Featured
-
-
Article |
 Cell volume expansion and local contractility drive collective invasion of the basement membrane in breast cancer
Cell volume expansion and local contractility drive collective invasion of the basement membrane in breast cancer
Forces resulting from global cell volume expansion and local cell contractions distort the basement membrane of an in vitro three-dimensional model of breast cancer, to promote collective cell invasion that precedes metastasis.
- Julie Chang
- , Aashrith Saraswathibhatla
- & Ovijit Chaudhuri
-
News & Views |
 Seriously non-thermal thermodynamics
Seriously non-thermal thermodynamics
Non-equilibrium thermodynamics describes activity-stabilized mixed states in complex active-matter systems.
- Tian Huang
- , Qi Pan
- & Steve Granick
-
Article |
 Compressive forces stabilize microtubules in living cells
Compressive forces stabilize microtubules in living cells
Microtubules respond to mechanical compression by deforming, becoming more stable, which results in CLASP2 recruitment to the distorted shaft—a process crucial for cell migration through confined spaces.
- Yuhui Li
- , Ondřej Kučera
- & Manuel Théry
-
Article
| Open Access Polarity and chirality control of an active fluid by passive nematic defects
Polarity and chirality control of an active fluid by passive nematic defects
Defects of a passive nematic liquid crystal made from actin filaments pattern the collective behaviour of active microtubules, creating macroscopic polar patterns and chiral loops.
- Alfredo Sciortino
- , Lukas J. Neumann
- & Andreas R. Bausch
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue fluidification promotes a cGAS–STING cytosolic DNA response in invasive breast cancer
Tissue fluidification promotes a cGAS–STING cytosolic DNA response in invasive breast cancer
Tissue fluidification in invasive breast carcinoma is accompanied by mechanical stresses that compromise nuclear integrity and liberate DNA, resulting in the activation of a pro-inflammatory response that shape tumour evolution and progression.
- Emanuela Frittoli
- , Andrea Palamidessi
- & Giorgio Scita
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanics of the cellular microenvironment as probed by cells in vivo during zebrafish presomitic mesoderm differentiation
Mechanics of the cellular microenvironment as probed by cells in vivo during zebrafish presomitic mesoderm differentiation
During mesodermal differentiation of living zebrafish embryos, individual cells probe the stiffness associated with the foam-like architecture of the tissue as a part of their mechanosensing responses.
- Alessandro Mongera
- , Marie Pochitaloff
- & Otger Campàs
-
Article |
 Matrix viscoelasticity controls spatiotemporal tissue organization
Matrix viscoelasticity controls spatiotemporal tissue organization
Viscoelasticity is a universal mechanical feature of the extracellular matrix. Here the authors show that the extracellular matrix viscoelasticity guides tissue growth and symmetry breaking, a fundamental process in morphogenesis and oncogenesis.
- Alberto Elosegui-Artola
- , Anupam Gupta
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 Steering from the rear
Steering from the rear
In the absence of biochemical gradients, cancer cell migration over fibrillar isotropic collagen can occur by a mechanical self-steering process involving asymmetric matrix deformation from the rear.
- Katarina Wolf
- & Peter Friedl
-
Letter |
 Weak catch bonds make strong networks
Weak catch bonds make strong networks
Reconstituted cytoskeleton networks linked with catch bonds display increased mechanical strength and crack resistance than those containing slip bonds, and simultaneously being more deformable, which allows for better adaptability to new mechanical environments.
- Yuval Mulla
- , Mario J. Avellaneda
- & Gijsje H. Koenderink
-
Article |
 Directed cell migration towards softer environments
Directed cell migration towards softer environments
Directed cell movement known as durotaxis, typically associated with cellular migration in response to a substrate gradient of increasing stiffness, is now shown to also occur in the opposite direction, following a gradient of decreasing stiffness.
- Aleksi Isomursu
- , Keun-Young Park
- & David J. Odde
-
Article |
 Self-generated gradients steer collective migration on viscoelastic collagen networks
Self-generated gradients steer collective migration on viscoelastic collagen networks
Cell clusters mechanically reorganize viscoelastic collagen networks, resulting in transient gradients in collagen density, alignment and stiffness that promote spontaneous persistent migration.
- Andrew G. Clark
- , Ananyo Maitra
- & Danijela Matic Vignjevic
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printed protein-based robotic structures actuated by molecular motor assemblies
3D printed protein-based robotic structures actuated by molecular motor assemblies
Three-dimensional printed protein-based robotic structures are actuated by exoskeleton-like coats of molecular motor assemblies upon the spatially targeted release of chemical fuel, resulting in micrometre-scale shape-morphing activity.
