Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of TMEM63C suggests it functions as a monomer
Cryo-EM structure of TMEM63C suggests it functions as a monomer
TMEM63s are mechanosensitive ion channels activated by hypo-osmolality. Here, the authors determine the cryo-EM structure of mouse TMEM63C confirming its predominant monomeric state and the significance of TM0-TM6 coupling in channel activity.
- Yuqi Qin
- , Daqi Yu
- & Shangyu Dang
-
Article
| Open Access An apical Phe-His pair defines the Orai1-coupling site and its occlusion within STIM1
An apical Phe-His pair defines the Orai1-coupling site and its occlusion within STIM1
The intermembrane complexes mediating calcium signals are crucial but poorly understood. Here the authors identify a Phe-His pair in the calcium-sensing STIM1 protein that controls both activation and pairing of STIM1 with Orai channels to generate calcium signals
- Yandong Zhou
- , Michelle R. Jennette
- & Donald L. Gill
-
Article
| Open Access Structural titration reveals Ca2+-dependent conformational landscape of the IP3 receptor
Structural titration reveals Ca2+-dependent conformational landscape of the IP3 receptor
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) are intracellular Ca2+ channels that produce Ca2+ oscillations in response to GPCR and RTK activation. Here, Paknejad et al. resolve the conformational landscape of IP3Rs that gives rise to the biphasic dependence on Ca2+ for channel activity.
- Navid Paknejad
- , Vinay Sapuru
- & Richard K. Hite
-
Article
| Open Access Cysteines 1078 and 2991 cross-linking plays a critical role in redox regulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR)
Cysteines 1078 and 2991 cross-linking plays a critical role in redox regulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR)
Oxidation of ryanodine receptor calcium channels play a critical role in the onset of many cardiac diseases. Here, authors identify specific amino acids that cause ryanodine receptor malfunction during oxidative stress.
- Roman Nikolaienko
- , Elisa Bovo
- & Aleksey V. Zima
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into the gating mechanisms of voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3
Molecular insights into the gating mechanisms of voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3
The CaV2.3 channel is involved in synaptic plasticity and neurological disorders. Here, authors resolve the human CaV2.3 structure to explore functional heterogeneity of VSDs and elucidated the closed- and open-state inactivation mechanisms of the channel.
- Yiwei Gao
- , Shuai Xu
- & Yan Zhao
-
Comment
| Open AccessRegulating voltage-gated ion channels with nanobodies
In this work, Morgenstern and colleagues describe an approach involving functionalized nanobodies which decrease the activity of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels associated with β1 subunits and promote their removal from the surface membrane of neurons and muscle.
- Declan Manning
- & L. Fernando Santana
-
Article
| Open Access Selective posttranslational inhibition of CaVβ1-associated voltage-dependent calcium channels with a functionalized nanobody
Selective posttranslational inhibition of CaVβ1-associated voltage-dependent calcium channels with a functionalized nanobody
Auxiliary subunit molecular diversity is an unexploited target for developing ion channel inhibitors. Here, the authors develop a general approach to inhibit ion channels based on the resident auxiliary subunit isoform to elucidate unique functions of distinct ion channel macromolecular complexes.
- Travis J. Morgenstern
- , Neha Nirwan
- & Henry M. Colecraft
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane curvature governs the distribution of Piezo1 in live cells
Membrane curvature governs the distribution of Piezo1 in live cells
This study demonstrates that the curvature of the cell membrane directly regulates the spatial distribution of Piezo1, a widely expressed mechanosensitive ion channel. Piezo1 may flatten upon activation and can mechanically inhibit membrane dynamics
- Shilong Yang
- , Xinwen Miao
- & Zheng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the R-type human Cav2.3 channel reveal conformational crosstalk of the intracellular segments
Structures of the R-type human Cav2.3 channel reveal conformational crosstalk of the intracellular segments
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel subtype Cav2.3 represents a potential drug target for neurological diseases. Here, authors report cryo-EM structures of Cav2.3 and its mutant to reveal the crosstalk of intracellular segments, which may facilitate future drug discovery.
