Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Achieving a wide angular response in single layer acoustic metalenses is challenging. By leveraging perfect acoustic symmetry conversion, the authors realize an aberration free metalens with a wide field-of-hearing, up to 140 degrees.
- Dongwoo Lee
- , Beomseok Oh
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Deuteration-enhanced neutron contrasts to probe amorphous domain sizes in organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction films
Deuteration-enhanced neutron contrasts to probe amorphous domain sizes in organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction films
The use of conventional X-ray scattering techniques is challenging to detect donor-acceptor contrast within amorphous intermixing regions. Here, the authors apply neutron scattering and targeted deuteration to enhance the contrast by one order of magnitude and reveal short-range aggregations of d-Y6.
- Guilong Cai
- , Yuhao Li
- & Xinhui Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 (LLZO) is a promising solid electrolyte but suffers from severe surface degradation in air. Here, authors use mapping of resonant Auger spectroscopy and various ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies to elucidate the dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on clean LLZO surfaces.
- Nian Zhang
- , Guoxi Ren
- & Xiaosong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven artificial food synthesis from CO2 provides an approach to overcome the limitations of natural photosynthesis, but it is very challenging. Here, the authors report a hybrid electrocatalytic-biocatalytic flow system, coupling photovoltaics-powered electrocatalysis (CO2 to formate) with a five enzyme cascade platform (formate to sugar), which achieves conversion of CO2 to C6 sugar (L-sorbose) with a solar-to-food energy conversion efficiency of 3.5%.
- Guangyu Liu
- , Yuan Zhong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
Spectroscopic visualization of reversible hydrogen spillover between palladium and metal–organic frameworks toward catalytic semihydrogenation
The authors report an in situ investigation of interfacial hydrogen spillover in Pd/ZIF-8 structures with X-ray and Raman techniques. A mechanistic picture of how Pd/ZIF-8 catalyst mediate alkyne semihydrogenation to alkynes is described.
- Qiaoxi Liu
- , Wenjie Xu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D materials
2D materials are being investigated for several applications in micro- and nanoelectronics, but their weak adhesion represents a critical challenge for device integration. Here, the authors propose a button shear testing method to evaluate the adhesion forces of various large-area 2D films on SiO2 and Si3N4 substrates.
- Josef Schätz
- , Navin Nayi
- & Max C. Lemme
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogating site dependent kinetics over SiO2-supported Pt nanoparticles
Interrogating site dependent kinetics over SiO2-supported Pt nanoparticles
Kim and co-workers introduce a new ‘kinetic site deconvolution’ method to identify active sites on heterogeneous catalysts by linking reaction rates to specific adsorption environments.
- Taek-Seung Kim
- , Christopher R. O’Connor
- & Christian Reece
-
Article
| Open Access Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Here, the authors design a microcavity-confined 2D heterojunction to realize the strong coupling among donor exciton, acceptor exciton, and cavity photon mode, leading to an unconventional energy transfer via polariton relaxation with an enhancement factor of ~440.
- Zehua Hu
- , Tanjung Krisnanda
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access High-strength and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminium alloy via Zr-core-Al-shell wire
High-strength and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminium alloy via Zr-core-Al-shell wire
Solidification cracking during fusion welding of high-strength aluminum alloys has been a long-standing issue. Here, the authors achieve reliable and crack-free welding of 2024 aluminum alloy using a Zr-core-Al-shell wire and the oscillating laser-arc hybrid welding technique.
- Jun Jin
- , Shaoning Geng
- & Xiangqi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into structural defect formation in individual InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots under UV oxidation
Insights into structural defect formation in individual InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots under UV oxidation
InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are promising candidates for advanced light-emitting diodes, but low emission efficiency due to oxidation hampers applications. Here, the authors provide insight into the structural defects that form on individual QDs during UV-facilitated oxidation.