- Haiyang Jia
- , Johannes Flommersfeld
- & Petra Schwille
-
News & Views |
 Muscle on demand
Muscle on demand
Light-activated protein actuators composed of bioengineered motors and molecular scaffolds achieve millimetre-scale mechanical work, which holds promise for microrobotics applications.
- Henry Hess
-
Article |
 Programmable icosahedral shell system for virus trapping
Programmable icosahedral shell system for virus trapping
Programmable triangular DNA blocks self-assemble into distinct icosahedral shells with specific geometry and apertures that can encapsulate viruses and decrease viral infection.
- Christian Sigl
- , Elena M. Willner
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
News & Views |
 Netrin-4 regulates stiffness and metastasis
Netrin-4 regulates stiffness and metastasis
The stiffness of the basement membrane is a determinant of the process of metastasis and patient survival. Netrin-4 is now shown to be a key regulator of the basement membrane stiffness.
- Patrick Mehlen
- & Laurent Fattet
-
Article |
 A printable active network actuator built from an engineered biomolecular motor
A printable active network actuator built from an engineered biomolecular motor
Patterned contracting networks composed of biomolecular motors and filaments achieve millimetre-scale actuation of mechanical structures with light-triggered molecular stimuli.
- Takahiro Nitta
- , Yingzhe Wang
- & Yuichi Hiratsuka
-
Article |
 Investigating the nature of active forces in tissues reveals how contractile cells can form extensile monolayers
Investigating the nature of active forces in tissues reveals how contractile cells can form extensile monolayers
It is now revealed, using cell cultures and in silico models, that weakening intercellular contacts is a fundamental process essential for switching from extensile to contractile tissue behaviour.
- Lakshmi Balasubramaniam
- , Amin Doostmohammadi
- & Benoît Ladoux
-
Article |
 Basement membrane stiffness determines metastases formation
Basement membrane stiffness determines metastases formation
The basement membrane stiffness is shown to be a more dominant determinant than pore size in regulating cancer cell invasion, metastasis formation and patient survival. This stiffness is now known to be affected by the ratio of netrin-4 to laminin, with more netrin-4 leading to softer basement membranes.
- Raphael Reuten
- , Sina Zendehroud
- & Janine T. Erler
-
Article |
 Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Molecular motors destroy a microtubule lattice as they walk on it, but it is now shown that a self-healing process incorporates new dimers in the damaged regions and prevents microtubule disassembly.
- Sarah Triclin
- , Daisuke Inoue
- & Manuel Théry
-
News & Views |
 Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
While integrin-based adhesions are thought to underlie many aspects of cell response to localized tension, another matrix receptor, syndecan-4, has now been shown to act as a mechanosensor, which triggers cell-wide integrin activation and adhesion reinforcement.
- Christophe Guilluy
- & Monika E. Dolega
-
Article |
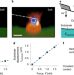 Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics
Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics
Atomic force microscopy indentation measurements of cells cultured on soft substrates may result in an underestimation of cell stiffness. A model has now been developed that takes this soft substrate effect into account, revealing that cortical cell stiffness is largely independent of substrate mechanics.
- Johannes Rheinlaender
- , Andrea Dimitracopoulos
- & Kristian Franze
-
News & Views |
 Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Cancer cells have now been shown to lack rigidity-sensing due to alteration in cytoskeletal sensor proteins, but can be reversed from a transformed to a rigidity-dependent growth state by the sensor proteins, resulting in restoration of contractility and adhesion.
- Edna C. Hardeman
- & Peter W. Gunning
-
News & Views |
 Proteins tailor pore geometry
Proteins tailor pore geometry
Using organic solvent shortens formation time of membrane nanosheets comprising proteins and copolymers, while tuning protein structure tailors the pore geometry, resulting in superior water permeation.
- Andrew G. Livingston
- & Zhiwei Jiang
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Protein channels are highly selective, but application in membranes is limited due to low protein content. Here, protein channels are embedded into block copolymers to form nanosheets using rapid solvent casting, with better water permeability and similar molecular exclusions relative to other membrane systems.
- Yu-Ming Tu
- , Woochul Song
- & Manish Kumar
-
Article |
 Protease-activated receptor signalling initiates α5β1-integrin-mediated adhesion in non-haematopoietic cells
Protease-activated receptor signalling initiates α5β1-integrin-mediated adhesion in non-haematopoietic cells
As in haematopoietic cells and platelets, agonist binding to protease-activated receptors PAR1 and PAR2 in non-haematopoietic cells also triggers signalling pathways that lead to α5β1-integrin-mediated cell adhesion.