- Xia Yao
- , Yan Wang
- & Nieng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational motions and ligand-binding underlying gating and regulation in IP3R channel
Conformational motions and ligand-binding underlying gating and regulation in IP3R channel
Here authors report cryo-EM structures of IP3R1 which provide atomic details of IP3, Ca2+ and ATP binding. Molecular motions of key domains and sidechains were found to regulate ligand binding and gating, which are validated by functional assays.
- Guizhen Fan
- , Mariah R. Baker
- & Irina I. Serysheva
-
Article
| Open Access Capture at the ER-mitochondrial contacts licenses IP3 receptors to stimulate local Ca2+ transfer and oxidative metabolism
Capture at the ER-mitochondrial contacts licenses IP3 receptors to stimulate local Ca2+ transfer and oxidative metabolism
The formation and dissolution of ER-Mitochondria contacts is unclear. Here, authors show that the IP3 receptor traffics in and out of the contacts and, when trapped, improves calcium signaling to stimulate energy metabolism.
- Máté Katona
- , Ádám Bartók
- & György Hajnóczky
-
Article
| Open Access 3D structure and in situ arrangements of CatSper channel in the sperm flagellum
3D structure and in situ arrangements of CatSper channel in the sperm flagellum
Sperm motility and male fertility requires function of the CatSper calcium channels. Here, using cryo-electron tomography, authors visualize the native in-cell 3D structure and higher-order organization of the CatSper as long zigzag rows along the sperm tail.
- Yanhe Zhao
- , Huafeng Wang
- & Jean-Ju Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for gating of cardiac ryanodine receptor explains the mechanisms for gain- and loss-of function mutations
Molecular basis for gating of cardiac ryanodine receptor explains the mechanisms for gain- and loss-of function mutations
Ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) is a Ca2+ release channel essential for cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Here, the authors use structural and functional analysis to reveal RyR2 gating mechanism and its alterations by pathogenic mutations.
- Takuya Kobayashi
- , Akihisa Tsutsumi
- & Haruo Ogawa
-
Article
| Open Access Structure, gating, and pharmacology of human CaV3.3 channel
Structure, gating, and pharmacology of human CaV3.3 channel
T-type calcium channels are implicated in many diseases. Here, multiple structures of CaV3.3 channel elucidate molecular mechanisms of T-type CaV channels activation at low voltage and interaction with different clinically used channel blockers.
- Lingli He
- , Zhuoya Yu
- & Yan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
IP3 receptors are intracellular calcium channels involved in numerous signaling pathways. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of type-3 IP3 receptors in multiple gating conformations, including the active state revealing the molecular mechanism of the receptor activation.
- Emily A. Schmitz
- , Hirohide Takahashi
- & Erkan Karakas
-
Article
| Open Access iRhom pseudoproteases regulate ER stress-induced cell death through IP3 receptors and BCL-2
iRhom pseudoproteases regulate ER stress-induced cell death through IP3 receptors and BCL-2
Cells that cannot cope with persistent endoplasmic reticulum stress will die. Here, the authors show that iRhom pseudoproteases regulate cell death by modulating the ability of BCL-2 to inhibit calcium flow through IP3R channels.
- Iqbal Dulloo
- , Peace Atakpa-Adaji
- & Matthew Freeman
-
Article
| Open Access Lsm12 is an NAADP receptor and a two-pore channel regulatory protein required for calcium mobilization from acidic organelles
Lsm12 is an NAADP receptor and a two-pore channel regulatory protein required for calcium mobilization from acidic organelles
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) potent Ca2+ mobilizing second messenger which uniquely triggers Ca2+ release from acidic endolysosomal organelles. Here the authors identify Lsm12 as an NAADP receptor essential for NAADP-evoked Ca2+ release from lysosomes via NAADP binding on its Lsm domain.
- Jiyuan Zhang
- , Xin Guan
- & Jiusheng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Arachidonic acid-regulated calcium signaling in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis promotes synovial inflammation
Arachidonic acid-regulated calcium signaling in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis promotes synovial inflammation
ORAI3 is part of pore forming calcium channels involved in T cell activation. Here the authors show that there is increased expression of ORAI3 in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and that the transcription factor IKAROS negatively regulates the ORAI3 promoter, indicating a regulatory loop that can control auto-reactivity of T cells in these patients.