- Hayeon Baek
- , Sungsu Kang
- & Jungwon Park
-
Article
| Open Access In situ modulating coordination fields of single-atom cobalt catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction
In situ modulating coordination fields of single-atom cobalt catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction
The electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction plays an important role in new energy technologies such as fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Here the authors present a cobalt catalyst with a symmetry-broken Cl−Co−N4 moiety capable of dynamically modulating electron occupancy at active sites during practical reaction conditions to optimize oxygen reduction performance.
- Meihuan Liu
- , Jing Zhang
- & Qinghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access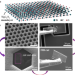 Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
The Young’s modulus of the MXene Ti3C2Tx, theoretically predicted to be 0.502 TPa, has not yet been experimentally confirmed. This work supplants previous reports using nanoindentation with the correctly measured Young’s modulus of 0.484 ± 0.013 TPa.
- Chao Rong
- , Ting Su
- & Fu-Zhen Xuan
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Relating the degree of network crosslinking as a descriptor to the desalination performance of crosslinked polymer membranes remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a parameter based on distinct amide bonds per unit mass of polyamide, to unravel the relationship between the crosslinked networks of polyamide membranes and their desalination performance.
- Yu-Ren Xue
- , Chang Liu
- & Zhi-Kang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Electrode potential in any electrochemical systems has long been discussed by classical Debye-Hückel theory which holds only under extremely dilute concentrations. Here, the authors establish the concept ‘liquid Madelung potential’ to comprehensively describe the potential shift at practical concentrations.
- Norio Takenaka
- , Seongjae Ko
- & Atsuo Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access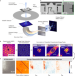 Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
High and medium-entropy alloys have shown excellent mechanical performance, yet the role of short-range order (SRO) on these properties has been unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that the reduction of SRO by deformation leads to rejuvenation, explaining their remarkable damage tolerance.
- Yang Yang
- , Sheng Yin
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Three dimensional classification of dislocations from single projections
Three dimensional classification of dislocations from single projections
Many material properties are governed by the internal dislocation network within the material. Here, the authors describe a method to determine the three dimensional position and type of dislocations from a measurement along only a single direction within a scanning transmission electron microscope.
- Tore Niermann
- , Laura Niermann
- & Michael Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access 3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
X-ray Free Electron Lasers allow fast structure determination. Here, the authors push the temporal limit of atomic level structure determination to 25 fs, the length of a single pulse, paving the way to the study of fast, non-repeatable processes.
- Gábor Bortel
- , Miklós Tegze
- & Gyula Faigel
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Blue QD-LEDs suffer from poor operational stability due to the carrier accumulation at transport layers. Here, the authors propose a strategy to mitigate the hole accumulation driven oxidation in hole transport layer, effectively elongating the operational lifetime of blue QD-LEDs.
- Wenjing Zhang
- , Bo Li
- & Huaibin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access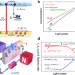 Resolving electron and hole transport properties in semiconductor materials by constant light-induced magneto transport
Resolving electron and hole transport properties in semiconductor materials by constant light-induced magneto transport
Here, the authors introduce a constant light-induced magneto-transport method which seamlessly integrates light, current, and a magnetic field to characterize electron and hole properties across an expansive array of materials.
- Artem Musiienko
- , Fengjiu Yang
- & Antonio Abate
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative analysis of printed nanostructured networks using high-resolution 3D FIB-SEM nanotomography
Quantitative analysis of printed nanostructured networks using high-resolution 3D FIB-SEM nanotomography
The physical properties of devices made of printed nanosheets and nanowires are determined by their intrinsic nanostructured network morphology. Here, the authors use FIB-SEM nanotomography to quantitatively analyze printed nanostructured networks via 3D reconstructions.
- Cian Gabbett
- , Luke Doolan
- & Jonathan N. Coleman
-
Article
| Open Access Tensile straining of iridium sites in manganese oxides for proton-exchange membrane water electrolysers
Tensile straining of iridium sites in manganese oxides for proton-exchange membrane water electrolysers
The acidic oxygen evolution reaction plays a crucial role in proton-exchange membrane water electrolysis devices. The authors developed a low-iridium catalyst with tensile-strain able to trigger a localized lattice oxygen-mediated mechanism to realize efficient and stable acid-OER performance.