- Patrizia M. Spoerri
- , Nico Strohmeyer
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article |
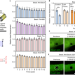 Syndecan-4 tunes cell mechanics by activating the kindlin-integrin-RhoA pathway
Syndecan-4 tunes cell mechanics by activating the kindlin-integrin-RhoA pathway
A mechanism of cell response to localized tension shows that syndecan-4 synergizes with EGFR to elicit a mechanosignalling cascade that leads to adaptive cell stiffening through PI3K/kindlin-2 mediated integrin activation.
- Antonios Chronopoulos
- , Stephen D. Thorpe
- & Armando E. del Río Hernández
-
News & Views |
 To buckle or not to buckle
To buckle or not to buckle
Epithelial layers under compression avoid buckling by active contraction, but only up to a well-defined threshold at 35% strain, beyond which buckling occurs.
- Ulrich S. Schwarz
-
News & Views |
 Building nanobridges for cell adhesion
Building nanobridges for cell adhesion
Nanofibre mimetic substrates reveal the presence of integrin nanoclusters bridged by unliganded receptors during early cell–matrix adhesion.
- E. Ada Cavalcanti-Adam
-
Article |
 Stopping transformed cancer cell growth by rigidity sensing
Stopping transformed cancer cell growth by rigidity sensing
A range of cancer cell types are shown to lack rigidity-sensing due to alteration in specific cytoskeletal sensor proteins and this sensing ability can be reversed from a transformed to a rigidity-dependent growth state by the sensor proteins, resulting in restoration of contractility and adhesion.
- Bo Yang
- , Haguy Wolfenson
- & Michael P. Sheetz
-
Article |
 Integrin nanoclusters can bridge thin matrix fibres to form cell–matrix adhesions
Integrin nanoclusters can bridge thin matrix fibres to form cell–matrix adhesions
Integrin-mediated adhesions required for cell spreading and growth have now been shown, using super-resolution microscopy, to form on fibrous matrices through the dense assembly of integrins in nanoclusters that contain both ligand-bound and unliganded integrins.
- Rishita Changede
- , Haogang Cai
- & Michael P. Sheetz
-
Article |
 Actomyosin controls planarity and folding of epithelia in response to compression
Actomyosin controls planarity and folding of epithelia in response to compression
Epithelial tissues behave as pre-tensed viscoelastic sheets that can buffer against compression and rapidly recover from buckling. Epithelial mechanical properties define a tissue-intrinsic buckling threshold that dictates the compressive strain above which tissue folds become permanent.
- Tom P. J. Wyatt
- , Jonathan Fouchard
- & Guillaume T. Charras
-
News & Views |
 Mastering their own fates through the matrix
Mastering their own fates through the matrix
With their ability to give rise to many different cell types, stem cells have long been a target of scientists who seek to achieve control over their differentiation. New evidence suggests that stem cells influence their own fates through protein deposition and physical remodelling of their microenvironment.
- Eric L. Qiao
- , Sanjay Kumar
- & David V. Schaffer
-
News & Views |
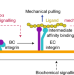 Platelet mechanosensing axis revealed
Platelet mechanosensing axis revealed
An intermediate affinity state of integrin αIIBβ3 has been identified to be a key player in platelet mechanosignalling.
- X. Frank Zhang
- & Xuanhong Cheng
-
Letter |
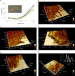 Cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns governed by intracellular forces
Cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns governed by intracellular forces
High-spatial-resolution mechanical imaging reveals that intracellular forces generate cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns.
- Nicola Mandriota
- , Claudia Friedsam
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article |
 Traction forces at the cytokinetic ring regulate cell division and polyploidy in the migrating zebrafish epicardium
Traction forces at the cytokinetic ring regulate cell division and polyploidy in the migrating zebrafish epicardium
The mechanism of cytokinetic failure in the migrating zebrafish epicardium leading to multinucleated cells is shown to be driven by the interaction of the cytokinetic ring and the extracellular matrix through adhesion reinforcement by high traction forces.
- Marina Uroz
- , Anna Garcia-Puig
- & Xavier Trepat
-
Article |
 An integrin αIIbβ3 intermediate affinity state mediates biomechanical platelet aggregation
An integrin αIIbβ3 intermediate affinity state mediates biomechanical platelet aggregation
An intermediate affinity state of integrins on platelets has been identified to be induced by a biomechanical activation pathway and is shown to promote platelet aggregation.
- Yunfeng Chen
- , Lining Arnold Ju
- & Cheng Zhu
-
News & Views |
 A tale about square dancers and maze runners
A tale about square dancers and maze runners
Single-particle tracking of nanoparticles dispersed in the cytoplasm of living cells shows that non-specific interactions with the intracellular environment are the major contributors for the anomalous diffusion characteristics of intracellular motion.