- Zhongde Ye
- , Yi Shen
- & Jörg J. Goronzy
-
Article
| Open Access Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM
Pathological conformations of disease mutant Ryanodine Receptors revealed by cryo-EM
Ryanodine Receptors (RyRs) release Ca2+ from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mutations in RyR are linked to malignant hyperthermia (MH), myopathies, and arrhythmias. Here, a collection of cryoEM structures provides insights into the molecular consequences of MHrelated RyR mutation R615C, and how apoCaM opens RyR1.
- Kellie A. Woll
- , Omid Haji-Ghassemi
- & Filip Van Petegem
-
Article
| Open Access Subnanometer-resolution structure determination in situ by hybrid subtomogram averaging - single particle cryo-EM
Subnanometer-resolution structure determination in situ by hybrid subtomogram averaging - single particle cryo-EM
Combining cryo-electron tomography with subtomogram averaging (StA) allows the in situ structure determination of proteins and protein complexes. Here, the authors present the hybrid StA (hStA) workflow that combines the advantages of single particle cryo-EM and StA and consists of a tomographic data collection scheme and a data processing workflow and they demonstrate how hStA can improve the resolution using two examples: the ion channel RyR1 and tobacco mosaic virus.
- Ricardo M. Sanchez
- , Yingyi Zhang
- & Mikhail Kudryashev
-
Article
| Open Access The native ORAI channel trio underlies the diversity of Ca2+ signaling events
The native ORAI channel trio underlies the diversity of Ca2+ signaling events
The essential role of ORAI1 channels in receptor-evoked Ca2+ signaling is well understood, but the roles of ORAI2 and ORAI3 remained obscure. Here authors show that ORAI2 and ORAI3 channels multimerize with ORAI1 to expand the range of sensitivity of receptor-activated Ca2+ signals, reflecting their enhanced basal STIM1-binding and heightened Ca2+-dependent inactivation.
- Ryan E. Yoast
- , Scott M. Emrich
- & Mohamed Trebak
-
Article
| Open Access Ca2+-regulated Ca2+ channels with an RCK gating ring control plant symbiotic associations
Ca2+-regulated Ca2+ channels with an RCK gating ring control plant symbiotic associations
CASTOR is a Lotus japonicus ion channel required for nuclear Ca2+ spiking and establishing rhizobial and mycorrhizal symbioses. Here, via structural and functional analysis, Kim et al. show that CASTOR is a Ca2+-selective channel activated via Ca2+ binding to a soluble gating ring consisting of tandem RCK domains.
- Sunghoon Kim
- , Weizhong Zeng
- & Youxing Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Selective recruitment of different Ca2+-dependent transcription factors by STIM1-Orai1 channel clusters
Selective recruitment of different Ca2+-dependent transcription factors by STIM1-Orai1 channel clusters
Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ sensing STIM proteins and plasma membrane Orai1 channels together regulate Ca2+ influx in eukaryotic cells. Here authors show that two Ca2+-dependent transcription factors, NFAT1 and c-fos, have different requirements for the number of STIM1-Orai1 clusters and on the Ca2+ flux through the clusters.
- Yu-Ping Lin
- , Daniel Bakowski
- & Anant B. Parekh
-
Article
| Open Access Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response
Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response
Piezo channels are mechanosensitive and rely on membrane composition to transduce physical stimuli into electrical signals. Here authors analyse the membrane components that modulate Piezo1 function using lipid profiling which shows that fatty acid metabolism can modulate ion channel activity.
- Luis O. Romero
- , Andrew E. Massey
- & Valeria Vásquez
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed azobenzene photoswitches for efficient two-photon neuronal excitation
Rationally designed azobenzene photoswitches for efficient two-photon neuronal excitation
Two-photon absorption capacity of azobenzene photoswitches usually comes with a reduction in thermal stability. Here, the authors developed photoswitches with high two-photon sensitivity and enhanced cis isomer thermal lifetime for the control of glutamate receptors.
