Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Polyhydride CeH9 with an atomic-like hydrogen clathrate structure
Polyhydride CeH9 with an atomic-like hydrogen clathrate structure
Obtainment of hydrogen-rich metal hydrides that are high-temperature superconductors has been demonstrated under very high pressure, but is still largely unexplored. Here the authors synthesize CeH9, with a structure related to solid metallic hydrogen, at relatively low pressure and without need for heating.
- Xin Li
- , Xiaoli Huang
- & Tian Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular movie of ultrafast coherent rotational dynamics of OCS
Molecular movie of ultrafast coherent rotational dynamics of OCS
Molecular movies provide crucial information of fundamental processes like energy and charge transfer, bond breaking etc. Here the authors show the time evolution of the rotational wave packet called the molecular movie of OCS molecules by Coulomb explosion imaging.
- Evangelos T. Karamatskos
- , Sebastian Raabe
- & Jochen Küpper
-
Article
| Open Access Strong coupling of collective intermolecular vibrations in organic materials at terahertz frequencies
Strong coupling of collective intermolecular vibrations in organic materials at terahertz frequencies
Here, the authors demonstrate strong coupling between collective, terahertz inter-molecular vibrations of organic materials and a Fabry-Pérot cavity. These results extend the applicability of polaritonic chemistry to large-scale organic systems, such as biological macromolecules and polymer chains.
- Ran Damari
- , Omri Weinberg
- & Sharly Fleischer
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying surface reaction intermediates with photoemission tomography
Identifying surface reaction intermediates with photoemission tomography
Identifying reaction pathways is a major challenge in chemistry, and proves particularly difficult for surface reactions. Here the authors show that imaging the molecular orbitals with photoemission tomography provides insight into the structure of surface intermediates allowing their identification.
- Xiaosheng Yang
- , Larissa Egger
- & F. Stefan Tautz
-
Article
| Open Access Strong and selective isotope effect in the vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation branching ratios of carbon monoxide
Strong and selective isotope effect in the vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation branching ratios of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide is the main C and O reservoir in interstellar media, where it undergoes photochemistry. The authors show that isotopic substitution affects not only its absorption. spectrum and photodissociation rates but also the branching ratio, key to understand isotopic. fractionation in the solar system
- Pan Jiang
- , Xiaoping Chi
- & Hong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Survival probability of stochastic processes beyond persistence exponents
Survival probability of stochastic processes beyond persistence exponents
The survival probability of a random walker is the probability that a particular target has not been reached by time t. Here the authors produce a formula for the prefactor involved in the expression of the survival probability which is shown to hold for both Markovian and non-Markovian processes.
- N. Levernier
- , M. Dolgushev
- & T. Guérin
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast structural rearrangement dynamics induced by the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution
Ultrafast structural rearrangement dynamics induced by the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution
The interaction of biomolecules with ionizing radiation induces structural changes which are still largely unknown. The authors use femtosecond wave packet spectroscopy to observe ultrafast structural dynamics that follow the photodetachment of phenoxide in aqueous solution.
- Tushar Debnath
- , Muhammad Shafiq Bin Mohd Yusof
- & Zhi-Heng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access On the origin of the extremely different solubilities of polyethers in water
On the origin of the extremely different solubilities of polyethers in water
Polyethers are ubiquitous in our daily lives, and display counterintuitive solubilities in water. Here the authors show, by ultrafast spectroscopies and computations, that solubility does not depend on steric factors but on the interaction of water molecules with the polymer’s charge distribution
- Bernd Ensing
- , Ambuj Tiwari
- & Sander Woutersen
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved molecular dynamics of single and double hydrogen migration in ethanol
Time-resolved molecular dynamics of single and double hydrogen migration in ethanol
Chemical dynamics in molecules involve particle migration and bond rearrangement. Here the authors show single and double hydrogen migration in ethanol cations and dications that are generated by using intense laser pulse interaction with a jet of ethanol molecules.
- Nora G. Kling
- , S. Díaz-Tendero
- & N. Berrah
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale mapping of hydrophobic layers on graphene and few-layer MoS2 and WSe2 in water
Atomic-scale mapping of hydrophobic layers on graphene and few-layer MoS2 and WSe2 in water
Interfacial water plays a crucial role in mediating hydrophobic interactions. Here, the authors directly image the interfacial water organization in graphene, few-layer MoS2 and WSe2 through 3D-AFM technique to unveil that the distance between adjacent layers is about 0.30 nm larger than theoretically predicted values.