- Hui Su
- , Chenyu Yang
- & Qinghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Chemical identification of the building blocks of biopolymers often considerably relies on the presence of markers, extensive simulations, or is not possible at all. Here, the authors report a molecular probe-sensitisation approach addressing the identification of a specific amino acid within different peptides.
- Xu Wu
- , Bogdana Borca
- & Uta Schlickum
-
Article
| Open Access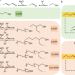 Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Achieving efficient carbon chain propagation remains a grand challenge for ethanol upgrading. Here, the authors report sulfur doped Ni@C-Sx catalysts with controllably exposed nickel sites that can dramatically improve direct-growth probability towards long-chain alcohols production.
- Juwen Gu
- , Wanbing Gong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Combining in situ nanoprobe techniques paves the way for gaining insights into structure-selectivity relations for electrocatalysts. Herein, the dynamic evolution of lattice strain in individual nanoparticles is directly visualized with nanoscale resolution in Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during the electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 into value-added chemicals.
- Marvin L. Frisch
- , Longfei Wu
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantifying chemical short-range order (CSRO) remains a formidable for volume-averaged or 2D microscopy methods. Here the authors introduce a machine-learning approach that breaks the resolution limitations of atom probe tomography to reveal the 3D atomistic architecture of CSRO in Fe-based alloys.
- Yue Li
- , Ye Wei
- & Baptiste Gault
-
Article
| Open Access Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Electrostrictors are materials that develop mechanical strain proportional to the square of the applied electric field. Here authors report. Zr-doped-Ceria as a new lead-free electrostrictive material with a similar electrostriction coefficient to the best electrostrictor material currently in use.
- Maxim Varenik
- , Boyuan Xu
- & Igor Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
In lithium-metal batteries, it is vital to quantify electrolyte side reactions occurring at the metal anode surface. Here, the authors introduce an electrochemical technique, using a series of small-step lithium deposition followed by open circuit voltage analysis, to accurately measure these reactions.
- Burak Aktekin
- , Luise M. Riegger
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Supported CoOx catalysts display higher reactivities towards CO oxidation, yet, corresponding catalytically active phases are still unclear, especially under reaction conditions. Here, by means of in-situ APXPS and ResPES, the authors demonstrate that the topographic restructuring and chemical restructuring occur on these CoOx working catalysts, and also highlight the unique catalytic properties of Co3+ sites.
- Hao Chen
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Miquel Salmeron
-
Article
| Open Access The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
Here, the authors investigate frequently observed variations in data between different electrochemical cells using in-situ electronic/electrochemical measurements, developing a vertical microcell strategy to eliminate the conductance issue and enhance measurement reproducibility.
- Hang Xia
- , Xiaoru Sang
- & Yongmin He
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
The design of programmable artificial photosynthetic cells is hindered by the requirement for cofactor generation for the biocatalytic module. Here, the authors report on the design of artificial photosynthetic cells using biotic–abiotic thylakoid–CdTe as hybrid energy modules, which enhance the regeneration of NADPH, NADH and ATP cofactors without external supplements by promoting proton-coupled electron transfer.
- Feng Gao
- , Guangyu Liu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access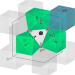 Quantitative three-dimensional local order analysis of nanomaterials through electron diffraction
Quantitative three-dimensional local order analysis of nanomaterials through electron diffraction
Correlated disorder can lead to phenomena that are inaccessible to ordered structures. Here the authors show that local order principles can be directly derived from the three-dimensional difference pair distribution function based on the single crystal diffuse scattering in 3D electron diffraction data from nanometre sized crystals.
- Ella Mara Schmidt
- , Paul Benjamin Klar
- & Lukas Palatinus
-
Article
| Open Access In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
Nanodiamonds containing NV centers are promising electron paramagnetic resonance sensors, however applications are hindered by their random orientation. Qin et al. propose a new protocol that makes the technique insensitive to the sensor’s orientation and present a proof-of-principle in situ demonstration.