- Gisela Cabré
- , Aida Garrido-Charles
- & Ramon Alibés
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.2
Structure of the hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.2
In plants, hyperosmolality stimuli triggers opening of the osmosensitive channels, leading to a rapid downstream signaling cascade. Here, the authors solve the cryo-EM structure of an osmosensitive channel from Arabidopsis OSCA1.2 in its inactivated state.
- Xin Liu
- , Jiawei Wang
- & Linfeng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV4 and KRAS and FGFR1 gain-of-function mutations drive giant cell lesions of the jaw
TRPV4 and KRAS and FGFR1 gain-of-function mutations drive giant cell lesions of the jaw
Giant cell lesions of the jaw (GCLJ) are debilitating benign tumors of unclear origin. The authors identify driver recurrent somatic mutations in TRPV4, KRAS and FGFR1 and show they converge on aberrant activation of the MAPK pathway. Their findings extend the spectrum of TRPV4 channelopathies and provide rationale for targeted therapies at the bedside in GCLJ.
- Carolina Cavalieri Gomes
- , Tenzin Gayden
- & Nada Jabado
-
Article
| Open Access Piezo1 is a mechanically activated ion channel and mediates pressure induced pancreatitis
Piezo1 is a mechanically activated ion channel and mediates pressure induced pancreatitis
Manipulation of the pancreas during surgery can induce acute pancreatitis due to zymogen activation. Here the authors show that the mechanoreceptor Piezo1 is activated by pressure and its activation leads to calcium dependent pancreatic injury whereas its inhibition is protective against pancreatitis.
- Joelle M.-J. Romac
- , Rafiq A. Shahid
- & Rodger A. Liddle
-
Article
| Open Access Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP
Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP
The popular genetically-encoded Ca2+ indicator, GCaMP, has several side-effects. Here the authors show that GCaMP containing CaM interferes with gating and signaling of L-type calcium channels, which disrupts Ca2+ dynamics and gene expression, and develop GCaMP-X to overcome these limitations.
- Yaxiong Yang
- , Nan Liu
- & Xiaodong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the polycystic kidney disease-like channel PKD2L1
Cryo-EM structure of the polycystic kidney disease-like channel PKD2L1
Polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1 protein (PKD2L1) is a voltage-dependent calcium-dependent nonselective ion channel involved in sour taste perception and regulation of pH-dependent action potential of spinal cord neurons. Here the authors present the 3.4 Å cryo-EM structure of PKD2L1 in the open state and propose a model for the gating mechanism.
- Qiang Su
- , Feizhuo Hu
- & Tingliang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ca2+ signals initiate at immobile IP3 receptors adjacent to ER-plasma membrane junctions
Ca2+ signals initiate at immobile IP3 receptors adjacent to ER-plasma membrane junctions
IP3 receptors mediate Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Here the authors show that only a small fraction of IP3 receptors initiate Ca2+ signals; these immobile IP3 receptors adjacent to the plasma membrane are optimally placed to control STIM1-dependent Ca2+ entry.
- Nagendra Babu Thillaiappan
- , Alap P. Chavda
- & Colin W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical chaperone improves muscle function in mice with a RyR1 mutation
A chemical chaperone improves muscle function in mice with a RyR1 mutation
Mutations in the RyR1 channel cause core myopathies. Here the authors show that ER stress and the unfolded protein response underlie the pathology caused by a common RyR1 channel mutation, and show that treatment with a chemical chaperone restores muscle function in mice.
- Chang Seok Lee
- , Amy D. Hanna
- & Susan L. Hamilton
-
Article
| Open Access STIM1 activates CRAC channels through rotation of the pore helix to open a hydrophobic gate
STIM1 activates CRAC channels through rotation of the pore helix to open a hydrophobic gate
Store-operated Ca2+channels (CRAC) are involved in several cellular functions. Here the authors identify a hydrophobic gate in the CRAC pore and show that CRAC activation by STIM1 involves rotation of the pore helix that hydrates this region to allow ion passage through the pore.
- Megumi Yamashita
- , Priscilla S.-W. Yeung
- & Murali Prakriya
-
Article
| Open Access The STIM1-binding site nexus remotely controls Orai1 channel gating
The STIM1-binding site nexus remotely controls Orai1 channel gating
How plasma membrane Orai Ca2+ channels are activated by STIM proteins to activate Ca2+signals is still not fully known. Here the authors show that a nexus region located at the Orai1 C-terminus allows channel gating without a direct interaction of STIM1 with the channel pore.
