire screens for phase-separating proteins lacking intrinsically disordered regions
Machine learning predictor PSPire screens for phase-separating proteins lacking intrinsically disordered regions
Here the authors report a machine learning model, PSPire, which integrates both residue-level and structure-level features and outperforms tools in identifying phase-separating proteins lacking intrinsically disordered regions.
- Shuang Hou
- , Jiaojiao Hu
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access DeepETPicker: Fast and accurate 3D particle picking for cryo-electron tomography using weakly supervised deep learning
DeepETPicker: Fast and accurate 3D particle picking for cryo-electron tomography using weakly supervised deep learning
Picking particles of biological macromolecules is critical for solving their structures in situ using cryo-electron tomograms. Here, authors develop DeepETPicker, a deep learning-based tool for fast, accurate, and automated picking of three-dimensional particles.
- Guole Liu
- , Tongxin Niu
- & Ge Yang
-
Article
| Open Access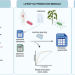 bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
bacLIFE: a user-friendly computational workflow for genome analysis and prediction of lifestyle-associated genes in bacteria
Many bacteria live in close association with eukaryotic hosts, exhibiting detrimental, neutral or beneficial effects on host growth and health. Here, the authors present a streamlined computational workflow for bacterial genome annotation, large-scale comparative genomics, and prediction of genes potentially involved in niche adaptation.
- Guillermo Guerrero-Egido
- , Adrian Pintado
- & Víctor J. Carrión
-
Article
| Open Access Biosensor and machine learning-aided engineering of an amaryllidaceae enzyme
Biosensor and machine learning-aided engineering of an amaryllidaceae enzyme
Amaryllidaceae alkaloids, such as the Alzheimer’s medication galantamine, are currently extracted from low-yielding daffodils. Here, authors pair biosensor-assisted screening with machine learning-guided protein design to rapidly engineer an improved Amaryllidaceae enzyme in a microbial host.
- Simon d’Oelsnitz
- , Daniel J. Diaz
- & Andrew D. Ellington
-
Article
| Open Access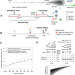 Evolving copy number gains promote tumor expansion and bolster mutational diversification
Evolving copy number gains promote tumor expansion and bolster mutational diversification
Understanding the timing and fitness of somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs) in cancer would shed light on cancer progression and evolution. Here, the authors develop Butte, a computational framework to estimate the timing of clonal SCNAs that encompass multiple gains, and apply it on whole-genome sequencing data from 184 samples.
- Zicheng Wang
- , Yunong Xia
- & Ruping Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning model for personalized prediction of positive MRSA culture using time-series electronic health records
Deep learning model for personalized prediction of positive MRSA culture using time-series electronic health records
Identification of patients at high risk of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection could improve treatment outcomes by optimising antimicrobial therapy. Here the authors develop a deep learning model that uses electronic health record data from the United States to predict MRSA culture positivity.
- Masayuki Nigo
- , Laila Rasmy
- & Degui Zhi
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic analysis of ChatGPT, Google search and Llama 2 for clinical decision support tasks
Systematic analysis of ChatGPT, Google search and Llama 2 for clinical decision support tasks
People will likely use ChatGPT to seek health advice. Here, the authors show promising performance of ChatGPT and open source models, but a lack of high accuracy considering medical question answering. Improvements are expected over time via domain-specific finetuning and integration of regulations.
- Sarah Sandmann
- , Sarah Riepenhausen
- & Julian Varghese
-
Article
| Open Access Riboformer: a deep learning framework for predicting context-dependent translation dynamics
Riboformer: a deep learning framework for predicting context-dependent translation dynamics
Riboformer is a deep learning-based framework that predicts changes in translation dynamics with codon-level precision. It corrects experimental artifacts in ribosome profiling data and identifies sequences causing ribosome stalling.
- Bin Shao
- , Jiawei Yan
- & Allen R. Buskirk
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-aided design and screening of an emergent protein function in synthetic cells
Machine learning-aided design and screening of an emergent protein function in synthetic cells
Here, the authors introduce a pipeline to screen machine learning generated variants of a protein that forms intracellular spatiotemporal patterns in E. coli, demonstrating the best variants can substitute the wildtype gene.
- Shunshi Kohyama
- , Béla P. Frohn
- & Petra Schwille
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing the fairness of AI prediction models by Quasi-Pareto improvement among heterogeneous thyroid nodule population
Enhancing the fairness of AI prediction models by Quasi-Pareto improvement among heterogeneous thyroid nodule population
Artificial Intelligence (AI) models for medical diagnosis often face challenges of generalizability and fairness. Here, the authors show that the Quasi-Pareto Improvement approach is widely applicable to improving AI models among less-prevalent subgroups, promoting equitable healthcare outcomes.
- Siqiong Yao
- , Fang Dai
- & Hui Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A coarse-grained bacterial cell model for resource-aware analysis and design of synthetic gene circuits
A coarse-grained bacterial cell model for resource-aware analysis and design of synthetic gene circuits
Competition for the host cell’s resources influences synthetic biology circuit behavior. Here the authors present an E. coli cell model that combines insights into bacterial resource allocation with a simplified model of competition, facilitating resource-aware circuit design.
- Kirill Sechkar
- , Harrison Steel
- & Guy-Bart Stan
-
Article
| Open Access Domain generalization enables general cancer cell annotation in single-cell and spatial transcriptomics
Domain generalization enables general cancer cell annotation in single-cell and spatial transcriptomics
Efficient and accurate annotation of malignant cells is crucial for single-cell and spatial transcriptomics in cancer. Here, the authors develop Cancer-Finder, a deep-learning algorithm that can identify malignant cells in cancer single-cell and spatial transcriptomics data with speed and precision.