- Manuel R. Uhlig
- , Daniel Martin-Jimenez
- & Ricardo Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access In situ observations of an active MoS2 model hydrodesulfurization catalyst
In situ observations of an active MoS2 model hydrodesulfurization catalyst
Although hydrodesulfurization is a key process in the chemical industry, a deep understanding of the catalyst structure under real reaction conditions is lacking. Here, the authors combine theoretical calculations with high-pressure scanning tunneling microscopy to elucidate the MoS2 catalyst structure under reaction conditions.
- Rik V. Mom
- , Jaap N. Louwen
- & Irene M. N. Groot
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusing wave paradox of phototactic particles in traveling light pulses
Diffusing wave paradox of phototactic particles in traveling light pulses
The amoebae Dictyostelium have previously been observed to migrate counter to the direction of a traveling chemical wave. Here the authors demonstrate that light-activated phototactic synthetic particles move counter to the pulse direction in a way which is reminiscent of the amoebae’s behavior.
- Celia Lozano
- & Clemens Bechinger
-
Article
| Open Access Low-energy electrons transform the nimorazole molecule into a radiosensitiser
Low-energy electrons transform the nimorazole molecule into a radiosensitiser
Radiosensitisers are believed to interfere with cancer cells by dissociating upon interaction with electrons. Here the authors observe instead that the dominant path for nitroimidazolic radiosensitisers involves formation of a non-dissociated radical anion, prerequisite for their accumulation in tumour cells.
- Rebecca Meißner
- , Jaroslav Kočišek
- & Stephan Denifl
-
Article
| Open Access Iminothioindoxyl as a molecular photoswitch with 100 nm band separation in the visible range
Iminothioindoxyl as a molecular photoswitch with 100 nm band separation in the visible range
The design of photoswitches which operate in the visible light regime, show a large separation of absorption bands and are functional in various solvents is challenging. Here the authors report Iminothioindoxyls as visible-light operated photoswitches with a band separation of 100 nm.
- Mark W. H. Hoorens
- , Miroslav Medved’
- & Wiktor Szymanski
-
Article
| Open Access Direct dioxygen evolution in collisions of carbon dioxide with surfaces
Direct dioxygen evolution in collisions of carbon dioxide with surfaces
Carbon dioxide can dissociate via different pathways depending on the amount of available energy. Here the authors investigate carbon dioxide collisions with metal substrates and observe a pathway producing molecular oxygen, which might explain the presence of oxygen in abiotic environments.
- Yunxi Yao
- , Philip Shushkov
- & Konstantinos P. Giapis
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time observation of X-ray-induced intramolecular and interatomic electronic decay in CH2I2
Real-time observation of X-ray-induced intramolecular and interatomic electronic decay in CH2I2
Understanding strong X-ray induced phenomena is important for applications of X-ray free-electron laser imaging. Here, the authors show time-resolved measurements of X-ray free-electron laser induced electronic decay of CH2I2 molecule probed with NIR pulses and identify mechanisms behind different transient states lifetimes.
- Hironobu Fukuzawa
- , Tsukasa Takanashi
- & Kiyoshi Ueda
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond time-resolved two-photon photoemission studies of ultrafast carrier relaxation in Cu2O photoelectrodes
Femtosecond time-resolved two-photon photoemission studies of ultrafast carrier relaxation in Cu2O photoelectrodes
While cuprous oxide is a promising solar-to-fuel conversion material, photoelectrochemical devices substantially underperform. Here, the authors use femtosecond time-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopy to correlate photoexcited electron energetics and dynamics with performance losses.
- Mario Borgwardt
- , Stefan T. Omelchenko
- & Dennis Friedrich
-
Article
| Open Access Resonance-enhanced three-photon luminesce via lead halide perovskite metasurfaces for optical encoding
Resonance-enhanced three-photon luminesce via lead halide perovskite metasurfaces for optical encoding
Lead halide perovskites attract high interest as semiconductor materials but their exceptional nonlinear properties have not been fully exploited. Here Fan et al. demonstrate third-order harmonic generation and 60-fold enhanced three-photon luminescence, enabling optical encoding applications.
- Yubin Fan
- , Yuhan Wang
- & Shumin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of the electroneutral sodium/proton antiporter PaNhaP from transition-path shooting
Mechanism of the electroneutral sodium/proton antiporter PaNhaP from transition-path shooting
Cation-proton antiporters mediate selective ion exchange across cellular membranes to control pH, salt concentration and cell volume. Here the authors present a transition-path sampling method that overcomes the timescale gap between simulations (µs) and transport processes (s), which allows them to resolve the Na+ and H+ transport cycle of the Na+/H+ antiporter NhaP from Pyrococcus abyssi.
