Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access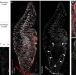 Supernumerary B chromosomes of Aegilops speltoides undergo precise elimination in roots early in embryo development
Supernumerary B chromosomes of Aegilops speltoides undergo precise elimination in roots early in embryo development
B chromosomes are supernumerary chromosomes exhibiting dramatic differences between different organs in same species. Here, the authors show programmed B chromosome elimination in goatgrass starts at the onset of embryo differentiation by nondisjunction of chromatids, anaphase lagging, and ends with the degradation of micronucleated DNA.
- Alevtina Ruban
- , Thomas Schmutzer
- & Andreas Houben
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleoporin 153 links nuclear pore complex to chromatin architecture by mediating CTCF and cohesin binding
Nucleoporin 153 links nuclear pore complex to chromatin architecture by mediating CTCF and cohesin binding
The nuclear pore complex components, nucleoporins, have been proposed to mediate spatial and temporal organization of chromatin. Here, the authors show that Nucleoporin 153 interacts with CTCF and cohesin, and mediates their binding across cis-regulatory elements and TAD boundaries in mouse embryonic stem cells.
- Shinichi Kadota
- , Jianhong Ou
- & Eda Yildirim
-
Article
| Open Access Stability and nuclear localization of yeast telomerase depend on protein components of RNase P/MRP
Stability and nuclear localization of yeast telomerase depend on protein components of RNase P/MRP
Pop1 and 6 are subunits of RNase P and RNase MRP, which process ribosomal and tRNAs. The authors show that when Pop1 and 6 are impaired, the telomerase subunit Est1 binds telomerase RNA at normal levels, but the binding is unstable. As a result, nuclear import of the telomerase holoenzyme is inhibited.
- P. Daniela Garcia
- , Robert W. Leach
- & Virginia A. Zakian
-
Article
| Open Access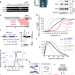 The BRCA2-MEILB2-BRME1 complex governs meiotic recombination and impairs the mitotic BRCA2-RAD51 function in cancer cells
The BRCA2-MEILB2-BRME1 complex governs meiotic recombination and impairs the mitotic BRCA2-RAD51 function in cancer cells
In meiosis, BRCA2 associates to MEILB2 localising at DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Here, the authors identify BRCA2 and MEILB2- associating protein 1 termed BRME1 to work together in regulating meiotic recombination.
- Jingjing Zhang
- , Manickam Gurusaran
- & Hiroki Shibuya
-
Article
| Open Access CdbA is a DNA-binding protein and c-di-GMP receptor important for nucleoid organization and segregation in Myxococcus xanthus
CdbA is a DNA-binding protein and c-di-GMP receptor important for nucleoid organization and segregation in Myxococcus xanthus
The second messenger c-di-GMP modulates multiple responses to environmental and cellular signals in bacteria. Here, Skotnicka et al. identify a protein that binds c-di-GMP and contributes to chromosome organization and segregation in Myxococcus xanthus, with DNA-binding activity regulated by c-di-GMP.
- Dorota Skotnicka
- , Wieland Steinchen
- & Lotte Søgaard-Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Proper chromosome alignment depends on BRCA2 phosphorylation by PLK1
Proper chromosome alignment depends on BRCA2 phosphorylation by PLK1
The BRCA2 tumour suppressor protein is known to play an important role in homologous recombination. Here the authors reveal how the phosphorylation of BRCA2 by Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) contributes to the regulation of mitosis.
- Åsa Ehlén
- , Charlotte Martin
- & Aura Carreira
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic screening identifies a SUMO protease dynamically maintaining centromeric chromatin
Genetic screening identifies a SUMO protease dynamically maintaining centromeric chromatin
Centromeres are a self-propagating chromatin structure that feature nucleosomes containing histone H3 variant CENP-A. Here, the authors screen for factors that play a role in CENP-A chromatin maintenance, finding that SUMO-protease SENP6 controls inheritance of chromatin bound CENP-A and is required for the maintenance of the centromere and kinetochore complex.
- Sreyoshi Mitra
- , Dani L. Bodor
- & Lars E. T. Jansen
-
Article
| Open Access Components of the ribosome biogenesis pathway underlie establishment of telomere length set point in Arabidopsis
Components of the ribosome biogenesis pathway underlie establishment of telomere length set point in Arabidopsis
Major effect loci controlling natural, heritable variation in telomere length are not known. Here, the authors use QTL mapping and transgenic manipulations in Arabidopsis to implicate the rRNA-processing genes NOP2A and RPL5 in telomere length set point regulation in this model species.