- Zhixing Zhong
- , Junchen Hou
- & Jia Song
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread stable noncanonical peptides identified by integrated analyses of ribosome profiling and ORF features
Widespread stable noncanonical peptides identified by integrated analyses of ribosome profiling and ORF features
By developing computational algorithms, the authors annotated translated open reading frames in five eukaryotes and found many stable peptides are encoded by putative ‘noncoding’ regions of genomes.
- Haiwang Yang
- , Qianru Li
- & Zhe Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Empirical data drift detection experiments on real-world medical imaging data
Empirical data drift detection experiments on real-world medical imaging data
Data drift is the systematic change in the underlying distribution of input features in prediction models, and can cause deterioration in model performance. Here, the authors highlight the importance of detecting data drift in clinical settings and evaluate methods for detecting drift in medical image data.
- Ali Kore
- , Elyar Abbasi Bavil
- & Mohamed Abdalla
-
Article
| Open Access Drug target prediction through deep learning functional representation of gene signatures
Drug target prediction through deep learning functional representation of gene signatures
Large-scale OMICs investigations of biological systems can be used to predict functional relationships between compounds, genes and proteins. Here, the authors develop a deep learning-based approach that significantly increases the number of high-quality compound-target predictions relative to existing methods.
- Hao Chen
- , Frederick J. King
- & Yingyao Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for evaluating clinical artificial intelligence systems without ground-truth annotations
A framework for evaluating clinical artificial intelligence systems without ground-truth annotations
Estimating the performance of clinical AI systems on data in the wild is complicated by distribution shift and the absence of ground-truth annotations. Here, we introduce SUDO, a framework for more reliably evaluating AI systems on data in the wild.
- Dani Kiyasseh
- , Aaron Cohen
- & Nicholas Altieri
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of plasma ctDNA fraction and prognostic implications of liquid biopsy in advanced prostate cancer
Prediction of plasma ctDNA fraction and prognostic implications of liquid biopsy in advanced prostate cancer
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is a highly aggressive disease, with a variable response to treatment. Here, the authors validate ctDNA fraction as a poor prognostic factor and develop a model to predict whether patients harbor sufficient ctDNA for informative blood-based genotyping.
- Nicolette M. Fonseca
- , Corinne Maurice-Dror
- & Alexander W. Wyatt
-
Article
| Open Access Functional regulation of aquaporin dynamics by lipid bilayer composition
Functional regulation of aquaporin dynamics by lipid bilayer composition
Membrane proteins depend on their lipid environments. Using aquaporin as a model, the authors show that the choice of lipid bilayer fundamentally affects membrane protein structure, thermodynamics, kinetic, and function, even to the point of lipid-based inhibition.
- Anh T. P. Nguyen
- , Austin T. Weigle
- & Diwakar Shukla
-
Article
| Open Access Rare disease research workflow using multilayer networks elucidates the molecular determinants of severity in Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes
Rare disease research workflow using multilayer networks elucidates the molecular determinants of severity in Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes
Congenital myasthenic syndromes are rare inherited neuromuscular disorders. Here, the authors attempt to explain diverse disease severity seen in 20 patients with shared CHRNE gene mutations with a multilayer network analysis that identifies individual-level impairments at the neuromuscular junction.
- Iker Núñez-Carpintero
- , Maria Rigau
- & Alfonso Valencia
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Manual processes to produce ocular prostheses are time-consuming and yield varying quality. Here, authors present an automatic digital end-to-end process for custom ocular prostheses. It creates shape and appearance from image data of an OCT device and produces them using a full-colour 3D printer.
- Johann Reinhard
- , Philipp Urban
- & Mandeep S. Sagoo
-
Article
| Open Access A release of local subunit conformational heterogeneity underlies gating in a muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
A release of local subunit conformational heterogeneity underlies gating in a muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Authors show that agonist binding to the muscle acetylcholine receptor releases local conformational heterogeneity transitioning all subunits into a symmetric open state. A release of conformational heterogeneity underlies allosteric communication.
- Mackenzie J. Thompson
- , Farid Mansoub Bekarkhanechi
- & John E. Baenziger
-
Article
| Open Access Statistical method scDEED for detecting dubious 2D single-cell embeddings and optimizing t-SNE and UMAP hyperparameters
Statistical method scDEED for detecting dubious 2D single-cell embeddings and optimizing t-SNE and UMAP hyperparameters
2D visualisation of single-cell data is highly impacted by the hyperparameter setting of the 2D embedding method, such as t-SNE and UMAP. Here, authors develop a statistical method scDEED to detect dubious cell embeddings and optimise the hyperparameter setting for trustworthy visualisation.
- Lucy Xia
- , Christy Lee
- & Jingyi Jessica Li
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemical reaction networks
- Cellular signalling networks
- Classification and taxonomy
- Communication and replication
- Computational models
- Computational neuroscience
- Computational platforms and environments
- Data acquisition
- Data integration
- Data mining
- Data processing
- Data publication and archiving
- Databases
- Functional clustering
- Gene ontology
- Gene regulatory networks
- Genome informatics
- Hardware and infrastructure
- High-throughput screening
- Image processing
- Literature mining
- Machine learning
- Microarrays
- Network topology
- Phylogeny
- Power law
- Predictive medicine
- Probabilistic data networks
- Programming language
- Protein analysis
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Protein function predictions
- Protein structure predictions
- Proteome informatics
- Quality control
- Scale invariance
- Sequence annotation
- Software
- Standards
- Statistical methods
- Virtual drug screening

 Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning