Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nanopore analysis of cis-diols in fruits
Nanopore analysis of cis-diols in fruits
Fruits contain a large variety of cis-diols but their rapid and direct analysis without complex sample pretreatment was not achieved. Here, the authors report a Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A nanopore modified with a phenylboronic acid adapter for recognition of 1,2-diphenols, alditols, α-hydroxy acids and saccharides in fruits.
- Pingping Fan
- , Zhenyuan Cao
- & Shuo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access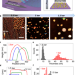 Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Molecules arranged in close proximity to a surface form molecular layers, exhibiting distinct properties. However, the creation of these layers is challenging. Here, the authors present a technique for generating molecular layers through crystallization induced by gas blowing onto a surface.
- Jincheng Tong
- , Nathan de Bruyn
- & Cinzia Casiraghi
-
Article
| Open Access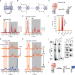 In-cell NMR suggests that DNA i-motif levels are strongly depleted in living human cells
In-cell NMR suggests that DNA i-motif levels are strongly depleted in living human cells
I-Motifs (iM) are non-canonical DNA structures potentially forming in the accessible, single stranded, cytosine-rich genomic region, but the specific contributions of several factors involved in their formation are unknown. Using in-cell NMR, the authors examined DNA i-motif formation in human cells at body temperature, suggesting i-M occur in a small portion (<1%) of genomic sites predisposed to its formation.
- Pavlína Víšková
- , Eva Ištvánková
- & Lukáš Trantírek
-
Article
| Open Access Janus microparticles-based targeted and spatially-controlled piezoelectric neural stimulation via low-intensity focused ultrasound
Janus microparticles-based targeted and spatially-controlled piezoelectric neural stimulation via low-intensity focused ultrasound
Wireless and localized stimulation of neural cells remains challenging. Here, the authors propose piezoelectric magnetic Janus microparticles that can target and stimulate neurons under low-intensity ultrasound through voltage-gated ion channels.
- Mertcan Han
- , Erdost Yildiz
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
Computing platforms based on chemical processes can be an alternative to digital computers in some scenarios but have limited programmability. Here the authors demonstrate a hybrid computing platform combining digital electronics and an oscillatory chemical reaction and demonstrate its computational capabilities.
- Abhishek Sharma
- , Marcus Tze-Kiat Ng
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access A non-canonical nucleophile unlocks a new mechanistic pathway in a designed enzyme
A non-canonical nucleophile unlocks a new mechanistic pathway in a designed enzyme
The authors previously showed that a histidine nucleophile and a flexible arginine can work in synergy to accelerate the Morita Baylis-Hillman (MBH) reaction. Here, they report another efficient MBHase that employs a non-canonical Nδ-methylhistidine nucleophile paired with a catalytic glutamate, providing an alternative mechanistic solution for MBH catalysis.
- Amy E. Hutton
- , Jake Foster
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article
| Open Access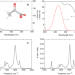 Aqueous pyruvate partly dissociates under deep ultraviolet irradiation but is resilient to near ultraviolet excitation
Aqueous pyruvate partly dissociates under deep ultraviolet irradiation but is resilient to near ultraviolet excitation
The photochemistry of the pyruvate anion plays an important role in the Earth’s atmosphere and aqueous environments. Here, the authors show that excitation of aqueous pyruvate by 200 nm light leads to decarboxylation with a quantum efficiency of 20%, while excitation by 340 nm light does not cause a reaction.
- Jan Thøgersen
- , Fani Madzharova
- & Frank Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access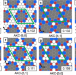 Prediction of highly stable 2D carbon allotropes based on azulenoid kekulene
Prediction of highly stable 2D carbon allotropes based on azulenoid kekulene
Discovery of 2D materials with useful electronic properties is challenging. Here, the authors use DFT to design a stable semiconducting 2D carbon allotrope for optoelectronic applications that has light charge carriers and unusual secondary bandgap.
- Zhenzhe Zhang
- , Hanh D. M. Pham
- & Rustam Z. Khaliullin
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic chloride ion adsorption on single iridium atom boosts seawater oxidation catalysis
Dynamic chloride ion adsorption on single iridium atom boosts seawater oxidation catalysis
The seawater oxidation reaction faces challenges from competitive chloride oxidation reaction. Herein, the authors have utilized chlorine adsorption to modulate the single-atom Ir coordination state and promote seawater oxidation and catalyst stability.
- Xinxuan Duan
- , Qihao Sha
- & Xiaoming Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Color construction of multi-colored carbon fibers using glucose
Color construction of multi-colored carbon fibers using glucose
Color construction of black carbon fibers is a challenge due to their stable physicochemical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate the tunable structural color of carbon fibers endowed by the dynamic growth of carbon spheres using glucose.
- Sijie Zhou
- , Chunhua Zhang
- & Weilin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
By virtue of the rotational motions of interlocked macrocycles, the authors describe a chameleon-like catenane host that can adjust its co-conformation for selective binding to copper(I) or sulfate ion. While the cationic copper(I) complex is achiral, the interlocked rings in the catenane host rotate and re-orient into a chiral co-conformation upon forming the anionic sulfate complex.
- Yueliang Yao
- , Yuen Cheong Tse
- & Ho Yu Au-Yeung
-
Article
| Open Access Silver-catalyzed direct conversion of epoxides into cyclopropanes using N-triftosylhydrazones
Silver-catalyzed direct conversion of epoxides into cyclopropanes using N-triftosylhydrazones
Epoxides are prominent small-ring O-heterocycles found in a variety of bioactive natural products and pharmaceuticals. Here, the authors report a silver carbene strategy to achieve O-to-C atom exchange of epoxides in a single step, affording diverse fluoroalkylcyclopropanes.
- Linxuan Li
- , Paramasivam Sivaguru
- & Xihe Bi
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of electric double layer rigidity on CO adsorption and electroreduction rate
Influence of electric double layer rigidity on CO adsorption and electroreduction rate
High-pressure infrared spectroscopy shows concentrated cations suppress CO adsorption. Here the authors report two electrochemical interfaces forming distinct double layer structures and reaction rates at elevating pressure and various potentials.
- Jiajie Hou
- , Bingjun Xu
- & Qi Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient all-small-molecule organic solar cells processed with non-halogen solvent
Efficient all-small-molecule organic solar cells processed with non-halogen solvent
The development of non-halogen solvent processed all-small-molecule organic solar cells was challenging. Here, the authors employ a small molecule donor with strong aggregation property to improve molecular pre-aggregation in tetrahydrofuran, realizing ternary device with efficiency of 16.1%.
- Wei Gao
- , Ruijie Ma
- & Gang Li
-
Article
| Open Access A structural and dynamic visualization of the interaction between MAP7 and microtubules
A structural and dynamic visualization of the interaction between MAP7 and microtubules
Integrated structural data show that the MAP7 microtubule binding domain stabilizes the microtubule lattice through binding along protofilaments. Both strong and weak interactions between MAP7 and the lattice extend beyond a single tubulin dimer and include the tubulin C-terminal tails.
- Agnes Adler
- , Mamata Bangera
- & Marc Baldus
-
Article
| Open Access Cation desolvation-induced capacitance enhancement in reduced graphene oxide (rGO)
Cation desolvation-induced capacitance enhancement in reduced graphene oxide (rGO)
Understanding local electrochemical processes can help improve electrochemical energy storage. Here, the authors report a charge storage mechanism in aqueous electrolyte for reduced graphene oxide using an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance.
- Kangkang Ge
- , Hui Shao
- & Patrice Simon
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
The nature of the molecule-metal interface is crucial for many technological applications. Here, the authors show that the photostability of the material can be sensitive to room light when coated with a single molecular layer, with implications for devices and processes.
- Chenyang Guo
- , Philip Benzie
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface synthesis relies on carefully designed molecular precursors that are thermally activated to afford desired, covalently coupled architectures. Here, the authors study the intramolecular reactions of vinyl groups in a poly-para-phenylene-based model system and provide a comprehensive description of the reaction steps taking place on the Au(111) surface under ultrahigh vacuum conditions.
- Marco Di Giovannantonio
- , Zijie Qiu
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic control of DNA condensation
Dynamic control of DNA condensation
Artificial biomolecular condensates are valuable tools to study the design principles of phase separation. Here, the authors demonstrate and characterize a model system of artificial DNA condensates whose kinetic formation and dissolution depends on DNA inputs that activate or deactivate the phase separating DNA subunits.
- Siddharth Agarwal
- , Dino Osmanovic
- & Elisa Franco
-
Article
| Open Access Dioxygen compatible electron donor-acceptor catalytic system and its enabled aerobic oxygenation
Dioxygen compatible electron donor-acceptor catalytic system and its enabled aerobic oxygenation
The photochemical properties of Electron Donor-Acceptor (EDA) complexes present exciting opportunities, but often require an inert atmosphere to maintain high efficiency. Here, the authors develop a photocatalytic system through rational design, which overcomes the oxygen-sensitive limitation of traditional EDA photocatalytic systems.
- Jialiang Wei
- , Junhong Meng
- & Ning Jiao
-
Article
| Open Access Dimethyl sulfate and diisopropyl sulfate as practical and versatile O-sulfation reagents
Dimethyl sulfate and diisopropyl sulfate as practical and versatile O-sulfation reagents
O-Sulfation is a vital post-translational modification in bioactive molecules, yet there are significant challenges for the synthesis. Here, the authors report a general and robust approach to O-sulfation by harnessing the tunable reactivity of dimethyl sulfate or diisopropyl sulfate under tetrabutylammonium bisulfate activation.
- Shuaishuai Yue
- , Guoping Ding
- & Jiakun Li
-
Article
| Open Access General alkyl fluoride functionalization via short-lived carbocation-organozincate ion pairs
General alkyl fluoride functionalization via short-lived carbocation-organozincate ion pairs
Many alkyl fluorides are readily available, but the synthetic applications trail behind the widely accepted utility of other halides. Here, the authors report a practical Csp3-F bond functionalization method that expands the currently restricted synthetic space of unactivated C(sp3)-F bonds, but also uses benzylic, propargylic and acyl fluorides.
- D. Lucas Kane
- , Bryan C. Figula
- & Christian Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Charging modulation of the pyridine nitrogen of covalent organic frameworks for promoting oxygen reduction reaction
Charging modulation of the pyridine nitrogen of covalent organic frameworks for promoting oxygen reduction reaction
The catalytic efficacy of covalent organic frameworks (COFs) is constrained by their restricted electro-transfer capability and weak binding affinities for reaction intermediates. Here the authors report COFs with various pyridinic-based units for tuning their catalytic activity towards oxygen reduction reaction.
- Xiubei Yang
- , Qizheng An
- & Gaofeng Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access OrthoID: profiling dynamic proteomes through time and space using mutually orthogonal chemical tools
OrthoID: profiling dynamic proteomes through time and space using mutually orthogonal chemical tools
Proteomics at the organelle contact site remains challenging due to the spatial and temporal dynamics of proteins. Here, the authors developed OrthoID, a mutually orthogonal dual enzymatic proteomics approach to explore the proteome at the contact site of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.
- Ara Lee
- , Gihyun Sung
- & Kimoon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Structurally coloured composite films are flexible optical materials with potential in a range of applications, but their production is impacted by long time-frames and limited materials. Here, the authors report a method for the production of large scale films by shearing supramolecular composites.
- Miaomiao Li
- , Bolun Peng
- & Jintao Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
By performing long ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of water under external electric fields, for up to 500 picoseconds, the authors identify a transition to a ferroelectric amorphous phase at ambient conditions.
- Giuseppe Cassone
- & Fausto Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Zirconium and hafnium catalyzed C–C single bond hydroboration
Zirconium and hafnium catalyzed C–C single bond hydroboration
Selective cleavage and subsequent functionalization of C−C single bonds present a fundamental challenge, and the use of inexpensive and Earth-abundant group IV metals for catalytic C−C single-bond cleavage is largely underdeveloped. Here, the authors report zirconium-catalyzed C−C single-bond cleavage and subsequent hydroboration reactions.
- Sida Li
- , Haijun Jiao
- & Lipeng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning light-driven oxidation of styrene inside water-soluble nanocages
Tuning light-driven oxidation of styrene inside water-soluble nanocages
Selective functionalization of C(sp2)–H bonds under ambient conditions is a persistent synthetic challenge in organic chemistry. Here the authors combine host-guest charge-transfer-based photoredox chemistry with supramolecular nano-confinement to achieve selective carbonylation of styrene by tuning the dioxygen concentration.
- Souvik Ghosal
- , Ankita Das
- & Jyotishman Dasgupta
-
Article
| Open Access Mirror-image ligand discovery enabled by single-shot fast-flow synthesis of D-proteins
Mirror-image ligand discovery enabled by single-shot fast-flow synthesis of D-proteins
Mirror-image phage display has the potential for high-throughput generation of biologically stable macrocyclic D-peptide binders but is hindered by the optimization required for D-protein chemical synthesis. Here, the authors report a general mirror-image phage display pipeline based on automated flow peptide synthesis and use it to prepare and characterize 12 L/D-protein pairs.
- Alex J. Callahan
- , Satish Gandhesiri
- & Bradley L. Pentelute
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom tailored atomically-precise nanoclusters for enhanced electrochemical reduction of CO2-to-CO activity
Single-atom tailored atomically-precise nanoclusters for enhanced electrochemical reduction of CO2-to-CO activity
Tailoring catalytic performance of atomically-precise metal nanoclusters catalysts is of great interest but remains challenging. Here, the authors report a co-eletropolymerization strategy to modify well-defined Au8 nanoclusters by single-atom sites to enhance its electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of CO2 towards CO.
- Yi-Man Wang
- , Fang-Qin Yan
- & Shuang-Quan Zang
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous strain tuning of oxygen evolution catalysts with anisotropic thermal expansion
Continuous strain tuning of oxygen evolution catalysts with anisotropic thermal expansion
Tuning compressive strain is an effective way to accelerate the oxygen evolution reaction kinetics. Here the authors show that anisotropic thermal expansion induces compressive strains on IrO6 octahedron in Sr2IrO4, shifting its d-band center downward and accelerating water oxidation kinetics beyond traditional thermal diffusion effects.
- Yu Du
- , Fakang Xie
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding activity-stability tradeoffs in biocatalysts by enzyme proximity sequencing
Understanding activity-stability tradeoffs in biocatalysts by enzyme proximity sequencing
Understanding the complex relationships between enzyme sequence, folding stability and catalytic activity is essential for applications, but current technologies cannot simultaneously resolve both stability and activity phenotypes and couple these to gene sequences at large scale. Here, the authors report Enzyme Proximity Sequencing (EP-Seq), a deep mutational scanning method to assay both expression level and catalytic activity of thousands of oxidoreductase variants from a cellular pool in a single experiment.
- Rosario Vanella
- , Christoph Küng
- & Michael A. Nash
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Understanding excitonic optical excitations is integral to improving optoelectronic and photovoltaic semiconductor devices. Here, Bennecke et al. use photoemission exciton tomography to unravel the multiorbital electron and hole contributions of entangled excitonic states in the prototypical organic semiconductor C60.
- Wiebke Bennecke
- , Andreas Windischbacher
- & Stefan Mathias
-
Article
| Open Access Nickel-catalyzed electrophiles-controlled enantioselective reductive arylative cyclization and enantiospecific reductive alkylative cyclization of 1,6-enynes
Nickel-catalyzed electrophiles-controlled enantioselective reductive arylative cyclization and enantiospecific reductive alkylative cyclization of 1,6-enynes
Transition metal-catalyzed asymmetric cyclization of 1,6-enynes is a powerful tool for the construction of chiral nitrogen-containing heterocycles, but limiting to the use of aryl or alkenyl metal reagents. Here, the authors report Ni-catalyzed enantioselective anti-arylative cyclization and enantiospecific cis-alkylative cyclization of 1,6-enynes.
- Wenfeng Liu
- , Yunxin Xing
- & Kun Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Chemoenzymatic indican for light-driven denim dyeing
Conventional blue denim dyeing has both environmental and health-related consequences. Here, Bidart et al. use enzyme engineering to develop a viable method for the bulk production of indican and demonstrate dying processes which could significantly reduce the negative consequences of this billion-dollar industry.
- Gonzalo Nahuel Bidart
- , David Teze
- & Ditte Hededam Welner
-
Article
| Open Access Remote-carbonyl-directed sequential Heck/isomerization/C(sp2)–H arylation of alkenes for modular synthesis of stereodefined tetrasubstituted olefins
Remote-carbonyl-directed sequential Heck/isomerization/C(sp2)–H arylation of alkenes for modular synthesis of stereodefined tetrasubstituted olefins
The synthesis of highly substituted olefins has been pursued for decades. Here, the authors show a carbonyl-directed sequential Heck/isomerization/C–H arylation of alkenes for modular synthesis of stereodefined all-carbon tetrasubstituted olefins.
- Runze Luan
- , Ping Lin
- & Weiping Su
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-site segmentally synergistic catalysis mechanism: boosting CoFeSx nanocluster for sustainable water oxidation
Dual-site segmentally synergistic catalysis mechanism: boosting CoFeSx nanocluster for sustainable water oxidation
Efficient oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts are essential for sustainable clean energy conversion. Here, the authors propose a Co-Fe dual-site to facilitate the ferromagnetic O-O bond coupling to achieve a great balance between activity and stability.
- Siran Xu
- , Sihua Feng
- & Jia-Nan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocurvature-induced field effects enable control over the activity of single-atom electrocatalysts
Nanocurvature-induced field effects enable control over the activity of single-atom electrocatalysts
Modulating interfacial electric fields provides a means to control electrocatalyst activity for a broad range of reactions. Here the authors show that this can be achieved by tuning the nanocurvature of carbon supported single-atom catalysts.
- Bingqing Wang
- , Meng Wang
- & Yanwei Lum
-
Article
| Open Access Distance effect of single atoms on stability of cobalt oxide catalysts for acidic oxygen evolution
Distance effect of single atoms on stability of cobalt oxide catalysts for acidic oxygen evolution
Dissolution of Co atoms in acidic media impedes the application of cobalt oxides in proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Here, the authors reveal a stabilizing effect induced by Ir single atoms on cobalt oxides that suppress Co dissolution.
- Zhirong Zhang
- , Chuanyi Jia
- & Jie Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access In situ copper faceting enables efficient CO2/CO electrolysis
In situ copper faceting enables efficient CO2/CO electrolysis
Copper electrocatalysts enable carbon dioxide/carbon monoxide reduction but suffer from low production rates. Here, the authors promote in situ growth of Cu(100) during electrolysis, enabling efficient and stable electrosynthesis of multicarbon products at industrially-relevant current densities
- Kaili Yao
- , Jun Li
- & Hongyan Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
In a combined experimental and theoretical study of the H + HD → H2 + D reaction at low collision energy (1.72 eV), the authors obtain detailed information on the quantum reaction dynamics surrounding a conical intersection.
- Shihao Li
- , Jiayu Huang
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Graphene oxide is in demand for various applications - however, this is complicated by changing physicochemical properties over time. Here, the authors show the intrinsic, metastable, and transient states of graphene oxide colloids upon ripening.
- Hayato Otsuka
- , Koki Urita
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked structures in polymer backbones can give interesting functionality, but can be challenging to prepare and control. Here, the authors report the development of polymers with a daisy chain unit in the backbone that are capable of shape memory behaviour.
- Shang-Wu Zhou
- , Danlei Zhou
- & Da-Hui Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination
Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination
Environmentally adaptive hydrogels have great potential as soft robotics but achieving self-regulated reversal shape deformation in homogenous hydrogels under a constant stimulus is challenging. Here, the authors report responsive hydrogels functionalized with two photoswitchable spiropyrans that exhibit self-regulated transient deformation reversal when subjected to constant illumination.
- Kexin Guo
- , Xuehan Yang
- & Chuang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of a point-of-care therapeutics sensor using protein engineering, electrochemical sensing and electronic integration
Creation of a point-of-care therapeutics sensor using protein engineering, electrochemical sensing and electronic integration
Low-cost point-of-care sensors are vital for precision medicine. Here, the authors have repurposed a glucometer for breast cancer therapeutic detection capable of sensing tamoxifen in human blood, utilizing blood glucose to power and amplify the therapeutic signals
- Rong Cai
- , Chiagoziem Ngwadom
- & Caroline M. Ajo-Franklin
-
Article
| Open Access Coverage enhancement accelerates acidic CO2 electrolysis at ampere-level current with high energy and carbon efficiencies
Coverage enhancement accelerates acidic CO2 electrolysis at ampere-level current with high energy and carbon efficiencies
The increased surface coverage of CO2 electroreduction (CO2R) intermediates promotes CO2R at high operating current densities under strongly acidic conditions. Here the authors report a 77.4% single-pass carbon efficiency for conversion of acidic CO2R to pure formic acid.
- Xiaohan Yu
- , Yuting Xu
- & Miao Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic exploration of polytetrafluoroethylene thermal plasma gasification through multiscale simulation coupled with experimental validation
Mechanistic exploration of polytetrafluoroethylene thermal plasma gasification through multiscale simulation coupled with experimental validation
PTFE waste, a growing ecological concern, urges the exploration of disposal methods. This study investigates PTFE’s plasma gasification, revealing POCD (oxygen) and FHD (steam) pathways. Experiments validate the above mechanism, showing an 80.12% fluorine recovery in 5 min under optimal conditions.
- Chu Chu
- , Long Long Ma
- & Guanyi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
The efficiency of upconversion electroluminescence remains very low for single-molecule emitters. Here, the authors report over one order of magnitude improvement in the emission efficiency via engineering energy-level alignments for triplet relayed upconversion involving only carrier injection.
- Yang Luo
- , Fan-Fang Kong
- & Zhen-Chao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient direct repairing of lithium- and manganese-rich cathodes by concentrated solar radiation
Efficient direct repairing of lithium- and manganese-rich cathodes by concentrated solar radiation
Rapid capacity decay and voltage drop hinder lithium- and manganese-rich cathode material (LMRO) development. Here, the authors apply concentrated solar radiation arrays on cycled LMRO electrodes, inducing inverse spinel phase to boost redox activity and reversibility, yielding enhanced electrochemical performance.
- Hailong Wang
- , Xin Geng
- & Xin He
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Homo-BacPROTAC-induced degradation of ClpC1 as a strategy against drug-resistant mycobacteria
Homo-BacPROTAC-induced degradation of ClpC1 as a strategy against drug-resistant mycobacteria