- Kei-ichi Okazaki
- , David Wöhlert
- & Gerhard Hummer
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of molecular architecture on ring polymer dynamics in semidilute linear polymer solutions
Effect of molecular architecture on ring polymer dynamics in semidilute linear polymer solutions
Understanding the dynamics of ring polymers is challenging are despite recent progress, understanding of the nonequilibrium behavior of ring polymers has not yet been achieved. Here, the authors directly observe the flow dynamics of DNA-based rings in semidilute linear polymer solutions using single molecule techniques.
- Yuecheng Zhou
- , Kai-Wen Hsiao
- & Charles M. Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
The mechanism of the non-radiative recombination in halide perovskite nanocrystals has not been fully understood. Here Gerhard et al. resolve the contributions of individual recombination centers by photoluminescence blinking measurements and identify ion migration as the underlying mechanism.
- Marina Gerhard
- , Boris Louis
- & Ivan G. Scheblykin
-
Article
| Open Access Side-group chemical gating via reversible optical and electric control in a single molecule transistor
Side-group chemical gating via reversible optical and electric control in a single molecule transistor
It remains a challenge to fully control molecular electronics. Here, Meng et al. show a reversible two-mode single-molecule switch, where the conductance through the molecular backbone is controlled by an in situ chemical gating via bias-dependent trans–cis isomerisation on an azobenzene sidegroup.
- Linan Meng
- , Na Xin
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access In situ reversible underwater superwetting transition by electrochemical atomic alternation
In situ reversible underwater superwetting transition by electrochemical atomic alternation
Materials with in situ reversible wettability have attractive properties for switching applications, but are a challenge to use especially for the inverse process of liquid spreading. Here, the authors propose an electrochemical strategy enabling in situ reversible superwetting conversion between underwater superoleophilicity and superoleophobicity by constructing a binary textured surface.
- Qianbin Wang
- , Bojie Xu
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Probing hydrogen bond strength in liquid water by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
Probing hydrogen bond strength in liquid water by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
Understanding how nuclear motions affect vibrational motions in molecular liquids remains challenging in modern condensed matter physics. Here the authors study the vibrational quantum effects in liquid water and show the sensitivity on the coherent evolution of OH bonds in core-excited states.
- Vinícius Vaz da Cruz
- , Faris Gel’mukhanov
- & Michael Odelius
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic insight into hydration shells around facetted nanoparticles
Atomic insight into hydration shells around facetted nanoparticles
Experimental structural insight into hydration shells around nanoparticles is challenging. Here the authors use X-ray scattering and pair distribution function analysis to reveal interatomic distances in the very first adsorbed water layer as well as extended restructured layers out to 15 Å, with a bulk-like signature.
- Sabrina L. J. Thomä
- , Sebastian W. Krauss
- & Mirijam Zobel
-
Article
| Open Access Negative differential resistance as a critical indicator for the discharge capacity of lithium-oxygen batteries
Negative differential resistance as a critical indicator for the discharge capacity of lithium-oxygen batteries
Understanding the fundamental chemistry in Li-O2 battery holds importance to the development of superior energy devices. Here the authors report that the oxygen reduction reaction in Li-O2 battery exhibits negative differential resistance, which can work as an indicator to the reaction pathway.
- Yoko Hase
- , Yasuhiro Komori
- & Shuji Nakanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Electroactive materials with tunable response based on block copolymer self-assembly
Electroactive materials with tunable response based on block copolymer self-assembly
Ferroelectric polymers are key building blocks for flexible electronic devices, but lack functionality and ability to tune their ferroelectric response. Here the authors show a method to introduce functionality in ferroelectric polymers while preserving ferroelectricity and tune the ferroelectric response by incorporating insulating polymer chains.
- Ivan Terzic
- , Niels L. Meereboer
- & Katja Loos
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling coherently driven hyperpolarization dynamics in signal amplification by reversible exchange
Unveiling coherently driven hyperpolarization dynamics in signal amplification by reversible exchange
There is increasing effort to improve the signal sensitivity and explore the hyperpolarization dynamics. Here the authors demonstrate the parahydrogen spin transfer dynamics in compounds containing 15N using SABRE hyperpolarization technique with different strengths of the magnetic field.
- Jacob R. Lindale
- , Shannon L. Eriksson
- & Warren S. Warren
-
Article
| Open Access Long-lasting field-free alignment of large molecules inside helium nanodroplets
Long-lasting field-free alignment of large molecules inside helium nanodroplets
Strong molecular alignment without a laser field present is important for fundamental experiments in molecular science, but so far this has not been obtained for complex molecules. Here the authors use a shaped laser pulse to demonstrate field-free alignment of complex molecules in helium droplets.
