Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A semi-synthetic regulon enables rapid growth of yeast on xylose
A semi-synthetic regulon enables rapid growth of yeast on xylose
Efficient assimilation of nutrients is essential for the production of value-added products in microbial fermentation. Here the authors design a semi-synthetic xylose regulon to improve growth characteristics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on this non-native sugar.
- Venkatesh Endalur Gopinarayanan
- & Nikhil U. Nair
-
Article
| Open Access Designed heterogeneous palladium catalysts for reversible light-controlled bioorthogonal catalysis in living cells
Designed heterogeneous palladium catalysts for reversible light-controlled bioorthogonal catalysis in living cells
Fine controlling chemical reactions over transition metal catalysts in living systems like enzymes remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a versatile light-controlled bioorthogonal catalyst by modifying macroporous silica-Pd0 with supramolecular complex of azobenzene and β-cyclodextrin.
- Faming Wang
- , Yan Zhang
- & Xiaogang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-free protein synthesis from genomically recoded bacteria enables multisite incorporation of noncanonical amino acids
Cell-free protein synthesis from genomically recoded bacteria enables multisite incorporation of noncanonical amino acids
Cell-free protein synthesis allows for producing proteins without the need of a host organism, thus sparing the researcher experimental hassle. Here, the authors developed a cell-free synthesis method that enables incorporating non-standard amino acids in the product.
- Rey W. Martin
- , Benjamin J. Des Soye
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering enhanced cellobiohydrolase activity
Engineering enhanced cellobiohydrolase activity
Cellobiohydrolases (CBHs) are critical for natural and industrial biomass degradation but their structure–activity relationships are not fully understood. Here, the authors present the biochemical and structural characterization of two CBHs, identifying protein regions that confer enhanced CBH activity.
- Larry E. Taylor II
- , Brandon C. Knott
- & Gregg T. Beckham
-
Article
| Open Access Surface tension-assisted additive manufacturing
Surface tension-assisted additive manufacturing
Integrating cell-laden hydrogels effectively into the 3D printing process is a challenge in the creation of tissue engineering scaffolds. Here, the authors describe an additive manufacturing technique to combine polymer and cell-containing networks with 3D-printed mechanical supports.
- Héloïse Ragelle
- , Mark W. Tibbitt
- & Robert Langer
-
Article
| Open Access Industrial brewing yeast engineered for the production of primary flavor determinants in hopped beer
Industrial brewing yeast engineered for the production of primary flavor determinants in hopped beer
Production of aromatic monoterpene molecules in hop flowers is affected by genetic, environmental, and processing factors. Here, the authors engineer brewer’s yeast for the production of linalool and geraniol, and show pilot-scale beer produced by engineered strains reconstitutes some qualities of hop flavor.
- Charles M. Denby
- , Rachel A. Li
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access CtIP fusion to Cas9 enhances transgene integration by homology-dependent repair
CtIP fusion to Cas9 enhances transgene integration by homology-dependent repair
The integration of exogenous DNA into the genome using CRISPR–Cas9 often presents a challenge to researchers. Here the authors fuse CtIP to Cas9 to stimulate recombination at target loci.
- M. Charpentier
- , A. H. Y. Khedher
- & J. P. Concordet
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free analysis of physiological hyaluronan size distribution with a solid-state nanopore sensor
Label-free analysis of physiological hyaluronan size distribution with a solid-state nanopore sensor
Involved in various diseases, hyaluronic acid is an important indicator of pathophysiology. Here, the authors report on a solid-state nanopore for the detection of the molecular weight and abundance of hyaluronic acid and demonstrate the system by studying an equine model of osteoarthritis
- Felipe Rivas
- , Osama K. Zahid
- & Adam R. Hall
-
Article
| Open Access Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Personalised medicine requires cell cultures from defined genetic backgrounds, but providing sufficient numbers of cells is a challenge. Here the authors develop gene cocktails to expand primary cells from a variety of different tissues and species, and show that expanded endothelial and hepatic cells retain properties of the differentiated phenotype.
- Christoph Lipps
- , Franziska Klein
- & Tobias May
-
Article
| Open Access Photosystem II Subunit S overexpression increases the efficiency of water use in a field-grown crop
Photosystem II Subunit S overexpression increases the efficiency of water use in a field-grown crop
Availability of irrigation water will be an increasing barrier to global crop yield increases. Here the authors show transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing Photosystem II Subunit S have less stomatal opening in response to light and a 25% reduction in water loss per CO2 assimilated under replicated field trials.