- Matthias Weiss
-
Article |
 Non-specific interactions govern cytosolic diffusion of nanosized objects in mammalian cells
Non-specific interactions govern cytosolic diffusion of nanosized objects in mammalian cells
Nanoparticle diffusion in the cytoplasm of living cells strongly deviates from random motion. Single-particle tracking analysis show that this is due to non-specific interactions with intracellular components.
- Fred Etoc
- , Elie Balloul
- & Mathieu Coppey
-
News & Views |
 Mechanics-guided developmental fate patterning
Mechanics-guided developmental fate patterning
A micropatterned human pluripotent stem cell-based developmental model was utilized to demonstrate the role of biophysical cues such as cell size and cytoskeletal contractile forces in directing patterning of neuroepithelial and neural plate border cells.
- Mukul Tewary
- & Peter W. Zandstra
-
News & Views |
 Instant integrin mechanosensing
Instant integrin mechanosensing
Single-cell force spectroscopy reveals rapid, biphasic integrin activation and reinforcement of cell–matrix bonds during the initial steps of fibroblast adhesion.
- Ning Wang
-
Article |
 Intracellular production of hydrogels and synthetic RNA granules by multivalent molecular interactions
Intracellular production of hydrogels and synthetic RNA granules by multivalent molecular interactions
An approach to form protein-based hydrogels in living cells that resemble physiological hydrogel-like size-dependent molecular sieves is presented. Synthetic RNA granules mimics are obtained by functionalizing these entities with RNA-binding motifs.
- Hideki Nakamura
- , Albert A. Lee
- & Takanari Inoue
-
Article |
 Fibronectin-bound α5β1 integrins sense load and signal to reinforce adhesion in less than a second
Fibronectin-bound α5β1 integrins sense load and signal to reinforce adhesion in less than a second
Integrins play an important role in the adhesion of cells to their matrix. Here, the authors investigate how fibroblasts respond to mechanical loads, at the onset of cell adhesion to fibronectin, in distinct phases that are modulated by integrins.
- Nico Strohmeyer
- , Mitasha Bharadwaj
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article |
 Long-lived force patterns and deformation waves at repulsive epithelial boundaries
Long-lived force patterns and deformation waves at repulsive epithelial boundaries
At tissue boundaries, cellular repulsive events are manifested as deformation waves that result from an oscillatory pattern of traction forces and intracellular stress that pull cellular adhesions away from the boundary.
- Pilar Rodríguez-Franco
- , Agustí Brugués
- & Xavier Trepat
-
Article |
 The processing and heterostructuring of silk with light
The processing and heterostructuring of silk with light
Femtosecond laser pulses can induce local bulging or plasma ablation of silk with limited structural damage, thus offering a technique for cutting, patterning, bending and welding of silk with various other materials.
- Mehra S. Sidhu
- , Bhupesh Kumar
- & Kamal P. Singh
-
Article |
 The microstructure and micromechanics of the tendon–bone insertion
The microstructure and micromechanics of the tendon–bone insertion
High-resolution imaging, composition analysis and mechanical testing provide a new insight into the structure and function of the Achilles enthesis.
- L. Rossetti
- , L. A. Kuntz
- & A. R. Bausch
-
Article |
 Endocytic reawakening of motility in jammed epithelia
Endocytic reawakening of motility in jammed epithelia
Increased cellular expression of RAB5A, an important regulator of endocytic processes, brings epithelial cells from a jammed state to coordinated motion, and can facilitate wound closure, gastrulation and migration in constrained environments.
- Chiara Malinverno
- , Salvatore Corallino
- & Giorgio Scita
-
Letter |
 Single-platelet nanomechanics measured by high-throughput cytometry
Single-platelet nanomechanics measured by high-throughput cytometry
A high-throughput hydrogel-based platelet-contraction cytometer is able to quantify single-platelet contraction forces and may function as a clinical diagnostic biophysical biomarker.
- David R. Myers
- , Yongzhi Qiu
- & Wilbur A. Lam
-
Letter |
 Mechanical plasticity of cells
Mechanical plasticity of cells
Experiments and theory show that plastic energy dissipation during cell deformation is linked to elastic cytoskeletal stresses.
- Navid Bonakdar
- , Richard Gerum
- & Ben Fabry
-
Article |
 A magnetic protein biocompass
A magnetic protein biocompass
A polymeric protein complex consisting of a newly identified magnetoreceptor protein and known magnetoreception-related photoreceptor cryptochromes exhibits spontaneous alignment in magnetic fields.
- Siying Qin
- , Hang Yin
- & Can Xie

 Immunoengineering can overcome the glycocalyx armour of cancer cells
Immunoengineering can overcome the glycocalyx armour of cancer cells