- Liliia R. Abdulkina
- , Callie Kobayashi
- & Eugene V. Shakirov
-
Article
| Open Access Global chromatin conformation differences in the Drosophila dosage compensated chromosome X
Global chromatin conformation differences in the Drosophila dosage compensated chromosome X
In Drosophila, dosage compensation involves a twofold transcriptional upregulation of the single male chromosome X. Here the authors show that global conformational differences are specifically present in the male X chromosome and detectable using Hi-C data, indicating that dosage compensation affects global chromosome structure.
- Koustav Pal
- , Mattia Forcato
- & Francesco Ferrari
-
Article
| Open Access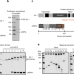 JASPer controls interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation by chromosomal kinase JIL-1 in Drosophila
JASPer controls interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation by chromosomal kinase JIL-1 in Drosophila
The chromosomal kinase JIL-1 is responsible for interphase histone H3S10 phosphorylation and has been proposed to protect active chromatin from heterochromatinisation. Here, the authors show that JIL-1 is stabilized and anchored to active genes and telomeric transposons by JASPer, which binds to H3K36me3 nucleosomes via its PWWP domain.
- Christian Albig
- , Chao Wang
- & Catherine Regnard
-
Article
| Open Access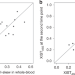 Heritability of skewed X-inactivation in female twins is tissue-specific and associated with age
Heritability of skewed X-inactivation in female twins is tissue-specific and associated with age
Skewing of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) occurs when the silencing of one parental X chromosome is non-random. Here, Zito et al. report XCI patterns in lymphoblastoid cell lines, blood, subcutaneous adipose tissue samples and skin samples of monozygotic and dizygotic twins and find XCI skew to associate with tissue and age.
- Antonino Zito
- , Matthew N. Davies
- & Kerrin S. Small
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of DNA damage response at telomeres improves the detrimental phenotypes of Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Inhibition of DNA damage response at telomeres improves the detrimental phenotypes of Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome causes premature aging. Here the authors show that activation of the DNA damage response at dysfunctional telomeres and transcription of telomeric non-coding RNAs contributes to the pathogenesis, which can be ameliorated by treatment with sequence-specific telomeric antisense oligonucleotides.
- Julio Aguado
- , Agustin Sola-Carvajal
- & Fabrizio d’Adda di Fagagna
-
Article
| Open Access A nucleotide resolution map of Top2-linked DNA breaks in the yeast and human genome
A nucleotide resolution map of Top2-linked DNA breaks in the yeast and human genome
Topoisomerase 2 (Top2) is known to resolve DNA topological stress through double strand breaks (DSBs), yet Top2 inhibition has been reported to result in a significant amount of single-strand breaks (SSBs). Here the authors develop CC-seq—a method that allows direct mapping of both Top2-linked SSBs and DSBs—and reveal a significant impact of primary DNA sequence on Top2 directed cleavage.
- William H. Gittens
- , Dominic J. Johnson
- & Matthew J. Neale
-
Article
| Open Access Tetraploidy causes chromosomal instability in acentriolar mouse embryos
Tetraploidy causes chromosomal instability in acentriolar mouse embryos
During cell division, tetraploidy can drive chromosomal instability (CIN) via supernumerary centrosomes, but it is unclear if this is the only route to CIN. Here the authors show that, in early mouse embryos, tetraploidy can drive chromosomal instability by altering microtubule dynamics and attachment.
- Lia Mara Gomes Paim
- & Greg FitzHarris
-
Article
| Open Access Principles of meiotic chromosome assembly revealed in S. cerevisiae
Principles of meiotic chromosome assembly revealed in S. cerevisiae
During meiotic prophase chromosomes organise into a series of chromatin loops, but the mechanisms of assembly remain unclear. Here the authors use Saccharomyces cerevisiae to elucidate how this elaborate three-dimensional chromosome organisation is linked to genomic sequence, and demonstrate an essential role for cohesin during this process.
- Stephanie A. Schalbetter
- , Geoffrey Fudenberg
- & Matthew J. Neale
-
Article
| Open Access CENP-A nucleosome clusters form rosette-like structures around HJURP during G1
CENP-A nucleosome clusters form rosette-like structures around HJURP during G1
Human centromeric nucleosomes contain the specific CENP-A histone variant, which replaces canonical histone H3 and epigenetically marks the centromeres. Here the authors show that CENP-A nucleosomes form large supramolecular clusters during the G1 phase of the cell cycle which are arranged as rosette-like structures.