- Zhuoyang Qin
- , Zhecheng Wang
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the aging process of solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx anode
Revealing the aging process of solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx anode
Observing the evolution of the solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx-based electrodes in Li-ion batteries is challenging. Here, authors use three-dimensional tomography to visualize the growth of the interphase on single SiOx particles and propose a mechanical confinement strategy to prevent aging.
- Guoyu Qian
- , Yiwei Li
- & Feng Pan
-
Article
| Open Access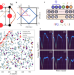 Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Analysis of experimental data in condensed matter is often challenging due to system complexity and slow character of physical simulations. The authors propose a framework that combines machine learning with theoretical calculations to enable real-time analysis for electron, neutron, and x-ray spectroscopies.
- Sathya R. Chitturi
- , Zhurun Ji
- & Joshua J. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Carbon is a key support for metal-catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination to vinyl chloride but its role remains elusive. Here, the authors, by means of operando spectroscopy, demonstrate the co-catalytic function of neighboring carbon and isolated metal atoms, constituting the active ensemble.
- Vera Giulimondi
- , Andrea Ruiz-Ferrando
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Comment
| Open Access Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Adopting standardized and reliable methodologies to accurately measure particle removal efficiency when developing fibrous materials for controlling airborne contamination is crucial. Here, the authors recommend best practices for experimental assessments and reporting to ensure a reliable evaluation of new airborne particle filtration media and technologies.
- Paolo Tronville
- , Vincenzo Gentile
- & Jesus Marval
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional specular optical rotation in the charge ordered state of Kagome metal CsV3Sb5
Unconventional specular optical rotation in the charge ordered state of Kagome metal CsV3Sb5
Kagome materials, such as CsV3Sb5, a rich array of correlated phase, including a time-reversal symmetry breaking phase, which could possibly be the result of loop currents. Attempts to verify this with magneto-optical measurements have yielded mixed results. Here, Farhang et al show that the magneto-optical signals are due to specular optical rotation. ‘
- Camron Farhang
- , Jingyuan Wang
- & Jing Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron detectors used in electron microscope are often unable to provide quantified information without calibration. Here, by combining existing detectors with hardware signal processing, the authors demonstrated that the detectors can be run in an electron counting mode enabling imaging at faster speeds, at lower electron doses, and reduces the barrier to quantitative measurements.
- Jonathan J. P. Peters
- , Tiarnan Mullarkey
- & Lewys Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Crackling noise microscopy
Crackling noise microscopy
The authors present crackling noise microscopy, a method for measurement of the crackling of individual nanoscale features based on AFM nanoindentation. They use it to investigate crackling noise and avalanches in the domains and domain walls of ferroelectric materials.
- Cam-Phu Thi Nguyen
- , Peggy Schoenherr
- & Jan Seidel
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Understanding the mechanical properties of materials is critical in many fields, from soft hydrogels to biological tissues, yet current measurement methods lack the spatial and time resolution to characterize samples with complex structures. Here, the authors show non-invasive elastography technique offering advancements in resolution, sensitivity, and measurement frequencies.
- Xu Feng
- , Guo-Yang Li
- & Seok-Hyun Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Operando neutron diffraction reveals mechanisms for controlled strain evolution in 3D printing
Operando neutron diffraction reveals mechanisms for controlled strain evolution in 3D printing
Residual stress affects most manufactured goods and is prevalent in casting, welding, and additive manufacturing. Here, the authors use operando neutron diffraction to elucidate mechanisms for lattice strain evolution during printing of a low-temperature transformation steel.
- A. Plotkowski
- , K. Saleeby
- & S. S. Babu
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing low-loss dielectric near-field modes of hexagonal boron nitride by photoemission electron microscopy
Revealing low-loss dielectric near-field modes of hexagonal boron nitride by photoemission electron microscopy
The application of time-resolved photoemission electron microscopy (TR-PEEM) to non-conducting materials is challenging. Here, the authors report the TR-PEEM characterization of near-field dielectric modes and photoemission properties of insulating hexagonal boron nitride structures on indium tin oxide/glass substrates.