- Adam S. Chatterley
- , Constant Schouder
- & Henrik Stapelfeldt
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane water for probing neuronal membrane potentials and ionic fluxes at the single cell level
Membrane water for probing neuronal membrane potentials and ionic fluxes at the single cell level
Non-invasive spatiotemporal probing of electric potentials in living neurons without chemical or genetic modification provides a major advancement to neuroscience. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of membrane water as a probe for neuronal membrane potentials and ionic flux.
- M. E. P. Didier
- , O. B. Tarun
- & S. Roke
-
Article
| Open Access Entangled polymer dynamics beyond reptation
Entangled polymer dynamics beyond reptation
Polymer dynamics at entangled conditions has generally been simplified as motions governed by the two ends of each polymer chain. Abadi et al. characterize linear and cyclic dsDNA molecules with high resolution, revealing position-dependent chain motions which cannot be described by the reptation theory.
- Maram Abadi
- , Maged F. Serag
- & Satoshi Habuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy of dilute gas-phase nanosystems
Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy of dilute gas-phase nanosystems
Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy has greatly advanced our understanding of molecular dynamics but was so far broadly limited to complex condensed phase probes. Bruder et al. extend the method to isolated nanosystems in the gas phase and study cold molecules in a superfluid helium environment.
- Lukas Bruder
- , Ulrich Bangert
- & Frank Stienkemeier
-
Article
| Open Access Unusually complex phase of dense nitrogen at extreme conditions
Unusually complex phase of dense nitrogen at extreme conditions
Nitrogen has a complex phase diagram with rich polymorphism, which is challenging to characterize due to the extreme conditions and uncertain stability ranges needed to do so. Here the authors resolve one of the most elusive phases of this model system, reporting a crystalline structure with unusual complexity.
- Robin Turnbull
- , Michael Hanfland
- & Eugene Gregoryanz
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Fast oxide ion conductors are the key materials for some technological devices. Here the authors report the creation and stabilization of oxygen vacancies in BiVO4 Scheelite with isolated tetrahedral anion structures for improved ionic conducting performance and understanding of the conduction mechanism.
- Xiaoyan Yang
- , Alberto J. Fernández-Carrión
- & Xiaojun Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Towards exact molecular dynamics simulations with machine-learned force fields
Towards exact molecular dynamics simulations with machine-learned force fields
Simultaneous accurate and efficient prediction of molecular properties relies on combined quantum mechanics and machine learning approaches. Here the authors develop a flexible machine-learning force-field with high-level accuracy for molecular dynamics simulations.
- Stefan Chmiela
- , Huziel E. Sauceda
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids
Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids
The ability to stabilise colloidal suspensions in solution against salt-induced aggregation is critical to many industrial applications, but it remains challenging at high salt concentration. To overcome this problem, Lan et al. introduce a raspberry-like colloidal particle with controllable morphology.
- Yang Lan
- , Alessio Caciagli
- & Erika Eiser
-
Article
| Open Access Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Water uptake of natural polymers is accompanied by swelling and changes in the internal structure of the polymeric system but the exact mechanism of water-uptake and swelling remained unknown. Here the authors use atom-scale simulations to identify a molecular mechanism which is responsible for hysteresis in sorption-induced swelling in natural polymers.
- Mingyang Chen
- , Benoit Coasne
- & Jan Carmeliet
-
Article
| Open Access Confined small-sized cobalt catalysts stimulate carbon-chain growth reversely by modifying ASF law of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis
Confined small-sized cobalt catalysts stimulate carbon-chain growth reversely by modifying ASF law of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis
Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) is theoretically limited by Anderson–Schulz–Flory (ASF) law. Here, the authors successfully tune the selectivity of products from diesel-range hydrocarbons to gasoline-range hydrocarbons in FTS by controlling the crystallite sizes of confined cobalt, and modify the ASF law.
- Qingpeng Cheng
- , Ye Tian
- & Xingang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
The description of van der Waals interactions should often account for coupling with pervasive electric fields, but this effect has been omitted in atomistic simulations. Here, the authors develop a model to study the effects of external charge on long-range van der Waals interactions.
- Andrii Kleshchonok
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access A facile strategy for realizing room temperature phosphorescence and single molecule white light emission
A facile strategy for realizing room temperature phosphorescence and single molecule white light emission
The demonstration of pure organic room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) luminogens with complementary emission is a key requirement for developing low-cost white light emitters. Here, the authors construct RTP-active organic salt compounds by exchanging the counterion with a heavy halide ion.