- Katarzyna Głowacka
- , Johannes Kromdijk
- & Stephen P. Long
-
Article
| Open Access ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules
ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules
One of the challenges of biologic drug therapy is delivery into target cells and tissues. Here the authors present ARMMs (arrestin domain containing protein 1 mediated microvesicles) as a versatile platform for packaging and delivery of a myriad of molecules, including p53, RNAs and CRISPR-Cas9.
- Qiyu Wang
- , Jiujiu Yu
- & Quan Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanowire arrays restore vision in blind mice
Nanowire arrays restore vision in blind mice
The restoration of light response using retinal prosthesis could be a way to restore vision following retinal degenerative disease. Here the authors develop gold-titania nanowire arrays that restore visual response in blind mice.
- Jing Tang
- , Nan Qin
- & Gengfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of single amino acid differences in uniformly charged homopolymeric peptides with aerolysin nanopore
Identification of single amino acid differences in uniformly charged homopolymeric peptides with aerolysin nanopore
Existing methods used for peptide analysis suffer from low sensitivity and specificity. Here the authors demonstrate the nanopore-based size-discrimination and purity analysis of short homopolymeric peptides with a single amino acid resolution.
- Fabien Piguet
- , Hadjer Ouldali
- & Abdelghani Oukhaled
-
Article
| Open Access Microhomology-assisted scarless genome editing in human iPSCs
Microhomology-assisted scarless genome editing in human iPSCs
Positive selection for gene targeting is a common and reliable method to generate isogenic disease models in human pluripotent stem cells. Here, the authors present engineered selection markers which achieve scarless excision by CRISPR-Cas9 and microhomology mediated end-joining.
- Shin-Il Kim
- , Tomoko Matsumoto
- & Knut Woltjen
-
Article
| Open Access A macromolecular approach to eradicate multidrug resistant bacterial infections while mitigating drug resistance onset
A macromolecular approach to eradicate multidrug resistant bacterial infections while mitigating drug resistance onset
Antibiotic resistance is a major threat across the whole healthcare spectrum. Here, the authors report on the development of biodegradable guanidinium functionalized polycarbonates and demonstrate antimicrobial activity against drug resistant infections.
- Willy Chin
- , Guansheng Zhong
- & Yi Yan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Two distinct domains contribute to the substrate acyl chain length selectivity of plant acyl-ACP thioesterase
Two distinct domains contribute to the substrate acyl chain length selectivity of plant acyl-ACP thioesterase
The substrate specificity of acyl-ACP thioesterase (TE) plays a crucial role in determining the product profile of type II fatty acid synthase. Utilizing two FatB-type acyl-ACP TEs, the authors here define determinants of substrate specificity and create synthetic enzymes with distinct catalytic traits.
- Fuyuan Jing
- , Le Zhao
- & Basil J. Nikolau
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of a trispecific antibody targeting the HIV-1 Env with elevated anti-viral activity
Rational design of a trispecific antibody targeting the HIV-1 Env with elevated anti-viral activity
Broadly neutralizing antibodies targeting HIV Env could potentially be utilized as therapeutics. Here, Steinhardt et al. engineer a trispecific antibody with specificity for the receptor-binding site, a conserved Env glycan patch and the Env membrane proximal region with nearly pan-isolate neutralization breadth and high potency.
- James J. Steinhardt
- , Javier Guenaga
- & Yuxing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Solid-phase synthesis of protein-polymers on reversible immobilization supports
Solid-phase synthesis of protein-polymers on reversible immobilization supports
Synthesis of protein-polymer conjugates typically relies on multi-step processes in solution and on challenging purification strategies. Here the authors show a robust synthesis approach which eliminates purification processes by immobilizing proteins reversibly on modified agarose beads before grafting from polymers via ATRP.
- Hironobu Murata
- , Sheiliza Carmali
- & Alan J. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane cholesterol mediates the cellular effects of monolayer graphene substrates
Membrane cholesterol mediates the cellular effects of monolayer graphene substrates
Understanding the biological role of graphene in eukaryotic cells is essential for future biomedicine applications. Here, the authors investigate the interaction of neurons and fibroblasts with graphene substrates, which increase cell membrane cholesterol and potentiate neurotransmitter release and receptor signaling.
- Kristina E. Kitko
- , Tu Hong
- & Qi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA-seq of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue using low-cost microfluidic instrumentation
Single-cell RNA-seq of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue using low-cost microfluidic instrumentation
Droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq is a powerful tool for cellular heterogeneity profiling in disease but is limited by instrumentation required. Here the authors develop a 3D printed microfluidic platform for massive parallel sequencing of rheumatoid arthritis tissues.