- Yaolong Li
- , Pengzuo Jiang
- & Qihuang Gong
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy photoemission final states beyond the free-electron approximation
High-energy photoemission final states beyond the free-electron approximation
Angular-resolved photoemission data is commonly used to determine the 3D electronic structure assuming free-electron final states. Strocov et al. show that even at high excitation energies the complexity of final states in various materials can go far beyond the free-electron picture.
- V. N. Strocov
- , L. L. Lev
- & J. Minár
-
Article
| Open Access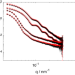 Measuring the counterion cloud of soft microgels using SANS with contrast variation
Measuring the counterion cloud of soft microgels using SANS with contrast variation
The existence of peripheric charged groups on poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAM) microgels together with the corresponding counter ion clouds has been proposed to be responsible for the spontaneous deswelling of pNIPAM microgels in concentrated suspensions but no direct measurement of such an ionic cloud exists. Here, the authors use small-angle neutron scattering with contrast variation with different ions to isolate the change in the form factor directly related to the counterion cloud and obtain its radius and width.
- Boyang Zhou
- , Urs Gasser
- & Alberto Fernandez-Nieves
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding capacity fade in organic redox-flow batteries by combining spectroscopy with statistical inference techniques
Understanding capacity fade in organic redox-flow batteries by combining spectroscopy with statistical inference techniques
Organic redox-flow batteries have the potential to cheaply store renewable electricity at grid scale but require further development. Here, the authors show that combining spectroscopic measurements with statistical inference techniques can shed light on why these batteries lose capacity over time.
- Sanat Vibhas Modak
- , Wanggang Shen
- & David G. Kwabi
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving nanostructure and chemistry of solid-electrolyte interphase on lithium anodes by depth-sensitive plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Resolving nanostructure and chemistry of solid-electrolyte interphase on lithium anodes by depth-sensitive plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The solid-electrolyte interphase is crucial for most batteries, but its characterization is challenging. Here, authors develop a depth-sensitive plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy method to enable in-situ and nondestructive resolving of its structure and chemistry as well as formation mechanisms.
- Yu Gu
- , En-Ming You
- & Bing-Wei Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Direct determination of high-order transverse ligand field parameters via µSQUID-EPR in a Et4N[160GdPc2] SMM
Direct determination of high-order transverse ligand field parameters via µSQUID-EPR in a Et4N[160GdPc2] SMM
Single molecule magnets (SMMs) are molecules with magnetic states separated by an energy barrier. These two (or more) states can serve as basis for quantum information processing, but this requires a detailed understanding of the ligand field of the molecule that forms the SMM. Here, Taran et al use a combination of two experimental techniques, µSQUID and EPR, to precisely measure the higher-order ligand field parameters.
- Gheorghe Taran
- , Eufemio Moreno-Pineda
- & Wolfgang Wernsdorfer
-
Article
| Open Access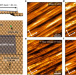 Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Catalytic CO2 dissociation pathways are selectively determined by surface geometry in heterogeneous catalysis. The authors find that the stepped Cu surfaces effectively affect CO2 activation in elementary reaction steps at the atomic level
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Youngseok Yu
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven flow synthesis of acetic acid from methane with chemical looping
Light-driven flow synthesis of acetic acid from methane with chemical looping
A light-driven, chemical looping approach to CH3COOH synthesis from methane using a Pd/PdO–WO3 nanocomposite is reported. Methane is converted to methyl and carbonyl intermediates at the Pd and PdO sites, respectively, to produce CH3COOH.
- Wenqing Zhang
- , Dawei Xi
- & Yujie Xiong

 Low-nuclearity CuZn ensembles on ZnZrOx catalyze methanol synthesis from CO2
Low-nuclearity CuZn ensembles on ZnZrOx catalyze methanol synthesis from CO2