- Yandong Zhou
- , Xiangyu Cai
- & Donald L. Gill
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting stoichiometry of macromolecular complexes in live cells using FRET
Detecting stoichiometry of macromolecular complexes in live cells using FRET
Measuring thein vivo stoichiometry of protein-protein interactions is challenging. Here the authors take a FRET-based approach, quantifying stoichiometry based on ratiometric comparison of donor and acceptor fluorescence, and apply their method to report on a Ca2+-induced switch in calmodulin binding to Ca2+ion channels.
- Manu Ben-Johny
- , Daniel N. Yue
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Protein kinase A modulation of CaV1.4 calcium channels
Protein kinase A modulation of CaV1.4 calcium channels
Phosphorylation of L-type calcium CaV channels by protein kinase A is essential for several physiological events. Here, the authors show how this kinase regulates CaV1.4 activity, suggesting a general regulatory mechanism for all L-type calcium channels.
- Lingjie Sang
- , Ivy E. Dick
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access TRPC5 channels participate in pressure-sensing in aortic baroreceptors
TRPC5 channels participate in pressure-sensing in aortic baroreceptors
The identity of mechanosensors within aortic baroreceptors that sense fluctuations in blood pressure is unclear. Here, Lau et al.show that a cation channel TRPC5 acts as a transducer of mechanical stimuli in aortic baroreceptor neurons in rodents.
- On-Chai Lau
- , Bing Shen
- & Xiaoqiang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Myoscape controls cardiac calcium cycling and contractility via regulation of L-type calcium channel surface expression
Myoscape controls cardiac calcium cycling and contractility via regulation of L-type calcium channel surface expression
Heart failure is a major public health issue but due to our poor disease understanding the current therapies are symptomatic. Here the authors identify Myoscape as a novel cardiac protein regulating membrane localization of the L-type calcium channel and heart's contractile force, thus promising new therapeutic avenues for heart failure.
- Matthias Eden
- , Benjamin Meder
- & Norbert Frey
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid shear triggers microvilli formation via mechanosensitive activation of TRPV6
Fluid shear triggers microvilli formation via mechanosensitive activation of TRPV6
Microvilli on epithelial cells can sense the surrounding fluid environment, but the regulatory mechanism behind their formation is mostly unknown. Here Miura et al.show that fluid shear stress serves as a trigger for microvilli formation via activation of the calcium ion channel TRPV6.
- Shigenori Miura
- , Koji Sato
- & Shoji Takeuchi
-
Article
| Open Access STIM1 dimers undergo unimolecular coupling to activate Orai1 channels
STIM1 dimers undergo unimolecular coupling to activate Orai1 channels
STIM1, the endoplasmic reticulum calcium sensor, is activated in response to calcium store depletion and translocates to the ER–plasma membrane junctions to activate Orai1 channels. Here the authors present a new model of unimolecular coupling between STIM1 and Orai1 whereby STIM1 dimers may be involved in crosslinking Orai1 channels.
- Yandong Zhou
- , Xizhuo Wang
- & Donald L. Gill
-
Article |
 STIM1 triggers a gating rearrangement at the extracellular mouth of the ORAI1 channel
STIM1 triggers a gating rearrangement at the extracellular mouth of the ORAI1 channel
The plasma membrane Ca2+ channel ORAI1 is gated directly by the ER-resident protein STIM1. Here Gudlur et al. show that STIM1 elicits conformational changes near the extracellular opening of the channel, involving the Ca2+-binding residue E106 and the pore-lining residue V102, which forms a barrier to ion conduction in the closed state.
- Aparna Gudlur
- , Ariel Quintana
- & Patrick G. Hogan
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo single-molecule imaging identifies altered dynamics of calcium channels in dystrophin-mutant C. elegans
In vivo single-molecule imaging identifies altered dynamics of calcium channels in dystrophin-mutant C. elegans
Single molecule fluorescence microscopy is a powerful technique to study protein dynamics in cells, but it has not been applied to adult animals. The authors use complementation-activated light microscopy in C. elegansto discover that dystrophin regulates the diffusion properties of voltage-dependent calcium ion channels at the surface of body-wall muscle cells.