- Jianguo Wang
- , Xinggui Gu
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Metallization and molecular dissociation of dense fluid nitrogen
Metallization and molecular dissociation of dense fluid nitrogen
Nitrogen is a model system still presenting unknown behaviors at the pressures and temperatures typical of deep planets’ interiors. Here the authors explore, by pulsed laser heating in a diamond anvil cell and optical measurements, the metallization and non-molecular states of nitrogen in a previously unexplored domain above 1 Mbar and at 2000-7000K.
- Shuqing Jiang
- , Nicholas Holtgrewe
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article
| Open Access Operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of solid electrolyte interphase formation and evolution in Li2S-P2S5 solid-state electrolytes
Operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of solid electrolyte interphase formation and evolution in Li2S-P2S5 solid-state electrolytes
Solid-state electrolytes may improve the performance of batteries; however, many are unstable towards metallic lithium, and little is known about the chemical evolution of the interfaces that form during cycling. Here, the authors use an operando method to map the formation and evolution of a solid-electrolyte interphase during cycling.
- Kevin N. Wood
- , K. Xerxes Steirer
- & Glenn Teeter
-
Article
| Open Access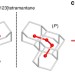 Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Deciphering absolute configuration of individual molecules directly by visual inspection remains a highly attractive goal. Here, the authors determine the absolute configuration and orientation of a single [123]tetramantane molecule adsorbed on Cu(111) using low temperature atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip.
- Daniel Ebeling
- , Marina Šekutor
- & Peter R. Schreiner
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic and structural anomalies of water nanodroplets
Thermodynamic and structural anomalies of water nanodroplets
Nanoscale water droplets can remain liquid far below the homogenous nucleation temperature, at which bulk cooled water inevitably crystallizes. Malek et al. show that water in nanodroplets as small as a few hundred molecules reproduce the thermodynamic anomalies of bulk water.
- Shahrazad M. A. Malek
- , Peter H. Poole
- & Ivan Saika-Voivod
-
Article
| Open Access The role of water in fault lubrication
The role of water in fault lubrication
Friction plays a key role in fault slip between tectonic plates. Here, the authors demonstrate through friction experiments on calcite in brines that pressure solution at high stresses and slow sliding velocities leads to a prominent decrease in friction and therefore is a weakening mechanism in fault strength.
- Yijue Diao
- & Rosa M. Espinosa-Marzal
-
Article
| Open Access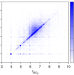 Mapping uncharted territory in ice from zeolite networks to ice structures
Mapping uncharted territory in ice from zeolite networks to ice structures
Ice is one of the most well-studied condensed matter systems, yet new phases are still being discovered. Here the authors report a large-scale computational study of the configuration space of water ice, creating a navigable “sketch-map” including new predicted phases as well as relationships between different structures.
- Edgar A. Engel
- , Andrea Anelli
- & Richard J. Needs
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular polarizability anisotropy of liquid water revealed by terahertz-induced transient orientation
Molecular polarizability anisotropy of liquid water revealed by terahertz-induced transient orientation
The intermolecular dynamics of liquid water impact most biological processes. Here, the authors use intense terahertz electromagnetic pulses to generate a transient, out-of-equilibrium state of the water network to show that the molecules become oriented and probe the polarizability of this anisotropic state.
- Peter Zalden
- , Liwei Song
- & Christian Bressler
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of different reactivities of para and ortho-water towards trapped diazenylium ions
Observation of different reactivities of para and ortho-water towards trapped diazenylium ions
Water molecules exist as two distinct nuclear-spin isomers denoted ortho and para. Here, the authors separate these two isomers in the gas phase to show that they exhibit different reactivities in a prototypical proton-transfer reaction.
- Ardita Kilaj
- , Hong Gao
- & Stefan Willitsch
-
Article
| Open Access Transient metal-centered states mediate isomerization of a photochromic ruthenium-sulfoxide complex
Transient metal-centered states mediate isomerization of a photochromic ruthenium-sulfoxide complex
An essential open question in functional transition metal complexes is the relative roles of charge-transfer and metal-centered excited states. Here the authors identify the important role of metal-centered excited states in the linkage photoisomerization of a photochromic Ru-sulfoxide complex.
- Amy A. Cordones
- , Jae Hyuk Lee
- & Tae Kyu Kim

 Three-dimensional aromaticity in an antiaromatic cyclophane
Three-dimensional aromaticity in an antiaromatic cyclophane