- Leonid Andronov
- , Khalid Ouararhni
- & Ali Hamiche
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of centromere recruitment of the CENP-A chaperone HJURP and its implications for centromere licensing
Mechanism of centromere recruitment of the CENP-A chaperone HJURP and its implications for centromere licensing
The CENP-A chaperone HJURP associates with Mis18α, Mis18β, and M18BP1 to target centromeres and deposit new CENP-A. Here the authors provide evidence that two repeats in human HJURP previously proposed to be functionally distinct are interchangeable and bind concomitantly to the 4:2:2 Mis18α:Mis18β:M18BP1 complex without dissociating it.
- Dongqing Pan
- , Kai Walstein
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Article
| Open Access The poly-SUMO2/3 protease SENP6 enables assembly of the constitutive centromere-associated network by group deSUMOylation
The poly-SUMO2/3 protease SENP6 enables assembly of the constitutive centromere-associated network by group deSUMOylation
While the biological roles of ubiquitin chains are well studied, little is known about the functions of SUMO polymers. Here, the authors identify poly-SUMOylation substrates and provide evidence that SUMO polymers regulate the accumulation of CCAN subunits at chromatin and centromeres.
- Frauke Liebelt
- , Nicolette S. Jansen
- & Alfred C. O. Vertegaal
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational heterogeneity in human interphase chromosome organization reconciles the FISH and Hi-C paradox
Conformational heterogeneity in human interphase chromosome organization reconciles the FISH and Hi-C paradox
Studies comparing Hi-C and FISH data show that in some cases the distance between one pair of loci is paradoxically larger compared to another pair with a smaller value of the contact probability. Here the authors use a theory based on a Generalized Rouse Model for Chromosomes to resolve this paradox.
- Guang Shi
- & D. Thirumalai
-
Article
| Open Access CSL controls telomere maintenance and genome stability in human dermal fibroblasts
CSL controls telomere maintenance and genome stability in human dermal fibroblasts
Conversion of dermal fibroblasts into Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) can play an important role in keratinocyte tumour development. Here the authors reveal that CSL plays a role in maintenance of telomeres and genomic integrity in both dermal fibroblasts and CAFs.
- Giulia Bottoni
- , Atul Katarkar
- & G. Paolo Dotto
-
Article
| Open Access Two-step chromosome segregation in the stalked budding bacterium Hyphomonas neptunium
Two-step chromosome segregation in the stalked budding bacterium Hyphomonas neptunium
In bacteria, DNA replication and segregation are commonly coupled. Here, by investigating the dynamics of these processes in the marine bacterium Hyphomonas neptunium, the authors unravel a two-step chromosomal segregation process reminiscent of eukaryotic mitosis, providing insights into the evolution of bacterial cell organization.
- Alexandra Jung
- , Anne Raßbach
- & Martin Thanbichler
-
Article
| Open Access PRC1 collaborates with SMCHD1 to fold the X-chromosome and spread Xist RNA between chromosome compartments
PRC1 collaborates with SMCHD1 to fold the X-chromosome and spread Xist RNA between chromosome compartments
The inactive X (Xi)-specific S1/S2 chromosome compartments are merged by SMCHD1, but how the S1/S2 structure is constructed is unclear. The authors find that PRC1 drives the formation of S1/S2s and that the stepwise folding process of the Xi facilitates Xist RNA spreading between Xi compartments.
- Chen-Yu Wang
- , David Colognori
- & Jeannie T. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access PLK1 facilitates chromosome biorientation by suppressing centromere disintegration driven by BLM-mediated unwinding and spindle pulling
PLK1 facilitates chromosome biorientation by suppressing centromere disintegration driven by BLM-mediated unwinding and spindle pulling
The kinase PLK1 has important roles during cell division, including mitotic entry and bipolar spindle formation. Here, the authors show that PLK1 also functions in centromere protection, with loss leading to DNA unwinding by Bloom’s syndrome helicase and subsequent collapse of chromosome alignment.
- Owen Addis Jones
- , Ankana Tiwari
- & Kok-Lung Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Loci for human leukocyte telomere length in the Singaporean Chinese population and trans-ethnic genetic studies
Loci for human leukocyte telomere length in the Singaporean Chinese population and trans-ethnic genetic studies
Shortening of leukocyte telomere length (LTL) is associated with age and increased risk for various chronic diseases. Here, the authors report genome-wide association studies for LTL in Singaporean Chinese populations and find that longer LTL associates with less severe outcomes of respiratory disease phenotypes.