- Hong Zhan
- , Ramunas Stanciauskas
- & Fabien Pinaud
-
Article
| Open Access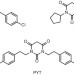 Modest CaV1.342-selective inhibition by compound 8 is β-subunit dependent
Modest CaV1.342-selective inhibition by compound 8 is β-subunit dependent
Compound 8-1-(3-chlorophenethyl)-3-cyclopentylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione was previously reported to be a selective inhibitor of the CaV1.3 calcium channel. Now, Huang et al. demonstrate that selectivity towards CaV1.3 relative to CaV1.2 is dependent on the type of β-subunit and CaV1.3 splice variant assayed.
- Hua Huang
- , Cheng Yang Ng
- & Tuck Wah Soong
-
Article
| Open Access Pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones are a new class of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channel activators
Pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones are a new class of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channel activators
Selective inhibitors of the L-type Ca2+ channel Cav1.3 are being developed as neuroprotective drugs. Here, Ortner et al. assess the pharmacological properties of a recently reported, selective Cav1.3 blocker and show that this agent is a Ca2+channel activator.
- Nadine J. Ortner
- , Gabriella Bock
- & Jörg Striessnig
-
Article |
 Endoplasmic reticulum calcium release through ITPR2 channels leads to mitochondrial calcium accumulation and senescence
Endoplasmic reticulum calcium release through ITPR2 channels leads to mitochondrial calcium accumulation and senescence
Cellular senescence is a protective mechanism that prevents replication of cells exposed to stresses such as replicative exhaustion, oncogenic signals and oxidative stress. Wiel et al.reveal a role for calcium signalling between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in senescence maintenance.
- Clotilde Wiel
- , Hélène Lallet-Daher
- & David Bernard
-
Article
| Open Access Fragile X mental retardation protein controls synaptic vesicle exocytosis by modulating N-type calcium channel density
Fragile X mental retardation protein controls synaptic vesicle exocytosis by modulating N-type calcium channel density
Mutations in the fragile X mental retardation protein are implicated in synaptic dysfunction in fragile X syndrome. Here, Ferron et al. show that fragile X mental retardation protein maintains proper neurotransmission by regulating the density of N-type calcium channels in the presynaptic terminal.
- Laurent Ferron
- , Manuela Nieto-Rostro
- & Annette C. Dolphin
-
Article
| Open Access STIM1/Orai1 coiled-coil interplay in the regulation of store-operated calcium entry
STIM1/Orai1 coiled-coil interplay in the regulation of store-operated calcium entry
When endoplasmic reticulum calcium levels are low, STIM1 binds to and opens Orai1 channels in the plasma membrane to replenish calcium stores. Stathopulos et al.present solution structures of the STIM1 coiled-coil domain in the presence and absence of Orai1, revealing the structural basis for this interaction.
- Peter B. Stathopulos
- , Rainer Schindl
- & Mitsuhiko Ikura
-
Article |
 Bio-inspired voltage-dependent calcium channel blockers
Bio-inspired voltage-dependent calcium channel blockers
Calcium channel blockers are used as treatments for hypertension, angina and pain. Yang et al.show that diverse cytosolic calcium channel-binding proteins act as blockers when targeted to the plasma membrane, and suggest how this property might be used to screen for small-molecule inhibitors.
- Tingting Yang
- , Lin-Ling He
- & Henry M. Colecraft
-
Article |
 Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Calmodulin regulation of Ca2+ channels is an important Ca2+-feedback system. The structural underpinnings of this modulation are unclear, but this study reports the molecular states underlying channel regulation.
- Manu Ben Johny
- , Philemon S. Yang
- & David T. Yue

 Selective blockade of Cav1.2 (α1C) versus Cav1.3 (α1D) L-type calcium channels by the black mamba toxin calciseptine
Selective blockade of Cav1.2 (α1C) versus Cav1.3 (α1D) L-type calcium channels by the black mamba toxin calciseptine