- William Stephenson
- , Laura T. Donlin
- & Rahul Satija
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic air/liquid pockets for guiding microscale flow
Dynamic air/liquid pockets for guiding microscale flow
Fouling of solid surfaces is a problem when designing microchannel systems for applications such as bioassays and drug delivery. Here Hou et al. propose a way to overcome this issue by controlling fluid flow by means of an immiscible functional liquid partly infiltrated in a porous solid matrix.
- Xu Hou
- , Jianyu Li
- & Joanna Aizenberg
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency RNA-based reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts
High-efficiency RNA-based reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have potential for regenerative medicine applications, but are generated with very low efficiency. Here, the authors show highly efficient reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts to iPSCs via the synergistic activity of synthetic modified mRNAs, mature miRNA mimics, and optimized culture methods.
- Igor Kogut
- , Sandra M. McCarthy
- & Ganna Bilousova
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic variations in ARE1 mediate grain yield by modulating nitrogen utilization in rice
Genetic variations in ARE1 mediate grain yield by modulating nitrogen utilization in rice
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms of nitrogen assimilation is crucial for developing crop cultivars with improved nitrogen utilization efficiency (NUE). Here the authors identify a new negative regulator of NUE and mutation of this gene increases 10–20% rice grain yield under nitrogen-limiting field conditions.
- Qing Wang
- , Jinqiang Nian
- & Jianru Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse genetic error modes constrain large-scale bio-based production
Diverse genetic error modes constrain large-scale bio-based production
The declining performance of scale-up bioreactor cultures is commonly attributed to phenotypic and physical heterogeneities. Here, the authors reveal multiple recurring intra-pathway error modes that limit engineered E. coli mevalonic acid production over time- and industrial-scale fermentations.
- Peter Rugbjerg
- , Nils Myling-Petersen
- & Morten O. A. Sommer
-
Article
| Open Access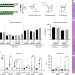 Selection of GalNAc-conjugated siRNAs with limited off-target-driven rat hepatotoxicity
Selection of GalNAc-conjugated siRNAs with limited off-target-driven rat hepatotoxicity
A subset of chemically-modified siRNAs conjugated to trivalent GalNAc may fail during nonclinical development due to rat hepatotoxicity. Here, the authors show that hepatotoxicity may be accounted for by microRNA-like off-target effects of siRNA and can be mitigated by a thermally destabilizing modification in the siRNA seed region.
- Maja M. Janas
- , Mark K. Schlegel
- & Vasant Jadhav
-
Article
| Open Access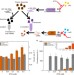 Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling of co-expressed genes
Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling of co-expressed genes
Competition between synthetic genetic circuits and host genes for shared resources can complicate circuit design and lead to failure. Here the authors demonstrate, mathematically and experimentally, the use of orthogonal ribosomes to decouple competing genes.
- Alexander P. S. Darlington
- , Juhyun Kim
- & Declan G. Bates
-
Article
| Open Access 3D microfluidic liver cultures as a physiological preclinical tool for hepatitis B virus infection
3D microfluidic liver cultures as a physiological preclinical tool for hepatitis B virus infection
Long-term in vitro models for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are important to understand this infection, but are lacking. Here the authors develop a microfluidic primary human hepatocyte organoid culture system that can be maintained over 40 days and recapitulates all of the steps of the HBV life cycle.
- A. M. Ortega-Prieto
- , J. K. Skelton
- & M. Dorner
-
Article
| Open Access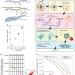 Single-cell full-length total RNA sequencing uncovers dynamics of recursive splicing and enhancer RNAs
Single-cell full-length total RNA sequencing uncovers dynamics of recursive splicing and enhancer RNAs
Total RNA sequencing has been used to profile poly(A) and non-poly(A) RNA expression, processing and the activity of enhancers. Here the authors develop RamDA-seq, a method for full-length total RNA sequencing in single cells.
- Tetsutaro Hayashi
- , Haruka Ozaki
- & Itoshi Nikaido
-
Article
| Open Access Sustained micellar delivery via inducible transitions in nanostructure morphology
Sustained micellar delivery via inducible transitions in nanostructure morphology
Nanocarrier administration is often performed via intermittent bolus injection while sustained delivery platforms are rarely reported. Here the authors demonstrate that the cylinder-to-sphere transitions of self-assembled filomicelle scaffolds can be used for sustained delivery with improved resorptive capacity and biocompatibility.