- Rajkumar Dorajoo
- , Xuling Chang
- & Chew-Kiat Heng
-
Article
| Open Access Interspecies conservation of organisation and function between nonhomologous regional centromeres
Interspecies conservation of organisation and function between nonhomologous regional centromeres
Although the centromere-specific histone CENP-A usually assembles on specific genomic sequences, centromeric DNA is not conserved. Here the authors characterize the genome and centromeres of related fission yeasts and provide evidence that Schizosaccharomyces centromere DNA possesses intrinsic conserved properties that promote assembly of CENP-A chromatin.
- Pin Tong
- , Alison L. Pidoux
- & Robin C. Allshire
-
Article
| Open Access FANCM limits ALT activity by restricting telomeric replication stress induced by deregulated BLM and R-loops
FANCM limits ALT activity by restricting telomeric replication stress induced by deregulated BLM and R-loops
In cancer cells, telomeres can be elongated through homology directed-repair pathways in a process known as Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT). Here, the authors reveal that FANCM regulates ALT activity and ALT cell proliferation by limiting the activity of uncontrolled BLM and telomeric R-loops.
- Bruno Silva
- , Richard Pentz
- & Claus M. Azzalin
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of a native-like CENP-A nucleosome aided by an antibody fragment
Atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of a native-like CENP-A nucleosome aided by an antibody fragment
CENP-A histone variants replace histones H3 at centromeres. Here the authors use a single-chain antibody fragment (scFv) to stabilize human CENP-A nucleosome containing a native α-satellite DNA and solved its structure by cryo-EM to 2.6 Å resolution, providing insight into the structure and function of the CENP-A nucleosome.
- Bing-Rui Zhou
- , K. N. Sathish Yadav
- & Ping Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Direct imaging of the circular chromosome in a live bacterium
Direct imaging of the circular chromosome in a live bacterium
Bacterial chromosomes are tightly packed, limiting structural analysis by imaging techniques. Here, by quantitative time-lapse single-cell imaging of widened Escherichia coli cells, Wu and Japaridze et al. show that the chromosome exhibits a ring-like torus topology and a dynamic domain structure.
- Fabai Wu
- , Aleksandre Japaridze
- & Cees Dekker
-
Article
| Open Access SWITCH 1/DYAD is a WINGS APART-LIKE antagonist that maintains sister chromatid cohesion in meiosis
SWITCH 1/DYAD is a WINGS APART-LIKE antagonist that maintains sister chromatid cohesion in meiosis
During cell division, Soronin antagonises WAPL to prevent premature loss of sister chromatid cohesion. Here the authors show that, despite a lack of sequence similarity, the Arabidopsis SWI1 protein functions as a novel Soronin-like WAPL antagonist, suggesting convergent evolution with animals.
- Chao Yang
- , Yuki Hamamura
- & Arp Schnittger
-
Article
| Open Access iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
DNA FISH allows for the visual analysis of chromosomal organisation in individual cells. Here the authors present iFISH, an open-source repository of ready-to-use DNA FISH probes along with tools for probe design.
- Eleni Gelali
- , Gabriele Girelli
- & Magda Bienko
-
Article
| Open Access SFPQ and NONO suppress RNA:DNA-hybrid-related telomere instability
SFPQ and NONO suppress RNA:DNA-hybrid-related telomere instability
LncRNA TERRA forms RNA-DNA hybrids at telomere sites leading to telomere instability. Here the authors identify the RNA interacting factors NONO and SFPQ as proteins that interact with TERRA and telomere chromatin and reveal putative roles for these factors in telomere integry maintenance by interfering with RNA:DNA hybrid formation.
- Eleonora Petti
- , Valentina Buemi
- & Stefan Schoeftner
-
Article
| Open Access Cdk1-mediated DIAPH1 phosphorylation maintains metaphase cortical tension and inactivates the spindle assembly checkpoint at anaphase
Cdk1-mediated DIAPH1 phosphorylation maintains metaphase cortical tension and inactivates the spindle assembly checkpoint at anaphase
Cell rounding at mitosis is driven by cortical tension and maintained through metaphase, although the mechanism is unknown. Here, the authors demonstrate that Cdk1 phosphorylation of DIAPH1 is required for both cortical tension maintenance and inactivation of the spindle assembly checkpoint.
- Koutarou Nishimura
- , Yoshikazu Johmura
- & Makoto Nakanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Mitotic chromosome binding predicts transcription factor properties in interphase
Mitotic chromosome binding predicts transcription factor properties in interphase
Mammalian transcription factors (TFs) differ broadly in their DNA binding properties. Here authors quantify mitotic chromosome binding (MCB) of 501 TFs and suggest that MCB can be used as a proxy for non-specific TF-DNA interactions that regulate TF search for specific genomic sites.
- Mahé Raccaud
- , Elias T. Friman
- & David M. Suter
-
Article
| Open Access LUBAC controls chromosome alignment by targeting CENP-E to attached kinetochores
LUBAC controls chromosome alignment by targeting CENP-E to attached kinetochores
During cell division, faithful chromosome segregation requires proper chromosome congression and dynamic maintenance of the aligned chromosomes. Here, the authors find that LUBAC promotes dynamic chromosome congression and alignment by targeting kinetochore motor CENP-E to the KMN network.
- Min Wu
- , Yan Chang
- & Huiyan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 does not control centromere function
Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 does not control centromere function
Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 has been proposed to control centromere assembly and function. Here, the authors use gene targeting at both endogenous CENP-A alleles and gene replacement in human cells to demonstrate that CENP-A that cannot be phosphorylated at serine 7 maintains correct CENP-C recruitment, faithful chromosome segregation and long-term cell viability.
- Viviana Barra
- , Glennis A. Logsdon
- & Daniele Fachinetti
-
Article
| Open Access The non-canonical SMC protein SmcHD1 antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalisation on the inactive X chromosome
The non-canonical SMC protein SmcHD1 antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalisation on the inactive X chromosome
The inactive X chromosome (Xi) has an atypical structure, with global loss of TADs, A/B compartments and formation of mega-domains. Here the authors show that the non-canonical SMC family protein, SmcHD1, important for developmental gene silencing on Xi, antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalization on the Xi in a transcription independent way.
- Michal R. Gdula
- , Tatyana B. Nesterova
- & Neil Brockdorff
-
Article
| Open Access The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
Telomerase RNA (hTR) is transcribed as a 3′-extended precursor. Here the authors examine the processing of hTR precursors of various lengths and show that processing occurs in distinct steps involving different nucleases PARN and RRP6.
- Chi-Kang Tseng
- , Hui-Fang Wang
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article
| Open Access Megadomains and superloops form dynamically but are dispensable for X-chromosome inactivation and gene escape
Megadomains and superloops form dynamically but are dispensable for X-chromosome inactivation and gene escape
The mammalian inactive X-chromosome (Xi) is organized into megadomains and superloops directed by the noncoding loci, Dxz4 and Firre. Here the authors provide evidence that megadomains do not precede Xist expression or Xi gene silencing, and suggest that Dxz4, Firre, and megadomains are dispensable for Xi silencing and escape from X-inactivation.
- John E. Froberg
- , Stefan F. Pinter
- & Jeannie T. Lee
-
Review Article
| Open Access The dark side of centromeres: types, causes and consequences of structural abnormalities implicating centromeric DNA
The dark side of centromeres: types, causes and consequences of structural abnormalities implicating centromeric DNA
Centromeres are the chromosomal domains that regulate assembly of the components required for chromosome separation. Here the authors review how centromeres are a potential source of genome instability and link centromere aberrations and rearrangements to human diseases such as cancer.
- V. Barra
- & D. Fachinetti
-
Article
| Open Access Local enrichment of HP1alpha at telomeres alters their structure and regulation of telomere protection
Local enrichment of HP1alpha at telomeres alters their structure and regulation of telomere protection
Chromatin dynamics is thought to play an important role in the maintenance of telomeres, yet how has remained poorly understood. Here the authors locally enrich heterochromatin protein 1α (HP1α) at human telomeres to provide insights into the crosstalk between epigenetic regulations and structural dynamics at the telomeres.
- Tracy T. Chow
- , Xiaoyu Shi
- & Elizabeth H. Blackburn
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for reactivating the mutant TERT promoter by cooperative binding of p52 and ETS1
Structural basis for reactivating the mutant TERT promoter by cooperative binding of p52 and ETS1
Incessant telomere synthesis in cancer cells depends on specific mutations in the TERT promoter, enabling its activation by transcription factors ETS1 and p52. Here, the authors elucidate the structural basis for p52/ETS1 binding to mutant TERT, suggesting a general mechanism for TERT reactivation in cancer.