- Nicholas B. Karabin
- , Sean Allen
- & Evan A. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access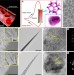 Bacterial capture efficiency in fluid bloodstream improved by bendable nanowires
Bacterial capture efficiency in fluid bloodstream improved by bendable nanowires
Bacteria and other pathogens entering the blood stream can have serious consequences, which can even lead to death. Here, the authors developed a sieve containing nano-sized claws that capture and hold these intruders, thus aiding their removal from patient’s blood
- Lizhi Liu
- , Sheng Chen
- & Tie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of chitinase-3-like-1 in T cell elicits Th1 and cytotoxic responses to inhibit lung metastasis
Regulation of chitinase-3-like-1 in T cell elicits Th1 and cytotoxic responses to inhibit lung metastasis
Chitinase-3-like-1 (Chi3l1) has been involved in inflammation and pulmonary metastasis. Here the authors show that Chi3l1 inhibits the T cell response by negatively regulating their activation and that, in a mouse model of melanoma, T cell-targeted silencing of Chi3l1 results in reduced lung metastasis.
- Do-Hyun Kim
- , Hong-Jai Park
- & Je-Min Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Adenoviral vector with shield and adapter increases tumor specificity and escapes liver and immune control
Adenoviral vector with shield and adapter increases tumor specificity and escapes liver and immune control
Viral gene therapy can be limited by the efficacy of virion sequestration, immune responses and the silencing of genetic payloads. Here the authors engineer an advenovirus protein coat which shields the virion from the immune system while targeting cancer cells.
- Markus Schmid
- , Patrick Ernst
- & Andreas Plückthun
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Breviscapine is the flavonoid extract from medical plant Erigeron breviscapus for the treatment of cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Here, the authors identify the key enzymes of the biosynthetic pathway from the plant genome and engineer yeast to produce breviscapine from glucose.
- Xiaonan Liu
- , Jian Cheng
- & Huifeng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Streamlined ex vivo and in vivo genome editing in mouse embryos using recombinant adeno-associated viruses
Streamlined ex vivo and in vivo genome editing in mouse embryos using recombinant adeno-associated viruses
CRISPR-Cas9 has been widely adopted for genetically manipulating rodents for scientific research. Here the authors transduce mouse embryos with CRISPR-Cas9 components using rAAVs in explant culture or in vivo to produce gene-edited animals.
- Yeonsoo Yoon
- , Dan Wang
- & Jaime A. Rivera-Pérez
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation
Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation
Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) is a widely used plastic and its accumulation in the environment has become global problem. Here the authors report the crystal structure of a Ideonella sakaiensis PET-degrading enzyme and propose a molecular mechanism for PET degradation.
- Seongjoon Joo
- , In Jin Cho
- & Kyung-Jin Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Double-layered protein nanoparticles induce broad protection against divergent influenza A viruses
Double-layered protein nanoparticles induce broad protection against divergent influenza A viruses
Relatively well conserved domains of influenza A virus (IAV) proteins are potential candidates for the development of a universal IAV vaccine. Here, Deng et al. combine two such conserved antigens (M2e and HA stalk) in a double-layered protein nanoparticle and show that it protects against divergent IAVs in mice.
- Lei Deng
- , Teena Mohan
- & Bao-Zhong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive profiling of the ligand binding landscapes of duplexed aptamer families reveals widespread induced fit
Comprehensive profiling of the ligand binding landscapes of duplexed aptamer families reveals widespread induced fit
Duplexed aptamers are a common biosensor format; however, how complementary strand sequence, length, and position modulate ligand binding is not well understood. Here, the authors introduce ACE-Scan to comprehensively map binding landscapes, uncovering hotspots of enhanced binding by induced fit.
- Jeffrey D. Munzar
- , Andy Ng
- & David Juncker
-
Article
| Open Access DNA multi-bit non-volatile memory and bit-shifting operations using addressable electrode arrays and electric field-induced hybridization
DNA multi-bit non-volatile memory and bit-shifting operations using addressable electrode arrays and electric field-induced hybridization
DNA based technology holds promise for non-volatile memory and computational tasks, yet the relatively slow hybridization kinetics remain a bottleneck. Here, Song et al. have developed an electric field-induced hybridization platform that can speed up multi-bit memory and logic operations.
- Youngjun Song
- , Sejung Kim
- & Xiaohua Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis
Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis
Capsaicin prevents atherosclerotic plaque formation by activating TRPV1 cation channels, but its toxicity precludes its use in clinical settings. Here, Tang and colleagues use copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch to locally and temporally activate TRPV1 in vascular smooth muscle cells and reduce plaque formation without apparent toxicity.