- Xueyong Xu
- , Yinghui Li
- & Haiwei Song
-
Article
| Open Access Spindle tubulin and MTOC asymmetries may explain meiotic drive in oocytes
Spindle tubulin and MTOC asymmetries may explain meiotic drive in oocytes
During ‘meiotic drive’, some chromosomes can bias their spindle orientation and thus be retained in the egg. Here, the authors find that this phenomenon can be driven by microtubule force asymmetry on chromosomes with differently sized centromeres and kinetochores.
- Tianyu Wu
- , Simon I. R. Lane
- & Keith T. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access CTC1-STN1 terminates telomerase while STN1-TEN1 enables C-strand synthesis during telomere replication in colon cancer cells
CTC1-STN1 terminates telomerase while STN1-TEN1 enables C-strand synthesis during telomere replication in colon cancer cells
The human CST complex (CTC1-STN1-TEN1) is essential for telomere homeostasis. Here the authors dissect the roles of individual CST subunits in telomere length maintenance through regulation of telomerase-mediated G-strand synthesis and DNA polymerase-mediated C-strand synthesis in colon cancer cells.
- Xuyang Feng
- , Shih-Jui Hsu
- & Carolyn M. Price
-
Article
| Open Access ATP synthase F1 subunits recruited to centromeres by CENP-A are required for male meiosis
ATP synthase F1 subunits recruited to centromeres by CENP-A are required for male meiosis
The histone H3 CENP-A is known to play a role during meiosis but its role in the testes in the fly is unknown. Here, the authors identify the mitochondrial metabolic protein complex ATP synthase F1 as interacting with CENP-A, promoting centromere cohesion during meiosis and affecting fly fertility.
- Caitríona M. Collins
- , Beatrice Malacrida
- & Elaine M. Dunleavy
-
Article
| Open Access HuR regulates telomerase activity through TERC methylation
HuR regulates telomerase activity through TERC methylation
Mutations in the RNA component TERC can cause telomerase dysfunction but the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, the authors show that RNA-binding protein HuR regulates telomerase function by enhancing the methylation of TERC, which is impaired by several disease-relevant TERC mutations.
- Hao Tang
- , Hu Wang
- & Wengong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access The genomic landscape of TERT promoter wildtype-IDH wildtype glioblastoma
The genomic landscape of TERT promoter wildtype-IDH wildtype glioblastoma
Glioblastoma can be classified based on IDH and TERT promoter mutations, but ~20% of glioblastoma do not have these mutations (TERTpWT-IDHWT glioblastoma). Here, the authors present a genetic landscape of TERTpWT-IDHWT glioblastoma, identifying a telomerase-positive subgroup driven by TERT-structural rearrangements and an ALT-positive subgroup with mutations in ATRX or SMARCAL1.
- Bill H. Diplas
- , Xujun He
- & Hai Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Aurora A-dependent CENP-A phosphorylation at inner centromeres protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue
Aurora A-dependent CENP-A phosphorylation at inner centromeres protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue
Sustained spindle tension applied to sister centromeres during mitosis leads to loss of sister chromatid cohesion which is known as cohesion fatigue. Here the authors show that Aurora A-dependent phosphorylation of CENP-A at the inner centromeres protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue.
- Grégory Eot-Houllier
- , Laura Magnaghi-Jaulin
- & Christian Jaulin
-
Article
| Open Access TERRA recruitment of polycomb to telomeres is essential for histone trymethylation marks at telomeric heterochromatin
TERRA recruitment of polycomb to telomeres is essential for histone trymethylation marks at telomeric heterochromatin
Long non-coding RNA TERRAs are essential for telomere protection and telomere length maintenance. Here the authors report a role for TERRAs in telomeric heterochromatin formation by recruiting Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 to telomeres.
- Juan J. Montero
- , Isabel López-Silanes
- & Maria A. Blasco
-
Article
| Open Access 53BP1 can limit sister-chromatid rupture and rearrangements driven by a distinct ultrafine DNA bridging-breakage process
53BP1 can limit sister-chromatid rupture and rearrangements driven by a distinct ultrafine DNA bridging-breakage process
Chromosome instability is associated with cancer formation. Here the authors identify in cultured human cancer cells a non-canonical DNA bridge breakage pathway leading to chromosome missegregation and rearrangements triggered by sister DNA intertwinements, which are limited by 53BP1.
- Ankana Tiwari
- , Owen Addis Jones
- & Kok-Lung Chan

 Multiplexed imaging of nucleome architectures in single cells of mammalian tissue
Multiplexed imaging of nucleome architectures in single cells of mammalian tissue