- Wen Gao
- , Yuhui Sun
- & Bo Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Pixelated spatial gene expression analysis from tissue
Pixelated spatial gene expression analysis from tissue
Spatial localization of genetic information is important for tissue heterogeneity but difficult to capture with current analytical techniques. Here the authors present “Pixelated RT-LAMP”, an approach that uses parallel on-chip reactions to provide the distribution of target sequences directly from tissue.
- A. Ganguli
- , A. Ornob
- & R. Bashir
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway design using de novo steps through uncharted biochemical spaces
Pathway design using de novo steps through uncharted biochemical spaces
Existing pathway design tools make use of existing reactions from databases or successively apply retrosynthetic rules. novoStoic provides an integrated optimization-based framework combining known reactions with novel steps in pathway design allowing for constraints on thermodynamic feasibility, product yield, pathway length and number of novel steps.
- Akhil Kumar
- , Lin Wang
- & Costas D. Maranas
-
Article
| Open Access Development of an oral once-weekly drug delivery system for HIV antiretroviral therapy
Development of an oral once-weekly drug delivery system for HIV antiretroviral therapy
Poor adherence to daily antiretrovirals can significantly affect treatment efficacy, but oral long-acting antiretrovirals are currently lacking. Here, the authors develop a once-weekly oral dosage form for anti-HIV drugs, assess its pharmacokinetics in pigs, and model its impact on viral resistance and disease epidemics.
- Ameya R. Kirtane
- , Omar Abouzid
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering human pluripotent stem cells into a functional skeletal muscle tissue
Engineering human pluripotent stem cells into a functional skeletal muscle tissue
The generation of functional skeletal muscle tissue from human pluripotent stem cells has not been reported. Here, the authors describe engineering of contractile skeletal muscle bundles in culture, which become vascularized and maintain functionality when transplanted into mice.
- Lingjun Rao
- , Ying Qian
- & Nenad Bursac
-
Article
| Open Access Biotransformation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to bioactive hepoxilins and trioxilins by microbial enzymes
Biotransformation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to bioactive hepoxilins and trioxilins by microbial enzymes
Hepoxilins (HXs) and trioxilins (TrXs) are lipid metabolites with roles in inflammation and insulin secretion. Here, the authors discover a prokaryotic source of HXs and TrXs, identify the biosynthetic enzymes and heterologously express HXs and TrXs in E. coli.
- Jung-Ung An
- , Yong-Seok Song
- & Deok-Kun Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile and on-demand biologics co-production in yeast
Versatile and on-demand biologics co-production in yeast
The ability to combine the production of multiple biologics into a single ‘on demand’ system could help in situations where resources are limited. Here the authors demonstrate a proof-of-concept approach for the co-production of three biologics, allowing singular, mixed and combination drug products.
- Jicong Cao
- , Pablo Perez-Pinera
- & Timothy K. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
Fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose has been unsuccessful. Here, the authors achieve the objective by one-step fermentation of metabolically engineered E. coli expressing a isocaprenoyl-CoA:2-hydroxyisocaproate CoA-transferase and an evolved polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase.
- Jung Eun Yang
- , Si Jae Park
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors
Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors
For synthetic gene circuits to behave as designed, ligand-inducible promoters should display predictable ON/OFF characteristics. Here the authors design multi-input hybrid promoters to build transcriptional logic gates.
- Ye Chen
- , Joanne M. L. Ho
- & Matthew R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Role of outer surface probes for regulating ion gating of nanochannels
Role of outer surface probes for regulating ion gating of nanochannels
Ion gating in biological channels is commonly controlled by functional elements. Here, the authors elucidate the contribution of outer-surface functional elements on ion gating of biomimetic nanochannels, providing insight into the design of effective nanochannel-based biosensors and electronics.
- Xinchun Li
- , Tianyou Zhai
- & Fan Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a genetically encodable FRET system using fluorescent RNA aptamers
Development of a genetically encodable FRET system using fluorescent RNA aptamers
FRET has been used to study protein conformational changes but has never been applied to RNA aptamers. Here the authors develop a genetically encodable RNA aptamer-based FRET system on single-stranded RNA origami scaffolds, and demonstrate it can be used to study RNA conformational changes.
- Mette D. E. Jepsen
- , Steffen M. Sparvath
- & Ebbe S. Andersen
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Fluorescent label-free quantitative detection of nano-sized bioparticles using a pillar array
Fluorescent label-free quantitative detection of nano-sized bioparticles using a pillar array